
强度&韧性 ·强度:给定条件下材料达到给定变形量做需要的应力, 或者材料发生断裂的应力。 。韧性:材料在塑性变形和断裂过程中吸收能量的能力。 Ultimate Tensile Stress(UTS) 0.2%Proof Stress Stress Yield Stress (o) Slope=Work-Hardening rate Plastic Fracture Stress, Elastic Limit Strain energy o de Limit of Proportionality volume /0 Modulus Fracture Energy N.B.-this is a typical "engineering stress"vs "engineering strain" curve. The true stress vs true strain curve is different Strain and its shape determines the UTS
强度 & 韧性 强度:给定条件下材料达到给定变形量做需要的应力, 或者材料发生断裂的应力。 韧性:材料在塑性变形和断裂过程中吸收能量的能力
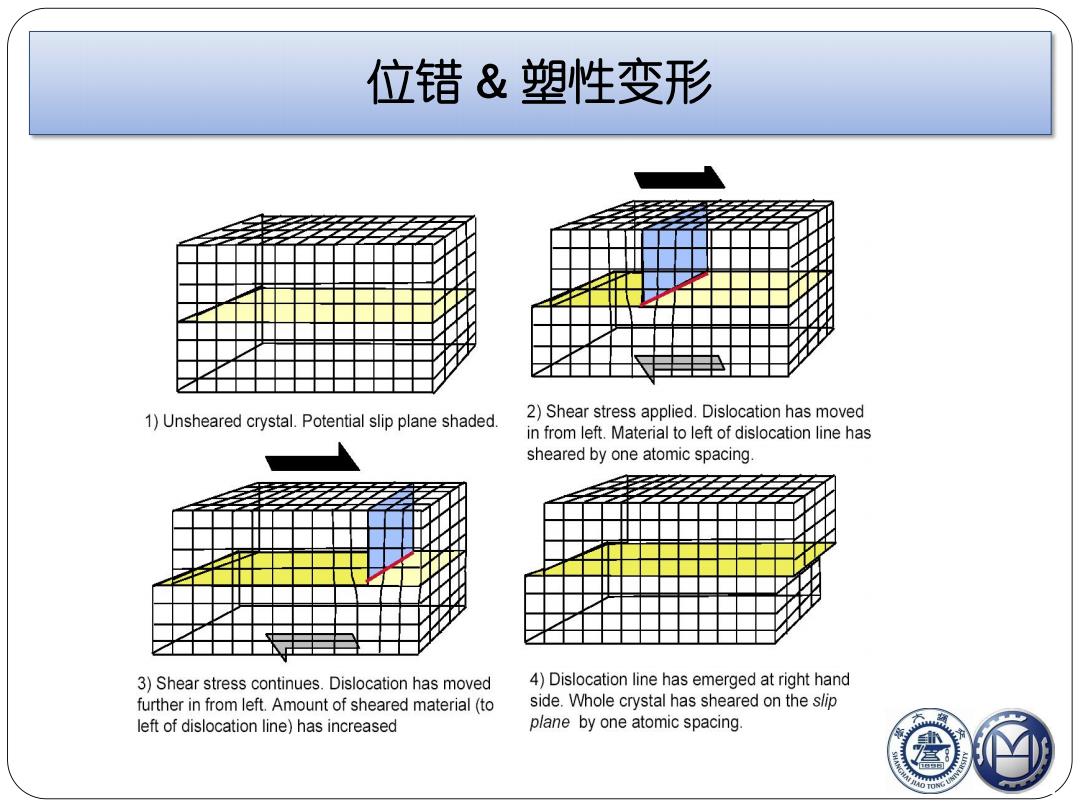
位错&塑性变形 1)Unsheared crystal.Potential slip plane shaded. 2)Shear stress applied.Dislocation has moved in from left.Material to left of dislocation line has sheared by one atomic spacing. 3)Shear stress continues.Dislocation has moved 4)Dislocation line has emerged at right hand further in from left.Amount of sheared material(to side.Whole crystal has sheared on the slip left of dislocation line)has increased plane by one atomic spacing
位错 & 塑性变形

佩尔斯力 (a) (b) (c) Peach-Koehler equation 佩尔斯力Peierls stress: F=(a·b)×s 移动一个位错所需要的应 Peierls stress 力 m-29即(a”) d= a V2+k2+2
Peach-Koehler equation Peierls stress 佩尔斯力 佩尔斯力 Peierls stress: 移动一个位错所需要的应 力
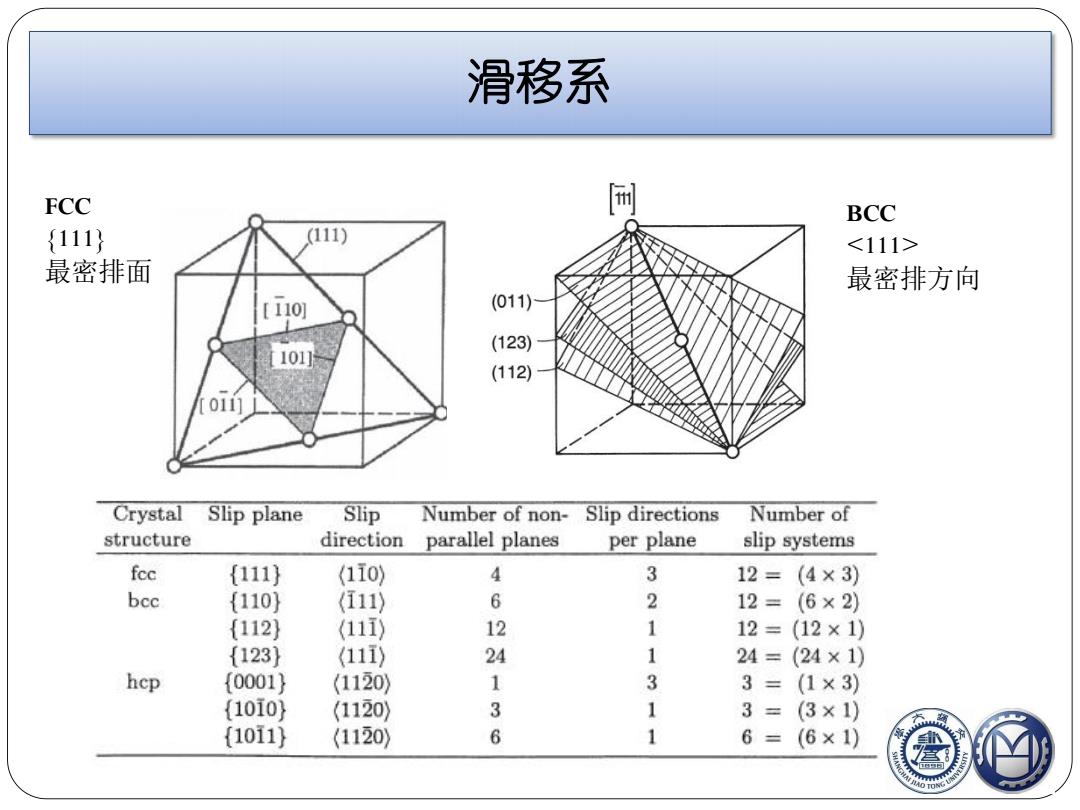
滑移系 FCC BCC {111} (111) 最密排面 最密排方向 [110 (011) (123) 101] (112) 0111 Crystal Slip plane Slip Number of non- Slip directions Number of structure direction parallel planes per plane slip systems fec {111) (110) 4 3 12= (4×3) bcc {110} (111) 6 2 12= (6×2) {112 (11i) 12 1 12=(12×1) {123) (111) 24 1 24=(24×1) hcp {0001} (1120 1 3 3=(1×3) (1010} (1120 3 1 3= (3×1) (1011} (1120) 6 1 6= (6×1)
FCC {111} 最密排面 BCC 最密排方向 滑移系
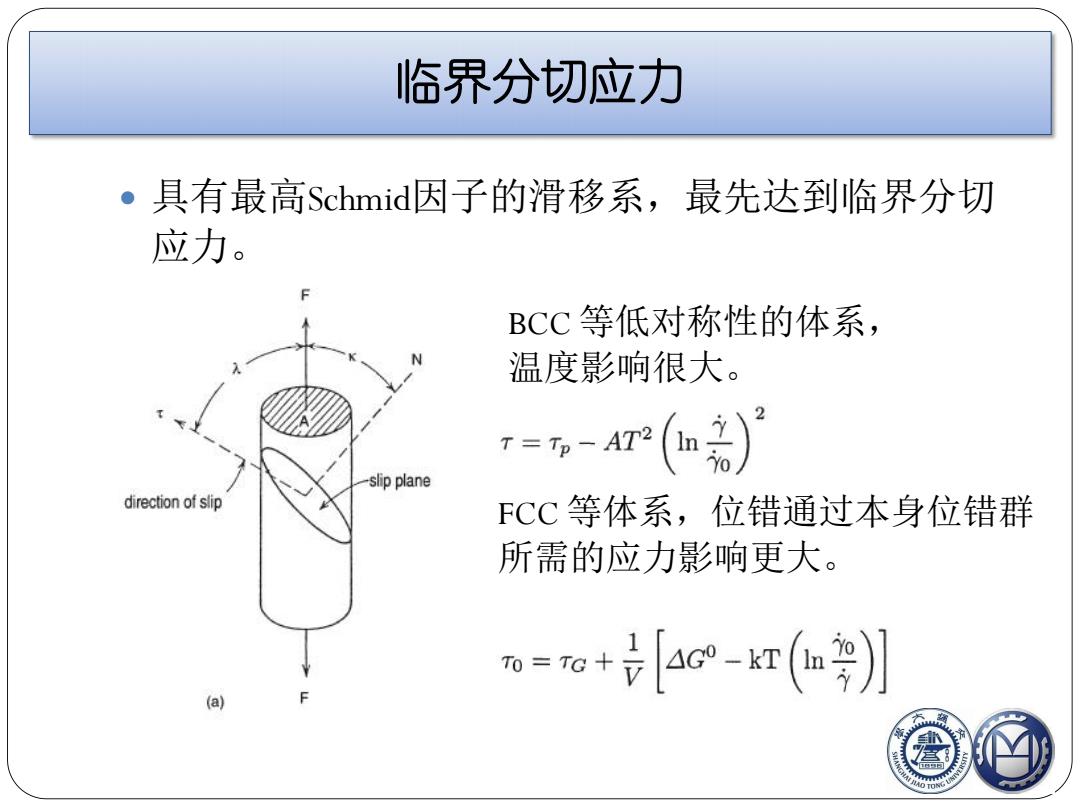
临界分切应力 ·具有最高Schmid因子的滑移系,最先达到临界分切 应力。 BCC等低对称性的体系, 温度影响很大。 T=T-AT2 slip plane direction of slip FCC等体系,位错通过本身位错群 所需的应力影响更大。 0=o+号[ac-k灯(a9月 (a)
临界分切应力 具有最高Schmid因子的滑移系,最先达到临界分切 应力。 BCC 等低对称性的体系, 温度影响很大。 FCC 等体系,位错通过本身位错群 所需的应力影响更大

韧脆转变 800 fracture stress elastic limit brittle fracture tantalum △ tungsten 0 ■ molybdenum 600 iron nickel 400 200 0 -200 0 200 400 600 800 1000 temperature[C】
韧脆转变
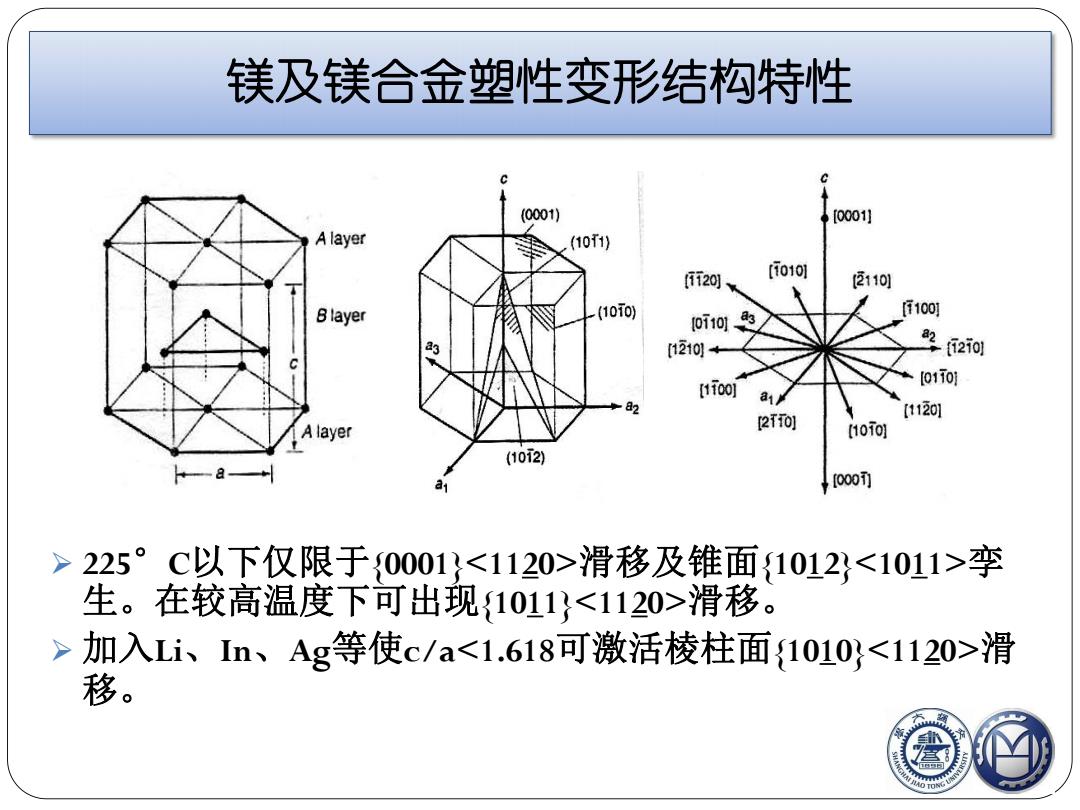
镁及镁合金塑性变形结构特性 (0001) [0001] A layer (10f1) i20、 [010 ②1101 Blayer (10i0) oi10® f100 1210+ 22i0l [1Too] [01T0] g82 111201 A layer 2T0) [10T0] (1012) [000币 > 225°C以下仅限于0001}滑移及锥面1012孪 生。在较高温度下可出现{1011}滑移。 > 加入Li、In、Ag等使c/a滑 移
镁及镁合金塑性变形结构特性 Ø 225°C以下仅限于{0001}滑移及锥面{1012}孪 生。在较高温度下可出现{1011}滑移。 Ø 加入Li、In、Ag等使c/a滑 移
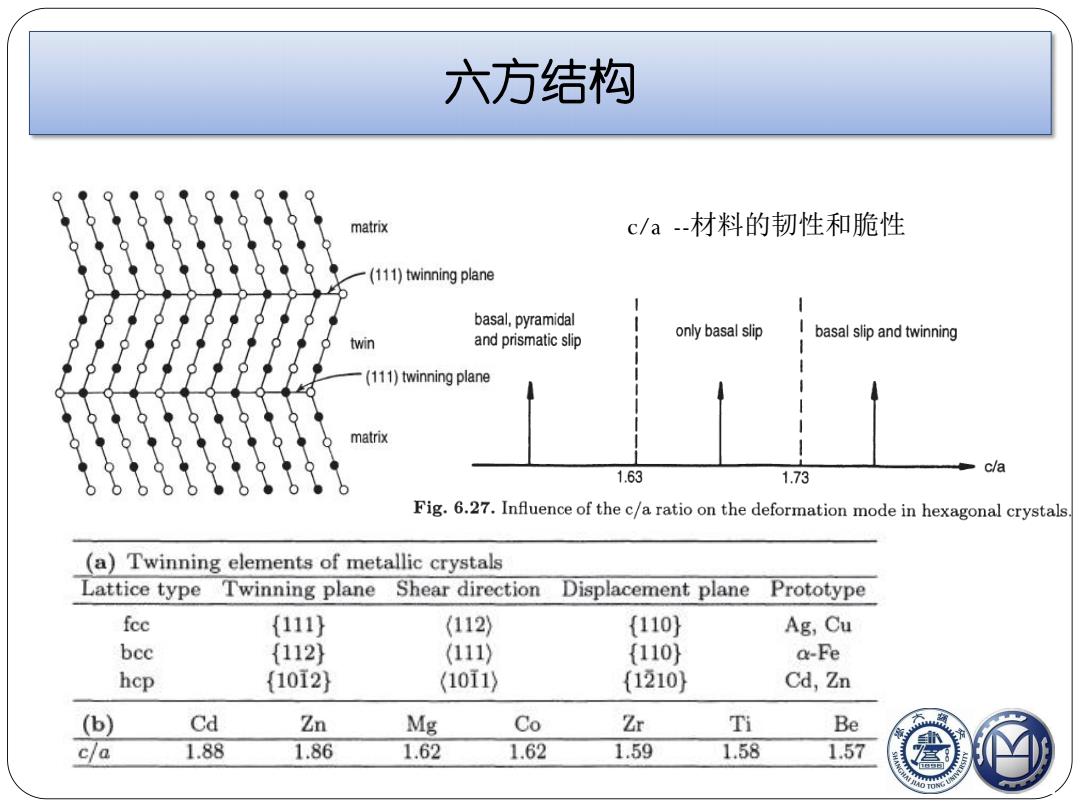
六方结构 matrix c/a-材料的韧性和脆性 (111)twinning plane basal,pyramidal only basal slip twin and prismatic slip I basal slip and twinning (111)twinning plane matrix c/a 1.63 1.73 Fig.6.27.Influence of the c/a ratio on the deformation mode in hexagonal crystals. (a)Twinning elements of metallic crystals Lattice type Twinning plane Shear direction Displacement plane Prototype fee {111} (112) {110 Ag,Cu bec {112) (111) {110} a-Fe hcp {10i2} (10I1) (1210} Cd,Zn (b) Cd Zn Mg Co Zr Ti Be c/a 1.88 1.86 1.62 1.62 1.59 1.58 1.57
六方结构 c/a --材料的韧性和脆性
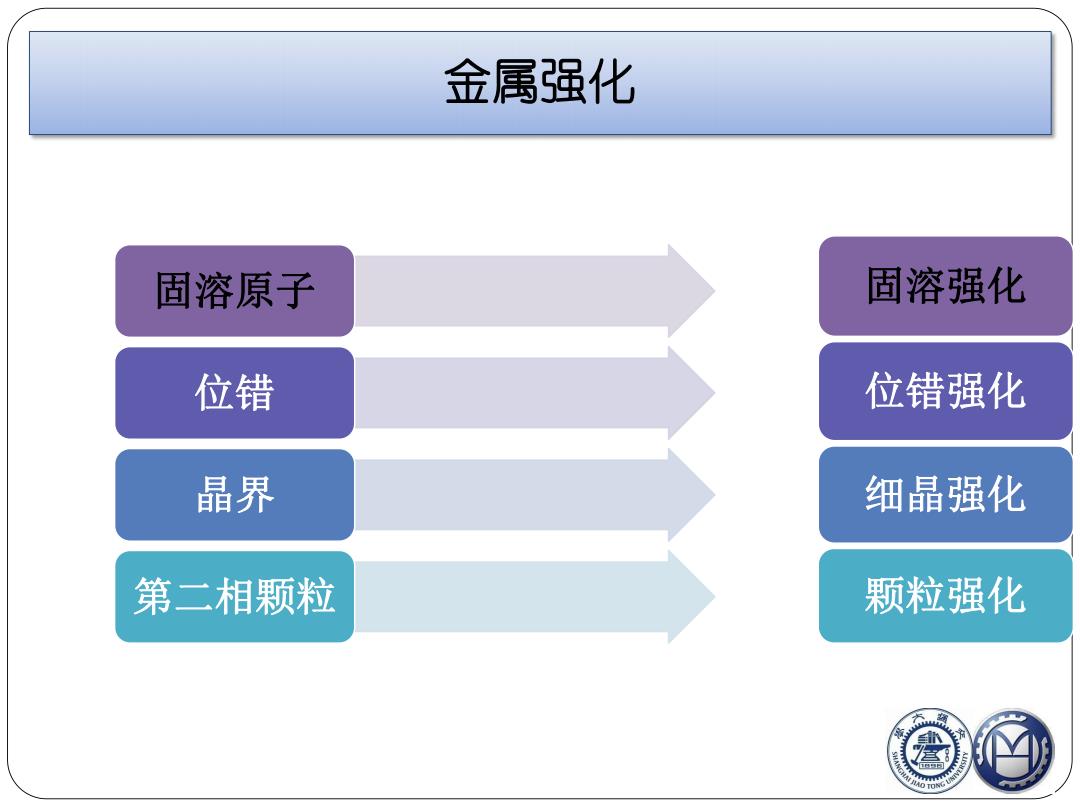
金属强化 固溶原子 固溶强化 位错 位错强化 晶界 细晶强化 第二相颗粒 颗粒强化
固溶原子 位错 晶界 第二相颗粒 固溶强化 位错强化 细晶强化 颗粒强化 金属强化
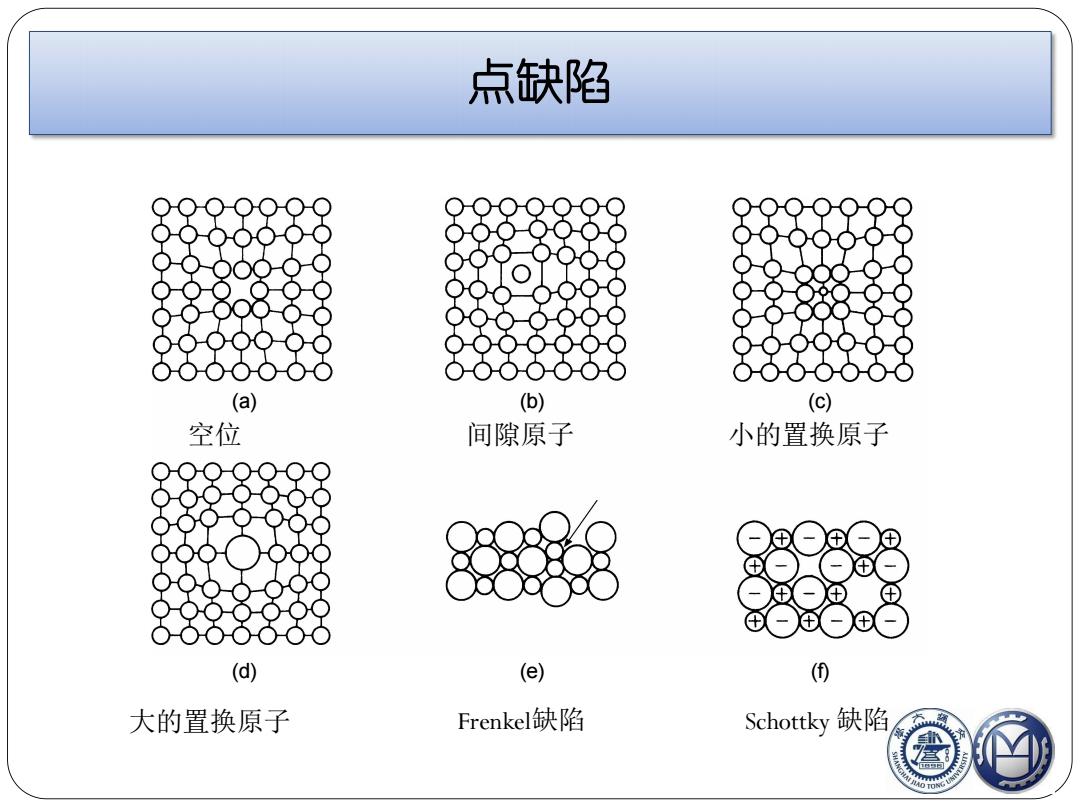
点缺陷 (a) (b) (c) 空位 间隙原子 小的置换原子 8 (d) (e) (⑤ 大的置换原子 Frenkel缺陷 Schottky缺陷
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) 空位 间隙原子 小的置换原子 大的置换原子 Frenkel缺陷 Schottky 缺陷 点缺陷