
变形与细晶强化综合-强烈塑性变形 颗粒强化 固溶强化 位错/变形强化 共同特点? 细晶强化 单相材料
颗粒强化 固溶强化 位错/变形强化 细晶强化 共同特点? 单相材料 变形与细晶强化综合-强烈塑性变形

变形过程与强化 变形过程中可控的变量: ·温度,变形量,变形速度,(压力,体积?) 对强度与组织的影响: 温度 速度 变形量
变形过程中可控的变量: 温度,变形量,变形速度,(压力,体积?) 对强度与组织的影响: 温度 速度 变形量 变形过程与强化

强烈塑性变形:SPD:Severe Plastic Deformation 强烈到什么程度? 以等效应变度量:4 纳米十亚微米的尺寸: <100nm;100-1000nm
强烈到什么程度? 以等效应变度量:4 纳米+亚微米的尺寸: <100nm ; 100-1000nm 强烈塑性变形:SPD:Severe Plastic Deformation

塑性变形 Cold rolling Cellular type or drawing ·Low angle GB Granular type SPD High angle GB 0 um
塑性变形 • Cellular type • Low angle GB Cold rolling or drawing • Granular type • High angle GB SPD 10 µm

SPD起源 主要方法 涉及的材料 应用进展 国内研究 国际活动 问题与方向 MN
SPD起源 主要方法 涉及的材料 应用进展 国内研究 国际活动 问题与方向

SPD起源 1990年之前: 俄罗斯Ufa航空技术大学RZ Valiev,IV Alexandrov 用HPT方法研究强烈塑性变形下的组织演变 国
1990年之前: 俄罗斯Ufa航空技术大学 RZ Valiev, IV Alexandrov 用HPT 方法研究强烈塑性变形下的组织演变 SPD起源

HPT:High Pressure Torsion Devices,where severe plastic torsion straining (SPTS)was conducted under high pressure,were first used in [1]Zhorin VA,Shashkin DP,Yenikoponyan NS.DAN SSSR 1984;278:144. [2]Kuznetsov RI,Bykov VI,Chernyshov VP,Pilyugin VP,Yefremov NA, Posheyev W.Sverdlovsk,IFM UNTS RAN,1985,Preprint 4/85 (in Russian). Successful formation of homogeneous nanostructures with high-angle grain boundaries via severe torsion straining [3]Valiev RZ,Kaibyshev OA,Kuznetsov RI,Musalimov RSh,Tsenev NK.DAN SSSR1988301(4):864. [4]Valiev RZ,Korznikov AV,Mulyukov RR.Mater Sci Eng 1993;A168:141. [5]Mishin OV,Gertsman VYu,Valiev RZ,Gottstein G.Scripta Mater 1996;35:873
HPT: High Pressure Torsion [1] Zhorin VA, Shashkin DP, Yenikoponyan NS. DAN SSSR 1984;278:144. [2] Kuznetsov RI, Bykov VI, Chernyshov VP, Pilyugin VP, Yefremov NA, Posheyev VV. Sverdlovsk, IFM UNTS RAN, 1985, Preprint 4/85 (in Russian). Devices, where severe plastic torsion straining (SPTS) was conducted under high pressure, were first used in Successful formation of homogeneous nanostructures with high-angle grain boundaries via severe torsion straining [3] Valiev RZ, Kaibyshev OA, Kuznetsov RI, Musalimov RSh, Tsenev NK. DAN SSSR 1988;301(4):864. [4] Valiev RZ, Korznikov AV, Mulyukov RR. Mater Sci Eng 1993;A168:141. [5] Mishin OV, Gertsman VYu, Valiev RZ, Gottstein G. Scripta Mater 1996;35:873
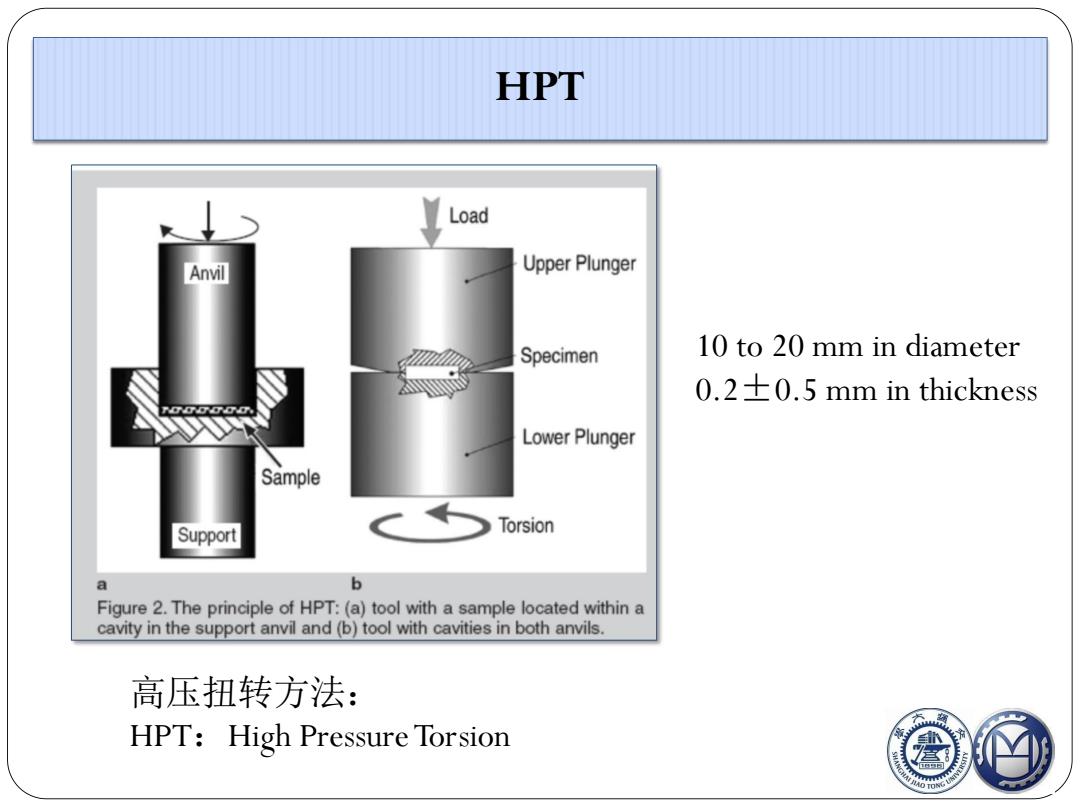
HPT Load Anvil Upper Plunger Specimen 10 to 20 mm in diameter 0.20.5 mm in thickness Lower Plunger Sample Support Torsion a b Figure 2.The principle of HPT:(a)tool with a sample located within a cavity in the support anvil and(b)tool with cavities in both anvils. 高压扭转方法: HPT:High Pressure Torsion ©
高压扭转方法: HPT:High PressureTorsion HPT 10 to 20 mm in diameter 0.2±0.5 mm in thickness

HPT high-pressure torsion 2πRN plunger 7= 1.It is not confirmed by experiments. 2.The initial thickness of the sample is reduced support 一次变形变形量控制 应变速率控制 可控但不均匀 可控
HPT high-pressure torsion 1. It is not confirmed by experiments. 2. The initial thickness of the sample is reduced 一次变形变形量控制 应变速率控制 可控但不均匀 可控
HPT high-pressure torsion >The refinement of a microstructure >The consolidation of powders nanostructured Ni powder v95%of the theoretical density The microhardness of the Ni samples fabricated by SPTS consolidation is the highest value of microhardness mentioned in the literature for nanocrystalline Ni
HPT high-pressure torsion ØThe refinement of a microstructure ØThe consolidation of powders nanostructured Ni powder ü95% of the theoretical density The microhardness of the Ni samples fabricated by SPTS consolidation is the highest value of microhardness mentioned in the literature for nanocrystalline Ni