海在家 15 PART ONE-SYMMETRIC CIPHERS ●Road Map for Part One Chp.2,Classical Encryption Techniques Chp.3,Block Cipher and the Data Encryption Standard 。 Chp.4,Finite Fields Chp.5,Advanced Encryption Standard Chp.6,More on Symmetric Ciphers Chp.7,Confidentiality Using Symmetric Encryption 甲风五 道置品 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security-2 2/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 2/81 Part One–Symmetric Ciphers ⚫ Road Map for Part One ⚫ Chp.2, Classical Encryption Techniques ⚫ Chp.3, Block Cipher and the Data Encryption Standard ⚫ Chp.4, Finite Fields ⚫ Chp.5, Advanced Encryption Standard ⚫ Chp.6, More on Symmetric Ciphers ⚫ Chp.7, Confidentiality Using Symmetric Encryption

海冷不卡 CHAPTER2一 1950 CLASSICAL ENCRYPTION TECHNIQUES Many savages at the present day regard their names as vital parts of themselves,and therefore take great pains to conceal their real names,lest these should give to evil-disposed persons a handle by which to injure their owners. -The Golden Bough,Sir James George Frazer 甲=层 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security-2 3/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 3/81 Chapter 2 – Classical Encryption Techniques ⚫ Many savages at the present day regard their names as vital parts of themselves, and therefore take great pains to conceal their real names, lest these should give to evil-disposed persons a handle by which to injure their owners. —The Golden Bough, Sir James George Frazer

密码学的演变历史(1) William Friedman ●1918,Villiam Friedman's The Index of Coincidence and its Applications in Cryptography William Frederick Friedman (Sept.24,1891- Nov.12,1969)美国陆军密码专家。1930年代,他 领导了陆军的一个研究部门Signals Intelligence Service(SIS),其中一部分服务一直延续到五十年 代。三十年代晚期,在他的指导下,Frank Rowlett 破解了日本人的PURPLE加密机(紫密),截获了日 本的大量外交和军事的秘密 。 甲风= 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security-2 4/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 4/81 密码学的演变历史(1) William Friedman ⚫ 1918, William Friedman’s The Index of Coincidence and its Applications in Cryptography ⚫ William Frederick Friedman (Sept. 24,1891 – Nov. 12, 1969) 美国陆军密码专家。1930年代,他 领导了陆军的一个研究部门Signals Intelligence Service (SIS),其中一部分服务一直延续到五十年 代。三十年代晚期,在他的指导下,Frank Rowlett 破解了日本人的PURPLE加密机(紫密),截获了日 本的大量外交和军事的秘密

密码学的演变历史(2)香农的贡献 ●1948年,Claude Shannon's发表 "The Communication Theory of Secrecy System' 成为现代密码学理论基础。 1949年,Shannon.在其著名的“信息论”发表一年之后, 又发表了论文“保密系统的通信理论”,首次将密码学 研究置于坚实的数学基础上。 该理论的重大贡献在于: 建立了通信保密/密码学严格的理论基础; 证明了一次一密(one--time pad)的密码系统是完善保密的,导致 了对流密码的研究和应用; 提出分组密码设计应该遵循的准则,如扩散性和混淆性; 证明了消息冗余使得破译者统计分析成功的理论值(唯一解距离) 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security -2 5/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 5/81 密码学的演变历史(2) 香农的贡献 ⚫ 1948年, Claude Shannon’s发表 “The Communication Theory of Secrecy System”, 成为现代密码学理论基础。 ⚫ 1949年,Shannon在其著名的“信息论” 发表一年之后, 又发表了论文“保密系统的通信理论”, 首次将密码学 研究置于坚实的数学基础上。 ⚫ 该理论的重大贡献在于: ⚫ 建立了通信保密/密码学严格的理论基础; ⚫ 证明了一次一密(one-time pad)的密码系统是完善保密的,导致 了对流密码的研究和应用; ⚫ 提出分组密码设计应该遵循的准则,如扩散性和混淆性; ⚫ 证明了消息冗余使得破译者统计分析成功的理论值(唯一解距离)

密码学的演变历史(2) 15 Claude Elwood Shannon (Apr.30,1916-Feb.24, 2001),美国电气工程师和数学家,被誉为信息论之父 "the father of information theory". 香农之有名在于他以1948年发表的那篇旷世论文而奠 定了现代信息论基础。其实早在1937年,当21岁的 香农还是MT的硕士研究生时,他便在他的硕士论文 中论述了布尔代数的电子实现和应用,可以构建和解 决任何逻辑的和数字的关系,因此奠定了数字计算机 和数字电路设计理论的基础。他的硕士论文一直被认 为是迄今最重要的硕士论文。 。1949-1967,密码学研究处于沉寂时期 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security -2 6/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 6/81 密码学的演变历史(2) ⚫ Claude Elwood Shannon (Apr. 30, 1916 – Feb. 24, 2001), 美国电气工程师和数学家,被誉为信息论之父 "the father of information theory". ⚫ 香农之有名在于他以1948年发表的那篇旷世论文而奠 定了现代信息论基础。其实早在1937年,当21岁的 香农还是MIT的硕士研究生时,他便在他的硕士论文 中论述了布尔代数的电子实现和应用,可以构建和解 决任何逻辑的和数字的关系,因此奠定了数字计算机 和数字电路设计理论的基础。他的硕士论文一直被认 为是迄今最重要的硕士论文。 ⚫ 1949-1967,密码学研究处于沉寂时期

密码学的演变历史(3) Feistel,Whitfield Diffie,Matin Hellman ●1971,IBM发明Luciffer Cipher,128位密钥作 分组加密。这项发明是由Horst Feistel(Jan.30,1915-Nov.14,1990)领导的, 他是密码学家,当时在BM负责设计加密器, 他的工作最终激发了7O年代Data Encryption Standard(DES)的研发高潮 ·1976-1977,美国国家标准局正式公布实施 DES ●1975,Vhitfield Diffie和Matin Hellman,发 表A New Direction in Cryptography,首次提 出适应网络保密通信的公开密钥思想,揭开 现代密码学研究的序幕,具有划时代的意义 ¥ 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security -2 7/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 7/81 密码学的演变历史(3) Feistel, Whitfield Diffie, Matin Hellman ⚫ 1971, IBM发明Luciffer Cipher, 128位密钥作 分组加密。这项发明是由Horst Feistel(Jan.30, 1915–Nov.14,1990)领导的, 他是密码学家,当时在IBM负责设计加密器, 他的工作最终激发了70年代Data Encryption Standard (DES)的研发高潮 ⚫ 1976-1977,美国国家标准局正式公布实施 DES ⚫ 1975, Whitfield Diffie 和 Matin Hellman, 发 表A New Direction in Cryptography, 首次提 出适应网络保密通信的公开密钥思想,揭开 现代密码学研究的序幕,具有划时代的意义

密码学的演变历史(4) 海车不 105 R.S.A..Abbas El Gamal,Lai Xuejia 1977-1978,Ronald Rivest,Adi Shamir,.Len Adleman:第一次提出公 开密钥密码系统的实现方法RSA 1981,成立International Association for Cryptology Research 1985,Abbas El Gamal提出概率密 码系统EIGamal方法 1990-1992,Lai Xuejia and James: IDEA,The International Data Encryption Algorithm 0 2000,AES,Advanced Encryption Standard 平N两 婚道 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security-2 8/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 8/81 密码学的演变历史(4) R.S.A., Abbas El Gamal, Lai Xuejia ⚫ 1977-1978,Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir, Len Adleman第一次提出公 开密钥密码系统的实现方法RSA ⚫ 1981,成立International Association for Cryptology Research ⚫ 1985,Abbas El Gamal提出概率密 码系统ElGamal方法 ⚫ 1990-1992,Lai Xuejia and James: IDEA, The International Data Encryption Algorithm ⚫ 2000, AES, Advanced Encryption Standard

密码学基本术语TERMINOLOGIES Cryptology保密学),源自希腊语(Greek) Kryptos:hidden;logos:word,是密码学和密码处理过程的研究 Cryptography:The Science and Study of Secret Writing, 编码学 ● Cryptanalysis:The Science and Study of Secret Breaking, 码破译学 ● Cipher:A secret method of writing加密方法 ● Encipher(encipherment),encryption:将明文转换成密文的过程 ● Decipher(decipherment),decryption:将密文还原成明文的过程 Plaintext(cleartext):原始的可读数据,明文 ● Ciphertext(Cryptogram):加密后的不可解读之文件,密文 ● Ky:密钥,对加密与解密过程进行控制的参数 E(m):Encryption Transformation加密变换 D(c):Decryption Transformation解密变换 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security-2 9/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 9/81 ⚫ Cryptology(保密学),源自希腊语(Greek) Kryptós: hidden; logos: word, 是密码学和密码处理过程的研究 ⚫ Cryptography: The Science and Study of Secret Writing,密码 编码学 ⚫ Cryptanalysis: The Science and Study of Secret Breaking,密 码破译学 ⚫ Cipher: A secret method of writing 加密方法 ⚫ Encipher (encipherment), encryption: 将明文转换成密文的过程 ⚫ Decipher (decipherment), decryption: 将密文还原成明文的过程 ⚫ Plaintext (cleartext): 原始的可读数据,明文 ⚫ Ciphertext (Cryptogram): 加密后的不可解读之文件,密文 ⚫ Key: 密钥,对加密与解密过程进行控制的参数 ⚫ E(m): Encryption Transformation 加密变换 ⚫ D(c): Decryption Transformation 解密变换 密码学基本术语 Terminologies
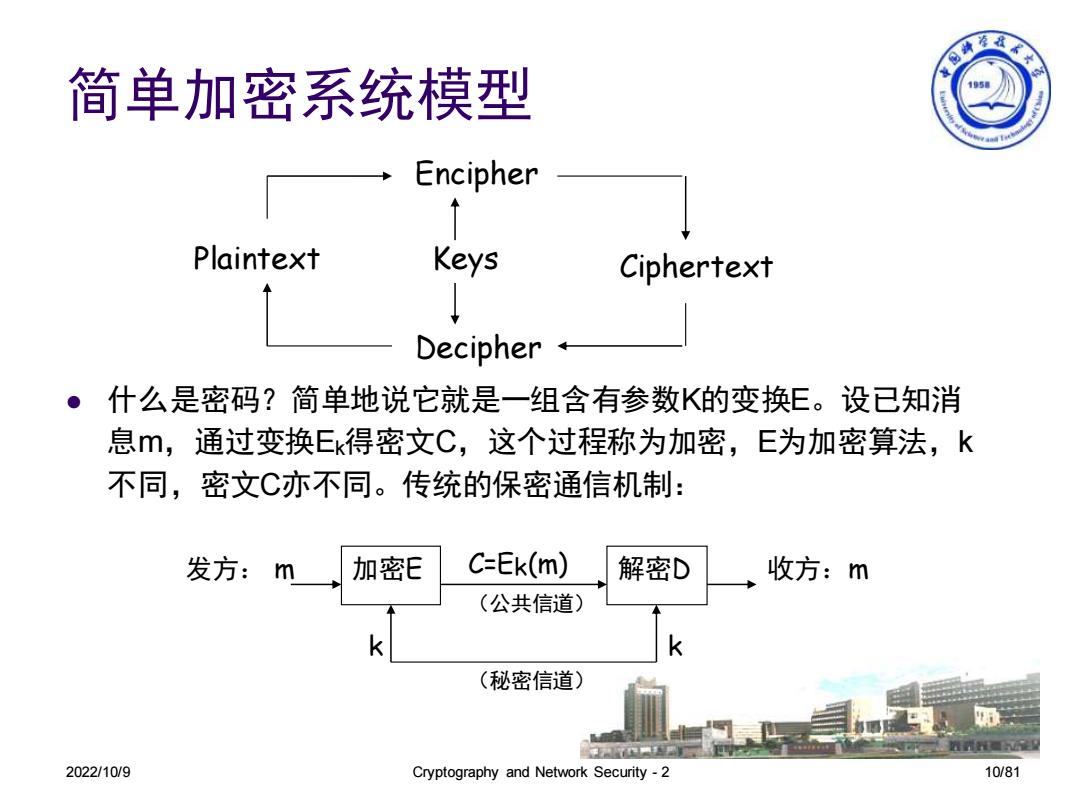
海拳家大 简单加密系统模型 15 Encipher Plaintext Keys Ciphertext Decipher 什么是密码?简单地说它就是一组含有参数K的变换E。设已知消 息m,通过变换Ek得密文C,这个过程称为加密,E为加密算法,k 不同,密文C亦不同。传统的保密通信机制: 发方:m 加密E C=Ek(m) 解密D 收方:m (公共信道) (秘密信道) 甲= 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security-2 10/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 10/81 ⚫ 什么是密码?简单地说它就是一组含有参数K的变换E。设已知消 息m,通过变换Ek得密文C,这个过程称为加密,E为加密算法,k 不同,密文C亦不同。传统的保密通信机制: Encipher Plaintext Keys Ciphertext Decipher 发方: m C=Ek(m) 收方:m k k (公共信道) 加密E 解密D (秘密信道) 简单加密系统模型

理论安全和实际安全 理论安全,或无条件安全Theoretical Secure(or Perfect Secure) 攻击者无论截获多少密文,都无法得到足够的信息来唯 地决定明文。Shannon用理论证明:欲达理论安全,加密 密钥长度必须大于等于明文长度,密钥只用一次,用完即 丢,即一次一密,One--time Pad,不实用。 实际安全,或计算上安全Practical Secure(or Computationally Secure) 如果攻击者拥有无限资源,任何密码系统都是可以被破译 的;但是在有限的资源范围内,攻击者都不能通过系统的 分析方法来破解系统,则称这个系统是计算上安全的或破 译这个系统是计算上不可行(Computationally Infeasible)。 道道 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security -2 11/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 11/81 ⚫ 理论安全,或无条件安全Theoretical Secure (or Perfect Secure) 攻击者无论截获多少密文,都无法得到足够的信息来唯一 地决定明文。Shannon用理论证明:欲达理论安全,加密 密钥长度必须大于等于明文长度,密钥只用一次,用完即 丢,即一次一密,One-time Pad,不实用。 ⚫ 实际安全,或计算上安全Practical Secure (or Computationally Secure) 如果攻击者拥有无限资源,任何密码系统都是可以被破译 的;但是在有限的资源范围内,攻击者都不能通过系统的 分析方法来破解系统,则称这个系统是计算上安全的或破 译这个系统是计算上不可行(Computationally Infeasible)。 理论安全和实际安全