
190 悠 、O入VIW1VE农、 Chapter 5.Phase diagrams ”大餐横城工置部 w SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Chapter 5. Phase diagrams

190> Exercises 1.Define (a)phase in a material and (b)a phase diagram. 2.Write the equation for Gibbs phase rule and define each of the terms 3.What are the four Hume-rothery rules for the solid solubility of one element in another 4.Cite three variables that determine the microstructure of an alloy 5.What thermodynamic condition must be met for a state of equilibrium to exit 6.What is the difference between the states of phase equilibrium and metastability SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Exercises 1. Define (a) phase in a material and (b) a phase diagram. 2. Write the equation for Gibbs phase rule and define each of the terms 3. What are the four Hume-rothery rules for the solid solubility of one element in another 4. Cite three variables that determine the microstructure of an alloy 5. What thermodynamic condition must be met for a state of equilibrium to exit 6. What is the difference between the states of phase equilibrium and metastability
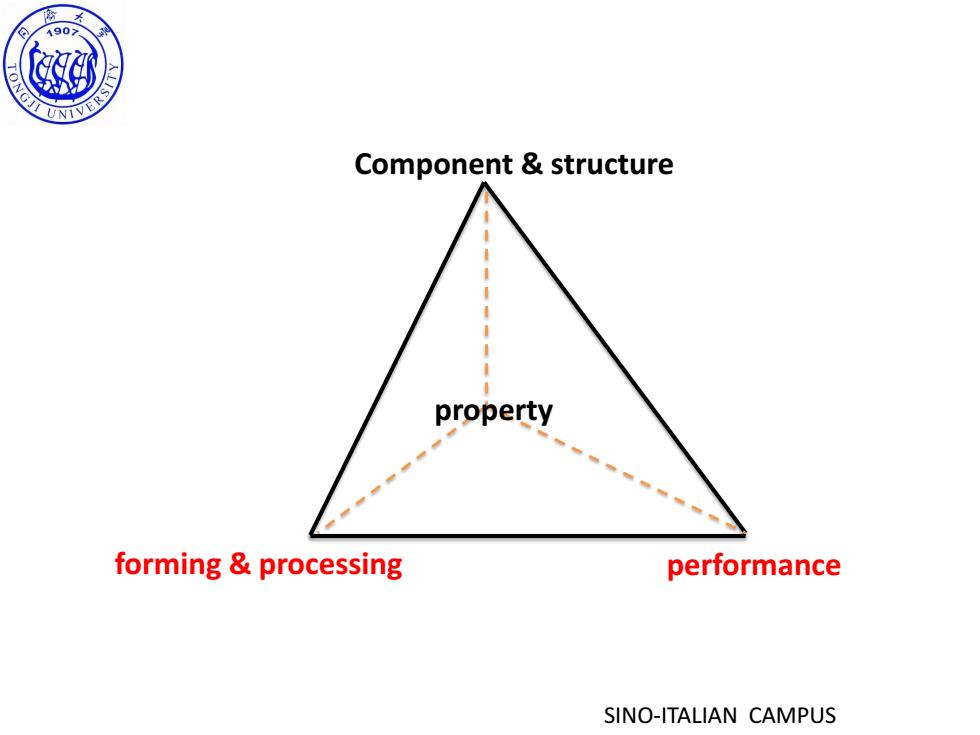
190习 TONGJI UNIVER、 Component structure property forming processing performance SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Component & structure forming & processing performance property

190> OUTLINE 1.Definition and basic concepts 2.The interpretation of diagram 3.The study of a development phase diagram 4.Study of a binary alloy phase diagram SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS OUTLINE 1. Definition and basic concepts 2. The interpretation of diagram 3. The study of a development phase diagram 4. Study of a binary alloy phase diagram

190> 5.1 Definitions Components:pure metals and/or compounds of which an alloy is composed. "system":a specific body of material under consideration.Or it may relate to the series of possible alloys consisting of the same compounds,but without regard to alloy composition. "Solvent"represents the element or compound that in the greatest amount(host atoms,host material). "Solute"is used to denote an element or compound present in a minor concentration. Solid solution SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS 5.1 Definitions Components: pure metals and/or compounds of which an alloy is composed. “system” : a specific body of material under consideration. Or it may relate to the series of possible alloys consisting of the same compounds, but without regard to alloy composition. “Solvent” represents the element or compound that in the greatest amount( host atoms, host material). ”Solute” is used to denote an element or compound present in a minor concentration. Solid solution
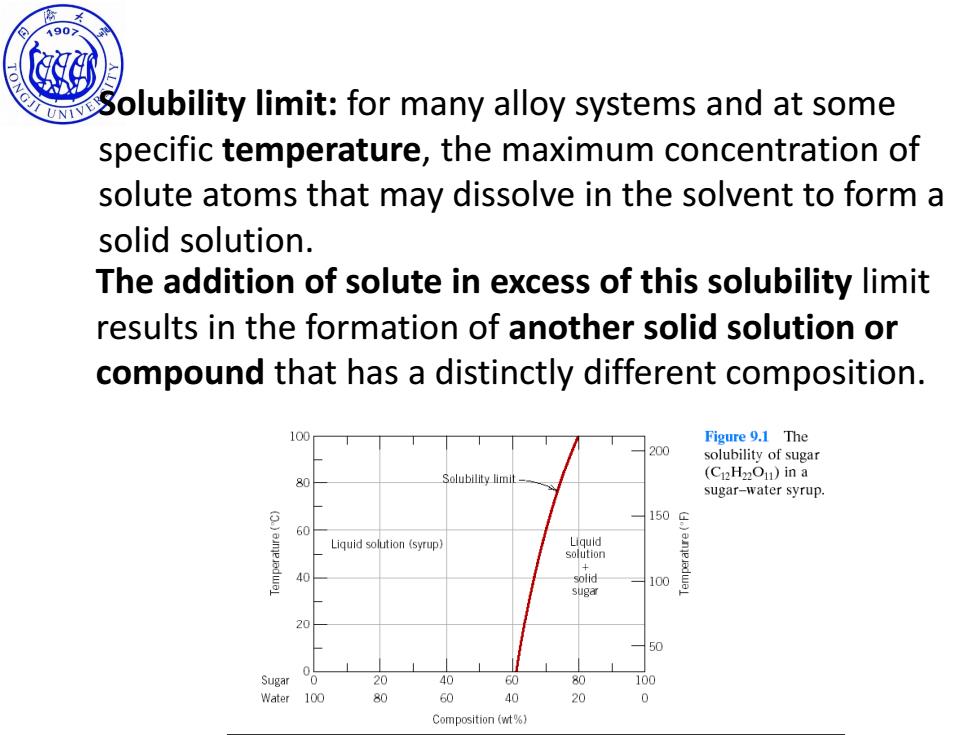
190> olubility limit:for many alloy systems and at some specific temperature,the maximum concentration of solute atoms that may dissolve in the solvent to form a solid solution. The addition of solute in excess of this solubility limit results in the formation of another solid solution or compound that has a distinctly different composition. 100 Figure 9.1 The 200 solubility of sugar Solubility limit (CnH22On)in a 80 sugar-water syrup. 60 560 Liquid solution (syrup) Liquld solution + 40 solid 100 sugar 20 50 Sugar 0 20 40 60 80 100 Water 100 80 60 40 20 0 Composition (wt%)
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Solubility limit: for many alloy systems and at some specific temperature, the maximum concentration of solute atoms that may dissolve in the solvent to form a solid solution. The addition of solute in excess of this solubility limit results in the formation of another solid solution or compound that has a distinctly different composition

190 A phase may be defined as a homogeneous portion of a system that has uniform physical and chemical characteristics. A phase can consider to be a pure material,but a pure material may contain two or phases. Monophase system “homogeneous'” Multiphase system "heterogeneous"or "mixture" SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS A phase may be defined as a homogeneous portion of a system that has uniform physical and chemical characteristics. Monophase system “homogeneous” Multiphase system “heterogeneous” or “mixture” A phase can consider to be a pure material, but a pure material may contain two or phases
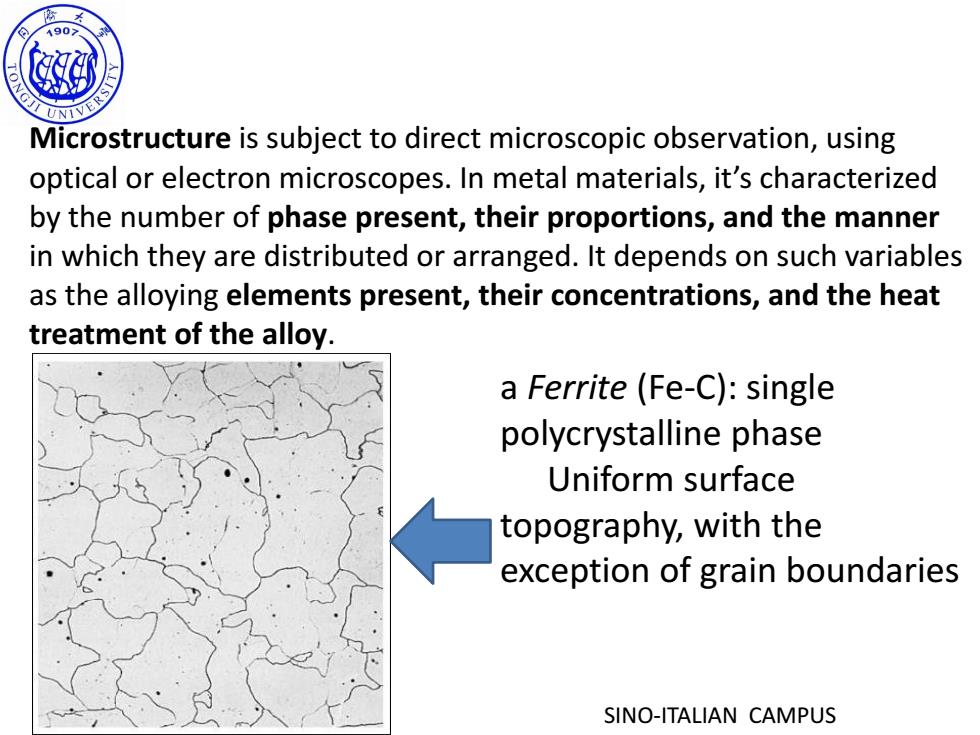
190> G Microstructure is subject to direct microscopic observation,using optical or electron microscopes.In metal materials,it's characterized by the number of phase present,their proportions,and the manner in which they are distributed or arranged.It depends on such variables as the alloying elements present,their concentrations,and the heat treatment of the alloy. a Ferrite (Fe-C):single polycrystalline phase Uniform surface topography,with the exception of grain boundaries SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Microstructure is subject to direct microscopic observation, using optical or electron microscopes. In metal materials, it’s characterized by the number of phase present, their proportions, and the manner in which they are distributed or arranged. It depends on such variables as the alloying elements present, their concentrations, and the heat treatment of the alloy. a Ferrite (Fe-C): single polycrystalline phase Uniform surface topography, with the exception of grain boundaries

190> Equilibrium is another essential concept and connected with the free energy(or entropy). free energy:function of the internal energy of a system,and also the randomness or disorder of the atoms or molecules.A system is at equilibrium if its free energy is at minimum under some specified combination of temperature,pressure,and composition. The term phase equilibrium refers to equilibrium as it applies to systems in which more than one phase may exist. SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Equilibrium is another essential concept and connected with the free energy(or entropy). free energy: function of the internal energy of a system, and also the randomness or disorder of the atoms or molecules. A system is at equilibrium if its free energy is at minimum under some specified combination of temperature, pressure, and composition. The term phase equilibrium refers to equilibrium as it applies to systems in which more than one phase may exist

190> Nonequilibrium or metastable state:a state of equilibrium is never completely achieved because the rate of approach to equilibrium is extremely slow; A metastable state or microstructure may persist indefinitely experiencing only extremely slight and almost imperceptible changes as time progresses.Often,metastable structures are of more practical significance than equilibrium ones. For example,some steel and aluminum alloys rely for their strength on the development of metastable microstructures during carefully designed heat treatments SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Nonequilibrium or metastable state: a state of equilibrium is never completely achieved because the rate of approach to equilibrium is extremely slow; A metastable state or microstructure may persist indefinitely, experiencing only extremely slight and almost imperceptible changes as time progresses. Often, metastable structures are of more practical significance than equilibrium ones. For example, some steel and aluminum alloys rely for their strength on the development of metastable microstructures during carefully designed heat treatments