
190> 悠© ONGJI UNIVERST Chap.4 Material properties SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Chap.4 Material properties

190> Exercises NGJ 1.What's material properties,they can be grouped into which ones? 2.What's the difference between structural material and functional material? 3.Define engineering stress and engineering strain 4.State elastic deformation and plastic deformation,and tell the difference between them. 5.State Hooke's law SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Exercises 1. What’s material properties, they can be grouped into which ones? 2. What’s the difference between structural material and functional material? 3. Define engineering stress and engineering strain 4. State elastic deformation and plastic deformation, and tell the difference between them. 5. State Hooke’s law

190> Exercises 1 1.Describe the ductile to brittle transition of metal.What type of metals are more susceptible to ductile to brittle transition? 2.Describe the mechanism of crack propagation for both ductile and brittle modes of fracture. 3.Explain why the strength of brittle materials are much lower than predicted by theoretical calculations 4.Define fracture toughness in terms of (a)a brief statement,and (b)an equation;define all parameters in this equation. SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Exercises 1. Describe the ductile to brittle transition of metal. What type of metals are more susceptible to ductile to brittle transition? 2. Describe the mechanism of crack propagation for both ductile and brittle modes of fracture. 3. Explain why the strength of brittle materials are much lower than predicted by theoretical calculations 4. Define fracture toughness in terms of (a) a brief statement, and (b) an equation; define all parameters in this equation

190 ONGJI UNIVERS元 4.1 Introduction Properties are the way in which the material behaves when external stresses are applied. SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Properties are the way in which the material behaves when external stresses are applied. 4.1 Introduction

190 NGJ ERS While in service use,all materials are exposed to external stimuli that evoke some type of response. For example,a specimen subjected to forces will experience deformation;or a polished metal surface will reflect light.Property is a material trait in terms of the kind and magnitude of response to a specific imposed stimulus.Generally,definitions of properties are made independent of material shape and size. SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS While in service use, all materials are exposed to external stimuli that evoke some type of response. For example, a specimen subjected to forces will experience deformation; or a polished metal surface will reflect light. Property is a material trait in terms of the kind and magnitude of response to a specific imposed stimulus. Generally, definitions of properties are made independent of material shape and size

190> Materials properties G Mechanical properties->Mechanical stresses, strength,etc Thermal properties->Linked to the heat transmission and to the thermal capacity Electrical and magnetic properties->Electric and magnetic fields,electric conductivity,etc. Optical properties-Include absorption, transmission,light diffusion Deteriorative->Chemical interactions with the environment.corrosion resistance SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Materials properties Mechanical properties→ Mechanical stresses, strength, etc… Thermal properties → Linked to the heat transmission and to the thermal capacity Electrical and magnetic properties→ Electric and magnetic fields, electric conductivity, etc. Optical properties→ Include absorption, transmission, light diffusion Deteriorative→Chemical interactions with the environment, corrosion resistance
190习 © 入VGJ入V1ER、 Structural material Engineering material Functional material SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Structural material Engineering material Functional material

190 Mechanical properties Many materials,when in service,are subjected to forces or loads The mechanical behavior of a material reflects the relationship between its response or deformation to an applied load or force. Important mechanical properties are strength, hardness,ductility,and stiffness. Usually materials are tested with standardized international procedures American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Mechanical properties Many materials, when in service, are subjected to forces or loads The mechanical behavior of a material reflects the relationship between its response or deformation to an applied load or force. Important mechanical properties are strength, hardness, ductility, and stiffness. Usually materials are tested with standardized international procedures - American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM)
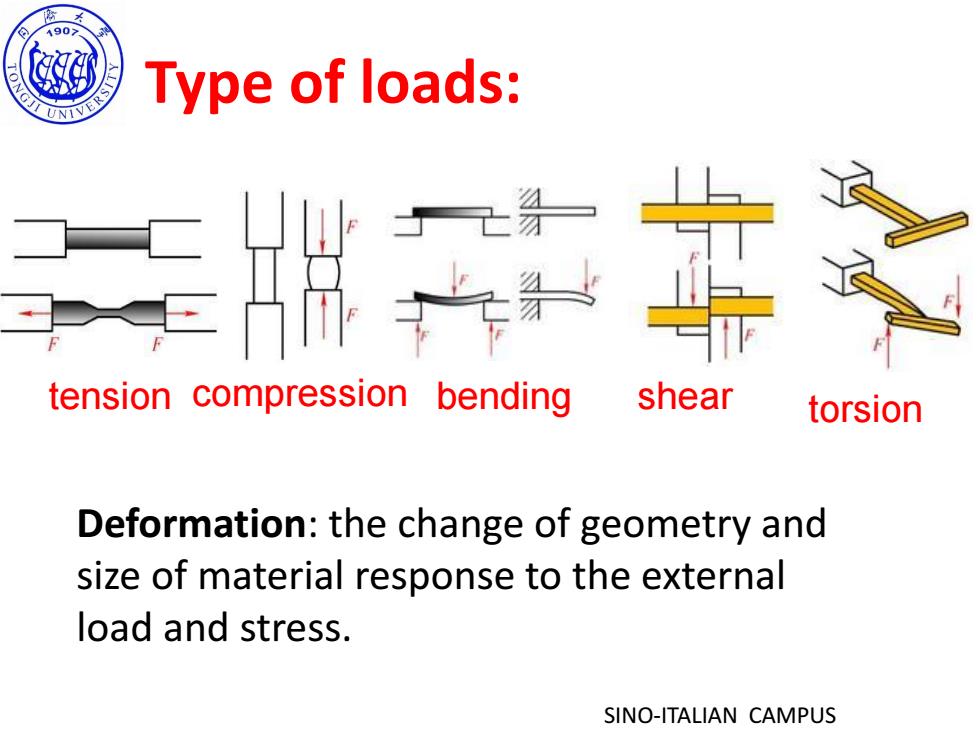
8 190> NGJI Type of loads: 实 tension compression bending shear torsion Deformation:the change of geometry and size of material response to the external load and stress. SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Deformation: the change of geometry and size of material response to the external load and stress. tension compression bending shear torsion Type of loads:

Strength Strength:the ability of resistant to deformation and fracture response to external loads It can be classified tensile strength,compressive strength,bending strength,shear strength and torsion strength according to different loads. The tensile-resistant strength can be given by tension test
Strength Strength: the ability of resistant to deformation and fracture response to external loads It can be classified tensile strength, compressive strength, bending strength, shear strength and torsion strength according to different loads. The tensile-resistant strength can be given by tension test