
2014/5/8 Iaflurnees ef conling degree Chapter 7 Cooling System T.1 Componeuts of Cooling5em冷每那成 爱功机冷却系 he groming小w触国ta frl comm年oL rhaut gat ratiies线s罐ies life ride cumfet.aad口rl >Campanr of Cadin到m净系成 1上Ce山t待每心 T3我adialar放是 ,1.A我adiatr Fan冷每风责 15Temt(节国■i 15作arh甲水票 1O州Cading抽冷年 凡冷大复 1/m 所限汽单国 窗凡冷去置 鸭结大究物 口a金ation af cooling市m清期系分类 Temperature of eagine at proper conling conditions Comparison between these two cooling systems Systems Temperature range意 Application disadvantages Widely wed in Water ■●olant in evlinder heid上353u363 Powerful cooling cooling Water Easy to re电lae Fasy to sta时n winte灯 nh线s Air Cylinder bead:423453玉 Cyliader wall:433~473K Air Big aobe cooling Big power los 花n线年真绿 鸭牌大甲代原州 阳情大摩汽海零滑 ☆代存甲 Air cooling s等tn Camponeuts of water cooling system 72Cedl冷每狼 物R冷? 猫 同将大汽摩恒 复日海木置 降修大示究率恒 曾R冷大 型 阳密大究中酒 1
2014/5/8 1 1/27 同济大学汽车学院 Chapter 7 Cooling System 发动机冷却系 7.1 Components of Cooling System (冷却系组成) 7.2 Coolant (冷却液) 7.3 Radiator (散热器) 7.4 Radiator Fan (冷却风扇) 7.5 Thermostat (节温器) 7.6 Water Pump (水泵) 7.7 Oil Cooling (机油冷却) 2/27 同济大学汽车学院 7.1 Components of Cooling System (冷却系组成) The growing demands with respect to fuel consumption, exhaust gas emissions, service life, ride comfort, and package have led to modern cooling systems for internal combustion engines in the motor vehicles. Cooling system is used to keep the engine at proper temperature (80±5℃). 3/27 同济大学汽车学院 Cooling degree Effects Too cold (1)More heat loss (2)For diesel engine, oil viscosity(粘度) increases which results in higher friction loss(摩擦损失);for gasoline engine, gasoline condenses in cylinder and flows into crankcase, influencing lubrication(润滑). (3)Mixture is difficult to be ignited (4)Increased oil viscosity results in serious wear Too hot (1)Lower volumetric efficiency(充气效率);lower power (2)Easier to deflagrate(爆燃) (3)Normal gap between moving components is destroyed which causes serious wear ; (4)Worse lubrication (5)Worse mechanical properties of parts causes damage Influences of cooling degree 4/27 同济大学汽车学院 Classification of cooling system (冷却系分类) Water cooling Air cooling 5/27 同济大学汽车学院 Temperature of engine at proper cooling conditions Systems Temperature range(温度范围) Water cooling Coolant in cylinder head: 353~363K Cylinder wall(气缸壁): below 470~550K Air cooling Cylinder head: 423~453K Cylinder wall: 433~473K 6/27 同济大学汽车学院 Systems Advantages and disadvantages Application Water cooling Powerful cooling Easy to regulate Easy to start in winter Widely used in automotive engines Air cooling Bad cooling Big noise Big power loss Small displacement engines and military vehicle engines (军车发动机) Comparison between these two cooling systems 7/27 同济大学汽车学院 Air cooling system video Air cooling system takes use of the rapid flow of air to take the heat from cylinder wall . 8/27 同济大学汽车学院 Components of water cooling system 上散热器水管 冷却风扇 补给水箱 节温器 暖气风箱 Basic components of water cooling system are coolant, radiator, radiator fan, water pump, thermostat and different hoses. 9/27 同济大学汽车学院 Coolant performs two critical functions. It keeps the radiator fluid from freezing in wintry conditions and keeps the engine from overheating. The main composition of coolant is water because of its huge specific heat capacity(比热容) and it is easy to get . However, if the water contains part of calcium (钙), magnesium(镁) and other mineral salts (矿物盐类)which will form scaling(结垢) in engines, the proper cooling process will be damaged. And electrochemical reaction erodes(电 化学反应腐蚀) cooling system. So without any additive(添加剂), we should only use soft water(软水) as coolant. 7.2 Coolant(冷却液) However , pure water freezes at 0°C which cannot meet the need. So we usually add antifreeze(防冻剂) in water to raise its boiling point and lower its freezing point(冰 点). Coolant contains: water/ antifreeze/additive
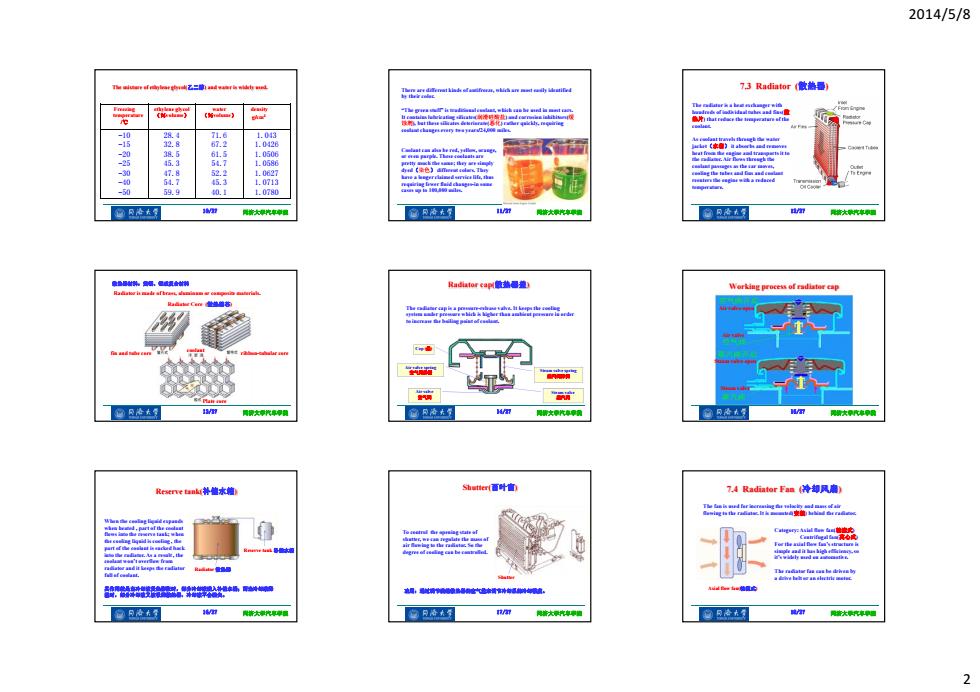
2014/5/8 7,3 Radiator散热量】 e -10 24 716 1.03 32.8 67.2 L.028 3.5 61.5 1.0506 L.0586 1.0827 54.7 45.3 1.0713 -50 59.9 0.1 1.0780 1型 同将大汽卓国 窗凡冷大司 风情★原酒 窗凡冷复 培大鲜汽率■ 重时W、项W Radiator cap到散热推 Working process of radiator cap 同骨大代厚甲用 得情大章汽甲滑 大代用 Reserve tank补德水塘 shte通叶直 T.4 Radiator Fan冷却风德) For the aual Dew faa'satrw ,山 The radatar fan eas每由hn的 aErive hekegr an slertrie isstec 界4 物月冷右餐 同将大汽摩恒 复日冷木置 n/ 降修大示究率植 @R冷大司 阳密大究率■ 2
2014/5/8 2 10/27 同济大学汽车学院 The mixture of ethylene glycol(乙二醇) and water is widely used. Freezing temperature /℃ ethylene glycol (%volume) water (%volume) density g/cm3 -10 -15 -20 -25 -30 -40 -50 28.4 32.8 38.5 45.3 47.8 54.7 59.9 71.6 67.2 61.5 54.7 52.2 45.3 40.1 1.043 1.0426 1.0506 1.0586 1.0627 1.0713 1.0780 11/27 同济大学汽车学院 There are different kinds of antifreeze, which are most easily identified by their color. “The green stuff” is traditional coolant, which can be used in most cars. It contains lubricating silicates(润滑硅酸盐) and corrosion inhibitors(缓 蚀剂), but these silicates deteriorate(恶化) rather quickly, requiring coolant changes every two years/24,000 miles. Coolant can also be red, yellow, orange, or even purple. These coolants are pretty much the same; they are simply dyed(染色) different colors. They have a longer claimed service life, thus requiring fewer fluid changes-in some cases up to 100,000 miles. 12/27 同济大学汽车学院 7.3 Radiator (散热器) The radiator is a heat exchanger with hundreds of individual tubes and fins(散 热片) that reduce the temperature of the coolant. As coolant travels through the water jacket(水套) it absorbs and removes heat from the engine and transports it to the radiator. Air flows through the coolant passages as the car moves, cooling the tubes and fins and coolant reenters the engine with a reduced temperature. 13/27 同济大学汽车学院 Radiator Core (散热器芯) 散热器材料:黄铜、铝或复合材料 Radiator is made of brass, aluminum or composite materials. fin and tube core ribbon-tubular core Plate core coolant 14/27 同济大学汽车学院 Radiator cap(散热器盖) The radiator cap is a pressure-release valve. It keeps the cooling system under pressure which is higher than ambient pressure in order to increase the boiling point of coolant. Steam valve 蒸汽阀 Air valve 空气阀 Steam valve spring 蒸汽阀弹簧 Air valve spring 空气阀弹簧 Cap (盖) 15/27 同济大学汽车学院 Working process of radiator cap Air valve open Air valve Steam valve open Steam valve 16/27 同济大学汽车学院 Reserve tank(补偿水箱) 其作用就是当冷却液受热膨胀时,部分冷却液流入补偿水桶;而当冷却液降 温时,部分冷却液又被吸回散热器,冷却液不会溢失。 Radiator 散热器 Reserve tank 补偿水箱 When the cooling liquid expands when heated , part of the coolant flows into the reserve tank; when the cooling liquid is cooling , the part of the coolant is sucked back into the radiator. As a result , the coolant won’t overflow from radiator and it keeps the radiator full of coolant. 17/27 同济大学汽车学院 功用:通过调节流经散热器的空气量来调节冷却系的冷却强度。 Shutter(百叶窗) Shutter To control the opening state of shutter, we can regulate the mass of air flowing to the radiator. So the degree of cooling can be controlled. 18/27 同济大学汽车学院 7.4 Radiator Fan (冷却风扇) The fan is used for increasing the velocity and mass of air flowing to the radiator. It is mounted(安装) behind the radiator. Category: Axial flow fan(轴流式) Centrifugal fan(离心式) For the axial flow fan’s structure is simple and it has high efficiency, so it’s widely used on automotive. The radiator fan can be driven by a drive belt or an electric motor. Axial flow fan(轴流式)
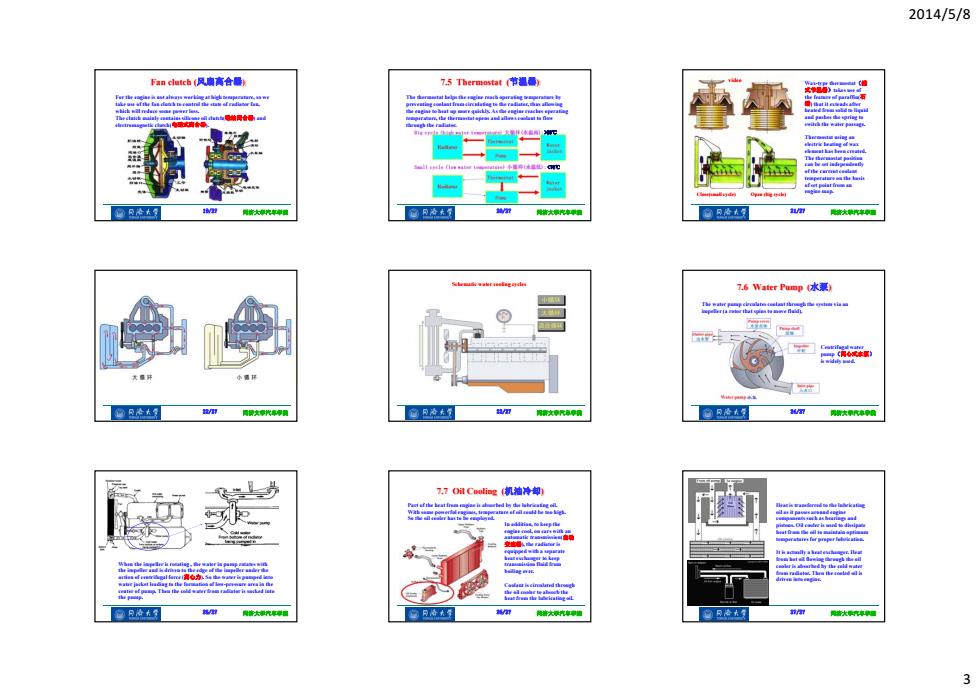
2014/5/8 下an clutch(风扇高合船 75 Thermostat节温播, 凡冷大复 同物大汽卓国 窗凡冷法气 得结大究面 合R冷大写 7.6 Water Pur四即水泵 单面rja mtr that ains特辆nd @及冷大复 /用 阳新大摩汽原平滑 大代甲用 7,701Co0iag机袖冷却) InAAmResta 包月冷去? 同将大弹汽摩帽 鸭著大示究率酒 @R冷大 阳密大究中酒 3
2014/5/8 3 19/27 同济大学汽车学院 Fan clutch (风扇离合器) For the engine is not always working at high temperature, so we take use of the fan clutch to control the state of radiator fan, which will reduce some power loss. The clutch mainly contains silicone oil clutch(硅油离合器) and electromagnetic clutch(电磁式离合器). 20/27 同济大学汽车学院 7.5 Thermostat (节温器) The thermostat helps the engine reach operating temperature by preventing coolant from circulating to the radiator, thus allowing the engine to heat up more quickly. As the engine reaches operating temperature, the thermostat opens and allows coolant to flow through the radiator. 89℃ 21/27 同济大学汽车学院 Close(small cycle) Open (big cycle) Wax-type thermostat(蜡 式节温器)takes use of the feature of paraffin(石 蜡) that it extends after heated from solid to liquid and pushes the spring to switch the water passage. Thermostat using an electric heating of wax element has been created. The thermostat position can be set independently of the current coolant temperature on the basis of set point from an engine map. video 22/27 同济大学汽车学院 23/27 同济大学汽车学院 Schematic water cooling cycles 24/27 同济大学汽车学院 7.6 Water Pump (水泵) The water pump circulates coolant through the system via an impeller (a rotor that spins to move fluid). Centrifugal water pump(离心式水泵) is widely used. 25/27 同济大学汽车学院 When the impeller is rotating , the water in pump rotates with the impeller and is driven to the edge of the impeller under the action of centrifugal force (离心力). So the water is pumped into water jacket leading to the formation of low-pressure area in the center of pump. Then the cold water from radiator is sucked into the pump. 26/27 同济大学汽车学院 7.7 Oil Cooling (机油冷却) Part of the heat from engine is absorbed by the lubricating oil. With some powerful engines, temperature of oil could be too high. So the oil cooler has to be employed. In addition, to keep the engine cool, on cars with an automatic transmission(自动 变速器), the radiator is equipped with a separate heat exchanger to keep transmission fluid from boiling over. Coolant is circulated through the oil cooler to absorb the heat from the lubricating oil. 27/27 同济大学汽车学院 Heat is transferred to the lubricating oil as it passes around engine components such as bearings and pistons. Oil cooler is used to dissipate heat from the oil to maintain optimum temperatures for proper lubrication. It is actually a heat exchanger. Heat from hot oil flowing through the oil cooler is absorbed by the cold water from radiator. Then the cooled oil is driven into engine