
Chapter 22 Suspension 同©大学 TONGII UNIVERSTTY Chapter 22.Suspension
Chapter 22 Suspension Chapter 22. Suspension

Chapter 22 Suspension 窗月桥大学 TONGII UNIVERSTTY Content The composition,function and elassification ofsuspension: >Structure form of common springs: >Structure form of common dampers; >rigid axle suspension >independent suspension >balanced suspension of multi-axle yehicle: active suspension and semi-active suspension
Chapter 22 Suspension Content The composition, function and classification of suspension; Structure form of common springs; Structure form of common dampers; rigid axle suspension ; independent suspension ; balanced suspension of multi-axle vehicle; active suspension and semi-active suspension

Chapter 22 Suspension 圖月儕大学 TONGII UNIVERSTTY Section 1.Overview 的 Audi O5
Chapter 22 Suspension Section 1. Overview

Chapter 22 Suspension 窗月桥大学 TONGII UNIVERSITY Function and Composition of the Suspension System >Definition:all the force delivering devices_between the vehicle frame_(or monocoque body)and the yehicle axle_( or wheel)are called suspension. >Function:transmit the vertical force,the longitudinal force the lateral force as well as the caused torques to the frame,in order to obtain a good ride comfort and stability
Chapter 22 Suspension Function: transmit the vertical force, the longitudinal force , the lateral force as well as the caused torques to the frame , in order to obtain a good ride comfort and stability. Function and Composition of the Suspension System Definition: all the force delivering devices between the vehicle frame (or monocoque body) and the vehicle axle ( or wheel) are called suspension
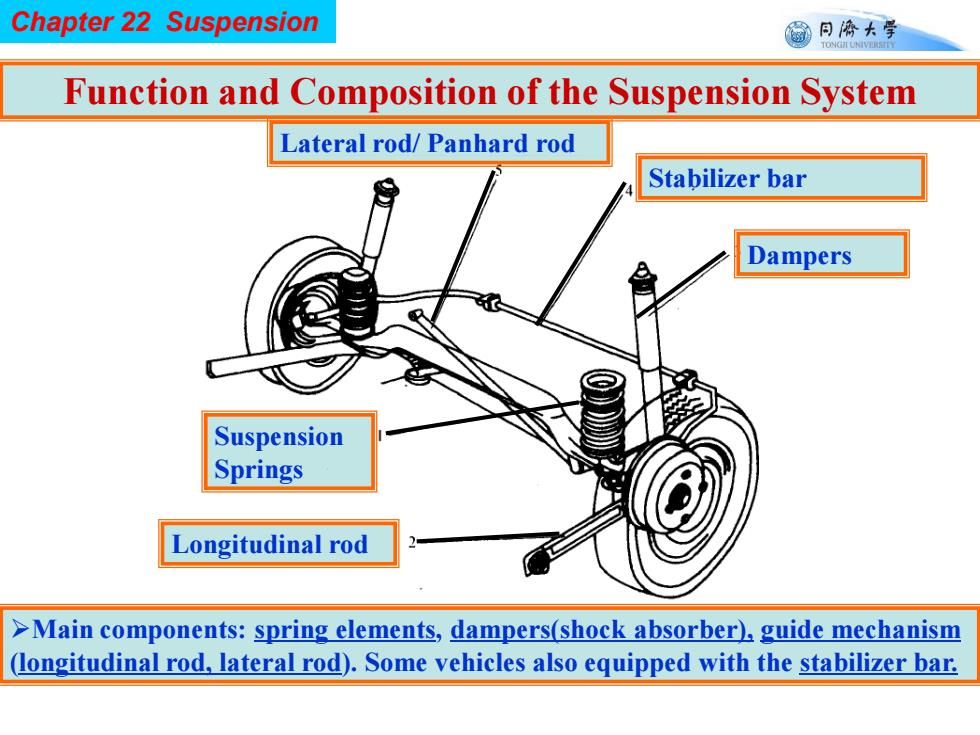
Chapter 22 Suspension 同©大学 TONGII UNIVERSTTY Function and Composition of the Suspension System Lateral rod/Panhard rod Stabilizer bar Dampers Suspension Springs Longitudinal rod >Main components:spring elements,dampers(shock absorber),guide mechanism (longitudinal rod,lateral rod).Some vehicles also equipped with the stabilizer bar
Chapter 22 Suspension Suspension Springs Dampers Stabilizer bar Longitudinal rod Lateral rod/ Panhard rod Function and Composition of the Suspension System Main components: spring elements, dampers(shock absorber), guide mechanism (longitudinal rod, lateral rod). Some vehicles also equipped with the stabilizer bar

Chapter 22 Suspension 同©大学 TONGII UNIVERSTTY Function of each components in suspension system >Spring elements:to make the connection of the frame and axle having elasticity and the ability of absorbing,buffering road impact and vibration. >Damping elements:attenuate of the vibration of the spring elements,absorb and dissipate vibrational energy. Guide arm:holding wheel trajectory,carrying and transmit > forces and torques. >Stabilizer(anti-roll bar):by steering condition,reducing body inclination and lateral angular vibration
Chapter 22 Suspension Function of each components in suspension system Spring elements: to make the connection of the frame and axle having elasticity and the ability of absorbing, buffering road impact and vibration. Damping elements: attenuate of the vibration of the spring elements, absorb and dissipate vibrational energy. Guide arm: holding wheel trajectory, carrying and transmit forces and torques. Stabilizer(anti-roll bar): by steering condition, reducing body inclination and lateral angular vibration
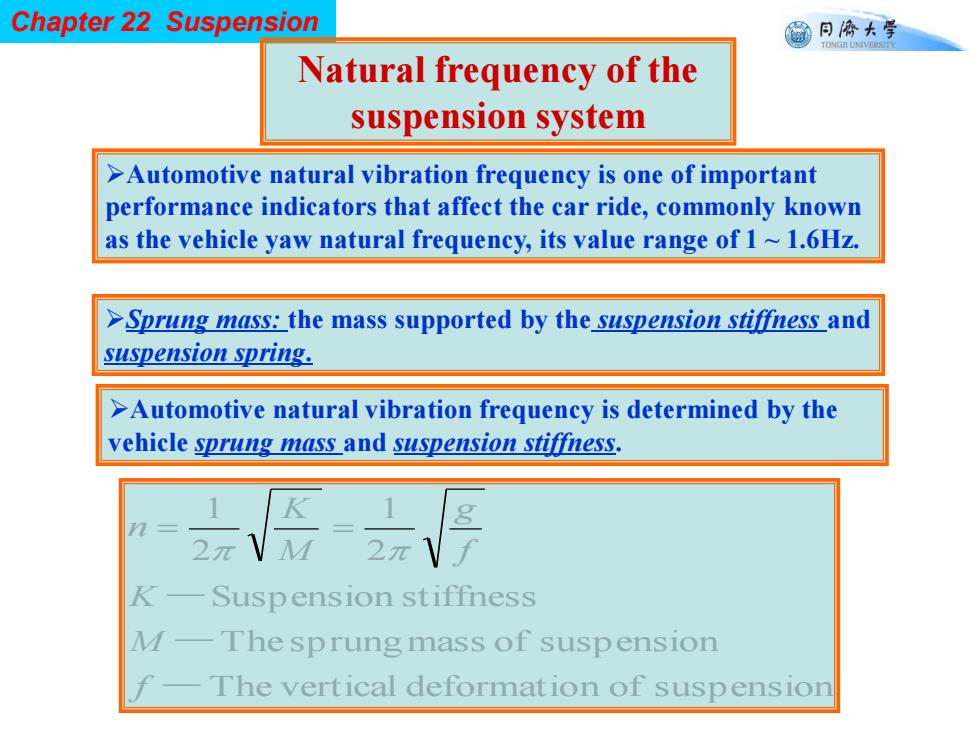
Chapter 22 Suspension 同©大学 TONGII UNIVERSTTY Natural frequency of the suspension system >Automotive natural vibration frequency is one of important performance indicators that affect the car ride,commonly known as the vehicle yaw natural frequency,its value range of 1~1.6Hz. >Sprung mass:the mass supported by the suspension stiffness and suspension spring. >Automotive natural vibration frequency is determined by the vehicle sprung mass and suspension stiffness. K-Suspension stiffness M-The sprung mass of suspension The vertical deformation of suspension
Chapter 22 Suspension Natural frequency of the suspension system The vertical deformation of suspension The sprungmass of suspension Suspension stiffness 2 1 2 1 — — — f M K f g M K n Automotive natural vibration frequency is one of important performance indicators that affect the car ride, commonly known as the vehicle yaw natural frequency, its value range of 1 ~ 1.6Hz. Sprung mass: the mass supported by the suspension stiffness and suspension spring. Automotive natural vibration frequency is determined by the vehicle sprung mass and suspension stiffness
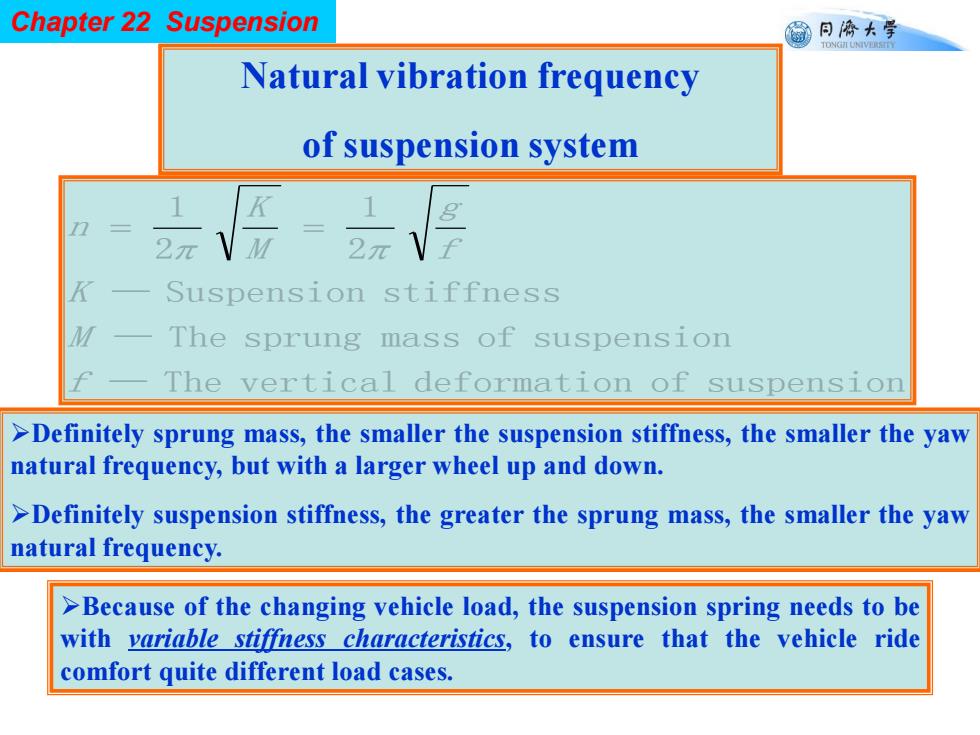
Chapter 22 Suspension 蜀同儕大学 TONGII UNIVERSITY Natural vibration frequency of suspension system 2元V Suspension stiffness The sprung mass of suspension The vertical deformation of suspension >Definitely sprung mass,the smaller the suspension stiffness,the smaller the yaw natural frequency,but with a larger wheel up and down. >Definitely suspension stiffness,the greater the sprung mass,the smaller the yaw natural frequency. >Because of the changing vehicle load,the suspension spring needs to be with variable stiffness characteristics,to ensure that the vehicle ride comfort quite different load cases
Chapter 22 Suspension Natural vibration frequency of suspension system — The vertical deformation of suspension — The sprung mass of suspension — Suspension stiffness 2 1 2 1 f M K f g M K n Definitely sprung mass, the smaller the suspension stiffness, the smaller the yaw natural frequency, but with a larger wheel up and down. Definitely suspension stiffness, the greater the sprung mass, the smaller the yaw natural frequency. Because of the changing vehicle load, the suspension spring needs to be with variable stiffness characteristics, to ensure that the vehicle ride comfort quite different load cases
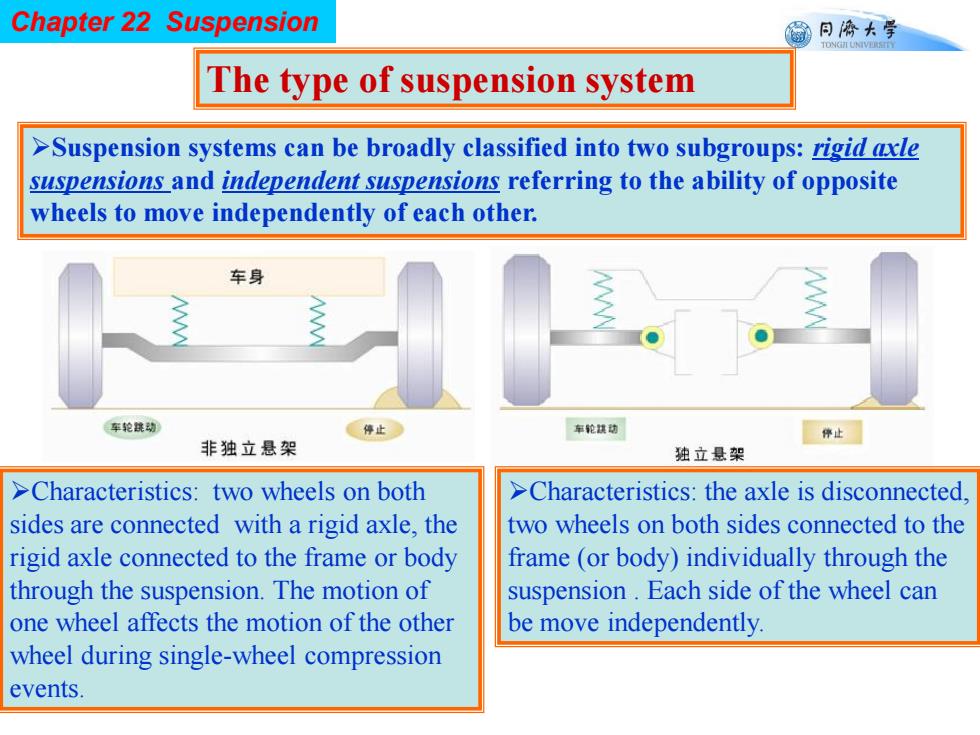
Chapter 22 Suspension 同©大学 TONGII UNIVERSTTY The type of suspension system >Suspension systems can be broadly classified into two subgroups:rigid axle suspensions and independent suspensions referring to the ability of opposite wheels to move independently of each other. 车身 车轮统动 停止 车轮扶动 停止 非独立悬架 独立悬架 >Characteristics:two wheels on both >Characteristics:the axle is disconnected. sides are connected with a rigid axle,the two wheels on both sides connected to the rigid axle connected to the frame or body frame (or body)individually through the through the suspension.The motion of suspension.Each side of the wheel can one wheel affects the motion of the other be move independently wheel during single-wheel compression events
Chapter 22 Suspension The type of suspension system Suspension systems can be broadly classified into two subgroups: rigid axle suspensions and independent suspensions referring to the ability of opposite wheels to move independently of each other. Characteristics: two wheels on both sides are connected with a rigid axle, the rigid axle connected to the frame or body through the suspension. The motion of one wheel affects the motion of the other wheel during single-wheel compression events. Characteristics: the axle is disconnected, two wheels on both sides connected to the frame (or body) individually through the suspension . Each side of the wheel can be move independently
Chapter 22 Suspension 日©大学 TONGII UNIVERSTTY The Types of Suspension System >According to the suspension >The suspension stiffness, controlled or suspension damping in motion can not not be adjusted. >Passive >Suspension stiffness,damping suspension can be adjusted automatically according to the traveling >Active condition. suspensions >Only a suspension damping of >Semi-active the suspension can be adjusted suspensions automatically
Chapter 22 Suspension According to the suspension controlled or not Passive suspension Active suspensions Semi-active suspensions The Types of Suspension System The suspension stiffness, suspension damping in motion can not be adjusted . Suspension stiffness , damping can be adjusted automatically according to the traveling condition. Only a suspension damping of the suspension can be adjusted automatically