2014/5/8 Chapter4 Fuel Supply System For Gasoline Engine Clanaiflestioe骨到 第四章 汽油机嫩油供给系统 图瑞我觉按 兴益项时文运斜储基 R冷大写 1/m 同物大汽卓国 窗凡冷法气 鸭按大汽中和 窗凡冷大复 v 喷★■ 4.1 Fuel of IC Engines(内他机的抛制 能速、红师贵查Hh尚悦业点花梅银。 Te neme the compound composed only of earboa 物提 是●气【05 天城气 ■再量 为看曼 1 30权上 雨牌大甲代原用 同带大章汽甲用 所大得代春用 hr式ormance of Gasoline代袖的性能指标) 登+4。 玉、就性指汽地受地机中世胸时,鱼声坐生的 艺器a 软性业每。 Kaock valur:the abi与af的niding每prudece deflagratios libary and sirvlooibfeogis Thredors,the ha ember ad 0号+鹅号 物地,压通比高:应得的代 小p-性 接帅骨含高。 rct the ahaity ad copltly booned offedd 03号42号 The gradesof gadline is determined 97碧叫药特 arcordia包he acta时rvalad 多信州先企锁顺质产坐路是 gavoliee.The higher of the aswa过of teat granrafed时tdy harning lgfud t/ 同将大汽摩帽 复R海大军 隐修大录究神 阳密大究率■ 1
2014/5/8 1 1/73 同济大学汽车学院 Chapter4 Fuel Supply System For Gasoline Engine 第四章 汽油机燃油供给系统 2/73 同济大学汽车学院 • The task of fuel supply system is to prepare a certain number of air-fuel mixture of certain concentration according to the working state of engine, then transporting the mixture into cylinder , and finally , pushing the exhaust gas out of cylinder. • 汽油供给系的任务是根据发动机的不同情况的要求,配制出一定数量和 浓度的可燃混合气,供入气缸,最后还要把燃烧后的废气排出气缸。 Fuel pump Fuel filter O2 sensor CTS ECU Idle air valve Air flow meter Pressure regulator Injector TPS 汽油 Gasoline 空气 Air 3/73 同济大学汽车学院 Classification(分类): Fuel Supply System with Carburetor 传统化油器式燃料供给系 Fuel Supply System with Gasoline Injection 现代汽油喷射式燃料供给系 4/73 同济大学汽车学院 4.1 Fuel of IC Engines (内燃机的燃料) 汽油 Gasoline 石油产品 柴油 Diesel 液化石油气(LPG) 天然气(CNG) Essential component of fuel is hydrogen(H) and carbon(C),with a little bit of oxygen(O), nitrogen(N),or sulfur(S) 主要成分是碳、氢,占97~ 98% 含少量硫、氧、氮等。 Petroleum products Crude Gas Gasoline Kerosene Diesel Lubricant Residua Distil-off temperature Relative evaporation 1. Light diesel 2. Kerosene 3. Motor petrol 4. Aviation petrol 5/73 同济大学汽车学院 • 仅由碳、氢两种元素组成的化合物统称碳氢化合物,简称烃。 •We name the compound composed only of carbon and hydrogen as hydrocarbon. 饱和烃 烷烃 开链烃 不饱和烃 烯烃、炔烃 •烃 环状烃 脂环烃 芳香烃 Hydrocarbon Open chain hydrocarbon Alicyclic hydrocarbon Saturated hydrocarbon Unsaturated hydrocarbon Cyclic hydrocarbon Dutrex Alkane Alkene , Alkyne 6/73 同济大学汽车学院 根据烃分子中碳原子数的不同可构成不同分子量,不同沸点的物质 Different number of carbon in hydrocarbon molecule means different boiling point C原子数 Number of carbon 沸点 Boiling point 品种 Species 分子量 性质变化趋势 Changing of nature C1 常温Room temperature 天然气 Natural gas 16 C2~C4 常温Room temperature 液化石油气 LPG 16~58 C5~C11 50~200 汽油 Gasoline 95~120 C11~C19 180~300 煤油 Kerosene 100~180 C16~C23 250~360 轻重柴油 Diesel 180~200 C23 360以上 渣油 220以上 密度小、易挥发、 稳定性好、易点燃 Smaller density /easy to volatilize/better stability/easy to be ignited 粘度增大、易自燃 Large Viscosity /Easy to spontaneous combustion 7/73 同济大学汽车学院 汽油是汽油机的燃料。汽油使用性能的好坏对发动机的动力性、经济性、可靠 性和使用寿命都有很大的影响。因此,车用汽油需要满足许多要求。 Performance of gasoline has a great impact on power , economy , reliability and service life of engines. Therefore, there is a number of requirements for motor gasoline. 影响汽油机性能的关键性指标主要是辛烷值和馏程等。 The key figures of the performance of gasoline include octane number and distillation range. 1、馏程:用燃油馏出某一百分比的温度范围来表示。 Distillation range : range of temperature in which the fuel is distilled off at a certain percentage. Performance of Gasoline (汽油的性能指标) 为了评价燃料的挥发性,以10%、50%和90%的馏出温度作为几个有代表意 义的点。 In order to evaluate the volatility of the fuel, selecting a series of distilled temperature as representative points, namely, 10%,50% and 90%. 8/73 同济大学汽车学院 10%馏出温度:体现发动机冷起动性能,表明汽油的蒸发性; 50%馏出温度:体现汽油机的加速性和工作稳定性,表明汽油中间馏份的 蒸 发能力; 90%馏出温度:体现燃料燃烧的完全性(因为不易蒸发的燃料难以形成良好 的混合气,易附着在进气道和缸壁上,而且易破坏缸壁的润滑条件 10% recovered (distilled) temperature reflect the cold start performance of engine 50 % recovered (distilled) temperature : reflect the acceleration performance and working stability 90 % recovered (distilled) temperature : reflect the ability of completely burned of fuel 2、热值:指1kg燃料完全燃烧后所产生的热量。 Heat value means the amount of heat generated by completely burning 1kg fuel 9/73 同济大学汽车学院 汽油的牌号根据汽油的辛烷值 确定。压缩比愈高,相应选择的汽 油牌号愈高。 The grades of gasoline is determined according to the octane level of gasoline . The higher of the compression ratio is, a higher of gasoline grade should be selected. 3、抗爆性:指汽油在发动机气缸中燃烧时,避免产生爆燃的 能力,亦即抗自燃能力。一般用辛烷值表示。辛烷值愈高, 抗爆性愈好。 Knock value: the ability of avoiding to produce deflagration when the gasoline is burning in the cylinder, always expressed by octane number
2014/5/8 4.2 The Characteristic of Air-Fuel Mixture 可椰福合气分 气离金汽类 安纯a:明妈气中女气是最比比为地线 气 机味aL道 ■ ‘业a山mh 编备由时袖学的他大热偏纯置 物s对an @R冷法复 同按大限汽中型 窗应冷去置 情式酒 色凡冷大司 培大单究中■ 气 tr宽线学oeHo n空宽Ho 2 工程 取 a地小前a日a: 44 色定工况 4每渔每1山: 。 t长山 霜 ,4 经然 个 辆 大 u 高清气物面山+ 香线物边d 直●14. 城 Earich i tier 同钾大甲代厚得精 阳听大京代中频 期大代率P滑 4.3 Carburetor 化袖器 盛 装时甲 custaat apeed high land 位R冷法7 同将大弹汽摩帽 位月海大写 视督汽甲■ 应日冷大 阳密大究率■ 2
2014/5/8 2 10/73 同济大学汽车学院 4.2 The Characteristic of Air-Fuel Mixture 可燃混合气成分 • 空燃比α:可燃混合气中空气质量与燃油质量之比为空燃比 • Air-Fuel ratio α: the ratio of air mass and fuel mass in the mixture • 过量空气系数 a : 燃烧1kg燃油实际供给的空气质量/完全燃烧1kg燃油 的化学计量空气质量 • Excess-air Factor a : the ratio of actual air mass and stoichiometric air mass for 1kg fuel. • a 1 : lean mixture 11/73 同济大学汽车学院 Relationship between composition of the mixture and performance of gasoline engine 可燃混合气成分与汽油机性能的关系 可燃混合气成分对发动机性能的影响: Influences of composition of the mixture to performance of engine: 1)标准混合气(stoichiometric mixture) a =1: 理论上能够完全燃烧的混合气,其中所含的氧气正好使全部燃料燃烧完毕。 2)稀混合气(lean mixture) a >1: 实际上可以完全燃烧的混合气,其中所含的氧气能保证燃料全部燃烧完毕。 3)浓混合气(rich mixture) a <1 : 混合气中燃料不能保证完全燃烧,但由于燃料分子密集,火焰传播快,发 动机的平均有效压力和功率大。 4)燃烧极限(inflammability limit): 0.4≤ a ≤ 1.4 当可燃混合气太稀( a ≥1.4)以及太浓( a ≤0.4)时,虽能点燃, 但火焰无法传播,导致发动机运转不稳定,直至熄火。 12/73 同济大学汽车学院 1.1 ge% 140 120 100 80 60 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 Pe% 0.88 a 1 2 过浓 有利 过稀 浓 稀 火焰传 播上限 火焰传 播下限 Graph of influence of mixture composition on performance 可燃混合气成分对发动机性能的影响曲线图 1——燃油消耗率 Fuel consumption rate 2——负荷 Load a be% too rich rich too lean lean favorable upper limit lower limit 13/73 同济大学汽车学院 混合气种类 Species a 发动机功率 Power 耗油率 性能 Performance 火焰传播上限 Upper limit 0.4 混合气不燃烧,发动机不工作 No combustion 过浓混合气 Too rich mixture 0.43-0.87 燃烧室积炭、排气管冒黑烟,放炮 Deposit/black smoke/blasting 功率混合气 Power mixture 0.88 最大 Largest 输出最大功率 Largest output power 标准混合气 Stoichiometric mixture 1.0 2% 4% 经济混合气 Economic mixture 1.11 8% 最小 Lowest 过稀混合气 Too lean mixture 1.13 1.33 回火、发动机过热、加速性变坏 Overheating/bad acceleration 火焰传播下限 Lower limit 1.4 混合气不燃烧,发动机不工作 NO combustion Influences of mixture concentration on engine performance 混合气的浓度对发动机性能的影响: e b 10-15% 14/73 同济大学汽车学院 Requirement for mixture of different engine conditions 发动机各工况对可燃混合气成分的要求 ⑴冷起动(Cold start): 极浓混合气 very rich mixture ⑵怠速和小负荷(Idle/small load): ⑶中等负荷(Medium load): 随节气门的开大,混合气由浓 变稀。 With the throttle opening wide , mixture becomes richer. ⑸加速(Acceleration): 额外供油 extra fuel supply ⑷大负荷(High load): 功率混合气 Power mixture。 少而浓的混合气 little rich mixture ☆怠速: 发动机在对外 无功率输出的情况下以 最低转速运转,此时混 合气燃烧释放的功,只 用以克服发动机内部的 阻力。 Idle speed : Engine operates at minimum speed without external power output 15/73 同济大学汽车学院 工况 Working condition 混合气浓度 Concentration 稳定工况 Stable condition 怠速和小负荷 Idle and low load =0.6~0.8 中等负荷 Medium =0.9~1.1 大负荷和全负荷 Big load and full load =0.85~0.95 过渡工况 Transient condition 冷起动 Cold start =0.2~0.6 暖机 Warmed up increases with speed 加速 Acceleration Enrich in time Requirement for mixture of different engine conditions 发动机各工况对可燃混合气成分的要求 16/73 同济大学汽车学院 warm up constant speed high load 17/73 同济大学汽车学院 4.3 Carburetor 化油器 fuel tank 油箱 fuel filter 汽油滤清器 fuel pump 汽油泵 Carburetor (mix) 化油器 air filter 空气 滤清器 Cylinder No longer preferred in passenger car engines Used for varieties in certain countries or two-wheeled vehicle drives. 18/73 同济大学汽车学院
2014/5/8 4.4 Fuel Injection System 。nd idd Cabore 汽油喷射觉袖供哈瓢峡 经上m 物R冷大习 同将大汽卓国 窗包冷法置 鸭情大究眼物 Category of fuel injection system 汽袖喷时系统的分类 LTn原高 直t满口mie by inpersien m 产经内、储 /用 鸭钾大甲代原州 阳大单代琴州 积☆汽率用 方式t接 事,汽时量式动损: 节气门位第用商器 单里气国 同将大弹汽摩帽 器 窗R冷大 ti/ 阳密大究率■ 3
2014/5/8 3 19/73 同济大学汽车学院 4.4 Fuel Injection System 汽油喷射燃油供给系统 电子控制式汽油喷射系统是通过 各种传感器判断发动机的运行状 态,发动机ECU对这些信号进行 分析、计算、比较、判断后发出 喷油脉冲和点火正时指令。 Electronically controlled fuel injection system combines the signals of different sensors to analyze the working state of engine, and then the ECU controls the injector to inject certain amount of fuel and gives suitable ignition timing signal . 20/73 同济大学汽车学院 History of electronic fuel injection system D-Jetronic L-Jetronic Motronic 21/73 同济大学汽车学院 Electronic Fuel Injection Influence on Automotive Power Economic Exhaust Others 1、在各种工况下均能配制最佳空燃比的混合气 Controlling the air-fuel ratio at ideal value + ++ ++ 0 2、取消了喉管,进气阻力减小,提高了发动机的充气效率 No throttle; reducing intake resistance; increasing volumetric efficiency ++ + + 0 3、燃油雾化质量高;各缸混合气均匀性好 Fuel well atomized; mixture more uniform between cylinders + + ++ 冷起动性能好 Well cold start 4、空燃比控制系统动态响应快 Fast dynamic response of air-fuel ratio controlling system +0 + 加速性能好 Well acceleration performance 5、断油功能 Fuel cut function 0+ + 0 6、能根据进气温度、海拔高度变化,对空燃比进行修正 Modifying air-fuel ratio according to air temperature and altitude 0+ + 0 Compared with Carburetor 22/73 同济大学汽车学院 Category of fuel injection system 汽油喷射系统的分类 Gasoline injection system can be classified into port fuel injection (PFI) and gasoline direct injection(GDI). The former needs much lower injection pressure than the latter. 汽油喷射按喷射位置分为进气道喷射和缸内喷射两种。前者 是低压喷射,后者前者是高压喷射。 23/73 同济大学汽车学院 1.按喷射系统执行机构分类: SPI—Single Point Injection (单点喷射) MPI—Multi Point Injection(多点喷射) 1.Fuel 2.Air 3.Throttle valve 4.Intake manifold 5.Injector 6.Engine 24/73 同济大学汽车学院 2.按喷射方式分类:Classified by injection mode Simultaneous injection 同时喷射 Grouping injection 分组喷射 Sequential injection 顺序喷射 25/73 同济大学汽车学院 3 .按空气量的计量方式分类 : (Classified by the way of measuring air mass) D型电控燃油喷射系统 D-type L型电控燃油喷射系统 L-type MAP Thermo time switch Pressure regulator Injector ECU Cold start injector Temperature sensor Filter Idle air valve TPS Fuel pump 26/73 同济大学汽车学院 Air mass meter Pressure regulator Injector TPS Filter Fuel pump ECU Idle air valve CTS 27/73 同济大学汽车学院
2014/5/8 Electronic System 兴 E 1,雷气腾候 k电T Hall Semar Wdee 山ah5eaaT 斯限汽单国 H/3 鸭情大物眼物 合R治大复 M/ 民培大鲜汽中■ 空气系主要件的构与工作原理 Fuel System Intake System 2孩 Fadl Tank Air Filter 药2家气3置 Fael Filter lde Comtroling Vahe Fael Rail Threede Poitian Sesr 同骨大代厚厚用 /万 得带大章汽甲用 民☆代海厚用 Air Cleamer空气滤液量 Throttle device节气门体 Air Mass Sensor空气流叠计 气门神气中,线一工7物气 拉热灯性. 款脑金 出u Prr 气限片有泰所保式架计减:色通式 物t 鸭华h或四。模 prlartietar-tpe het-tnu trt hot-fth 四 dtm。 物R冷专 同将大汽摩帽 包日海去 /m 降修大示究率恒 窗R冷大 阳密大究率■ 4
2014/5/8 4 28/73 同济大学汽车学院 4.5 Component of Electronic Fuel Injection System 电控燃油喷射(EFI)系统基本组成 电控燃油喷射系统一般由三个子系统组成。 • 1、空气供给系统 • 1. Air-supply system • 2、燃油供给系统 • 2. Fuel-supply system • 3、电子控制系统 • 3. Electronically controlling system Video 29/73 同济大学汽车学院 EFI 爆 震 传 感 器 E C U 节 气 门 位 置 传 感 器 进 气 压 力 温 度 传 感 器 水 温 传 感 器 霍 尔 传 感 器 氧 传 感 器 汽 油 箱 电 动 汽 油 泵 汽 油 滤 清 器 燃 油 分 配 管 压 力 调 节 器 喷 油 器 空 气 滤 清 器 节 气 门 体 怠 速 控 制 阀 节 气 门 位 置 传 感 器 进 气 压 力 温 度 传 感 器 电控装置ECU Electronic control unit 燃油系统 Fuel system 进气系统 Intake system 30/73 同济大学汽车学院 Electronic System ECU Knock Sensor Throttle Position Sensor Intake Air Pressure Sensor Temperature Sensor Intake Air temperature Sensor Hall Sensor Lambda Sensor 31/73 同济大学汽车学院 Fuel System Fuel Tank Electronic Fuel Pump Fuel Filter Fuel Rail Pressure Regulator Injector Intake System Air Filter Throttle Body Idle Controlling Valve Intake Manifold Pressure Sensor Intake Air Temperature Sensor Throttle Position Sensor 32/73 同济大学汽车学院 Air-supply System 空气供给系统 空气供给系统的作用是向发动机提供新鲜的空气。它主要由空气滤清器、 空气流量计、节气门、进气总管、进气歧管和怠速空气控制阀等组成。 The role of the air-supply system is to provide fresh air to the engine. It mainly consists of the air filter, the air flow meter , throttle , intake tube , intake manifold and the idle air control valve and other components . Air filter Air flow meter Throttle Idle valve Intake tube Cylinder Intake manifold MAP 33/73 同济大学汽车学院 Component of intake system Air Coolant Throttle Cavity resonator Manifold Air flow sensor Air filter 34/73 同济大学汽车学院 Air Cleaner 空气滤清器 用于滤除空气中的灰尘,一般 都为纸质滤心。 Used to filter the dust in the air, and generally have a paper filter element. 35/73 同济大学汽车学院 Throttle device 节气门体 • 节气门体安装在进气管中,来控制发动机正常工况下的进气量。 • Throttle body is mounted in the intake manifold, to control the mass of intake air at normal condition. • The throttle body mainly includes throttle, position sensor and idle air valve. 主要由节气门、位置传感 器和怠速空气道等组成 36/73 同济大学汽车学院 Air Mass Sensor 空气流量计 空气流量计的功用是测量进入发动机的空气流量,并将测量的结果转换为 电信号传输给电控单元。 In order to be able to determine the air mass flow drawn in by the engine , either a manifold pressure sensor(MAP) or an air mass sensor is employed. The output signal serves predominantly for controlling the fuel volume as an input parameter for the ignition map and for determining the exhaust-gas recirculation rate. 空气流量计有多种形式,如电位计式、热线式、 热膜式和涡流式等。 There are a variety of forms , such as potentiometer-type, hot-wire type, hot-film type and swirl type

2014/5/8 同族大代车单塑 窗凡冷大幻 鸭情大物眼物 窗凡冷复 Manifold Air Pressure Sensot 进气管压力MAP怜意喜 装经将 植spd0女ol waly 患墙收制同 转.A 点世然的 京武兰岩兰台 量安考名种独定内运 鸭牌大甲代原州 阳情大摩汽海零滑 积☆汽存早用 Fuel Supply System 赠抽供给弧峡 7企意级路翠是 值塞 R冷 同将大弹汽摩帽 复日海大至 降密大示究率恒 应R冷大 阳密大究率■ 5
2014/5/8 5 37/73 同济大学汽车学院 电位计式空气流量计 potentiometer -type 卡门涡流式空气流量计 Swirl type 热线式空气流量计 Hot-wire type 热膜式空气流量计 Hot-film type Video Video 38/73 同济大学汽车学院 Potentiometer-type Hot-line type Hot-film type 39/73 同济大学汽车学院 40/73 同济大学汽车学院 Manifold Air Pressure Sensor 进气管压力(MAP)传感器 在发动机工作时,节气门开大,进气量增多,进气管压力相应增加。因此, 进气管压力的大小反映了进气量的多少。 When the engine is working , with the throttle opening , the mass of intake air growing , the manifold air pressure increases at the same time. As a result, the value of the manifold air pressure reflects the amount of intake air. Video 41/73 同济大学汽车学院 Supplementary Air Valve 补充空气阀 补充空气阀是实现发动机快怠速的装置。当发动机冷起动时,部分空气经补充空 气阀进入发动机,使发动机的进气量增加。由于这部分空气是经过空气流量计计 量过的,因此喷油量将相应地有所增加,从而提高了怠速转速,缩短了暖车时间。 Supplementary air valve is a fast idle device. With this device , the mass of air drawn in the engine could increase when the engine starts, so as the fuel volume. As a result , the idle speed is improved. 42/73 同济大学汽车学院 Idle speed control valve 怠速控制阀 在节气门体汽油喷射系统中,节气 门体上装有步进电机式怠速控制阀。 其功用是自动调节发动机的怠速转 速,使发动机在设定的怠速转速下 稳定运转。在使用空调器或转向助 力器的汽车上,电控单元通过怠速 控制阀自动提高怠速转速,以防止 发动机因负荷加大而熄火。 Idle speed control valve is used to modify the idle speed of engines, to ensure the engine to work normally. 43/73 同济大学汽车学院 Fuel Supply System 燃油供给系统 燃油供给系统的作用是向发动机供给燃烧所需的汽油。它主要由电动燃油泵、燃 油滤清器、燃油压力脉动阻尼器、燃油压力调节器、喷油器和燃油管路等组成。 Fuel supply system mainly consists of fuel pump, filter, pressure pulsation damper, pressure regular, injector and fuel rail. Fuel rail Pressure regulator Injector Fuel filter Inlet pipe Return pipe Fuel tank 44/73 同济大学汽车学院 Video 45/73 同济大学汽车学院 Fuel Tank汽油箱 汽油箱的功用是储存汽油。在汽油箱上还装有油面指示表传感器、出 油开关和放油螺塞等。The fuel tank is also equipped with the fuel level instruction sensor , fuel switch and the fuel drain plug . 汽油滤清器 Fuel filter 汽油箱支架 tank bracket 滤网 Filter 加油延伸管 放油螺栓 Drain plug 出油开关 Fuel switch 油面指示表 传感器浮子 加油管 Fuel filling pipe

2014/5/8 最塔钠频车汽抽短 Fuel tank cap汽被箱盖 P阳lfi1tr汽袖越演悬 的州:康电中本骨领。入线到家工作着海再 执物气首物口 作用:唐的汽抽桶。 m 的图证 邦子 也ecd山学巴姓级 窗R冷大习 同将大汽卓国 位凡海去写 阳结大究酒 窗凡冷习 培大鲜汽率■ el Pumo汽洁逐 na号ANT悬M 盐节款起韩加 ed to mt the hed aet域lat @R冷大? 鸭牌大甲代原州 大代甲用 e1对料rult有旋压将节量 s售s尚4ne蚊a 面制车■ 进能速节集 位R冷7 /m 同将大汽摩恒 降修大示究率植 阳密大究率■ 6
2014/5/8 6 46/73 同济大学汽车学院 桑塔纳轿车汽油箱 快速排气管接口 Quick exhaust pipe interface 供油管接口 Fuel interface 回油管接口 Return fuel interface 油面传感器插座 Fuel level sensor socket 集滤器 Filter 浮子 floater 47/73 同济大学汽车学院 蒸汽阀 空气阀 弹簧 弹簧 Fuel tank cap汽油箱盖 •作用:密封汽油箱。 Used to seal the fuel tank working process of the cap 汽油箱盖的工作过程 spring Steam valve spring Air valve 48/73 同济大学汽车学院 Fuel filter 汽油滤清器 • 功用:除去汽油中的水分和杂质,使汽油能达到发动机工作的需要。 • To remove the moisture and impurities in the gasoline, and fulfill the working requirement of engine. 进、出油口不可装反 49/73 同济大学汽车学院 Fuel Pump 汽油泵 • 功用:将汽油从油箱中吸出,经管路和汽油滤 清器,然后泵入化油器浮子式。 • Used to suck the fuel out of fuel tank. 50/73 同济大学汽车学院 Mechanical fuel pump 机械式汽油泵工作原理演示 Fuel outlet Diaphragm Spring Pull rod Internal rocker arm Inlet valve Diaphragm External rocker arm Eccenter Return spring Camshaft 51/73 同济大学汽车学院 进油口 Fuel inlet 出油口 Fuel outlet 滤网 Filter 回位弹簧 Return spring 摇臂 Rocker arm Fuel pump for SANTANA 桑塔纳发动机汽油泵 52/73 同济大学汽车学院 滚柱式电动燃油泵 Roller cell fuel pump 涡轮式电动燃油泵 Turbine fuel pump 53/73 同济大学汽车学院 Fuel pressure regulator 油压调节器 油压调节器的功用是使燃油供给系统的压力与进气管压力之差即喷油压力 保持恒定。 Used to keep the injection pressure invariable. 喷油压力 = 燃油压力 - 进气歧管压力 Injection pressure = fuel pressure – manifold pressure 54/73 同济大学汽车学院 Pressure pulsation damper 油压脉动缓冲器 油压脉动缓冲器的作用就是减小燃油管路中油压的脉动和脉动噪声,并能在发动 机停机后保持油路中有一定的压力,以利于发动机重新起动。 Used to reduce the pressure pulsations and pulsation noise in the fuel pipe, and can maintain a certain pressure after the engine stop working, so the engine is easy to restart

2014/5/8 自个 的凡冷大复 同族大代车单塑 窗凡冷法写 B/3 合R冷大复 ntm项裤香 Cald start isjectee and thermn timr-wwilch 作出弹速和销时州丹无差共工作睡懂 出a W/S 鸭牌大甲代原州 /万 阳情大摩汽海零滑 @凡冷大复 民☆代海厚用 Electronically Controlling System Seor传感得 Tenperetur43ao度0通■ 电子控制系峡 使烟变通求高通)地气应: 黄惠、卧光种和电弹是越量 馆 igaal roin difterrat iads of erand cntnod the of 时cted isto ma尚M的s pewer dlemrat.As a m动, b呢e8a制r我at bet casdiea 物R冷法牙 /分 同将大弹汽摩帽 应月语写 镜/m 降著大示究率恒 @R冷大司 州 阳密大究率■ 7
2014/5/8 7 55/73 同济大学汽车学院 Pressure regulation for high pressure injection In direct gasoline-injection engines, the A/F mixture is formed directly in the combustion chamber. During the intake stroke, the fuel is injected at high pressure into the combustion chamber . Different with the low pressure injection, the high pressure injection system is equipped with a high pressure pump. Fuel from the low pressure pump is compressed and transmitted into common rail. The pressure is regulated by ECU, pressure sensor and pressure control valve. 56/73 同济大学汽车学院 Fuel pressure sensor mounted on the fuel rail selects the pressure valves and transmits them to ECU. ECU decides whether the current pressure meet requirement of engine. If the pressure is low, high pressure pump will keep increasing it. If the pressure is higher than requirement, ECU makes the pressure control valve open, and fuel flows back to tank from rail. 57/73 同济大学汽车学院 Typical G-DI engine system layout 58/73 同济大学汽车学院 Injector 喷油器 喷油器的功用是按照电控单元的指令将一定数量的汽油适时地喷入进气道或进 气管内,并与其中的空气混合形成可燃混合气。 The function of injector is injecting a certain amount of gasoline into manifold timely according to the signal from ECU. 59/73 同济大学汽车学院 Cold start injector 冷起动喷嘴 冷起动喷嘴的功用是当发动机低温起动时,向进气管喷入一定数量附加的汽 油,以加浓混合气。 Used to inject a certain amount of extra gasoline to enrich the mixture when the engine cold starts. 60/73 同济大学汽车学院 Cold start injector and thermo time-switch 61/73 同济大学汽车学院 Electronically Controlling System 电子控制系统 传感器、执行元件和电子控制单元三部分组成。 Electronically controlling system consists of different sensors, power element and electronic control unit(ECU). 电子控制系统的功用是根据各种传感器的信号,由计算机ECU进行综合 分析和处理,通过执行装置控制喷油量等,使发动机具有最佳性能。 The function of the electronically controlling system is to rely on the ECU comprehensively analyzing and calculating the signals from different kinds of sensors, and control the mass of fuel injected into manifold by the power element. As a result , the engine could work at best condition. sensors ECU Power element Signals in Signals out 62/73 同济大学汽车学院 Sensor 传感器 Sensors are used to select signals of the engine working condition, and to transmit these signals to ECU. Lambda sensor Load sensor Rotation speed sensor Temperature sensor Throttle position sensor Knock sensor 63/73 同济大学汽车学院 包括发动机温度传感器(水温传感器)和进气温度传感器。 Include coolant temperature sensor and intake temperature sensor. 负特性 negative characteristic Temperature Sensors 温度传感器 thermistors thermistors Coolant temperature sensor Intake temperature sensor temperature resistance
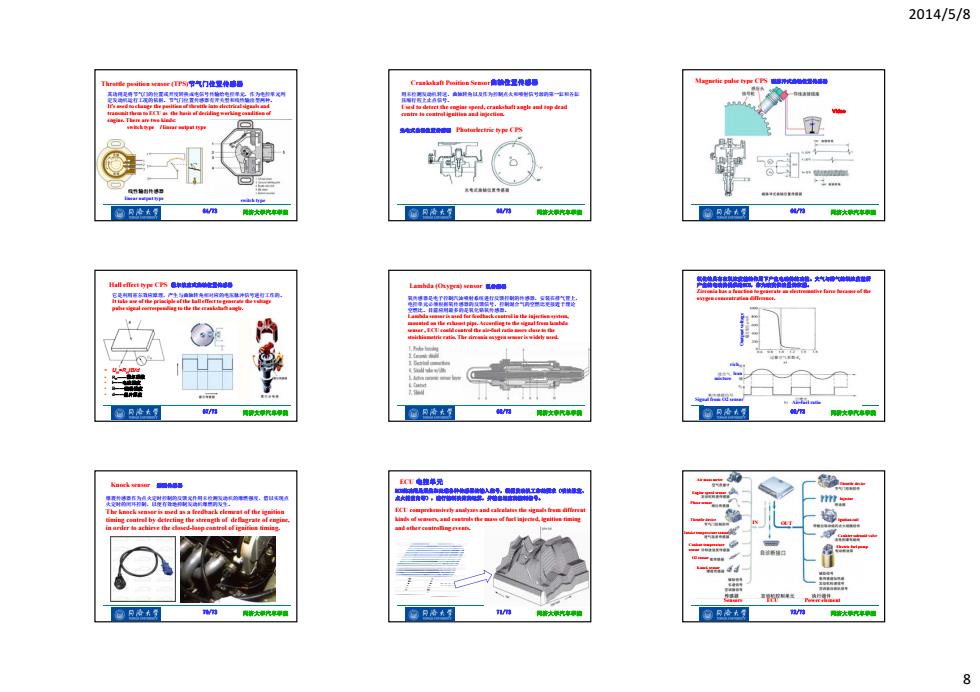
2014/5/8 Thratde positien eae4TFS节气门径复换感海 Crankkaft Poition5seer袖位里0后 风登图鱼州尚在为离大制5对塔阳一电不 A wmad 式春维a细性s☆g时两(西 流电花金址结置生银国 e体线无#绿地能中操国 h 窗及冷大复 同病大汽中塑 窗凡冷法复 鸭情大究眼物 将大汽率■ Hall effect ty pe C万twe Lamhda ()srnuar 精登* hve fane haeca时eM色 山 同骨大代厚甲用 阳情大摩汽海零滑 民积☆代汽春厚用 Kauck srasur 旋单元 The knack senser is wed as a feedbark clemrat af the ignitian iming coatrel by cireting the strength of defgratr af engim 如da我d cuatrola the ma或adg时封相mnag in arder ta achirve the claved-daep of timing 窗月冷去? 骨特大汽家 位月冷子 鸭密大学究卓■ w/ 阳密大究率酒 8
2014/5/8 8 64/73 同济大学汽车学院 Throttle position sensor (TPS)节气门位置传感器 其功用是将节气门的位置或开度转换成电信号传输给电控单元,作为电控单元判 定发动机运行工况的依据。节气门位置传感器有开关型和线性输出型两种。 It’s used to change the position of throttle into electrical signals and transmit them to ECU as the basis of deciding working condition of engine. There are two kinds: switch type / linear output type switch type linear output type 线性输出传感器 65/73 同济大学汽车学院 Crankshaft Position Sensor曲轴位置传感器 用来检测发动机转速、曲轴转角以及作为控制点火和喷射信号源的第一缸和各缸 压缩行程上止点信号。 Used to detect the engine speed, crankshaft angle and top dead centre to control ignition and injection. 光电式曲轴位置传感器 Photoelectric type CPS 66/73 同济大学汽车学院 Magnetic pulse type CPS 磁脉冲式曲轴位置传感器 Video 67/73 同济大学汽车学院 Hall effect type CPS 霍尔效应式曲轴位置传感器 UH=RHIB/d RH——霍尔系数 I——电流强度 B——磁场强度 d——基片厚度 它是利用霍尔效应原理,产生与曲轴转角相对应的电压脉冲信号进行工作的。 It take use of the principle of the hall effect to generate the voltage pulse signal corresponding to the the crankshaft angle. 68/73 同济大学汽车学院 Lambda (Oxygen) sensor 氧传感器 氧传感器是电子控制汽油喷射系统进行反馈控制的传感器,安装在排气管上, 电控单元必须根据氧传感器的反馈信号,控制混合气的空燃比更接近于理论 空燃比。目前应用最多的是氧化锆氧传感器。 Lambda sensor is used for feedback control in the injection system, mounted on the exhaust pipe. According to the signal from lambda sensor , ECU could control the air-fuel ratio more close to the stoichiometric ratio. The zirconia oxygen sensor is widely used. 69/73 同济大学汽车学院 氧化锆具有在氧浓度差的作用下产生电动势的功能。大气与排气的氧浓度差所 产生的电动势提供给ECU,作为改变供油量的依据。 Zirconia has a function to generate an electromotive force because of the oxygen concentration difference. mixture Signal from O2 sensor Air-fuel ratio Output voltage rich lean 70/73 同济大学汽车学院 Knock sensor 爆震传感器 爆震传感器作为点火定时控制的反馈元件用来检测发动机的爆燃强度,借以实现点 火定时的闭环控制,以便有效地抑制发动机爆燃的发生。 The knock sensor is used as a feedback element of the ignition timing control by detecting the strength of deflagrate of engine, in order to achieve the closed-loop control of ignition timing. 71/73 同济大学汽车学院 ECU 电控单元 ECU的功用是采集和处理各种传感器的输入信号,根据发动机工作的要求(喷油脉宽、 点火提前角等),进行控制决策的运算,并输出相应的控制信号。 ECU comprehensively analyzes and calculates the signals from different kinds of sensors, and controls the mass of fuel injected, ignition timing and other controlling events. 72/73 同济大学汽车学院 Sensors ECU Power element IN OUT Air mass meter Engine speed sensor Phase sensor Throttle device Intake temperature sensor Coolant temperature sensor O2 sensor Knock sensor Injector Throttle device Ignition coil Canister solenoid valve Electric fuel pump