
Asymmetric Key Cryptography Haipeng Dai haipengdai@nju.edu.cn 313 CS Building Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
Asymmetric Key Cryptography Haipeng Dai haipengdai@nju.edu.cn 313 CS Building Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
Problems of Symmetric key Cryptosystems In symmetric key cryptosystems,before any ciphertext can be transmitted between two parties,a prior secure transmission of the key k is required. -In practice,this is often very difficult to achieve. Can we design an asymmetric key cryptosystem such that: -An entity has two key:a public key PUa and a private key PRa -X=D(PR,E(PU,X))for confidentiality -X=D(PUa E(PRa,X))for authentication(non-repudiation) The idea of a public-key cryptosystem was proposed by Diffie and Hellman in 1976. RSA Cryptosystem was first invented in 1977 by Rivest, Shamir,and Adleman. 2
2 Problems of Symmetric key Cryptosystems In symmetric key cryptosystems, before any ciphertext can be transmitted between two parties, a prior secure transmission of the key k is required. ─ In practice, this is often very difficult to achieve. Can we design an asymmetric key cryptosystem such that: ─ An entity has two key: a public key PUa and a private key PRa ─ X = D(PRa, E(PUa, X)) for confidentiality ─ X = D(PUa, E(PRa, X)) for authentication (non-repudiation) The idea of a public-key cryptosystem was proposed by Diffie and Hellman in 1976. RSA Cryptosystem was first invented in 1977 by Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman

Misconceptions Concerning Public-Key Encryption Public-key encryption is more secure from cryptanalysis than symmetric encryption Public-key encryption is a general-purpose technique that has made symmetric encryption obsolete There is a feeling that key distribution is trivial when using public-key encryption,compared to the cumbersome handshaking involved with key distribution centers for symmetric encryption 3
3 Misconceptions Concerning Public-Key Encryption Public-key encryption is more secure from cryptanalysis than symmetric encryption Public-key encryption is a general-purpose technique that has made symmetric encryption obsolete There is a feeling that key distribution is trivial when using public-key encryption, compared to the cumbersome handshaking involved with key distribution centers for symmetric encryption

Principles of Public-Key Cryptosystems The concept of public-key cryptography evolved from an attempt to attack two of the most difficult problems associated with symmetric encryption: Key distribution How to have secure communications in general without having to trust a KDC with your key Digital signatures How to verify that a message comes intact from the claimed sender Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman from Stanford University achieved a breakthrough in 1976 by coming up with a method that addressed both problems and was radically different from all previous approaches to cryptography 4
4 The concept of public-key cryptography evolved from an attempt to attack two of the most difficult problems associated with symmetric encryption: Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman from Stanford University achieved a breakthrough in 1976 by coming up with a method that addressed both problems and was radically different from all previous approaches to cryptography Principles of Public-Key Cryptosystems • How to have secure communications in general without having to trust a KDC with your key Key distribution • How to verify that a message comes intact from the claimed sender Digital signatures
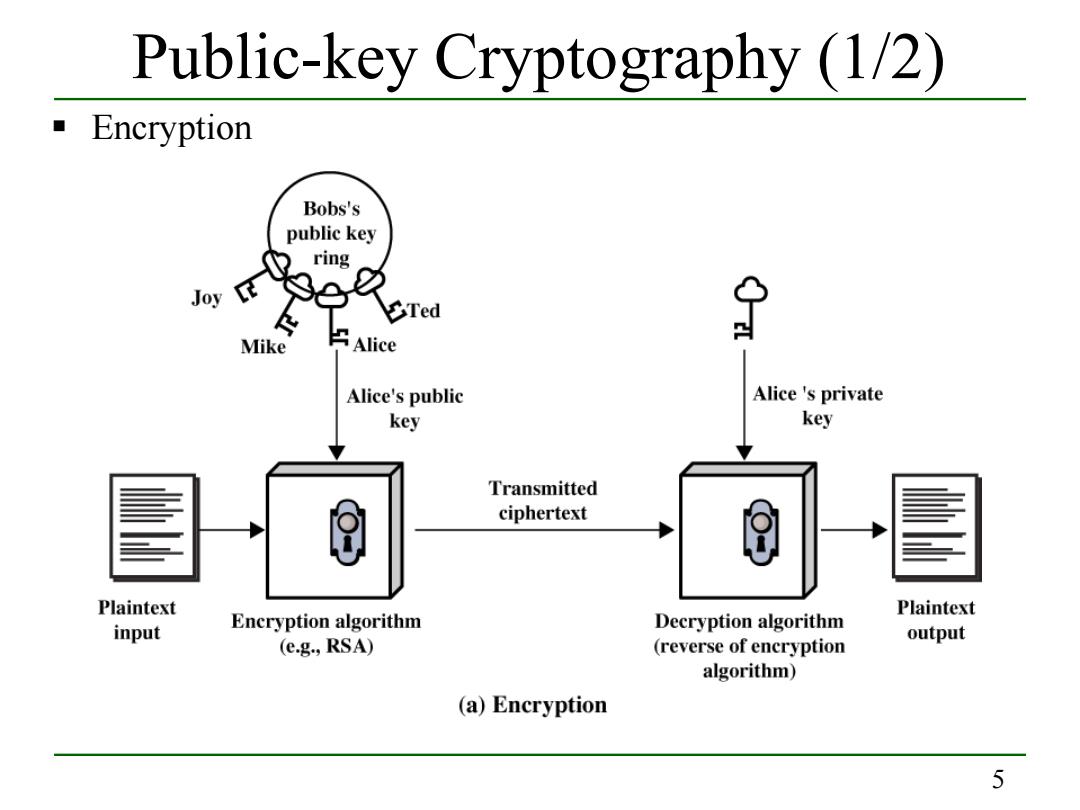
Public-key Cryptography (1/2) Encryption Bobs's public key ring Joy Mike Alice Alice's public Alice 's private key key Transmitted ciphertext Plaintext Plaintext input Encryption algorithm Decryption algorithm (e.g.,RSA) output (reverse of encryption algorithm) (a)Encryption 5
5 Public-key Cryptography (1/2) Encryption
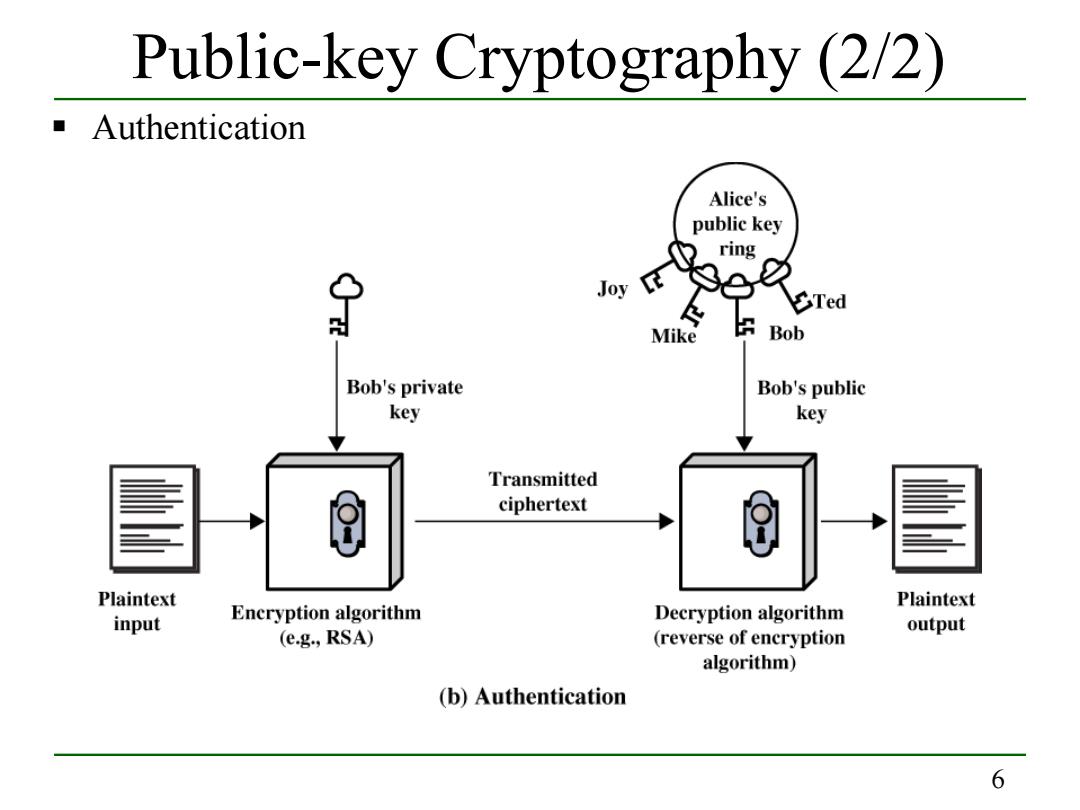
Public-key Cryptography (2/2) Authentication Alice's public key ring Joy 9e1 必 Ted Mike Bob Bob's private Bob's public key key Transmitted ciphertext Plaintext Plaintext Decryption algorithm input Encryption algorithm output (e.g.,RSA) (reverse of encryption algorithm) (b)Authentication 6
6 Public-key Cryptography (2/2) Authentication

Conventional and Public-Key Encryption Conventional Encryption Public-Key Encryption Needed to Work: Needed to Work: 1.The same algorithm with the same key is 1.One algorithm is used for encryption and used for encryption and decryption. a related algorithm for decryption with a pair of keys,one for encryption and one 2.The sender and receiver must share the for decryption. algorithm and the key. 2. The sender and receiver must each have Needed for Security: one of the matched pair of keys (not the same one). 1.The key must be kept secret. Needed for Security: 2.It must be impossible or at least impractical to decipher a message if the 1.One of the two keys must be kept secret. key is kept secret. 2.It must be impossible or at least 3.Knowledge of the algorithm plus impractical to decipher a message if one samples of ciphertext must be of the keys is kept secret. insufficient to determine the key. 3. Knowledge of the algorithm plus one of the keys plus samples of ciphertext must be insufficient to determine the other key. 7
7 Conventional and Public-Key Encryption

Public-Key Cryptosystem:Secrecy Cryptanalyst PRb Source A Destination B Message X Encryption Decryption Destination Source Algorithm Y=EPUb,X灯 Algorithm X= DPRb,Y门 PUb PRb Key Pair Source 8
8 Public-Key Cryptosystem: Secrecy
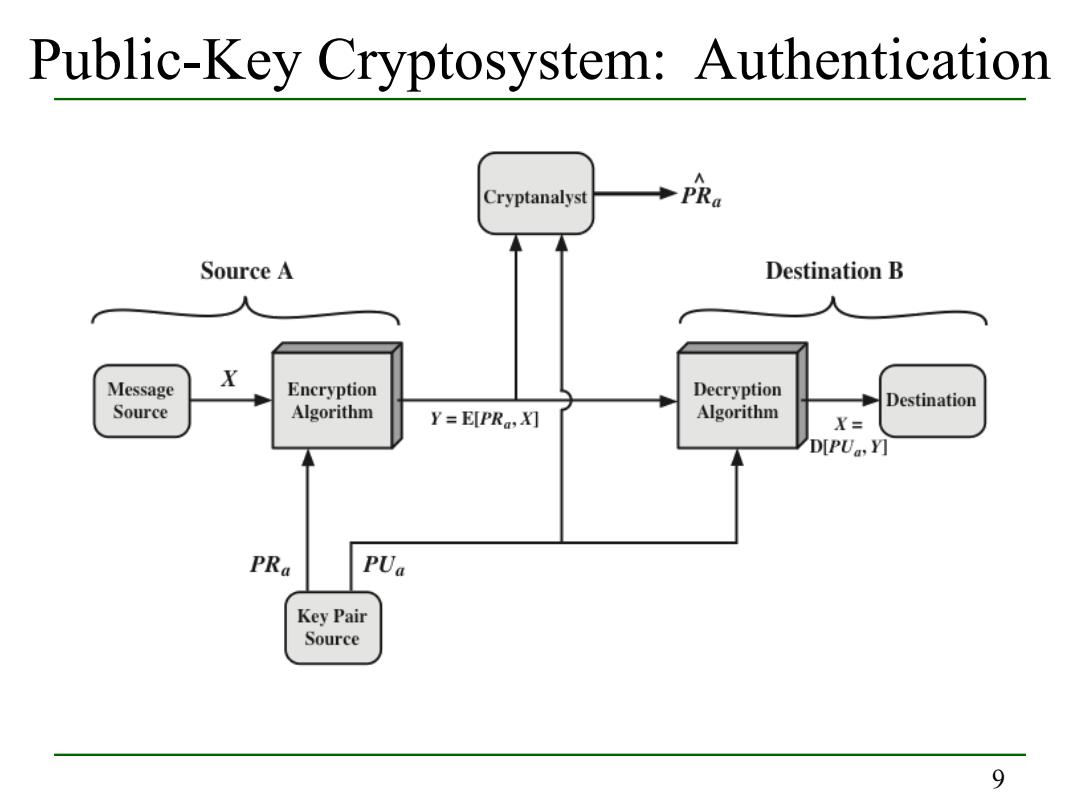
Public-Key Cryptosystem:Authentication Cryptanalyst PRa Source A Destination B Message X Encryption Decryption Destination Source Algorithm Y=EPRa,X灯 Algorithm X= D[PU,Y] PRa PUa Key Pair Source 9
9 Public-Key Cryptosystem: Authentication
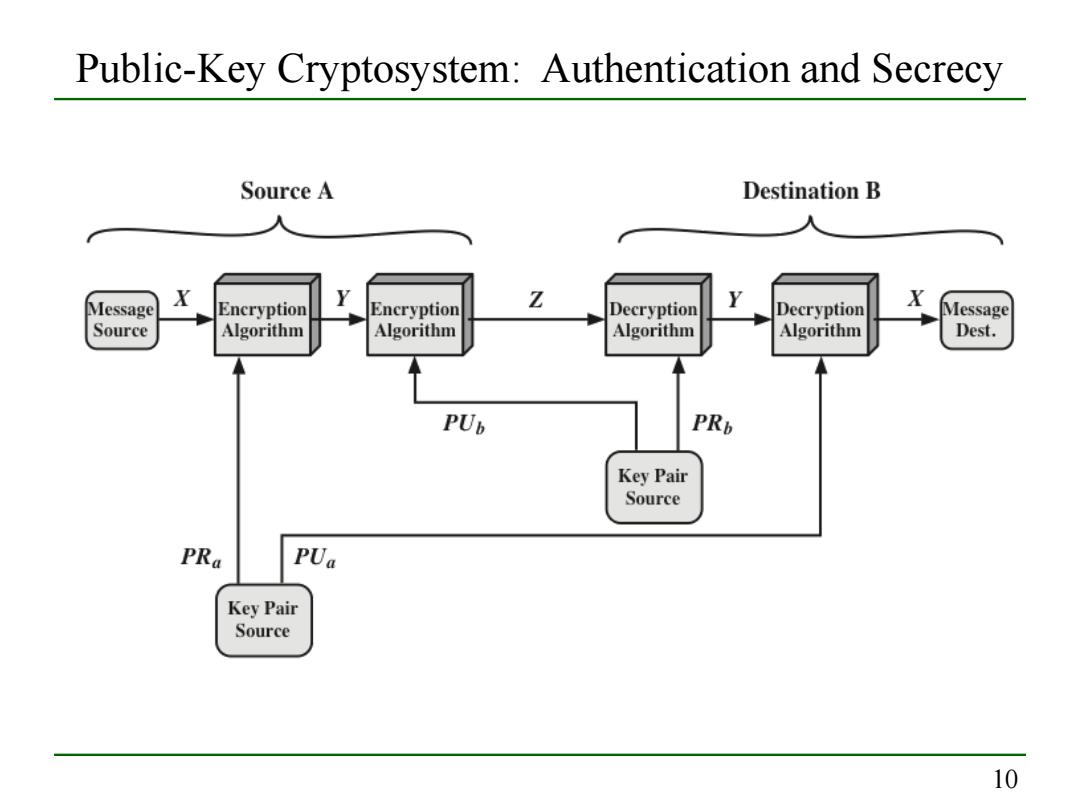
Public-Key Cryptosystem:Authentication and Secrecy Source A Destination B Message X Encryption Y Encryption Z Decryption Decryption X Message Source Algorithm Algorithm Algorithm Algorithm Dest. PUb PRb Key Pair Source PRa PUa Key Pair Source 10
10 Public-Key Cryptosystem: Authentication and Secrecy