
Kerberos Haipeng Dai haipengdai@nju.edu.cn 313 CS Building Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
Kerberos Haipeng Dai haipengdai@nju.edu.cn 313 CS Building Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
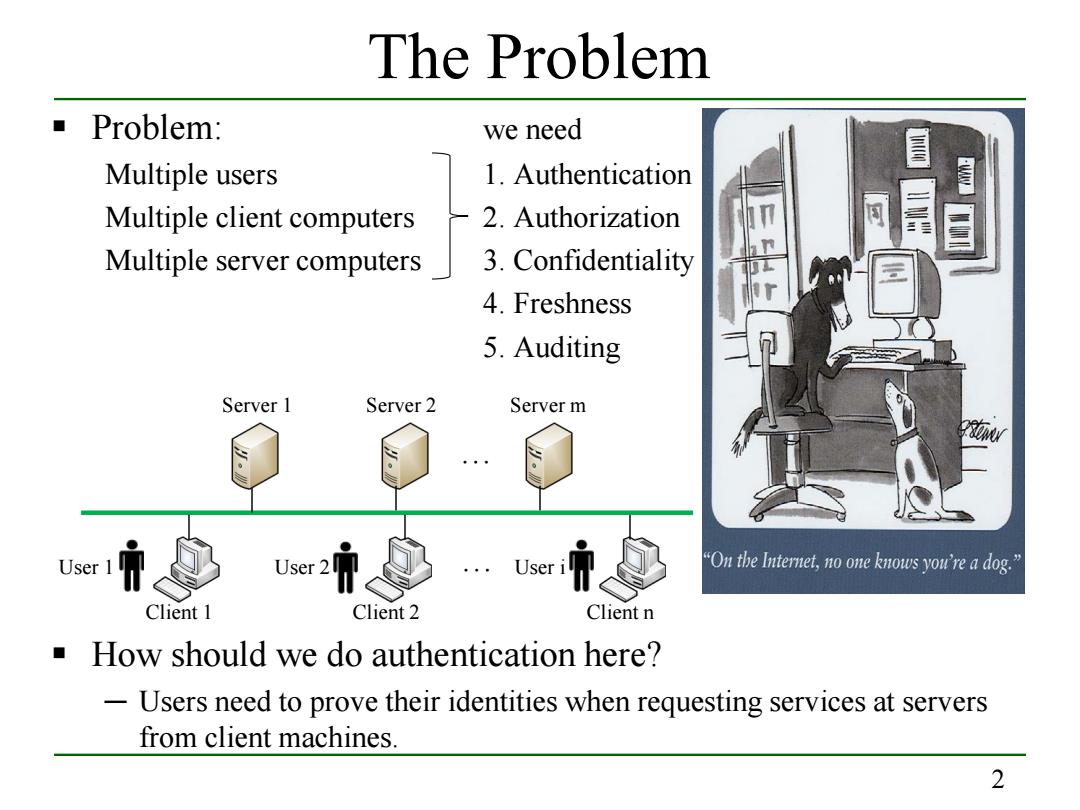
The Problem Problem: we need Multiple users 1.Authentication Multiple client computers -2.Authorization Multiple server computers 3.Confidentiality 4.Freshness 5.Auditing Server 1 Server 2 Server m "On the Internet,no one knows you're a dog." Client 1 Client 2 Client n How should we do authentication here? Users need to prove their identities when requesting services at servers from client machines. 2
2 The Problem Problem: we need Multiple users 1. Authentication Multiple client computers 2. Authorization Multiple server computers 3. Confidentiality 4. Freshness 5. Auditing How should we do authentication here? ─ Users need to prove their identities when requesting services at servers from client machines. Server 1 Server 2 Server m … Client 1 Client 2 Client n User 1 User 2 … User i

Kerberos Kerberos is an authentication and authorization protocol ■ Kerberos uses a trusted third party authentication service that enables clients and servers to establish authenticated and secure communication. ■ Kerberos provides single sign-on capability using a centralized repository of accounts. ■ Relies entirely on symmetric cryptography Kerberos provides an audit trail of usage. -How?You should be able to answer after this lecture Developed at MIT:two versions,Version 4 and Version 5 (specified as RFC1510) http://web.mit.edu/kerberos/www Used in many systems,e.g.,Windows 2000 and later as default authentication protocol In Greek mythology,Kerberos means a many headed dog, commonly three,perhaps with a serpent's tail,the guardian of the entrance of Hades." -the modern Kerberos was intended to have three components to guard a network's gate:authentication,accounting,and audit. 3
3 Kerberos Kerberos is an authentication and authorization protocol Kerberos uses a trusted third party authentication service that enables clients and servers to establish authenticated and secure communication. Kerberos provides single sign-on capability using a centralized repository of accounts. Relies entirely on symmetric cryptography Kerberos provides an audit trail of usage. ─ How? You should be able to answer after this lecture. Developed at MIT: two versions, Version 4 and Version 5 (specified as RFC1510) http://web.mit.edu/kerberos/www Used in many systems, e.g., Windows 2000 and later as default authentication protocol In Greek mythology, Kerberos means a many headed dog, commonly three, perhaps with a serpent's tail, the guardian of the entrance of Hades." ─ the modern Kerberos was intended to have three components to guard a network's gate: authentication, accounting, and audit

Requirements Security -A network eavesdropper should not be able to obtain the necessary information to impersonate a user. Transparency -Users shouldn't notice authentication taking place beyond the requirement to enter a password. Scalability -The system should be capable of supporting large numbers of clients and servers. Reliability -For all services that rely on Kerberos for access control,lack of availability of the Kerberos service means lack of availability of the supported services. 4
4 Requirements Security ─ A network eavesdropper should not be able to obtain the necessary information to impersonate a user. Transparency ─ Users shouldn’t notice authentication taking place beyond the requirement to enter a password. Scalability ─ The system should be capable of supporting large numbers of clients and servers. Reliability ─ For all services that rely on Kerberos for access control, lack of availability of the Kerberos service means lack of availability of the supported services

Threat Model User impersonation -A user may gain access to a particular workstation and pretend to be another user operating from that workstation. Network address impersonation -A user may alter the network address of a workstation so that the requests sent from the altered workstation appear to come from the impersonated workstation. Eavesdropping,tampering and replay -A user may eavesdrop on exchanges and use a replay attack to gain entrance to a server or to disrupt operations. 5
5 Threat Model User impersonation ─ A user may gain access to a particular workstation and pretend to be another user operating from that workstation. Network address impersonation ─ A user may alter the network address of a workstation so that the requests sent from the altered workstation appear to come from the impersonated workstation. Eavesdropping, tampering and replay ─ A user may eavesdrop on exchanges and use a replay attack to gain entrance to a server or to disrupt operations

Straightforward Solution 1 Solution 1:Each client handles authentication authorization by itself using its database. Drawbacks: -All user databases need to be synchronized across all client PCs. Management tasks like adding or deleting a user need to be performed on every client PC.Obviously this solution is not scalable with the number of client PCs. 6
6 Straightforward Solution 1 Solution 1: Each client handles authentication & authorization by itself using its database. Drawbacks: ─ All user databases need to be synchronized across all client PCs. Management tasks like adding or deleting a user need to be performed on every client PC. Obviously this solution is not scalable with the number of client PCs

Straightforward Solution 2 Solution 2:Each server handles authentication authorization by itself using its database. Drawbacks: -All user databases need to be synchronized across all servers. Management tasks like adding or deleting a user need to be performed on every server.This solution is not scalable with the number of servers.It is hard to manage user accounts and access rights. 7
7 Straightforward Solution 2 Solution 2: Each server handles authentication & authorization by itself using its database. Drawbacks: ─ All user databases need to be synchronized across all servers. Management tasks like adding or deleting a user need to be performed on every server. This solution is not scalable with the number of servers. It is hard to manage user accounts and access rights

Kerberos Key management: -Every server does have a shared key with AS -Every user has a password with AS -Every client does NOT have a shared key with AS Clients mean the client PCs.Users mean human users. ●Why? We want the clients to be"dummies".This not only makes the management of clients easier but also makes the system secure against client compromises 8
8 Kerberos Key management: ─ Every server does have a shared key with AS ─ Every user has a password with AS ─ Every client does NOT have a shared key with AS ● Clients mean the client PCs. Users mean human users. ● Why? – We want the clients to be “dummies”. This not only makes the management of clients easier but also makes the system secure against client compromises
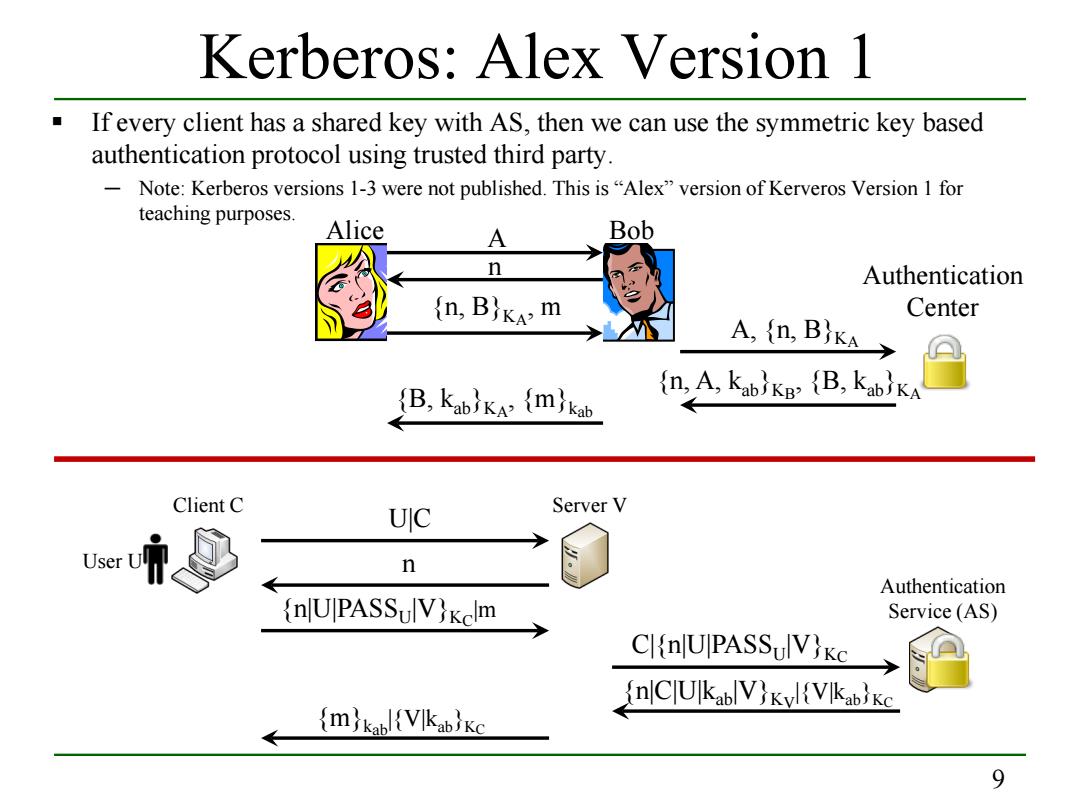
Kerberos:Alex Version 1 If every client has a shared key with AS,then we can use the symmetric key based authentication protocol using trusted third party. Note:Kerberos versions 1-3 were not published.This is"Alex"version of Kerveros Version 1 for teaching purposes. Alice A Bob n Authentication (n,B)KA:m Center A,{,BKA→ (B,KabKa (mkab (n,A,kablkB (B,kabika Client C UIC Server V User n Authentication (nJUPASSulV}Kclm Service(AS) ClinlUIPASSulV)Kc nlClUlkablV}Kyl(Vlkabke (m)kabl{VIkabKc 9
9 Kerberos: Alex Version 1 If every client has a shared key with AS, then we can use the symmetric key based authentication protocol using trusted third party. ─ Note: Kerberos versions 1-3 were not published. This is “Alex” version of Kerveros Version 1 for teaching purposes. Client C Server V User U Authentication {n|U|PASSU|V}K Service (AS) C|m U|C n C|{n|U|PASSU|V}KC {n|C|U|kab|V}KV|{V|kab}KC {m}kab|{V|kab}KC Alice A Bob n {n, B}KA, m A, {n, B}KA {n, A, kab}KB, {B, kab}KA Authentication Center {B, kab}KA, {m}kab

Kerberos:Alex Version 2 Authentication Client C User U UPASSulV Sever(AS) Server V (UlAddressclV)Kv Ul{UlAddressclV}ky ticket Why does the ticket include Addressc? -Otherwise another malicious client can steal a ticket and replay it. -Yes,an attacker can still replay it by changing the address of a compromised client,but he has to wait client C to power off. Why encrypted with Ky? -Prevent ticket from being forgeable. Defect of this protocol: -Password of U is sent in plaintext. -How to encrypt user U's password? Since both Client C and AS knows U's password,they can generate a key from MD(PASSu). 10
10 Kerberos: Alex Version 2 Why does the ticket include AddressC? ─ Otherwise another malicious client can steal a ticket and replay it. ─ Yes, an attacker can still replay it by changing the address of a compromised client, but he has to wait client C to power off. Why encrypted with KV? ─ Prevent ticket from being forgeable. Defect of this protocol: ─ Password of U is sent in plaintext. ─ How to encrypt user U’s password? ● Since both Client C and AS knows U’s password, they can generate a key from MD(PASSU). Server V Client C User U Authentication U|PASS Sever (AS) U|V {U|AddressC|V}KV U|{U|AddressC|V}KV ticket