
在生物农药上的应用 生物技术
在生物农药上的应用 生物技术

Stanford medical professor Stanley Cohen and biochemist Herbert Boyer from the University of California, San Francisco, were in Honolulu to attend a meeting on plasmids, the ringlets of DNA contained in bacteria. Stanley Cohen
Stanford medical professor Stanley Cohen and biochemist Herbert Boyer from the University of California, San Francisco, were in Honolulu to attend a meeting on plasmids, the ringlets of DNA contained in bacteria. Stanley Cohen

1953 DNA structure proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick 1960 Arthur Kornberg synthesizes DNA in vitro 1970 Hamilton Smith and Kent Wilcox isolate the first restriction enzyme 1971 The first biological engineering company, Cetus, founded 1972 Paul Berg uses a restriction enzyme to form a hybrid circular molecule 1973 Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer develop DNA cloning and recombinant DNA
1953 DNA structure proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick 1960 Arthur Kornberg synthesizes DNA in vitro 1970 Hamilton Smith and Kent Wilcox isolate the first restriction enzyme 1971 The first biological engineering company, Cetus, founded 1972 Paul Berg uses a restriction enzyme to form a hybrid circular molecule 1973 Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer develop DNA cloning and recombinant DNA

生物农药定义 • 化学农药专家:应包括微生物活体、 昆虫天敌、部分植物源农药;不包括 农用抗生素、植物生长调节剂、转基 因农药。 • 国外:农用抗生素列为化学农药的范 畴。 争论点 ?
生物农药定义 • 化学农药专家:应包括微生物活体、 昆虫天敌、部分植物源农药;不包括 农用抗生素、植物生长调节剂、转基 因农药。 • 国外:农用抗生素列为化学农药的范 畴。 争论点 ?

• 寡糖 • 丙烷脒 • 激活蛋白 • 多粘类芽孢杆菌 • 地衣类芽孢杆菌 • 海洋地衣芽孢杆菌 • 嗜线虫致病杆菌 • 绿色木霉 • 抑霉菌素 • 放线菌新菌株 • 植物活性物质 新型生物农药品种
• 寡糖 • 丙烷脒 • 激活蛋白 • 多粘类芽孢杆菌 • 地衣类芽孢杆菌 • 海洋地衣芽孢杆菌 • 嗜线虫致病杆菌 • 绿色木霉 • 抑霉菌素 • 放线菌新菌株 • 植物活性物质 新型生物农药品种

防病 防止病害 生物农药的功用 杀虫 防止虫害 除草 防止草害 提高自然 产物的生物 农药活性 生物技术
防病 防止病害 生物农药的功用 杀虫 防止虫害 除草 防止草害 提高自然 产物的生物 农药活性 生物技术

1 An overview of DNA cloning Some conception need to know Some useful technology important to gene manipulation Enzymes for DNA cloning Vectors
1 An overview of DNA cloning Some conception need to know Some useful technology important to gene manipulation Enzymes for DNA cloning Vectors

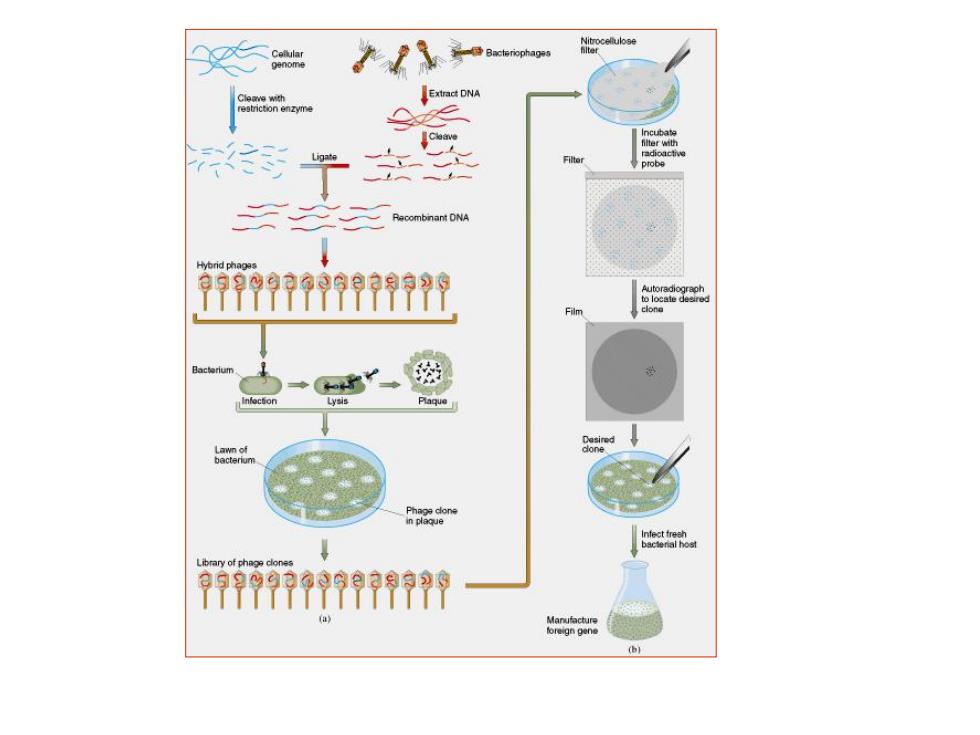
Conception DNA cloning is to place a relatively short fragment of a genome, which might contain the gene or other sequence of interest, in an autonomously replicating piece of DNA, known as a vector, forming recombinant DNA, which can be replicated independently of the original genome, and normally in other host species altogether. Propagation of the host organism containing the recombinant DNA forms a set of genetically identical organism, or a clone. This process is called DNA cloning
Conception DNA cloning is to place a relatively short fragment of a genome, which might contain the gene or other sequence of interest, in an autonomously replicating piece of DNA, known as a vector, forming recombinant DNA, which can be replicated independently of the original genome, and normally in other host species altogether. Propagation of the host organism containing the recombinant DNA forms a set of genetically identical organism, or a clone. This process is called DNA cloning
rceaub3e Extract DNA probe 辨9999种999 lea3 Film 7辨9979799999 e

ØHost organism/cell: where the plasmids get multiplied and propagated faithfully, which is crucial for DNA cloning. ØHosts for DNA cloning vector Prokaryotic host : E. coli ( most cases) Eukaryotic host : Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), large fragments of human genome
ØHost organism/cell: where the plasmids get multiplied and propagated faithfully, which is crucial for DNA cloning. ØHosts for DNA cloning vector Prokaryotic host : E. coli ( most cases) Eukaryotic host : Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), large fragments of human genome