
Section III BacteriologyPathogenesis of Bacterial InfectionSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Section III Bacteriology Pathogenesis of Bacterial Infection SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

KEY TERMS PathogenExtra/intracellular pathogenCompromised hostOpportunistic infection InfectionExotoxinEndotoxin Infectious diseases Koch's postulatesAutoimmunity TransmissionBioterrorismAdhesion PenetrationInvasiveness/spreadSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
KEY TERMS Pathogen Opportunistic infection Infection Infectious diseases Koch’s postulates Transmission Adhesion Penetration Invasiveness/spread Extra/intracellular pathogen Compromised host Exotoxin Endotoxin Autoimmunity Bioterrorism SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

GLOSSARYAeasonaachmnhossInvaoThposswheyacteriaanmaparasitewhichbacteriasticktothesurfacesofhostcells.Oncefugindirustispin the bodybacriahntthymNonpathogenAmicroorganismthatdoesnotcausedisinitialstepintheinfectionprocess.Thetermsadherease:maybepartofthenormalfloraenceadsonandatachmntarftenusedintchangeably.OpportunisticpathogenAnagentcapableofcausinCarrierAeronoranmalwithasymptomaticinfectiodiseaseonlywhenthehost'sresistanceisimpaired(iewhenthepatientis"mmunocompromised")thatcanbetransmittedtoanothersusceptiblepersonPathgenmicoorganmapablecaungdiseasor animal.InfectionMultiplicatiofaninfectiousagentwithinthePathogenicityTheabilityofaninfectiousagenttocausepody.Multiplicationfthebacteriathatarepartfthdisease seealso virulenceToxigenicityTheabilityfamicroorganismproduceamahtrsakerallynotconsideredaninfectionontheotherhandtoxinthatcontributestothedevelopmentofdiseaseViruunttiltaumultplicatioanbriaamaspecies)evenifthepersonisasymptomaticsdisease.Virulentagentscausedisease when introduceddeemed an infection.intothehostinsmallnumbers.Virulenceinvolvesinvasionand toxigenicity (see above)SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
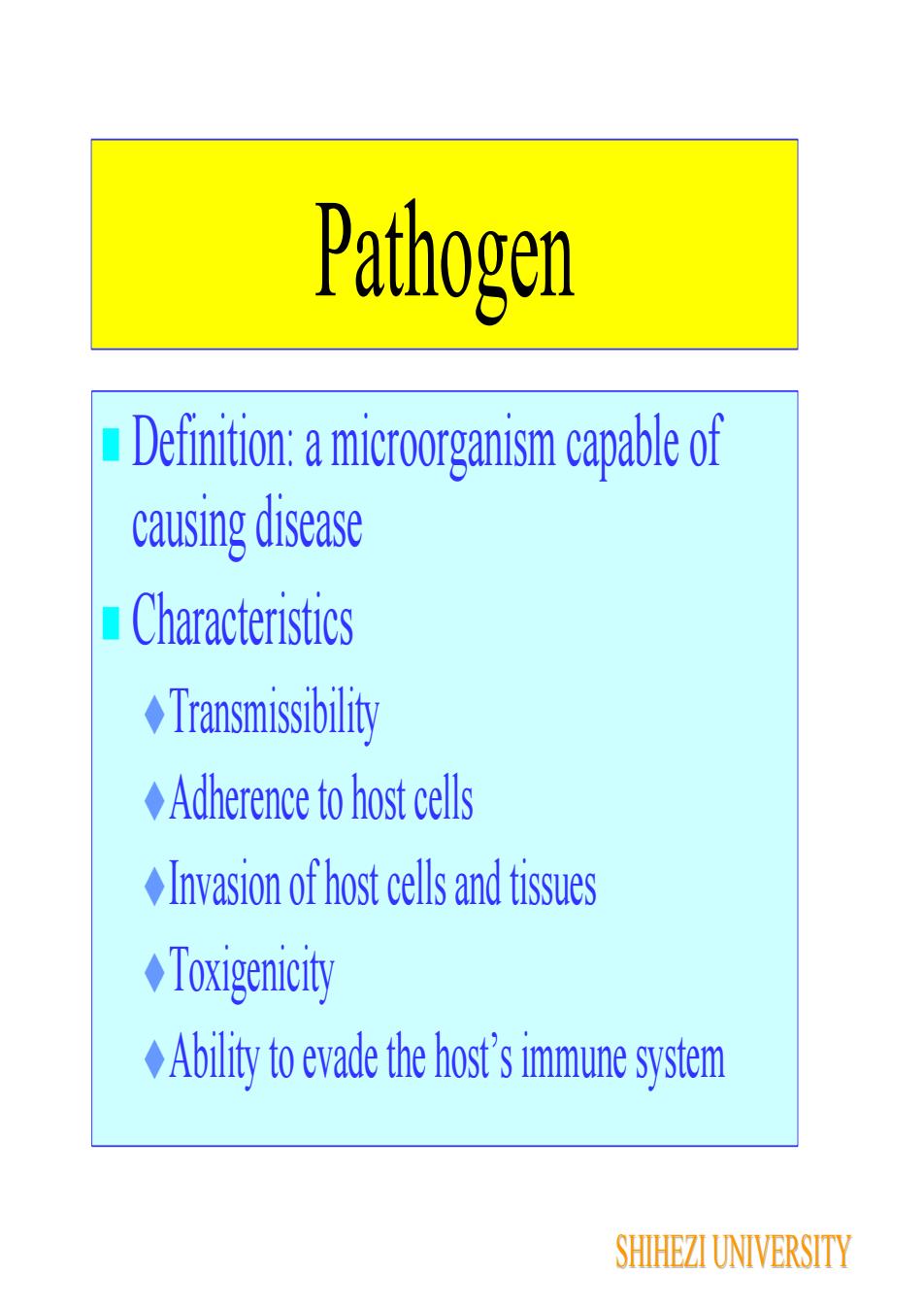
Pathogen Definition: a microorganism capable ofcausing diseaseCharacteristicsTransmissibility Adherence to host cellsInvasion of host cells and tissuesToxigenicityAbility to evade the host's immune systemSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Pathogen Definition: a microorganism capable of causing disease Characteristics Transmissibility Adherence to host cells Invasion of host cells and tissues Toxigenicity Ability to evade the host’s immune system SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
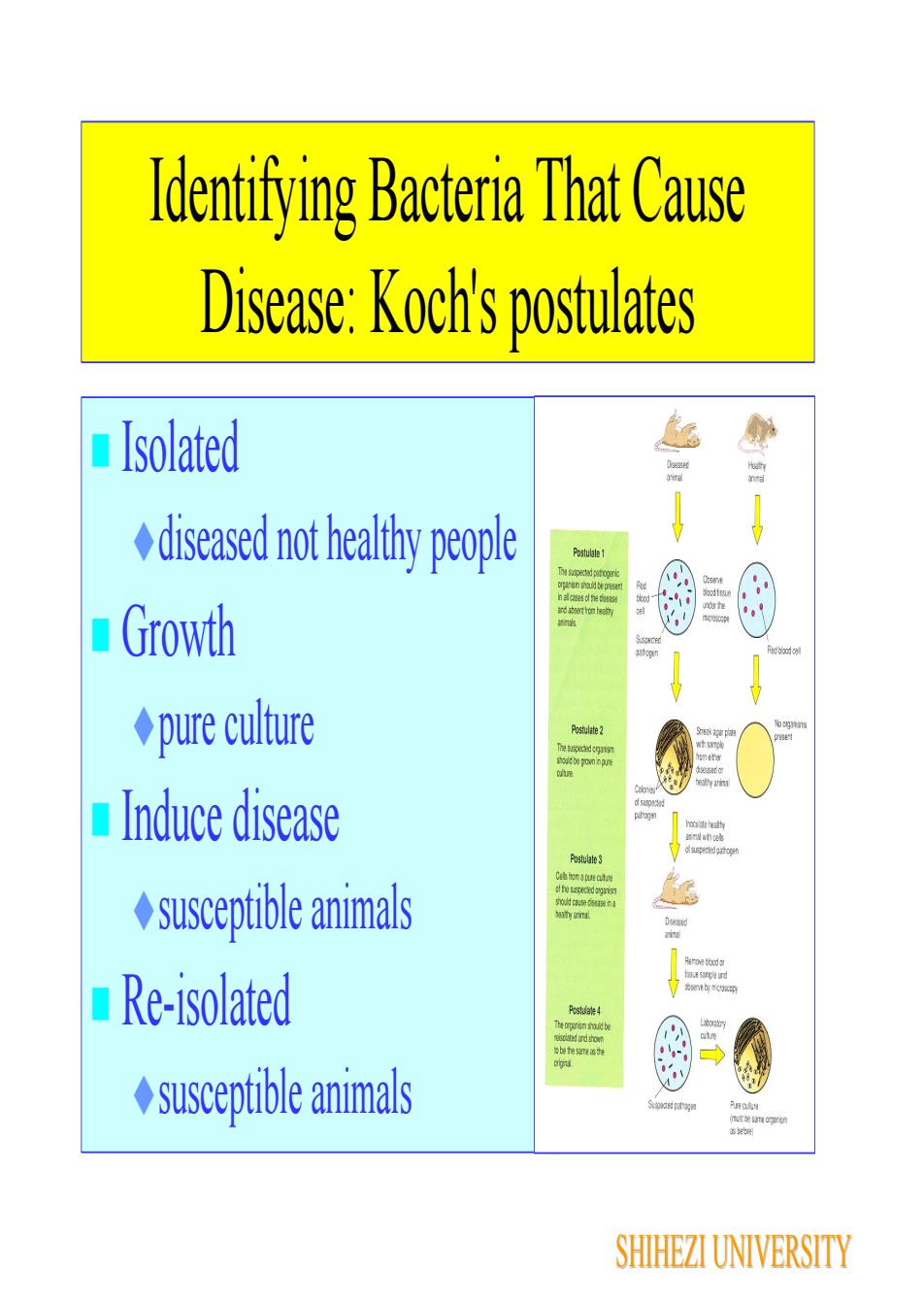
Identifying Bacteria That CauseDisease:Koch's postulates Isolateddiseased not healthy peoplePostulale 1The sutpectad penogirnipaninshauldtencasdlftetoard ataerthon ecthnGrowthmnddbiod on pure culture39Postulate2hesusoecdona8gmetashoaid be ponimpreueolthyanindsuspec Induce diseasepithognosalehealhatBsuspendpatogerPostulate3Calb tomapuectechtesedogait susceptible animalsshold caisedehaty armeoetentbymosep Re-isolatedPestulate 4The opaniomshoud bedudstonibeteseasteF susceptible animalsPurealnesoidsfpatrognasbesameogerisnas beteSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Identifying Bacteria That Cause Disease: Koch's postulates Isolated diseased not healthy people Growth pure culture Induce disease susceptible animals Re-isolated susceptible animals SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
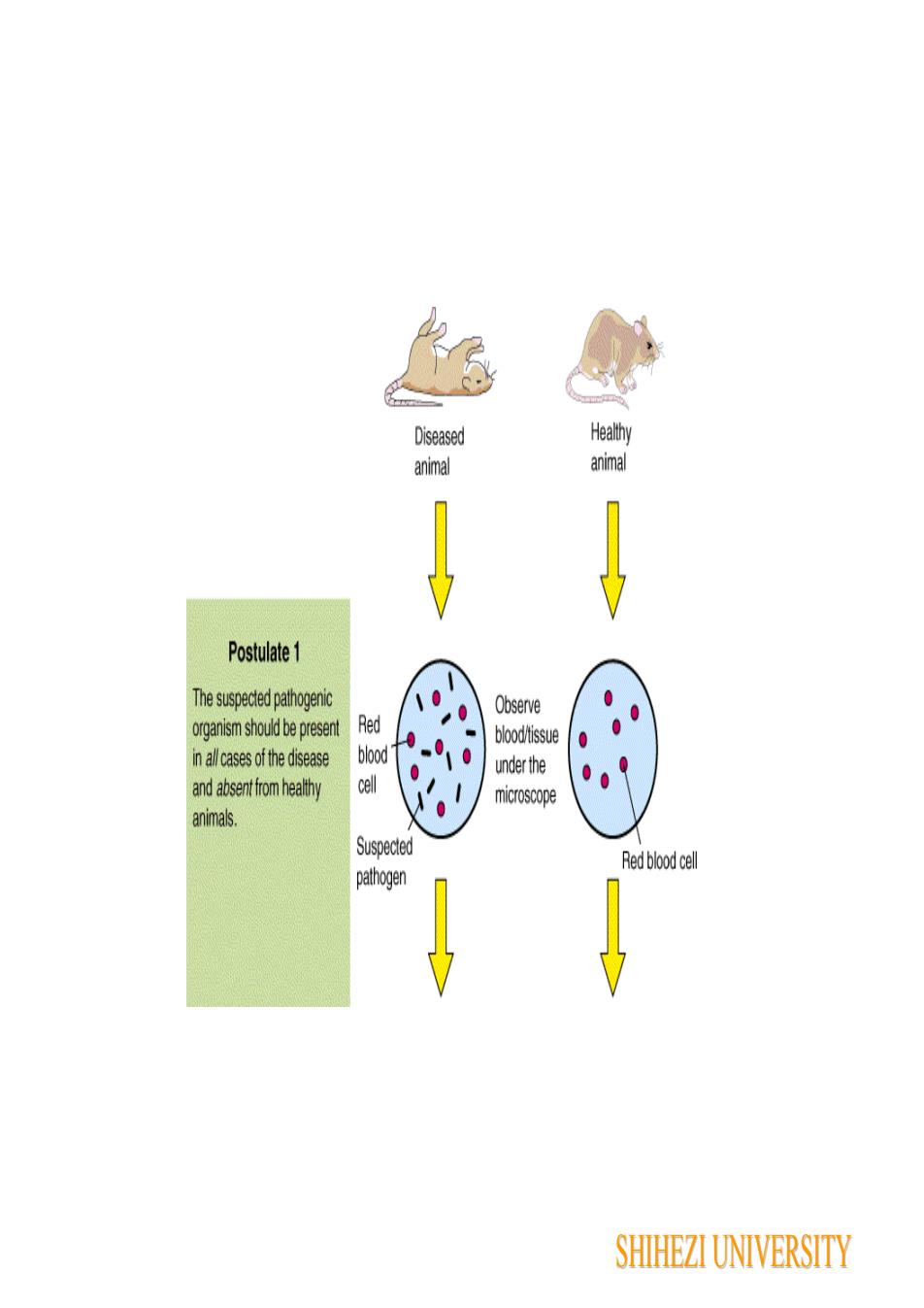
HealthyDiseasedanimalanimalPostulate1The suspected pathogenicObserveRedorganismshouldbepresentblood/issuebloodinall casesofthediseaseunderthecelland absentfrom healthymicroscopeanimas.SuspectedRed blood cellpathogenSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
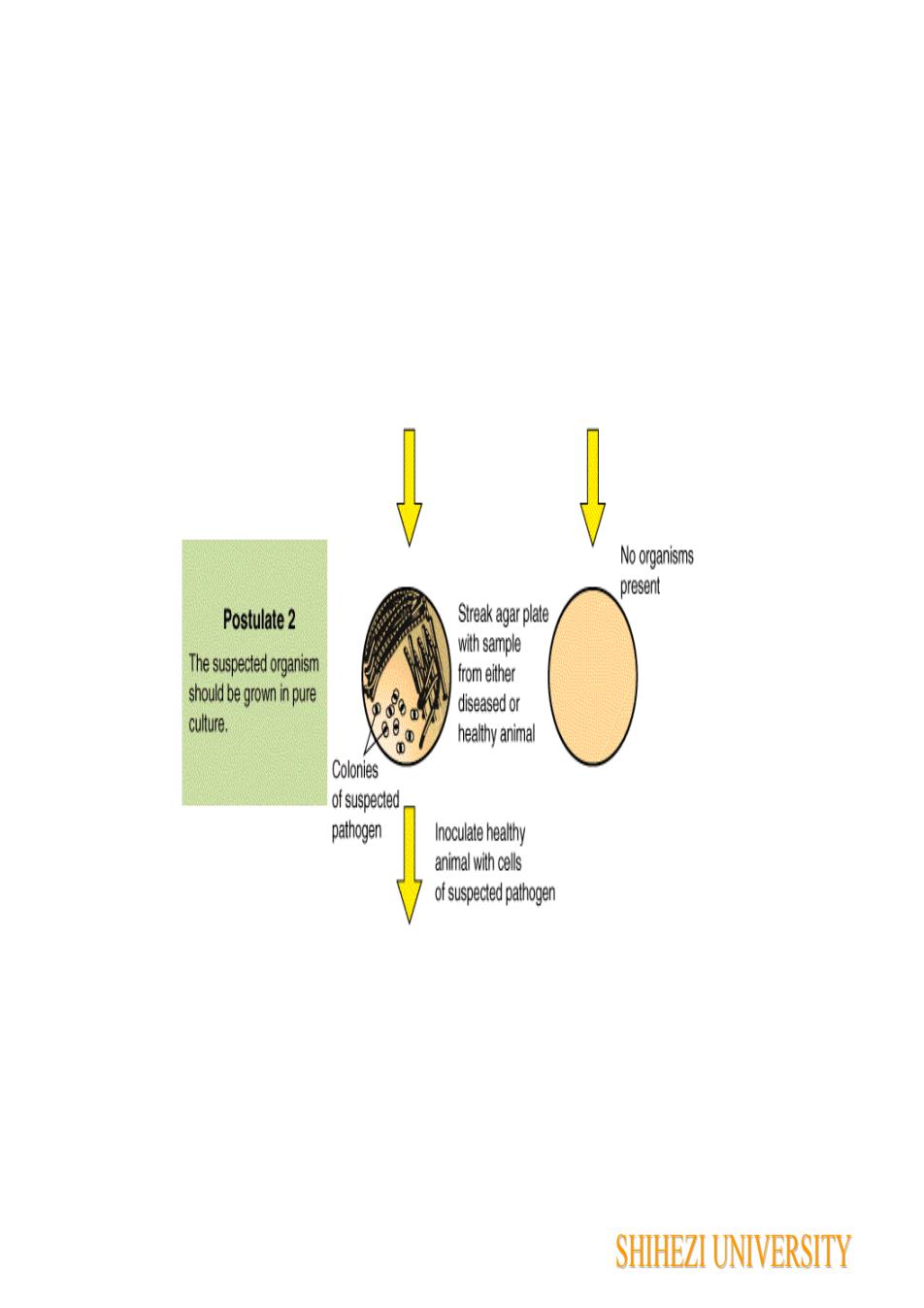
No organismspresentStreak agar platePostulate2with sampleThe suspectedorganismfrom eithershould be grownin purediseased orculture.healthy animalColoniesof suspectedpathogenInoculate healthyanimal withcellsof suspected pathogenSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
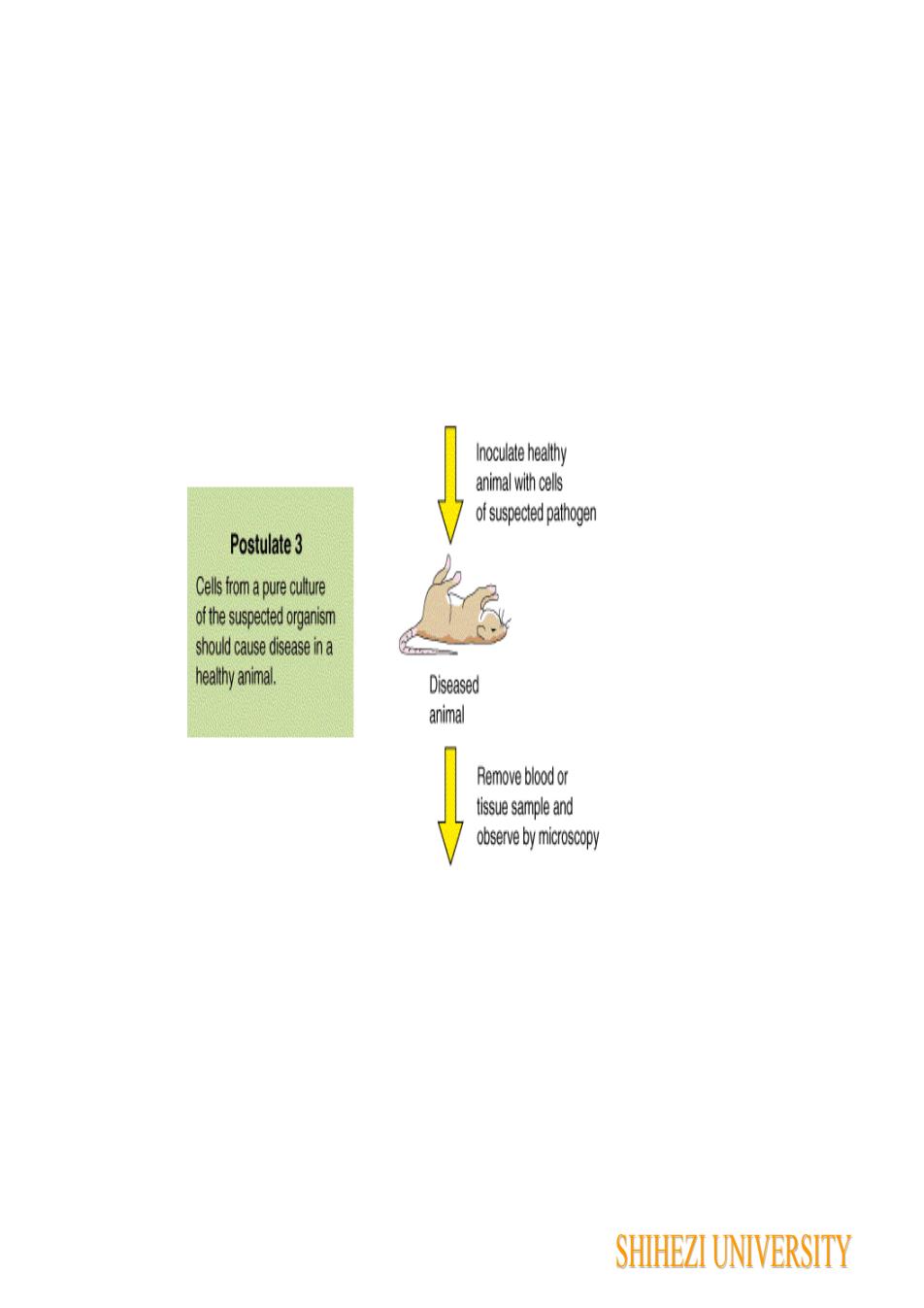
Inoculate heathyanimal with ellsof suspected pathogenPostulate 3Cells froma pure cutureofthesuspectedorganismshouldcausediseaseinahealthy animal.DiseasedanimalRemove blood ortisue sample andobserve by microscopySHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
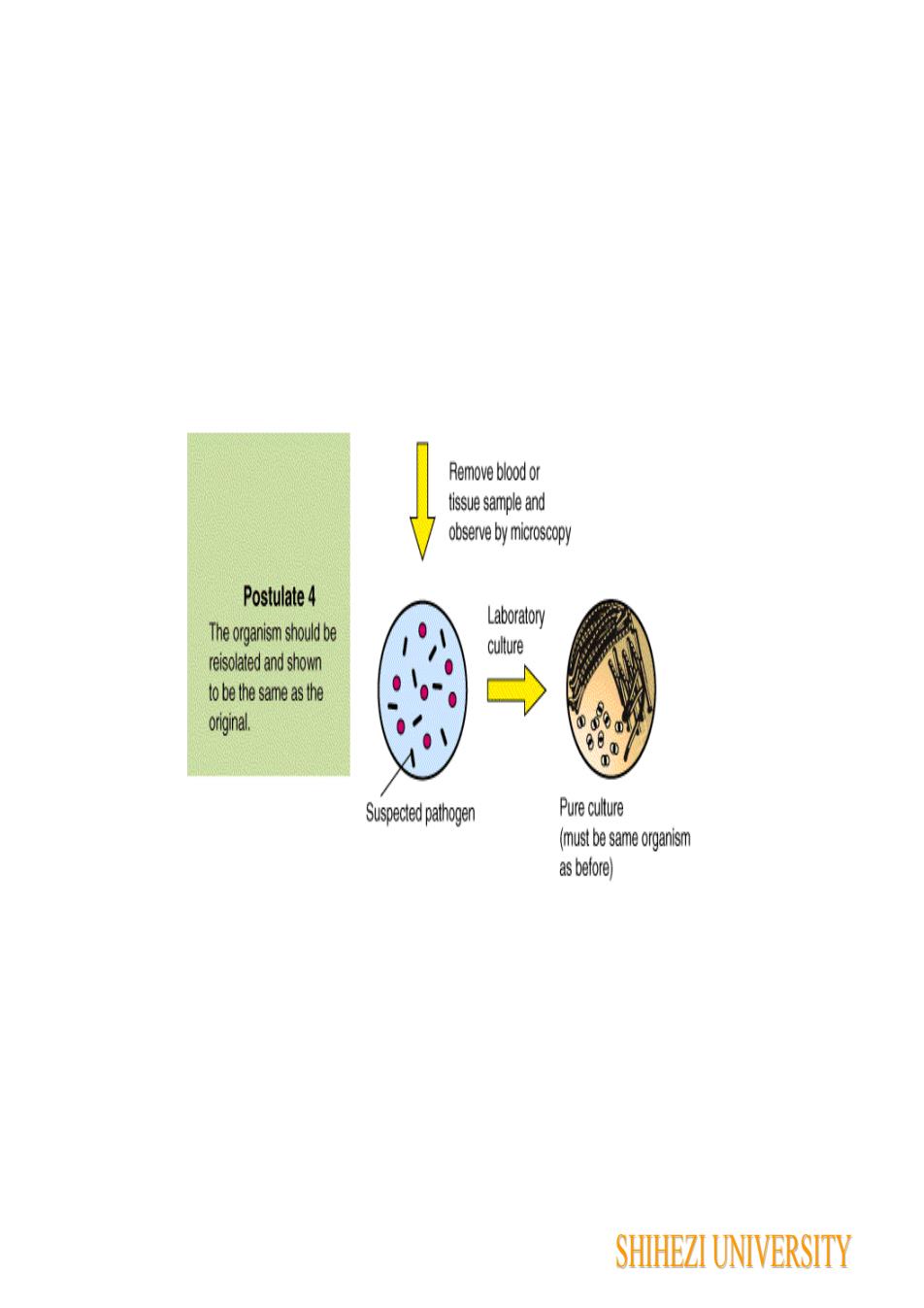
Remove blood ortissue sample andobserve by microscopyPostulate 4LaboratoryThe organism should beculturereisolatedand shownto bethe same as theorginal.0Q080Pure cuureSuspected pathogen(must besameorganismas before)SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Table9GuidelinesforestablishingthecausesofinfectiousdiseasesMolecular Koch'sPostulatesKoch's Postulates1. The microorganism1. The phenotype or prop-should be found in allerty underinvestigationcases of the disease inshould be significantyquestion,and its distri-associated with patho-bution in the bodygenic trains ofa speciesshould be in accordanceand not with nonpatho-with the lesionsgenic trains.observed.2. The microorganism2. Specificinactvation ofshould be grown in purethe gene or genesasso-culture in vitro (or outsideciated with the sus-the body of the host) forpected virulence tritseveral generations.should lead to ameasurable decrease inpathogenicity orvirulence.3. When such a pure cul-3. Reversion or replaceture isinoculated intoment ofthe mutatedsusceptible animalgene with the wild-typespecies the typical dis-gene should lead torestoration of patho-ease must result.genicity or virulence.4. The microorganism mustagain be isolated fromthe lesions of suchexperimentaly produceddisease.SHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY