
RFID Based Library Management System Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)is a new generation of Auto Identification and Data collection technology which helps to automate business processes and allows identification of large number of tagged objects like books,using radio waves.RFID based Library Management system(LMS)would allow fast transaction flow for the library and will prove immediate and long term benefits to library in traceability and security.The proposed system is based on UHF RFID readers,supported with antennas at gate and transaction sections,and library cards containing RFID-transponders which are able to electronically store information that can be read written even without the physical contact with the help of radio medium.This paper presents the experiments conducted to set up RFID based LMS. INTRODUCTION RFID technology is being implemented in a number of industries.Supply chain implementation is perhaps one of the most frequently mentioned applications of RFID tags and equipment. Retailers such as“Wal-Mart”and grocery stores such as“Albertson's”have begun to make it mandatory for their suppliers to tag merchandise destined for their stores.There is,however,a key difference to the library's inventory as compared to that of a warehouse or a retail outlet.In the warehouse and retail supply chain,goods come in and leave.Only occasionally are they returned. The retail sector is looking at RFID as a"throwaway"technology that hands an item to a customer which gets discarded.Yet the item wise unit cost of including an RFID tag is much more than the cost of printing a barcode on a package.In libraries,items are taken out and returned many times. Thus the same RFID tag is re-used many times. The libraries across the globe started to use RFID to speed up the self check in/out processes,to control the theft and to ease the inventory control in library.The barcode technology is slowly getting replaced by the RFID technology.The RFID tag does not have to be visible for detection. It can be read even when it is embedded in an item,such as in the cardboard cover of a book or in the packaging of a product.It can also store data such as stack number,accession number,book number,author information etc.,while barcode is limited to just an identification number. RFID in Library A library is a collection of information,sources,resources,books,and services,and the structure in which it is housed.Apart from books many libraries are now also repositories and access points for maps,prints,or other documents on various storage media such as microform (microfilm/microfiche),audio tapes,CDs,LPs,cassettes,videotapes,and DVDs.Libraries have materials arranged in a specified order according to a library classification system,so that items may be located quickly and collections may be browsed efficiently.Reference stacks are different which has only reference books and only selected members. The following are the tasks to be performed in the library. Circulation:handling user accounts and issuing/returning and shelving of materials. Collection,development,order materials,maintain materials'budgets. Technical Services work behind the scenes cataloguing and processing new materials and de accessioning weeded materials. Basic tasks in library management include the planning of acquisitions of materials,arranging the acquired materials according to the library classification,preservation of materials the de accessioning of materials,patron borrowing of materials,and developing and administering library computer systems.Among these,the proposed system will automate the following tasks
RFID Based Library Management System Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a new generation of Auto Identification and Data collection technology which helps to automate business processes and allows identification of large number of tagged objects like books, using radio waves. RFID based Library Management system (LMS) would allow fast transaction flow for the library and will prove immediate and long term benefits to library in traceability and security. The proposed system is based on UHF RFID readers, supported with antennas at gate and transaction sections, and library cards containing RFID-transponders which are able to electronically store information that can be read / written even without the physical contact with the help of radio medium. This paper presents the experiments conducted to set up RFID based LMS. INTRODUCTION RFID technology is being implemented in a number of industries. Supply chain implementation is perhaps one of the most frequently mentioned applications of RFID tags and equipment. Retailers such as “Wal-Mart” and grocery stores such as “Albertson’s” have begun to make it mandatory for their suppliers to tag merchandise destined for their stores. There is, however, a key difference to the library’s inventory as compared to that of a warehouse or a retail outlet. In the warehouse and retail supply chain, goods come in and leave. Only occasionally are they returned. The retail sector is looking at RFID as a "throwaway" technology that hands an item to a customer which gets discarded. Yet the item wise unit cost of including an RFID tag is much more than the cost of printing a barcode on a package. In libraries, items are taken out and returned many times. Thus the same RFID tag is re-used many times. The libraries across the globe started to use RFID to speed up the self check in/out processes, to control the theft and to ease the inventory control in library. The barcode technology is slowly getting replaced by the RFID technology. The RFID tag does not have to be visible for detection. It can be read even when it is embedded in an item, such as in the cardboard cover of a book or in the packaging of a product. It can also store data such as stack number, accession number, book number, author information etc., while barcode is limited to just an identification number. RFID in Library A library is a collection of information, sources, resources, books, and services, and the structure in which it is housed. Apart from books many libraries are now also repositories and access points for maps, prints, or other documents on various storage media such as microform (microfilm/microfiche), audio tapes, CDs, LPs, cassettes, videotapes, and DVDs. Libraries have materials arranged in a specified order according to a library classification system, so that items may be located quickly and collections may be browsed efficiently. Reference stacks are different which has only reference books and only selected members. The following are the tasks to be performed in the library. Circulation: handling user accounts and issuing/returning and shelving of materials. Collection, development, order materials, maintain materials’ budgets. Technical Services work behind the scenes cataloguing and processing new materials and de accessioning weeded materials. Basic tasks in library management include the planning of acquisitions of materials, arranging the acquired materials according to the library classification, preservation of materials the de accessioning of materials, patron borrowing of materials, and developing and administering library computer systems. Among these, the proposed system will automate the following tasks

using RFID technology, Accessing number of books at a time Searching a particular book to check its presence in the library Locating the physical location of the book Accounting/Stock verification of the materials The RFID based LMS facilitates the fast issuing,reissuing and returning of books with the help of RFID enabled modules.It directly provides the book information and library member information to the library management system and does not need the manual typing.It also provides monitoring and searching system.The monitoring module will continuously monitor the movement of books across the gates,so that the books taken out without prior issuing will be traced out easily and will alarm the librarians.The searching module provides the fast searching of books using RFID handheld reader.The physical location of the books can be easily located using this module Utmost care has been taken to provide following features to the Library using RFID technology: To remove manual book keeping of records Traceability of books and library members as they move Improved utilization of resources like manpower,infrastructure etc. Less time consumption as line of sight and manual interaction are not needed for RFID-tag reading. To provide 2 meters read range antennas To minimize the manual intervention To minimize the manual errors To provide the long lasting labels To provide fast searching of books Reasons for choosing UHF in Library Application UHF technology was chosen for library application due to its long read range,speed of frequency and low cost.The read range of mercury 4 reader is up to 2 meters,which is sufficient to monitor the movement of books across the gates.The read range of handheld reader is up to 30 cms which will be useful for locating a particular book in a rack.With the new EPC Global Gen 2 standard,over 1000 tags can be read per second in applications where they are insulated from RF noise.UHF also has the option to slow down the read process to 100 tags per second with high reliability in RF noisy applications. All of these benefits make the UHF technology the ideal choice for Library applications. RFID Integration Modules In order to provide RFID integration with LMS,three modules namely-Transaction Module, Monitoring Module and Searching Module were developed.Their functionalities are described below. Transaction Module The interaction of transaction module is given in(fig.3).The RFID interface is provided in the transaction forms like issue,reissue,return and fine status forms.The Manual intervention is minimized as the automatic identification of books and library members will be achieved because of RFID.The books and employee ID cards should be placed near the antenna.The tags will be scanned by the reader and the book id and the employee id will be transmitted to the s/w module running in the librarian's PC and which in turn will store the transaction information in database
using RFID technology, Accessing number of books at a time Searching a particular book to check its presence in the library Locating the physical location of the book Accounting/Stock verification of the materials The RFID based LMS facilitates the fast issuing, reissuing and returning of books with the help of RFID enabled modules. It directly provides the book information and library member information to the library management system and does not need the manual typing. It also provides monitoring and searching system. The monitoring module will continuously monitor the movement of books across the gates, so that the books taken out without prior issuing will be traced out easily and will alarm the librarians. The searching module provides the fast searching of books using RFID handheld reader. The physical location of the books can be easily located using this module. Utmost care has been taken to provide following features to the Library using RFID technology: To remove manual book keeping of records Traceability of books and library members as they move Improved utilization of resources like manpower, infrastructure etc. Less time consumption as line of sight and manual interaction are not needed for RFID-tag reading. To provide 2 meters read range antennas To minimize the manual intervention To minimize the manual errors To provide the long lasting labels To provide fast searching of books Reasons for choosing UHF in Library Application UHF technology was chosen for library application due to its long read range, speed of frequency and low cost. The read range of mercury 4 reader is up to 2 meters, which is sufficient to monitor the movement of books across the gates. The read range of handheld reader is up to 30 cms which will be useful for locating a particular book in a rack. With the new EPC Global Gen 2 standard, over 1000 tags can be read per second in applications where they are insulated from RF noise. UHF also has the option to slow down the read process to 100 tags per second with high reliability in RF noisy applications. All of these benefits make the UHF technology the ideal choice for Library applications. RFID Integration Modules In order to provide RFID integration with LMS, three modules namely - Transaction Module, Monitoring Module and Searching Module were developed. Their functionalities are described below. Transaction Module The interaction of transaction module is given in (fig. 3).The RFID interface is provided in the transaction forms like issue, reissue, return and fine status forms. The Manual intervention is minimized as the automatic identification of books and library members will be achieved because of RFID. The books and employee ID cards should be placed near the antenna. The tags will be scanned by the reader and the book id and the employee id will be transmitted to the s/w module running in the librarian’s PC and which in turn will store the transaction information in database
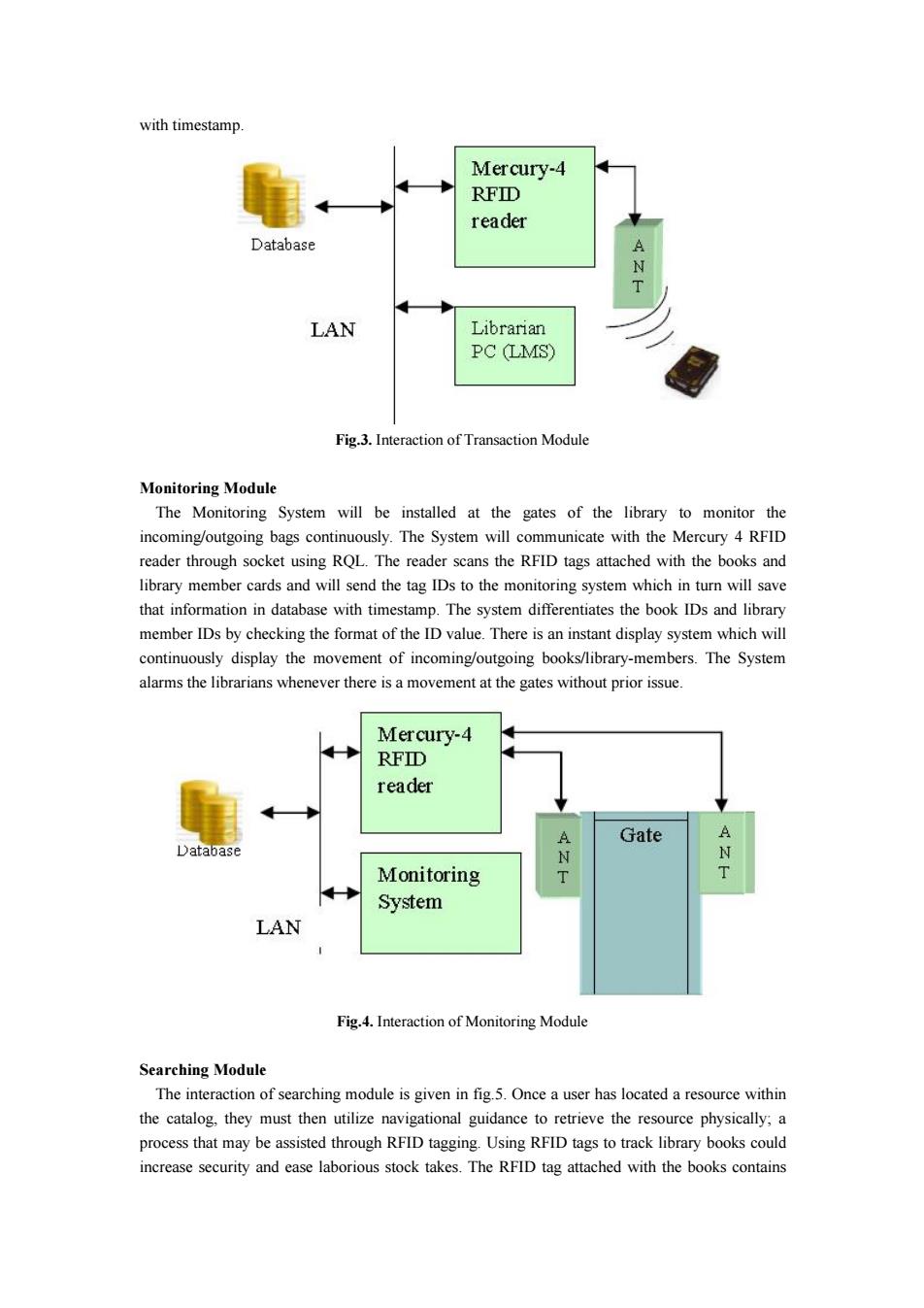
with timestamp. Mercury-4 RFID reader Database A 入 LAN Librarian PC LMS) Fig.3.Interaction of Transaction Module Monitoring Module The Monitoring System will be installed at the gates of the library to monitor the incoming/outgoing bags continuously.The System will communicate with the Mercury 4 RFID reader through socket using RQL.The reader scans the RFID tags attached with the books and library member cards and will send the tag IDs to the monitoring system which in turn will save that information in database with timestamp.The system differentiates the book IDs and library member IDs by checking the format of the ID value.There is an instant display system which will continuously display the movement of incoming/outgoing books/library-members.The System alarms the librarians whenever there is a movement at the gates without prior issue. Mercury-4 RFID reader Gate Database Monitoring T T System LAN Fig.4.Interaction of Monitoring Module Searching Module The interaction of searching module is given in fig.5.Once a user has located a resource within the catalog,they must then utilize navigational guidance to retrieve the resource physically;a process that may be assisted through RFID tagging.Using RFID tags to track library books could increase security and ease laborious stock takes.The RFID tag attached with the books contains
with timestamp. Fig.3. Interaction of Transaction Module Monitoring Module The Monitoring System will be installed at the gates of the library to monitor the incoming/outgoing bags continuously. The System will communicate with the Mercury 4 RFID reader through socket using RQL. The reader scans the RFID tags attached with the books and library member cards and will send the tag IDs to the monitoring system which in turn will save that information in database with timestamp. The system differentiates the book IDs and library member IDs by checking the format of the ID value. There is an instant display system which will continuously display the movement of incoming/outgoing books/library-members. The System alarms the librarians whenever there is a movement at the gates without prior issue. Fig.4. Interaction of Monitoring Module Searching Module The interaction of searching module is given in fig.5. Once a user has located a resource within the catalog, they must then utilize navigational guidance to retrieve the resource physically; a process that may be assisted through RFID tagging. Using RFID tags to track library books could increase security and ease laborious stock takes. The RFID tag attached with the books contains
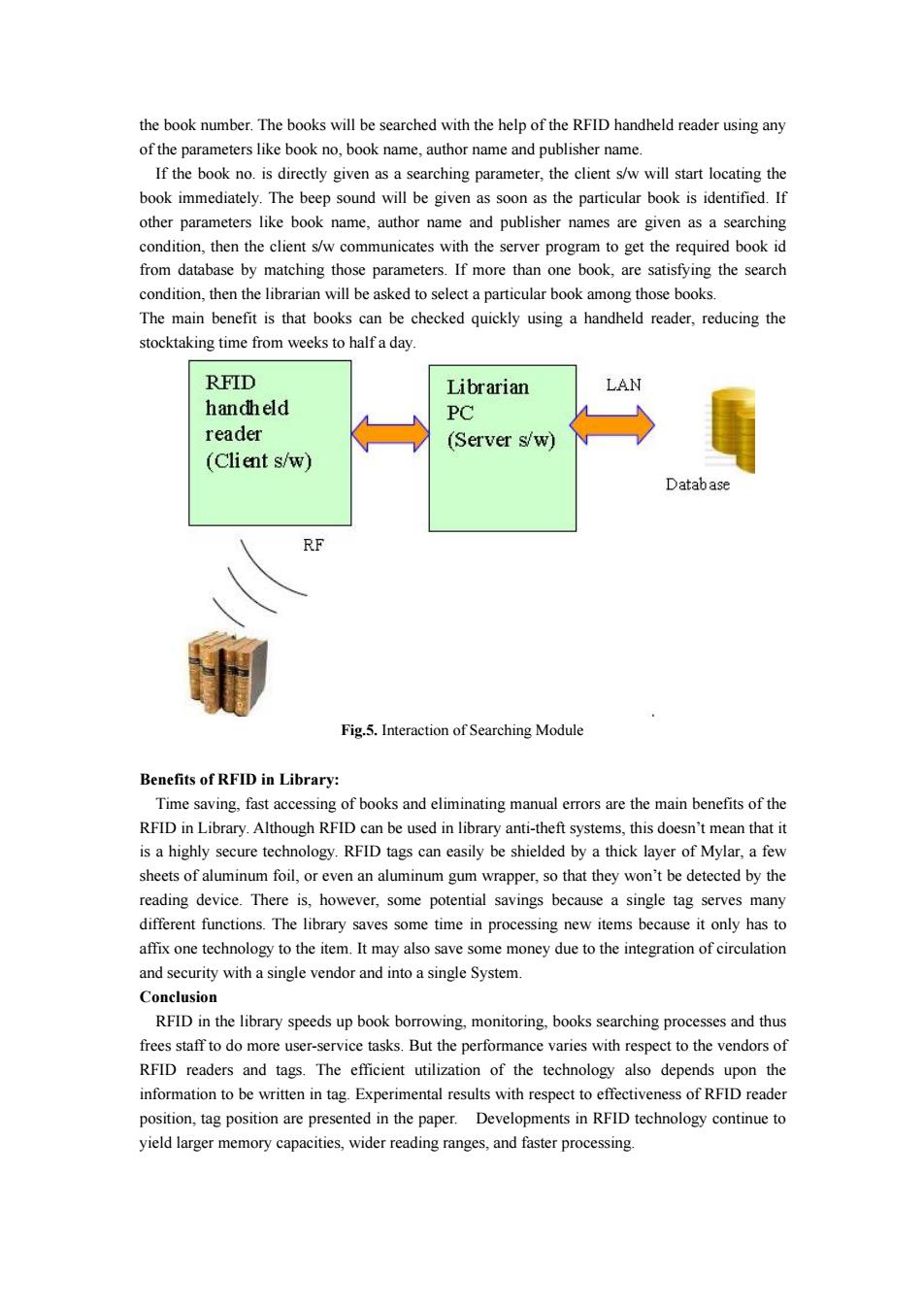
the book number.The books will be searched with the help of the RFID handheld reader using any of the parameters like book no,book name,author name and publisher name. If the book no.is directly given as a searching parameter,the client s/w will start locating the book immediately.The beep sound will be given as soon as the particular book is identified.If other parameters like book name,author name and publisher names are given as a searching condition,then the client s/w communicates with the server program to get the required book id from database by matching those parameters.If more than one book,are satisfying the search condition,then the librarian will be asked to select a particular book among those books. The main benefit is that books can be checked quickly using a handheld reader,reducing the stocktaking time from weeks to half a day RFID Librarian LAN handheld PC reader (Server s/w) (Client s/w) Database RE Fig.5.Interaction of Searching Module Benefits of RFID in Library: Time saving,fast accessing of books and eliminating manual errors are the main benefits of the RFID in Library.Although RFID can be used in library anti-theft systems,this doesn't mean that it is a highly secure technology.RFID tags can easily be shielded by a thick layer of Mylar,a few sheets of aluminum foil,or even an aluminum gum wrapper,so that they won't be detected by the reading device.There is,however,some potential savings because a single tag serves many different functions.The library saves some time in processing new items because it only has to affix one technology to the item.It may also save some money due to the integration of circulation and security with a single vendor and into a single System. Conclusion RFID in the library speeds up book borrowing,monitoring,books searching processes and thus frees staff to do more user-service tasks.But the performance varies with respect to the vendors of RFID readers and tags.The efficient utilization of the technology also depends upon the information to be written in tag.Experimental results with respect to effectiveness of RFID reader position,tag position are presented in the paper.Developments in RFID technology continue to yield larger memory capacities,wider reading ranges,and faster processing
the book number. The books will be searched with the help of the RFID handheld reader using any of the parameters like book no, book name, author name and publisher name. If the book no. is directly given as a searching parameter, the client s/w will start locating the book immediately. The beep sound will be given as soon as the particular book is identified. If other parameters like book name, author name and publisher names are given as a searching condition, then the client s/w communicates with the server program to get the required book id from database by matching those parameters. If more than one book, are satisfying the search condition, then the librarian will be asked to select a particular book among those books. The main benefit is that books can be checked quickly using a handheld reader, reducing the stocktaking time from weeks to half a day. Fig.5. Interaction of Searching Module Benefits of RFID in Library: Time saving, fast accessing of books and eliminating manual errors are the main benefits of the RFID in Library. Although RFID can be used in library anti-theft systems, this doesn’t mean that it is a highly secure technology. RFID tags can easily be shielded by a thick layer of Mylar, a few sheets of aluminum foil, or even an aluminum gum wrapper, so that they won’t be detected by the reading device. There is, however, some potential savings because a single tag serves many different functions. The library saves some time in processing new items because it only has to affix one technology to the item. It may also save some money due to the integration of circulation and security with a single vendor and into a single System. Conclusion RFID in the library speeds up book borrowing, monitoring, books searching processes and thus frees staff to do more user-service tasks. But the performance varies with respect to the vendors of RFID readers and tags. The efficient utilization of the technology also depends upon the information to be written in tag. Experimental results with respect to effectiveness of RFID reader position, tag position are presented in the paper. Developments in RFID technology continue to yield larger memory capacities, wider reading ranges, and faster processing