Design of P-3623 Composite Slab Professor Shiming Chen College of Civil Engineering Tongji University
Design of P-3623 Composite Slab Professor : Shiming Chen College of Civil Engineering Tongji University
90 Bearing Capacity of Composite Slabs Bending resistance Ultimate limited Diagonal shear resistance state design Longitudinal shear resistance Serviceability limited Deflections state design
Bearing Capacity of Composite Slabs Ultimate limited state design Bending resistance Diagonal shear resistance Longitudinal shear resistance Serviceability limited state design Deflections
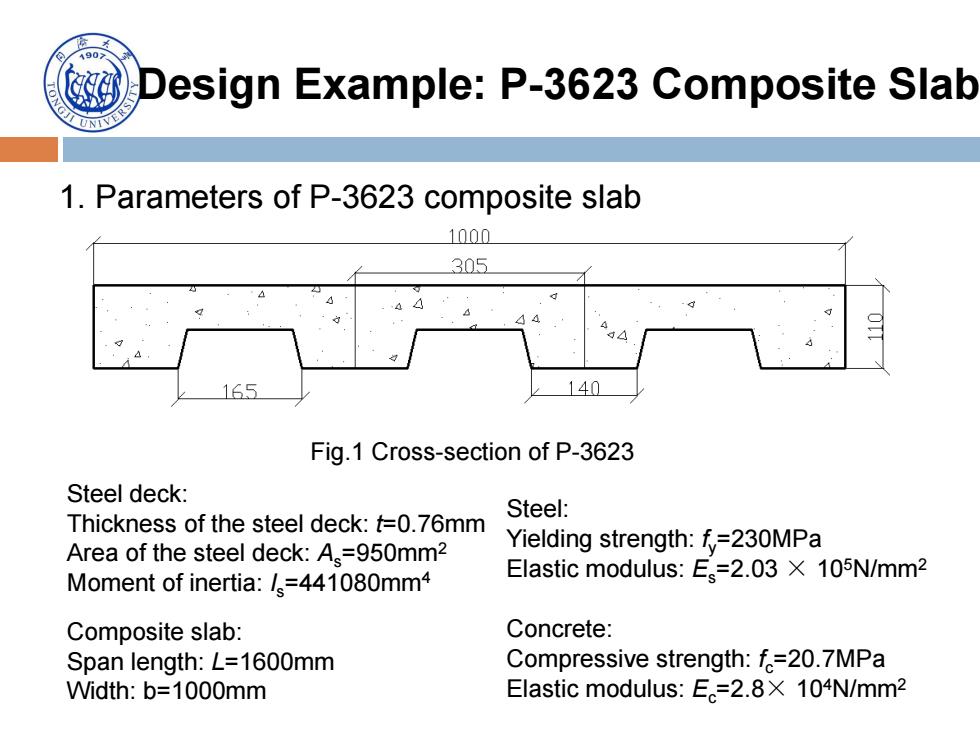
Design Example:P-3623 Composite Slab 1.Parameters of P-3623 composite slab 1000 305 140 Fig.1 Cross-section of P-3623 Steel deck: Thickness of the steel deck:t=0.76mm Steel: Area of the steel deck:A=950mm2 Yielding strength:f=230MPa Moment of inertia:/=441080mm4 Elastic modulus:Es=2.03 X 105N/mm2 Composite slab: Concrete: Span length:L=1600mm Compressive strength:f=20.7MPa Width:b=1000mm Elastic modulus:E。=2.8×104N/mm2
Design Example: P-3623 Composite Slab 1. Parameters of P-3623 composite slab Fig.1 Cross-section of P-3623 Steel deck: Thickness of the steel deck: t=0.76mm Area of the steel deck: As=950mm2 Moment of inertia: Is=441080mm4 Composite slab: Span length: L=1600mm Width: b=1000mm Steel: Yielding strength: fy=230MPa Elastic modulus: Es=2.03 × 105N/mm2 Concrete: Compressive strength: fc=20.7MPa Elastic modulus: Ec=2.8× 104N/mm2

90 Positive bending resistance Assume neutral axis lies in concrete slab above the steel deck fA,=fbx。 x-4-230x950 fb20.7×1000 =10.56mm<51mm Neutral axis does locate in concrete slab above the steel deck So,bending resistance is M,=xfbx.(h-x。/2)=0.8×20.7×1000×10.56×(84.5-10.56/2)=13.85kWm In midspan:M. The ultimate design load: qu= 8M_8x13.85=49.24kW/m2 b12 1×1.52
Positive bending resistance Assume neutral axis lies in concrete slab above the steel deck y s c c f A f bx 230 950 10.56 51 20.7 1000 y s c c f A x mm mm f b Neutral axis does locate in concrete slab above the steel deck So, bending resistance is : 0 ( / 2) 0.8 20.7 1000 10.56 (84.5 10.56/ 2) 13.85 M f bx h x kN m u c c c 1 2 8 In midspan: M q bl u u 2 2 2 8 8 13.85 49.24 / 1 1.5 u u M q kN m bl The ultimate design load:

Positive bending resistance As the slab span changes,the ultimate design load changes; The table below shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the bending resistance Table 1.The ultimate design loads L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 qu(kN/mm 49.24 40.70 34.20 29.14 2) 25.12 21.88 19.24 17.04 15.20 13.64 12.31 11.17 10.17
Positive bending resistance As the slab span changes, the ultimate design load changes; The table below shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the bending resistance L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 qu (kN/mm 2 ) 49.24 40.70 34.20 29.14 25.12 21.88 19.24 17.04 15.20 13.64 12.31 11.17 10.17 Table 1. The ultimate design loads
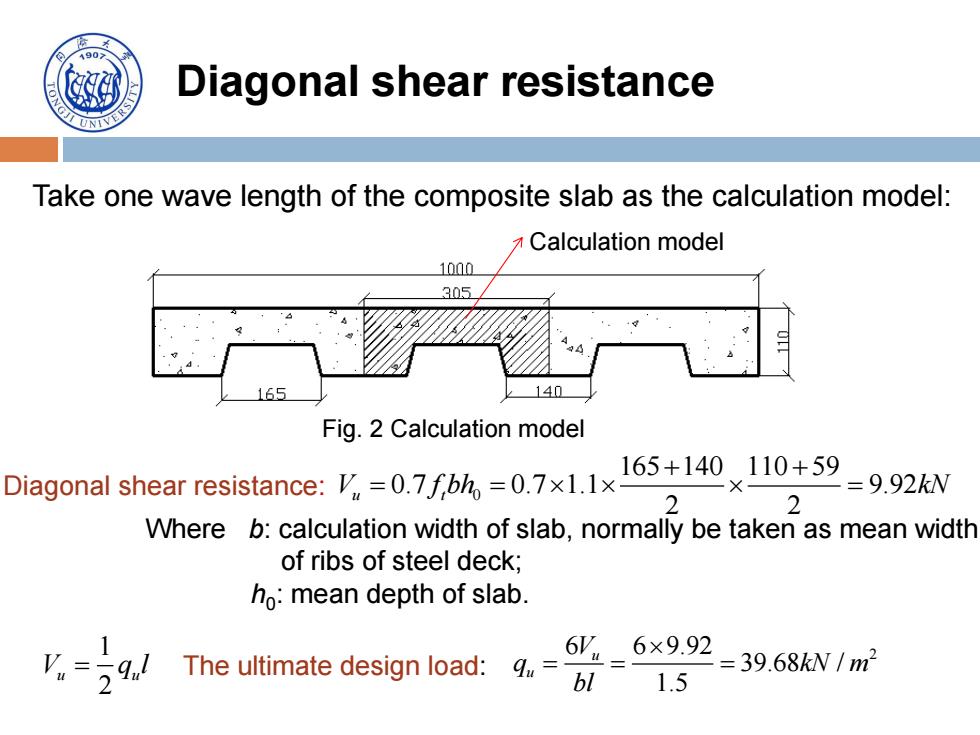
190 Diagonal shear resistance Take one wave length of the composite slab as the calculation model: Calculation model 1000 305 140 Fig.2 Calculation model Diagonal shear resistance:.7.7xx10059 2 2 2=9.92kW Where b:calculation width of slab,normally be taken as mean width of ribs of steel deck; ho:mean depth of slab. The ultimate design load: 6-6×9.92 =39.68kW/m2 bl 1.5
Diagonal shear resistance Take one wave length of the composite slab as the calculation model: 0 165 140 110 59 0.7 0.7 1.1 9.92 2 2 V f bh kN u t Calculation model Where b: calculation width of slab, normally be taken as mean width of ribs of steel deck; h0 : mean depth of slab. Fig. 2 Calculation model 1 2 V q l u u 6 6 9.92 2 39.68 / 1.5 u u V q kN m bl Diagonal shear resistance: The ultimate design load:
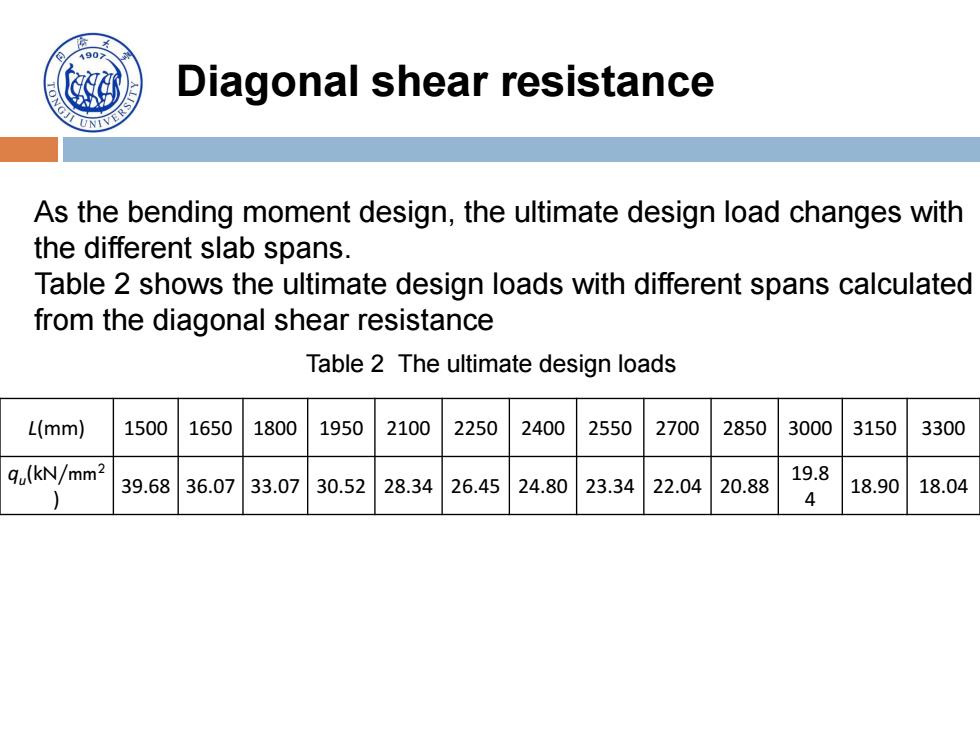
Diagonal shear resistance As the bending moment design,the ultimate design load changes with the different slab spans Table 2 shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the diagonal shear resistance Table 2 The ultimate design loads L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 qu(kN/mm2 39.68 36.07 33.07 30.52 28.34 26.45 24.80 23.34 22.04 20.88 19.8 18.90 18.04 4
Diagonal shear resistance As the bending moment design, the ultimate design load changes with the different slab spans. Table 2 shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the diagonal shear resistance L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 qu (kN/mm2 ) 39.68 36.07 33.07 30.52 28.34 26.45 24.80 23.34 22.04 20.88 19.8 4 18.90 18.04 Table 2 The ultimate design loads

90 Longitudinal shear resistance m-k method: Take two groups of data from the profiled steel manufacturers:L=1650mm and L=1950mm 1=1650mm,q=12.51kW/m2 1=1950m,q=9.39kN/m2 +利 V=bd (mL 59x=125,4= 950 +k)× Using the two groups of data,then 2×12.51x1650=1000x51xm 000×1/4×1650 1.25 950 ×9.39×1950=1000×51×( 1000x174x1950+)×125 The solution is: m=80.63 k=0.06727
Longitudinal shear resistance m-k method: Take two groups of data from the profiled steel manufacturers: L=1650mm and L=1950mm 2 l mm q kN m 1650 , 12.51 / 2 l mm q kN m 1950 , 9.39 / , 1 ( ) p L Rd p s s A V bd m k bL , 1 1 , 1.25, 2 4 V ql L l L Rd s s Using the two groups of data, then 1 950 1 12.51 1650 1000 51 ( ) 2 1000 1/ 4 1650 1.25 m k 1 950 1 9.39 1950 1000 51 ( ) 2 1000 1/ 4 1950 1.25 m k The solution is: 80.63 0.06727 m k

Longitudinal shear resistance S0,上则=bd,(80.63是+0.06727) bL Y When the slab span is taken as L=1500mm. The ultimate design load: bd,m子+月 950 bL. 1000×51×(80.63× +0.06727)× 9m= 1000×1/4×1500 125=14.77kW1m2 1/21 1/2×1500 Table 3 shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the longitudinal shear resistance Table 3 The ultimate design loads L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 q(kN/mm2) 14.77 12.51 10.77 9.39 8.28 7.38 6.63 6.00 5.46 5.00 4.61 4.26 3.96
Longitudinal shear resistance So, , 1 (80.63 0.06727) p L Rd p s s A V bd bL When the slab span is taken as L=1500mm, 1 1 (80.63 0.06727) 2 p u p s s A q l bd bL 2 1 950 1 ( ) 1000 51 (80.63 0.06727) 1000 1/ 4 1500 1.25 14.77 / 1/ 2 1/ 2 1500 p p s s u A bd m k bL q kN m l L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 qu (kN/mm2 ) 14.77 12.51 10.77 9.39 8.28 7.38 6.63 6.00 5.46 5.00 4.61 4.26 3.96 Table 3 shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the longitudinal shear resistance Table 3 The ultimate design loads The ultimate design load:
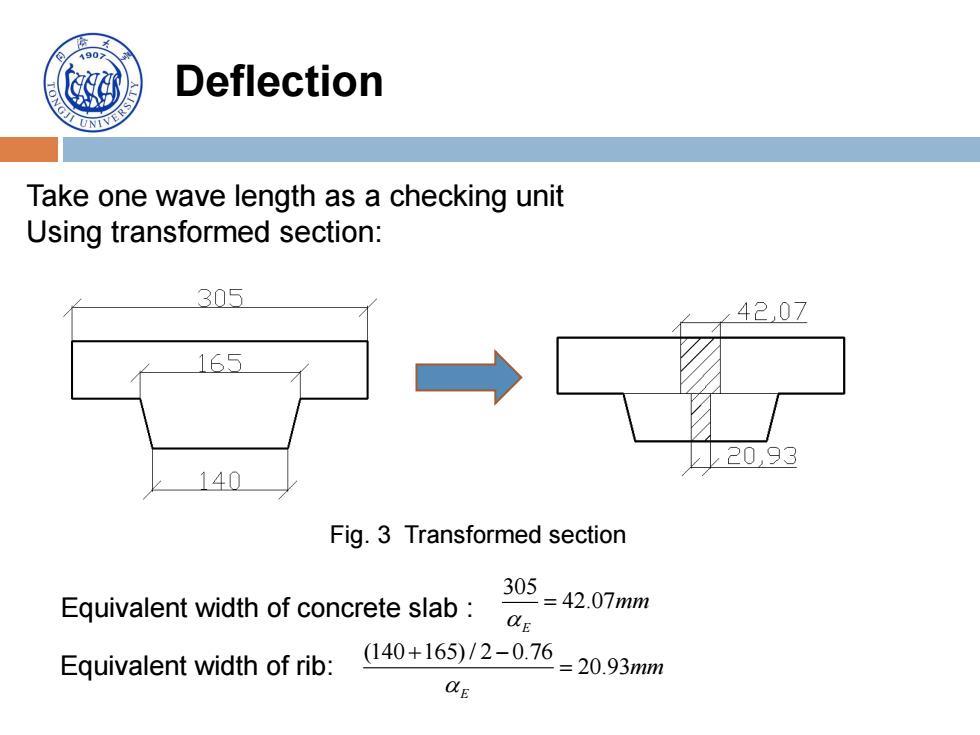
4907 Deflection Take one wave length as a checking unit Using transformed section: 305 4207 165 上20,93 140 Fig.3 Transformed section Equivalent width of concrete slab 305=42.07mm E Equivalent width of rib: (140+165)/2-0.76 =20.93mm CE
Deflection Take one wave length as a checking unit Using transformed section: Equivalent width of concrete slab : 305 42.07 E mm Equivalent width of rib: (140 165) / 2 0.76 20.93 E mm Fig. 3 Transformed section