
Advanced Theory of Concrete Structures Chapter 3 Bond and Anchorage Yong Zhou College of Civil Engineering,Tongji University 土亦工程学院 yongzhou@tongji.edu.cn COLLEGEOPCVILINGAINETRING
Yong Zhou College of Civil Engineering, Tongji University yongzhou@tongji.edu.cn Chapter 3 Bond and Anchorage Advanced Theory of Concrete Structures
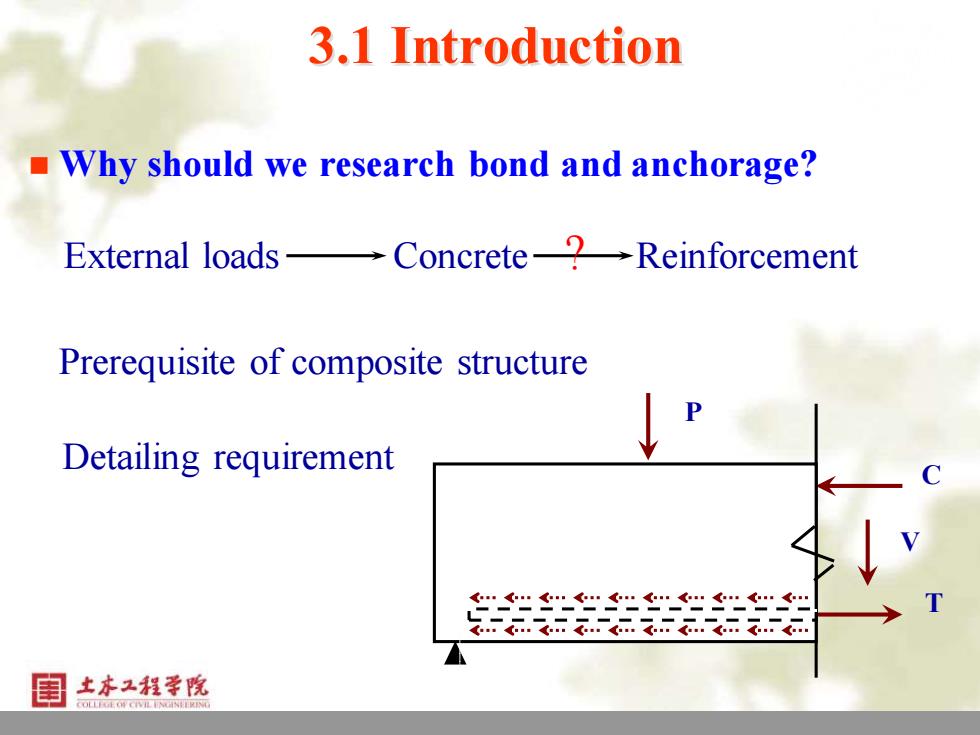
3.1 Introduction Why should we research bond and anchorage? External loads一Concrete-?→Reinforcement Prerequisite of composite structure Detailing requirement 土水工程学院
2 3.1 Introduction ◼ Why should we research bond and anchorage? External loads Concrete ? Reinforcement Prerequisite of composite structure Detailing requirement C T V P
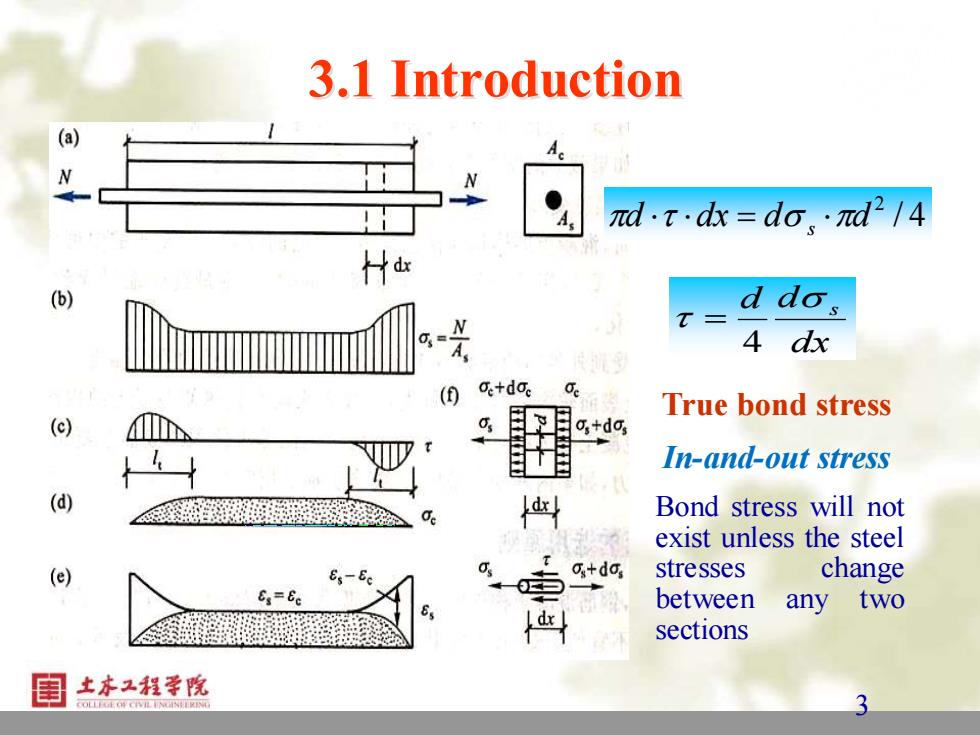
3.1 Introduction N d.tdk=do、·πd2/4 Ha (6) N T= d dos A dx ,+dc. True bond stress (c) o,+do, In-and-out stress (d) Bond stress will not exist unless the steel (e) Os +do 圭 stresses change between any two sections 土本工程学院 3
3 3 3.1 Introduction dx d d s 4 = / 4 2 d dx d d = s True bond stress In-and-out stress Bond stress will not exist unless the steel stresses change between any two sections
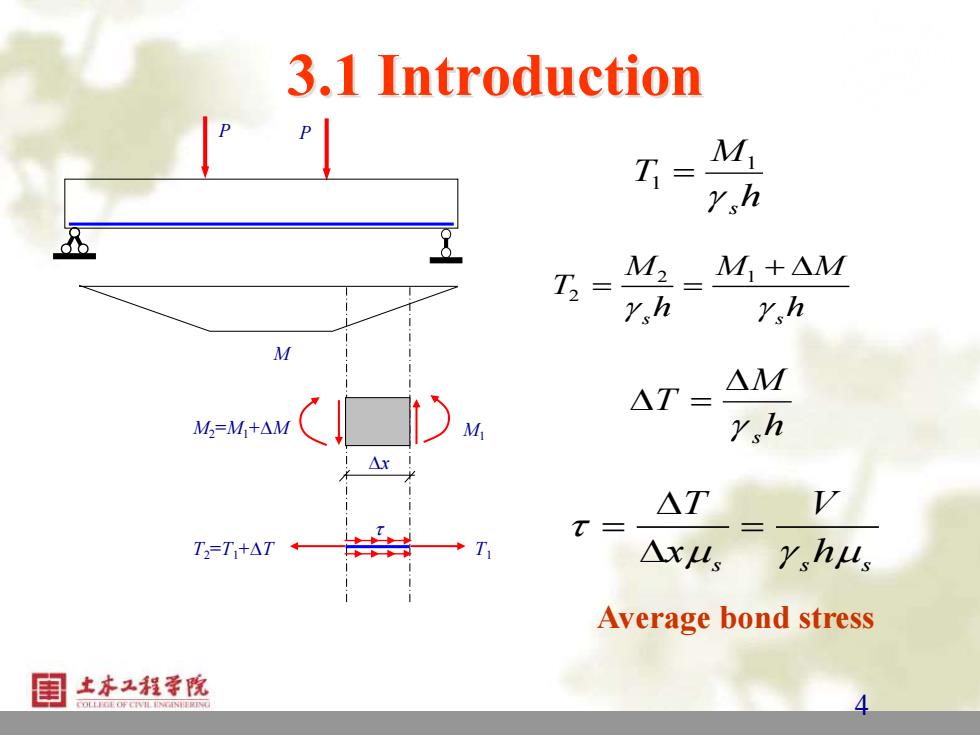
3.1 Introduction T= M Y h T2= M2 M+AM rh rh M △M △T= M=M+AM M rh △r AT V T= T=T+AT T △x4s rhus Average bond stress 土本工程学院
4 4 3.1 Introduction P P M T2=T1+T T1 x M2=M1+M M1 h M T s 1 1 = 2 1 2 s s M M M T h h + = = h M T s = s s s T V x h = = Average bond stress
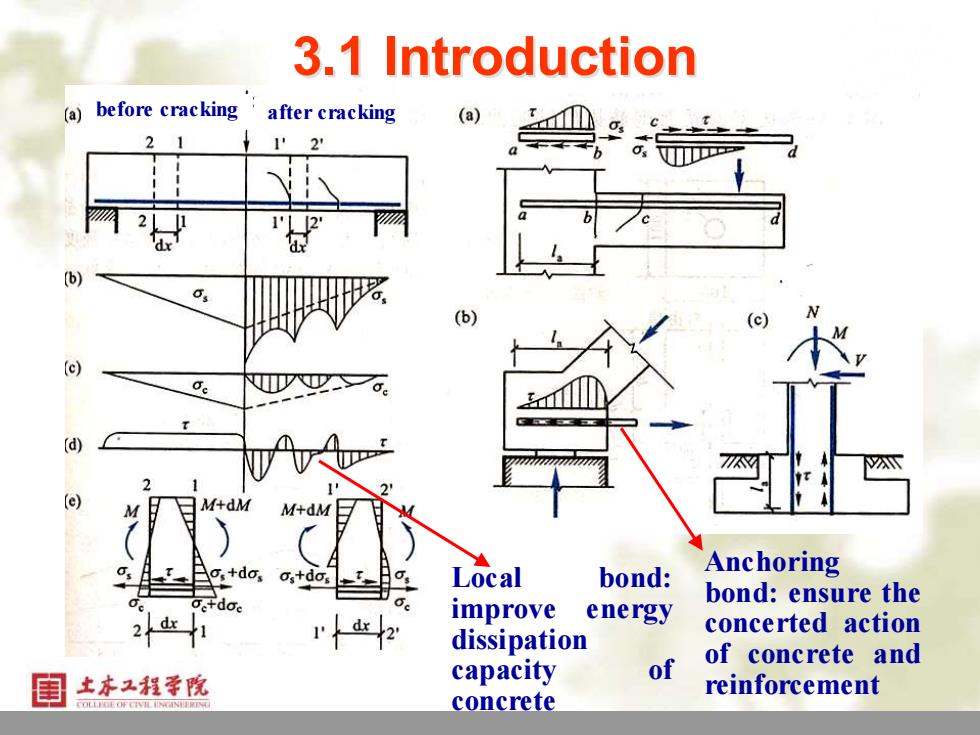
3.1 Introduction (a)before cracking after cracking (a) 2 1 21 12 (b) (b) (c) (d) T 2 M M+dM M+dM Anchoring os+dos os+dos Local bond: bond:ensure the dx improve energy concerted action dissipation of concrete and 目土本工程幸院 capacity of reinforcement concrete
5 3.1 Introduction before cracking after cracking Local bond: improve energy dissipation capacity of concrete Anchoring bond: ensure the concerted action of concrete and reinforcement

3.1 Introduction Components of Bond Chemical adhesion Friction Mechanical interlock ■ Embedded end anchorage 土本工程学院
6 3.1 Introduction ◼ Components of Bond ◼ Chemical adhesion ◼ Friction ◼ Mechanical interlock ◼ Embedded end anchorage

3.1 Introduction Splice length sleeve Pullout test 细 画 (local bond) Lap splice test Development length Half-beam test (anchorage) Development length test 目土本2程幸院
7 3.1 Introduction Pullout test (local bond) Development length Half-beam test (anchorage) Splice length Lap splice test Development length test sleeve

3.2 Bond mechanism ■Plain Bar-Friction 00 fu=20 N/mm2 100 φl6 plain bar 3 sleeve 日 mildly rusted 2 no rusted 鈿 5 cold-stretched wire 0.250.500.75 1.01.251.5 Slip (mm) 土本工程学院 T特N打N时度事4
8 3.2 Bond mechanism ◼ Plain Bar ─ Friction sleeve Slip (mm) cold-stretched wire mildly rusted no rusted plain bar
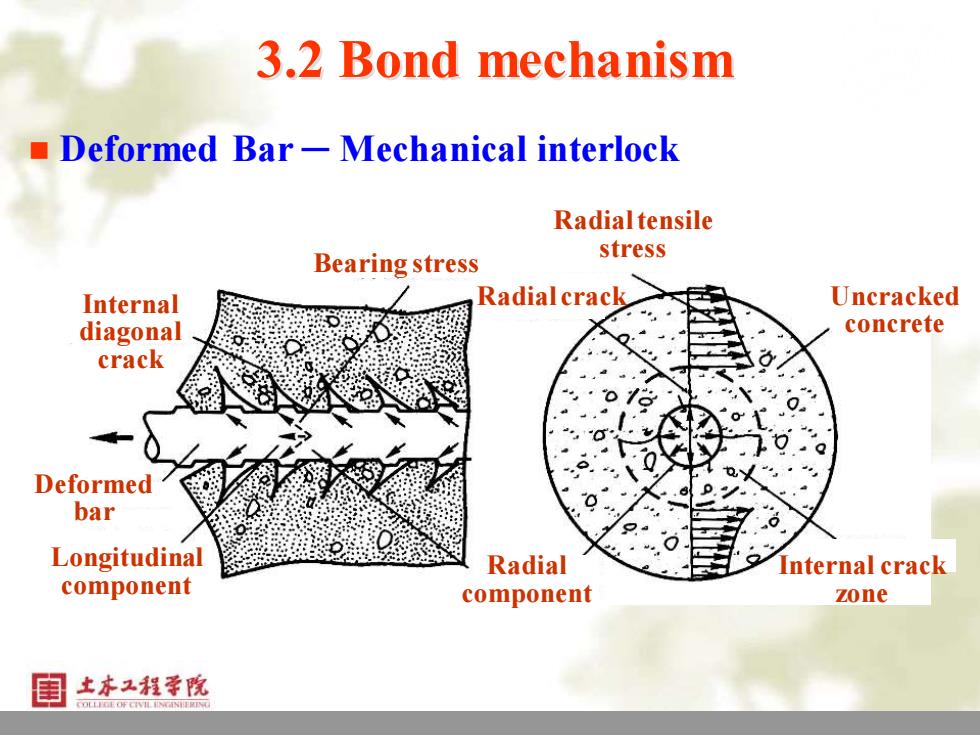
3.2 Bond mechanism Deformed Bar-Mechanical interlock Radial tensile stress Bearing stress Internal Radial crack Uncracked diagonal concrete crack Deformed bar Longitudinal Radial Internal crack component component zone 上本工程学院
9 3.2 Bond mechanism ◼ Deformed Bar ─ Mechanical interlock Internal diagonal crack Deformed bar Longitudinal component Bearing stress Radial tensile stress Uncracked concrete Radial crack Radial component Internal crack zone
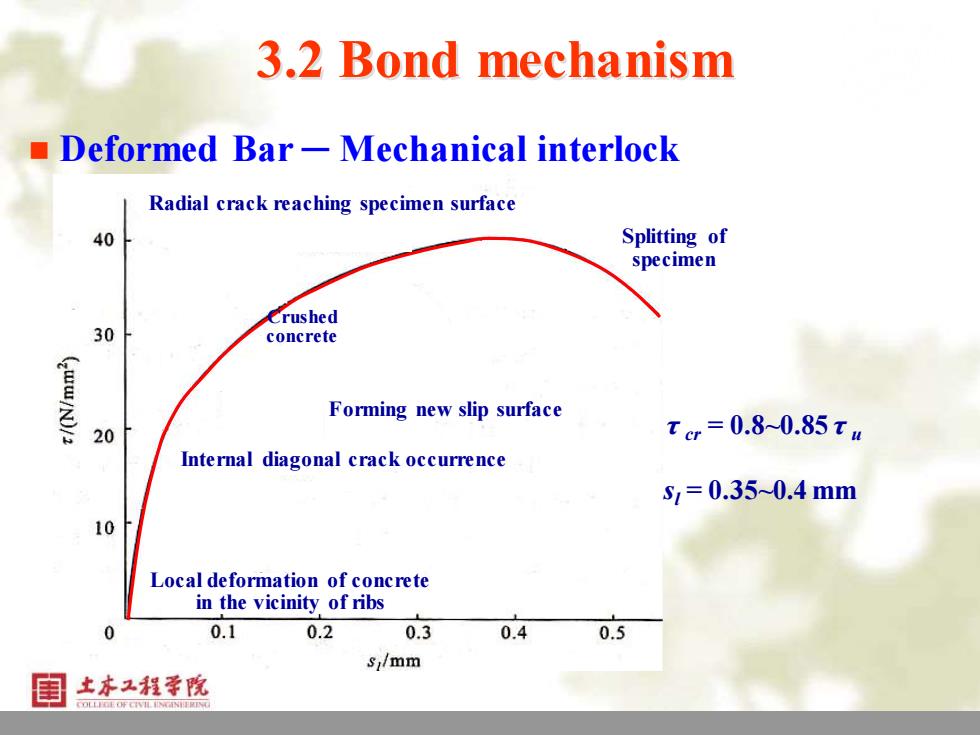
3.2 Bond mechanism ■ Deformed Bar-Mechanical interlock Radial crack reaching specimen surface 40 Splitting of specimen Crushed 30 concrete Forming new slip surface 20 tc=0.80.85tu Internal diagonal crack occurrence 51=0.350.4mm 10 Local deformation of concrete in the vicinity of ribs 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 si/mm 土本工程学院
10 3.2 Bond mechanism ◼ Deformed Bar ─ Mechanical interlock Local deformation of concrete in the vicinity of ribs Internal diagonal crack occurrence Crushed concrete Forming new slip surface Radial crack reaching specimen surface Splitting of specimen τ cr = 0.8~0.85 τ u sl = 0.35~0.4 mm