
抗心律失常药 Anti-Arrhythmic Drug
抗心律失常药 Anti-Arrhythmic Drug

Content o Physiology of normal cardiac rhythm o Definition and mechanisms of arrhythmias o Classification of drugs to treat arrhythmias o Important anti-arrhythmic drugs (mechanism and pharmacological characteristics) o Arrhythmias in clinical practice
Content Physiology of normal cardiac rhythm Definition and mechanisms of arrhythmias Classification of drugs to treat arrhythmias Important anti-arrhythmic drugs (mechanism and pharmacological characteristics) Arrhythmias in clinical practice
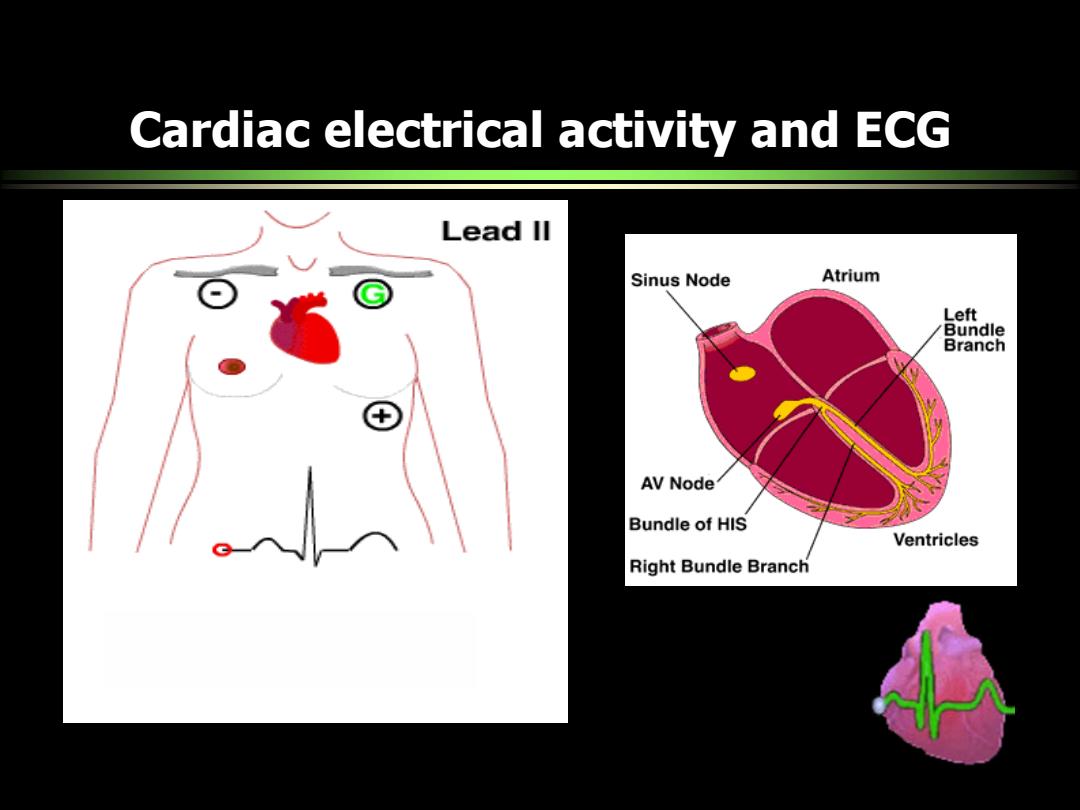
Cardiac electrical activity and ECG Lead ll Sinus Node Atrium Left Bundle Branch AV Node Bundle of HIS Ventricles Right Bundle Branch
Cardiac electrical activity and ECG
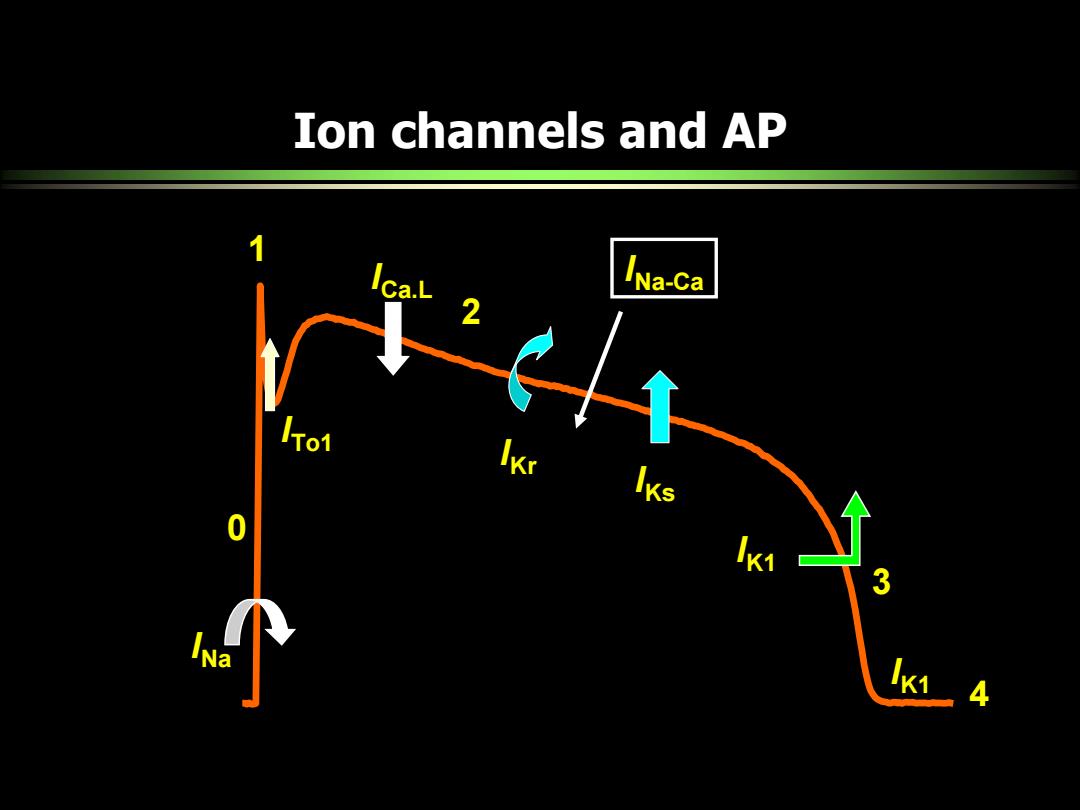
Ion channels and AP Ica.L INa-ca 0A 0 3 INa 4
Ion channels and AP 0 1 2 3 4 INa ICa.L IKr IKs IK1 IK1 ITo1 INa-Ca

2 inward outward 3 Phase 4 Na+current Ca2+ L-type current T-type transient ITot (4-AP-sensitive) outward current ITo2 (Ca2+-activated) delayed rectifiers e (Ik) la or Ikp inward rectifier,Ik1 pacemaker current,(,see above) Na+-Ca2+exchange Nat,K+-ATPase
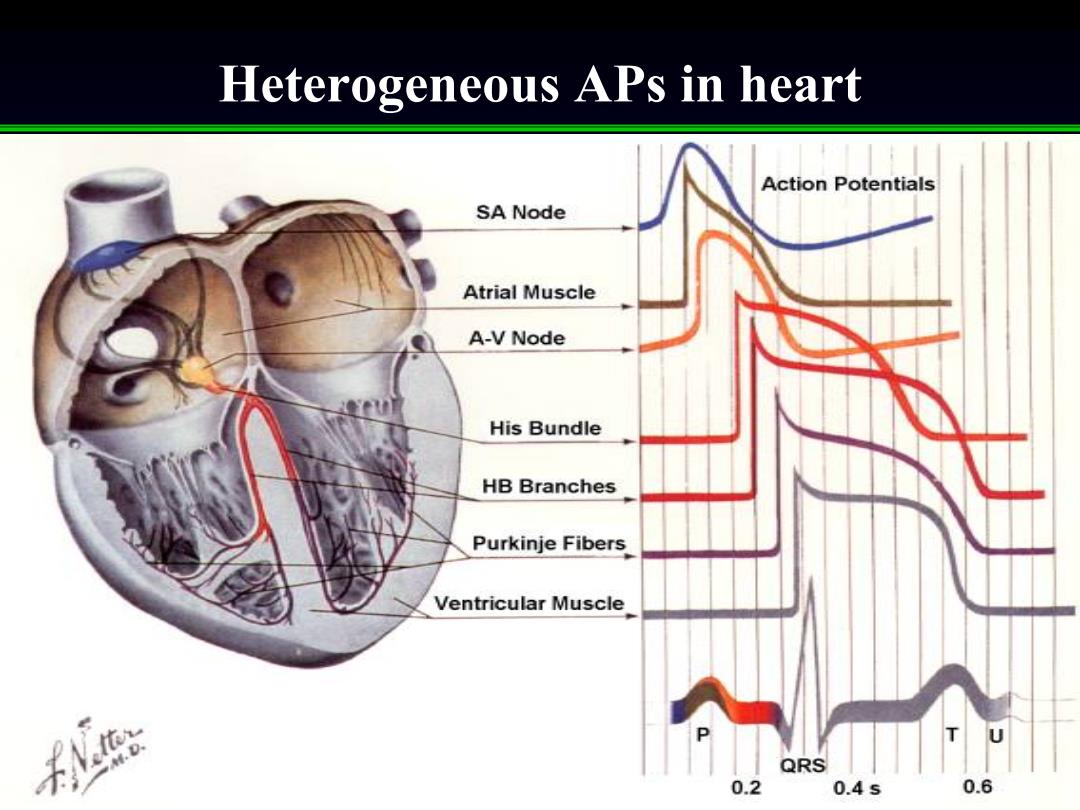
Heterogeneous APs in heart Action Potentials SA Node Atrial Muscle A-V Node His Bundle HB Branches Purkinje Fibers Ventricular Muscle 0 M.D QRS 0.2 0.4s 0.6
Heterogeneous APs in heart
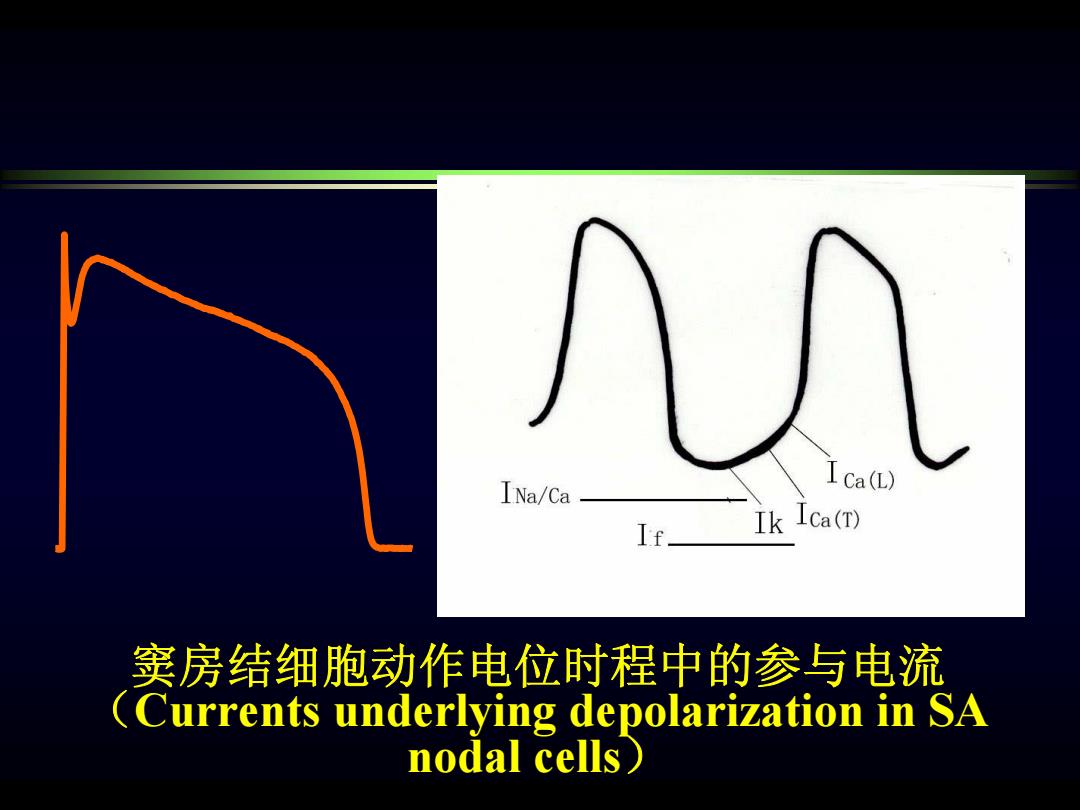
INa/Ca ICa(L) If Ik Ica(T) 窦房结细胞动作电位时程中的参与电流 Currents underlying depolarization in SA nodal cells)
窦房结细胞动作电位时程中的参与电流 (Currents underlying depolarization in SA nodal cells )
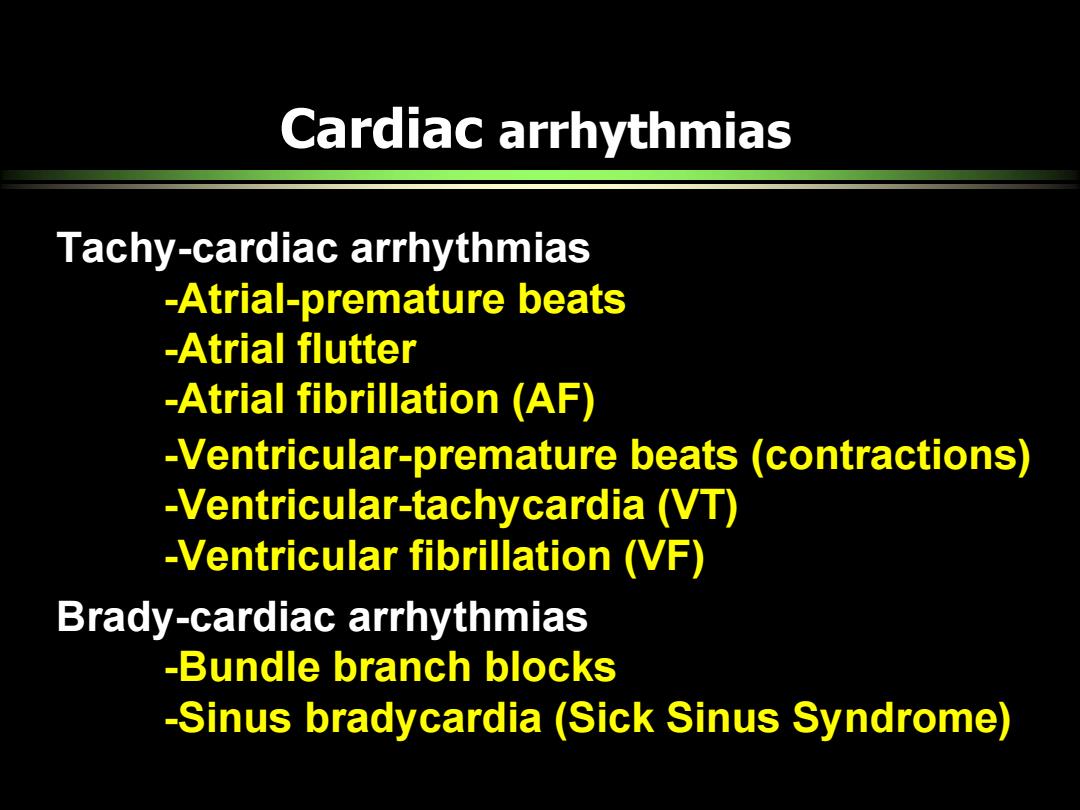
Cardiac arrhythmias Tachy-cardiac arrhythmias -Atrial-premature beats -Atrial flutter -Atrial fibrillation (AF) -Ventricular-premature beats (contractions) -Ventricular-tachycardia (VT) -Ventricular fibrillation (VF) Brady-cardiac arrhythmias -Bundle branch blocks -Sinus bradycardia(Sick Sinus Syndrome)
Cardiac arrhythmias Tachy-cardiac arrhythmias -Atrial-premature beats -Atrial flutter -Atrial fibrillation (AF) -Ventricular-premature beats (contractions) -Ventricular-tachycardia (VT) -Ventricular fibrillation (VF) Brady-cardiac arrhythmias -Bundle branch blocks -Sinus bradycardia (Sick Sinus Syndrome)
Mechanisms of Arrhythmias Disturbance of impulse formation oDisturbance of impulse conduction ●both
Mechanisms of Arrhythmias Disturbance of impulse formation Disturbance of impulse conduction both
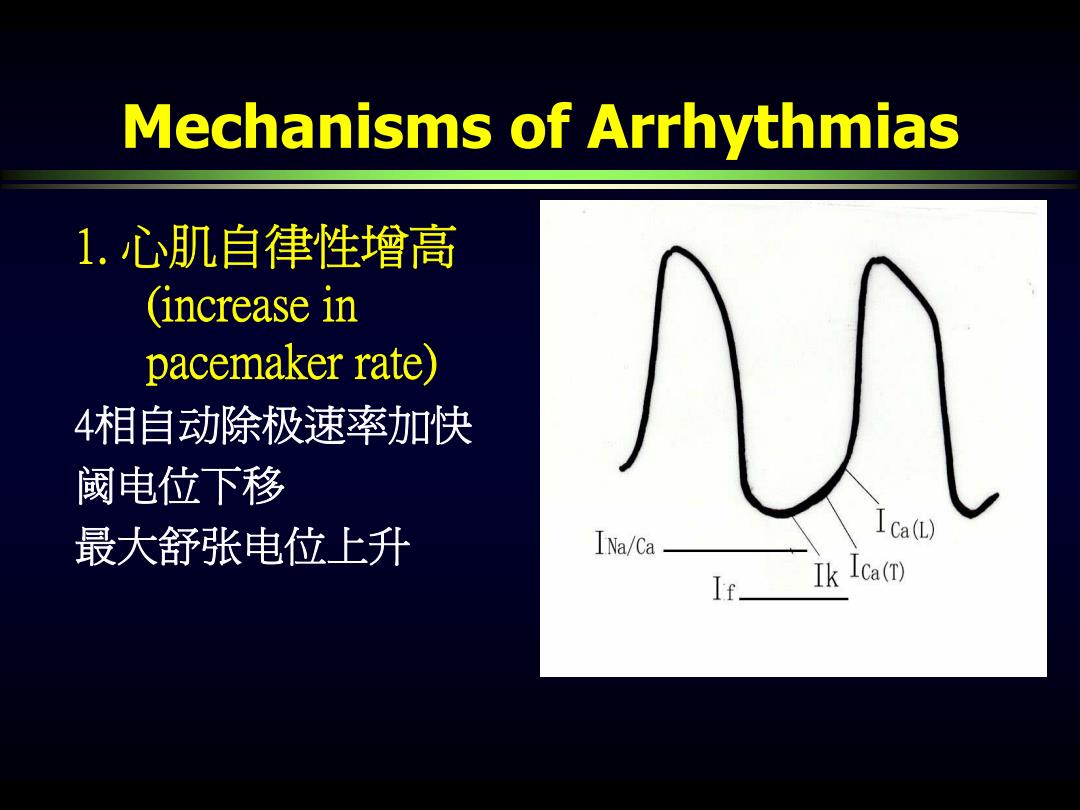
Mechanisms of Arrhythmias 1.心肌自律性增高 (increase in pacemaker rate) 4相自动除极速率加快 阈电位下移 最大舒张电位上升 INa/Ca 1Ca(L) It. Ik Ica(T)
Mechanisms of Arrhythmias 1. 心肌自律性增高 (increase in pacemaker rate) 4相自动除极速率加快 阈电位下移 最大舒张电位上升