
Drugs for Congestive Heart Failure
Drugs for Congestive Drugs for Congestive Heart Failure Heart Failure

What Are The Symptoms of Heart Failure? Think FACES ... -Fatigue -Activities limited Chest congestion -Edema or ankle swelling -Shortness of breath
Think FACES... •Fatigue •Activities limited •Chest congestion •Edema or ankle swelling •Shortness of breath What Are The Symptoms What Are The Symptoms of Heart Failure? of Heart Failure?

New York Heart Association NYHA NYHA I级:日常活动不出现心力衰竭症状 NYHAⅡ级:日常话动即诱发症状 NYHAⅢ级:轻度运动即诱发症状 NYHA IV级:休息状态即出现症状
New York Heart Association (NYHA) New York Heart Association (NYHA) NYHA Ⅰ级:日常活动不出现心力衰竭症状 NYHA Ⅱ级:日常活动即诱发症状 NYHA Ⅲ级:轻度运动即诱发症状 NYHA Ⅳ级:休息状态即出现症状

Cardiac dysfunction Contractility↓,Relaxation) Cardiac output↓ Cardiac Vessel B1-R↓ Constriction 米RAAtCA ↓ Contractility Sodium and water Compliance↓ *Preloadt Resistance Compliance↓ retention Afterload Blood ardiac hypertrophy and volume reconstruction Vessel hypertrophy and reconstruction ↓ Returning blood Edema volume↑ Phathophysiology of Heart Failure
Cardiac dysfunction (Contractility↓,Relaxation↓) Cardiac output ↓ Sodium and water retention Blood volume↑ Edema Vessel Constriction Resistance↑ Compliance↓ Afterload↑ Vessel hypertrophy and reconstruction Cardiac β1-R↓ Contractility Compliance↓ Cardiac hypertrophy and reconstruction Returning blood volume↑ Preload↑ RAA↑CA↑ Phathophysiology of Heart Failure

Drugs used in CHF Cardiac glycosides:digoxin,cedilanide RAS inhibitors: DiuretiCS:hydrochlorothiazide,furosemide Beta-blockers Vasodilators Others
Drugs used in CHF Drugs used in CHF Cardiac glycosides: digoxin, cedilanide RAS inhibitors: Diuretics: hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide Beta-blockers Vasodilators Others
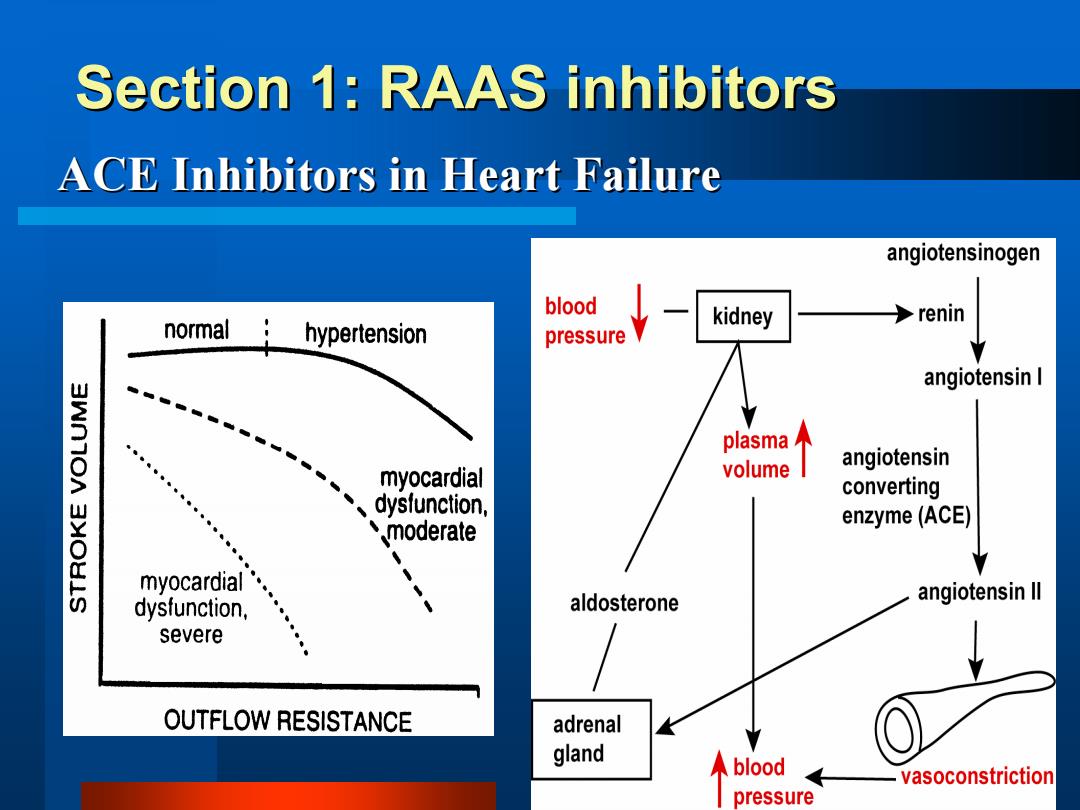
Section 1:RAAS inhibitors ACE Inhibitors in Heart Failure angiotensinogen blood normal kidney renin hypertension pressure angiotensin I 3WNTOA plasma myocardial volume angiotensin converting dysfunction, moderate enzyme(ACE) myocardial dysfunction, aldosterone angiotensin ll severe OUTFLOW RESISTANCE adrenal gland blood vasoconstriction pressure
Section 1: RAAS inhibitors Section 1: RAAS inhibitors ACE Inhibitors in Heart Failure ACE Inhibitors in Heart Failure

Mechanism of Action of ACEI ●Afterload reduction ●Preload reduction Reduction of facilitation of sympathetic nervous system o Reduction of cardiac hypertrophy Drugs of choice in heart failure (with diuretics) Current investigational use:Acute myocardial infarction
Mechanism of Action Mechanism of Action of ACEI of ACEI Afterload reduction Preload reduction Reduction of facilitation of sympathetic nervous system Reduction of cardiac hypertrophy Drugs of choice in heart failure (with diuretics) Current investigational use: Acute myocardial infarction

Aldosterone antagonist Spironolactone Aldosterone antagonist,K-sparing diuretic Prevention of aldosterone effects on: Kidney Heart? Aldosterone inappropriately elevated in CHF Mobilizes edema fluid in heart failure Prevention of hypokalemia induced by loop diuretics (protection against digitalis toxicity?) Prolongs life in CHF patients
Aldosterone Aldosterone antagonist antagonist Aldosterone antagonist, K-sparing diuretic Prevention of aldosterone effects on: – Kidney – Heart? Aldosterone inappropriately elevated in CHF Mobilizes edema fluid in heart failure Prevention of hypokalemia induced by loop diuretics (protection against digitalis toxicity?) Prolongs life in CHF patients Spironolactone Spironolactone

Section 2:Diuretics hydrochlorothiazide Mechanism of Action in Heart Failure Preload reduction:reduction of excess plasma volume and edema fluid o Afterload reduction:lowered blood pressure
Section 2: Section 2: Diuretics Diuretics Preload reduction: reduction of excess plasma volume and edema fluid Afterload reduction: lowered blood pressure Mechanism of Action in Heart Failure Mechanism of Action in Heart Failure hydrochlorothiazide

Section 3 B-Adrenoceptor blockers Mechanism of action: 1.Antagonize the sympathetic nerve activity ①↓damage on cardiac muscle from CA ②↓renin,↓RAS,↓cardiac load ③↑B-R,come back the transmit ability ④↑sensitivity of B-R to catecholamines 2.Antioxidation blocking a-R carvedilol 3.Antiarrhythmia and improve myocardial ischemia
Section 3 Section 3 β-Adrenoceptor Adrenoceptor blockers blockers Mechanism of action: 1. Antagonize the sympathetic nerve activity ①↓damage on cardiac muscle from CA ②↓renin , ↓RAS,↓ cardiac load ③↑β-R,come back the transmit ability ④↑sensitivity of β-R to catecholamines 2. Antioxidation , blocking α1 -R — carvedilol 3. Antiarrhythmia and improve myocardial ischemia