
Communications ·Dr.Zhang Yan(张岩) Associate professor in School of Pharmacy Research interest:GPCR based drug discovery Email:zhangyan sjtu@sjtu.edu.cn ·Phone:021-34207497 Office:Pharmacy Building 5-115 1
Communications • Dr. Zhang Yan (张岩) • Associate professor in School of Pharmacy • Research interest: GPCR based drug discovery • Email: zhangyan_sjtu@sjtu.edu.cn • Phone: 021-34207497 • Office: Pharmacy Building 5-115 1

Chapter 4 Overview of Peripheral Nervous System Neurotransmitters and Receptors 2
Chapter 4 Overview of Peripheral Nervous System Neurotransmitters and Receptors 2
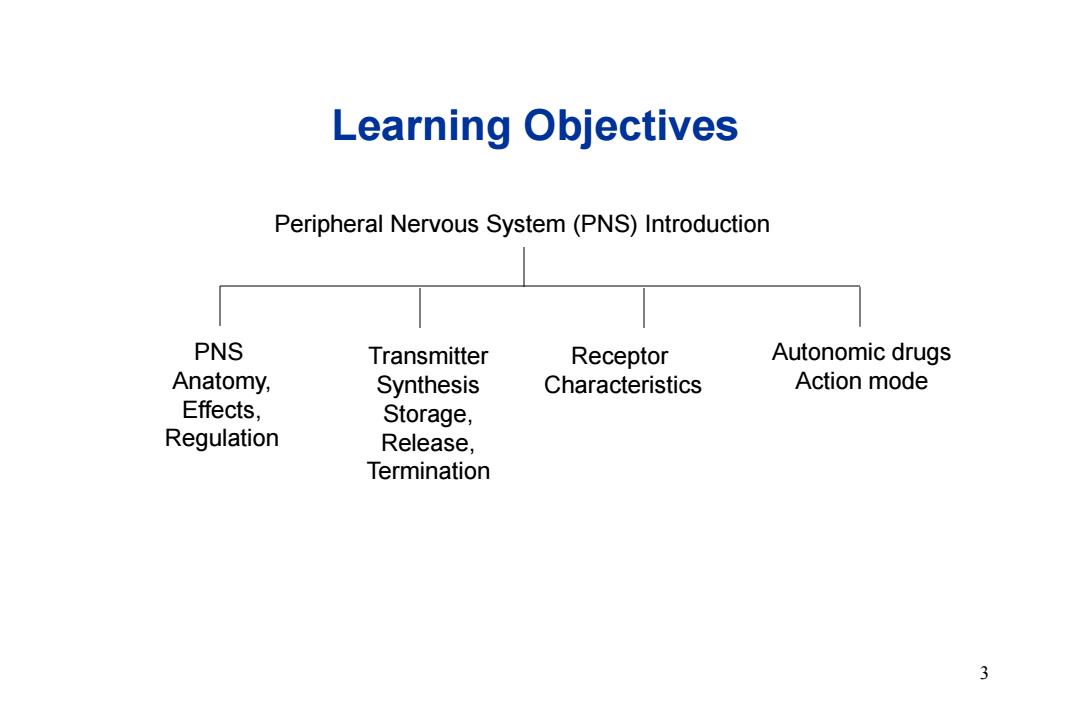
Learning Objectives Peripheral Nervous System(PNS)Introduction PNS Transmitter Receptor Autonomic drugs Anatomy, Synthesis Characteristics Action mode Effects, Storage, Regulation Release, Termination 3
Learning Objectives Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Introduction PNS Anatomy, Effects, Regulation Transmitter Synthesis Storage, Release, Termination Receptor Characteristics Autonomic drugs Action mode 3

Introduction of Peripheral Nervous System 4
Introduction of Peripheral Nervous System 4
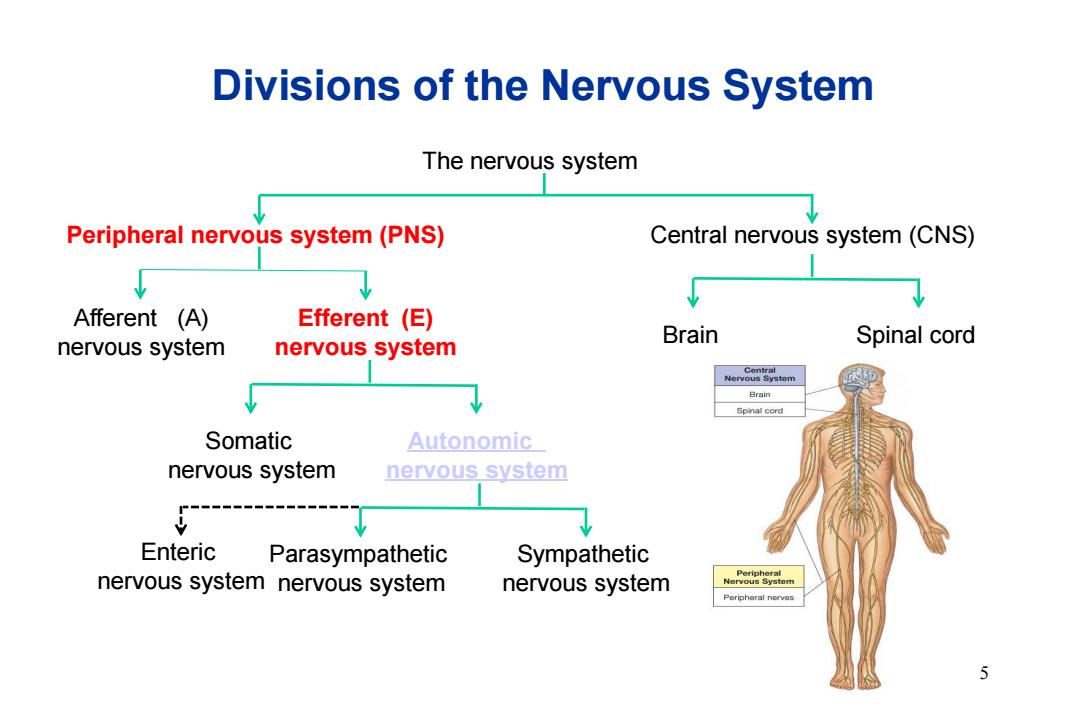
Divisions of the Nervous System The nervous system Peripheral nervous system(PNS) Central nervous system(CNS) Afferent (A) Efferent(E) Brain nervous system nervous system Spinal cord Ce信tr启l Nervous System Brain Spinal cord Somatic Autonomic nervous system nervous system Enteric Parasympathetic Sympathetic Peripheral nervous system nervous system nervous system Nervous System Periphoral norves 5
Divisions of the Nervous System The nervous system Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) Afferent (A) nervous system Efferent (E) nervous system Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Brain Spinal cord Enteric nervous system 5
Comparison of somatic and autonomic nerves Somatic:Controls voluntary Autonomic:Controls the muscle movement automatic functions of the body 6
Somatic: Controls voluntary muscle movement Autonomic: Controls the automatic functions of the body 6 Comparison of somatic and autonomic nerves
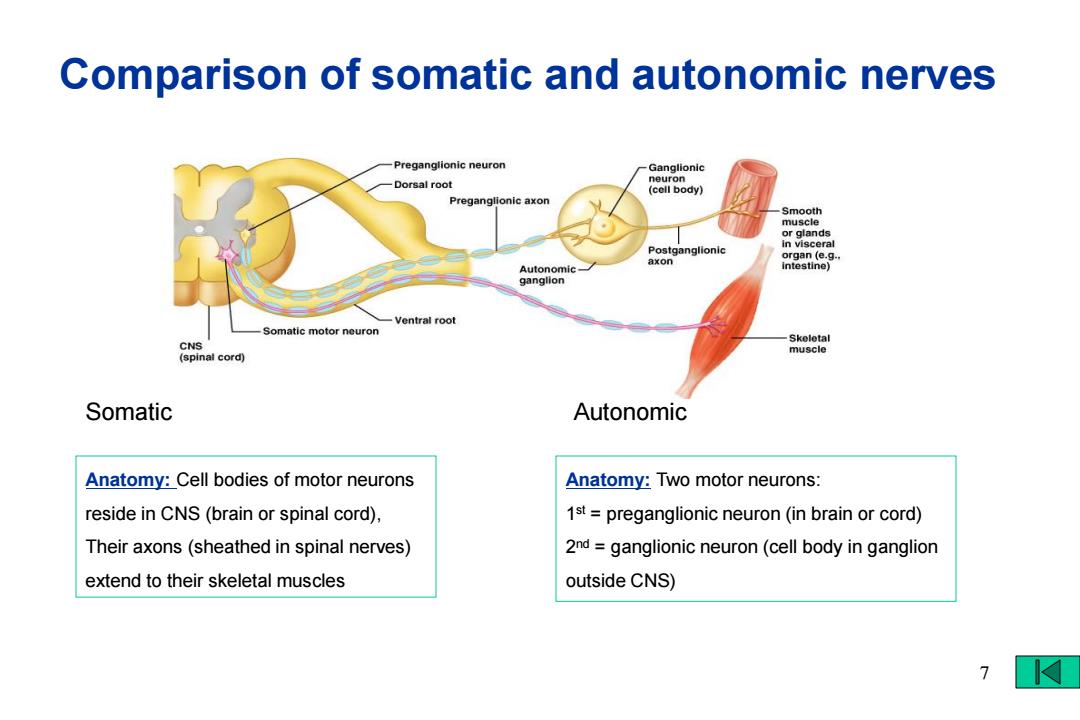
Comparison of somatic and autonomic nerves Preganglionic neuron Ganglionic Dorsal root neuron (cell body) Preganglionic axon Smooth muscle or glands in visceral Postganglionic axon organ (e.g.. Autonomic intestine) ganglion -Ventral root Somatic motor neuron Skeletal CNS muscle (spinal cord) Somatic Autonomic Anatomy:Cell bodies of motor neurons Anatomy:Two motor neurons: reside in CNS(brain or spinal cord), 1st preganglionic neuron(in brain or cord) Their axons(sheathed in spinal nerves) 2nd ganglionic neuron(cell body in ganglion extend to their skeletal muscles outside CNS)
Comparison of somatic and autonomic nerves Anatomy: Two motor neurons: 1 st = preganglionic neuron (in brain or cord) 2 nd = ganglionic neuron (cell body in ganglion outside CNS) Anatomy: Cell bodies of motor neurons reside in CNS (brain or spinal cord), Their axons (sheathed in spinal nerves) extend to their skeletal muscles Somatic Autonomic 7
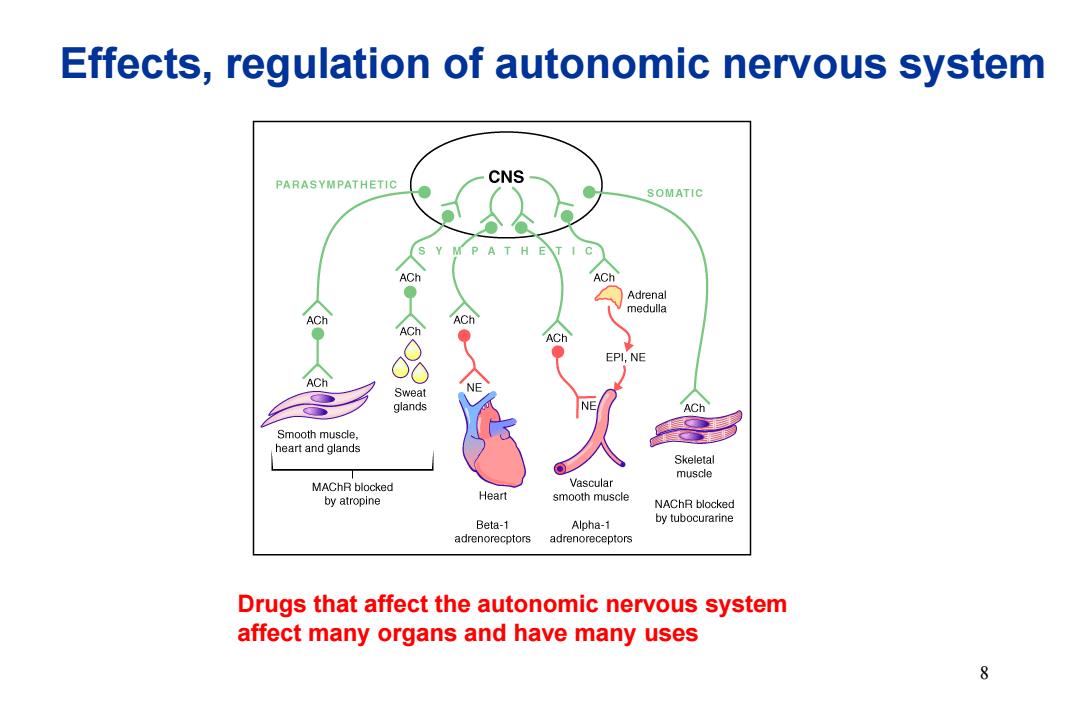
Effects,regulation of autonomic nervous system PARASYMPATHETIC CNS SOMATIC S Y MP A T H ET I C ACh ACh Adrenal medulla 8 EPI,NE ACh Sweat glands ACh Smooth muscle, heart and glands Skeletal muscle MAChR blocked Vascular by atropine Heart smooth muscle NAChR blocked Beta-1 Alpha-1 by tubocurarine adrenorecptors adrenoreceptors Drugs that affect the autonomic nervous system affect many organs and have many uses 8
8 Effects, regulation of autonomic nervous system Drugs that affect the autonomic nervous system affect many organs and have many uses
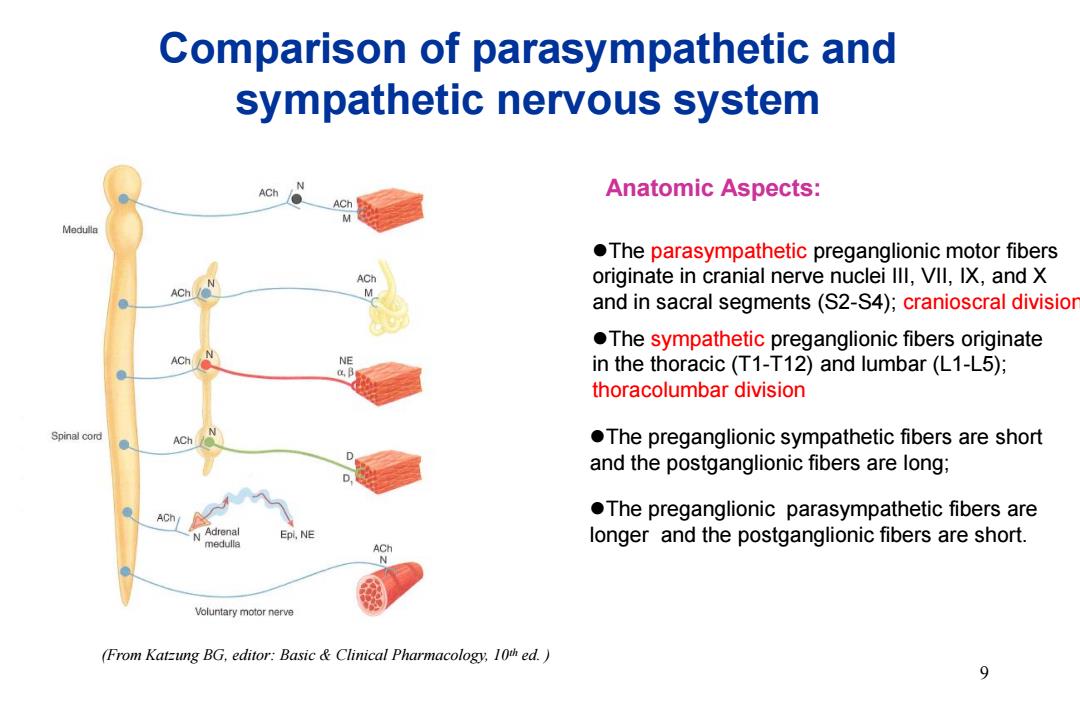
Comparison of parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system ACh Anatomic Aspects: ACh Medulla The parasympathetic preganglionic motor fibers originate in cranial nerve nuclei Ill,VIl,IX,and X and in sacral segments(S2-S4);cranioscral divisior .The sympathetic preganglionic fibers originate ACh in the thoracic(T1-T12)and lumbar(L1-L5); thoracolumbar division Spinal cord ACh .The preganglionic sympathetic fibers are short and the postganglionic fibers are long; ACh .The preganglionic parasympathetic fibers are Adrenal Epi,NE medulla longer and the postganglionic fibers are short. ACh Voluntary motor nerve (From Katzung BG,editor:Basic Clinical Pharmacology,10th ed. 9
(From Katzung BG, editor: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 10th ed. ) Comparison of parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system Anatomic Aspects: The parasympathetic preganglionic motor fibers originate in cranial nerve nuclei III, VII, IX, and X and in sacral segments (S2-S4); cranioscral division The sympathetic preganglionic fibers originate in the thoracic (T1-T12) and lumbar (L1-L5); thoracolumbar division The preganglionic sympathetic fibers are short and the postganglionic fibers are long; The preganglionic parasympathetic fibers are longer and the postganglionic fibers are short. 9
Sympathetic nervous system: Parasympathetic nervous system: Fight or flight response: Rest or digest response Automatically accelerates heart .Automatically slows the body down after rate,breathing, a stressful event. ·dilates pupils, Heart rate and breathing slow down, .slows down digestion and urination. blood pressure decrease,pupils constrict and digestion speeds up. 10
Sympathetic nervous system: Fight or flight response: •Automatically accelerates heart rate, breathing, •dilates pupils, •slows down digestion and urination. Parasympathetic nervous system: Rest or digest response •Automatically slows the body down after a stressful event. •Heart rate and breathing slow down, blood pressure decrease, pupils constrict and digestion speeds up. 10