
Opioid Analgesics drug abuse
Opioid Analgesics & drug abuse

Pain 0 an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli the most common reason for physician consultation interfering with a person's quality of life and general functioning protective response of human body
Pain • an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli • the most common reason for physician consultation • interfering with a person's quality of life and general functioning • protective response of human body
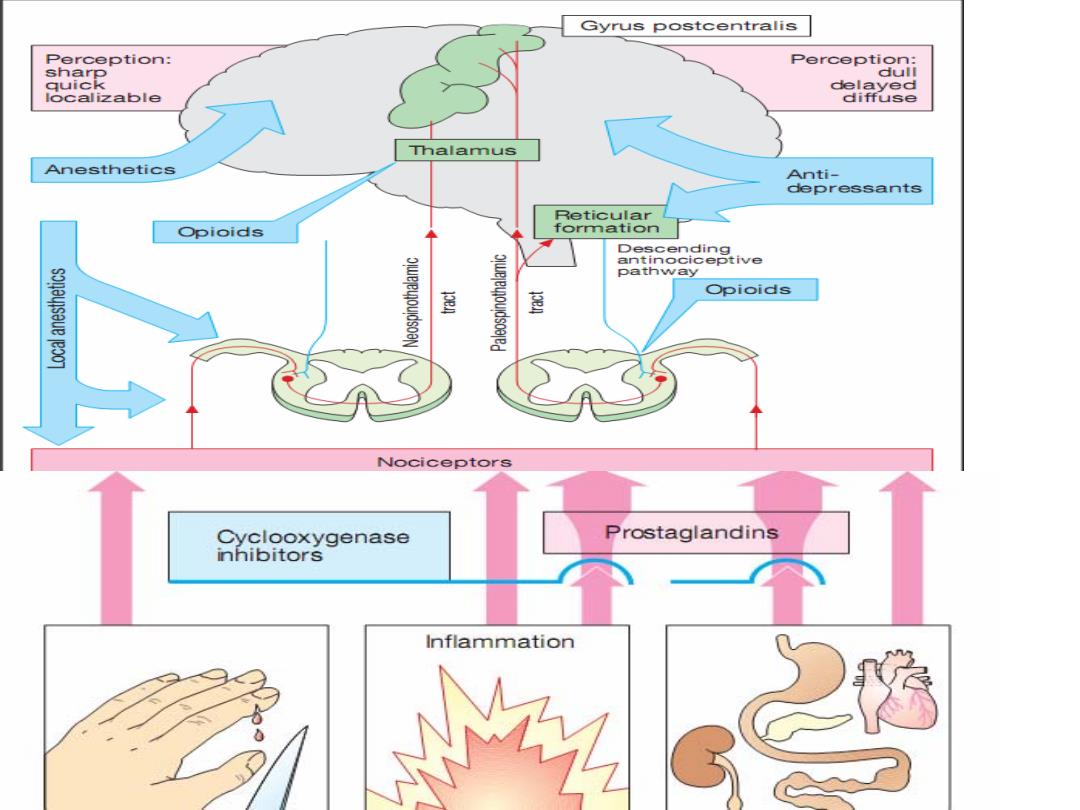
Gyrus postcentralis Perception: Perception: sharp dull quick delayed localizable diffuse Thalamus Anesthetics Anti- depressants Reticular Opioids formation Descending antinociceptive pathway Opioids 至 色 Nociceptors Cyclooxygenase Prostaglandins inhibitors Inflammation
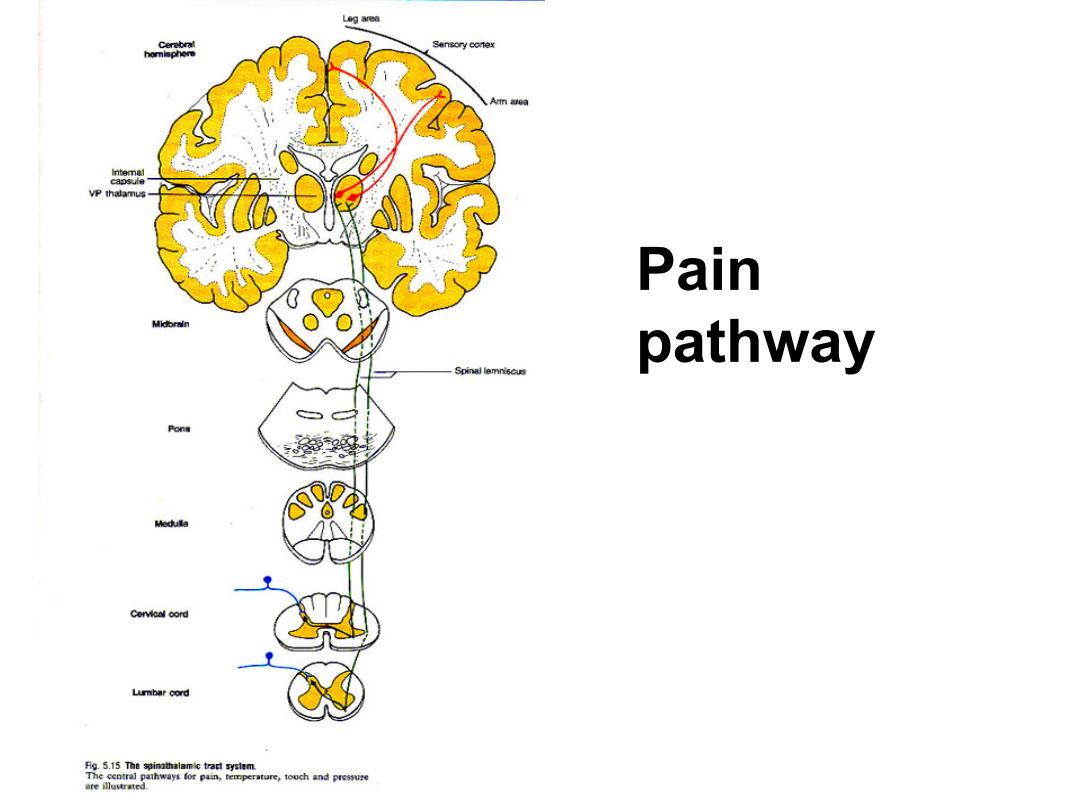
Leg area Cerebral Sensory cortex homisphere interal capsule Pain Mldbrain pathway Spinal lemniscus Pons Medulla Cervical cord Lurmbar cord Fig.5.15 The spinthalamic tract system. The central pathways for pain,temperature,touch and pressure
Pain pathway
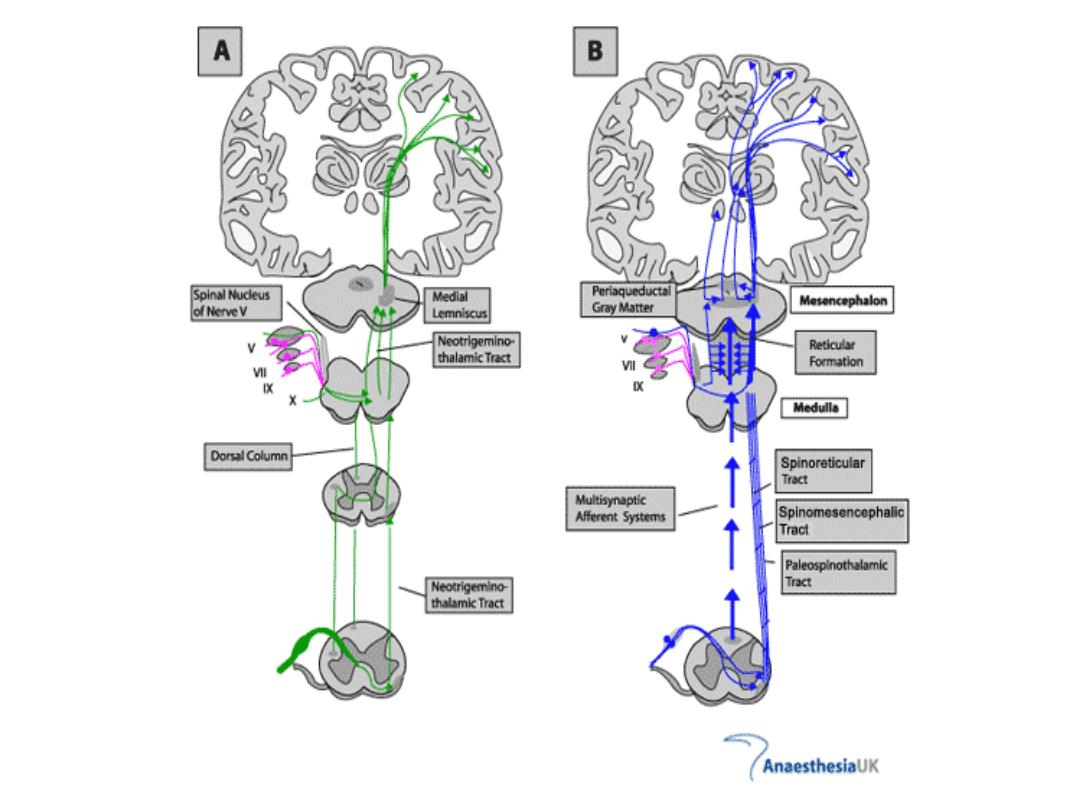
A B Spinal Nudeus Medial Periaqueducta Gray Matter Mesencephalon of NerveV Lemniscus Neotrigemino- Reticular thalamicTract Formation Medulla Dorsal Column Spinoreticular Tract Multisynaptic Afferent Systems Spinomesencephalic Tract Paleospinothalamic Neotrigemino- Tract thalamic Tract AnaesthesiaUK

Pain killers ·Opiates and morphinomimetics(阿片类及类似物) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs(NSAIDs): discussed in other chapter Non-selective cyclooxygenases inhibitors: aspirin,ibuprofen,.. √COX-2 inhibitors:celecoxib(塞来昔布),. ·Other analgesics:flupirtine(氟吡订),rotundine (罗通定),ziconotide(齐考诺肽)
Pain killers • Opiates and morphinomimetics (阿片类及类似物) • Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): discussed in other chapter Non-selective cyclooxygenases inhibitors: aspirin, ibuprofen, … COX-2 inhibitors: celecoxib (塞来昔布), … • Other analgesics: flupirtine (氟吡汀), rotundine (罗通定), ziconotide(齐考诺肽), …

Basic pharmacology of the opioid analgesics capsule poppy sticky juice ↓ black opium-morphine etc.extracted
Basic pharmacology of the opioid analgesics poppy capsule ↓ sticky juice ↓ black opium →morphine, etc. extracted

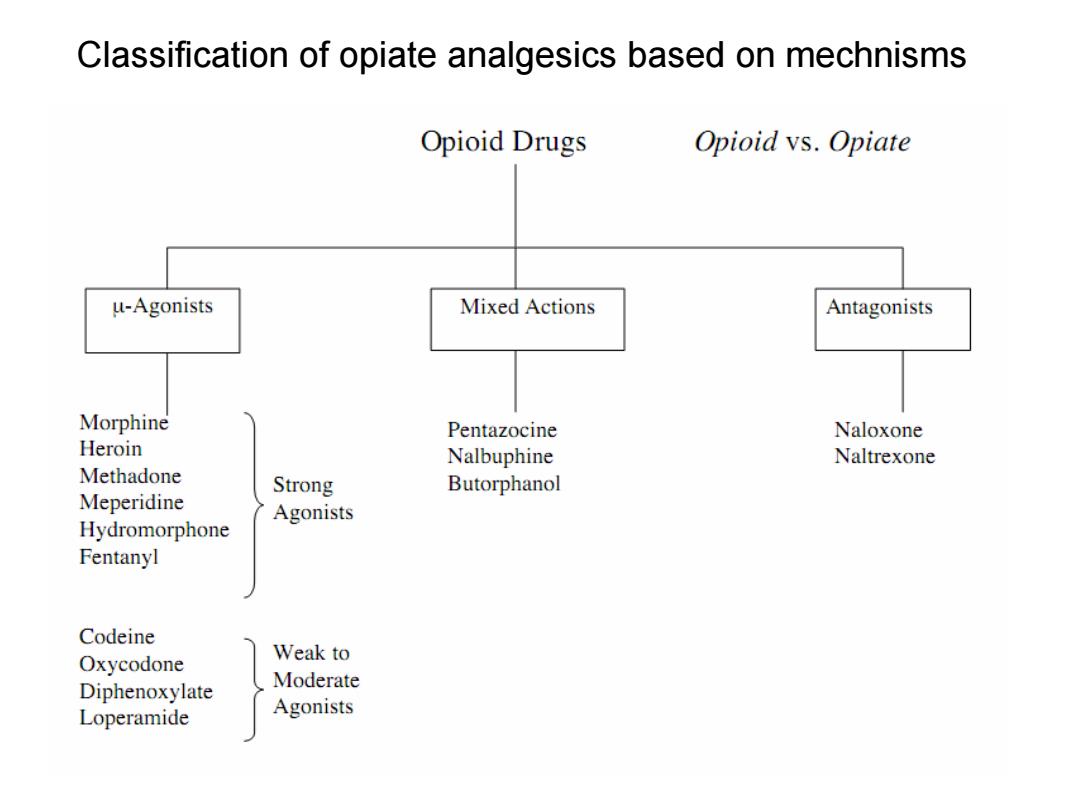
Classification of opiate analgesics based on mechnisms Opioid Drugs Opioid vs.Opiate u-Agonists Mixed Actions Antagonists Morphine Pentazocine Naloxone Heroin Nalbuphine Naltrexone Methadone Strong Butorphanol Meperidine Agonists Hydromorphone Fentanyl Codeine Oxycodone Weak to Diphenoxylate Moderate Loperamide Agonists
Classification of opiate analgesics based on mechnisms

Opioid analgesics Natural phenanthrene ·morphine10%(吗啡) ·codeine0.5%(可待因) o Semisynthetic -heroin(海洛因),not used clinically -buprenorphine(丁丙诺啡),partial agonist synthetic -pethidine(哌替啶) -methadone(美沙酮) -fentanyl(芬太尼) -remifentanil(瑞芬太尼) -oxygodone(羟考酮)
Opioid analgesics • Natural – phenanthrene • morphine 10%(吗啡) • codeine 0.5% (可待因 ) • Semisynthetic – heroin (海洛因),not used clinically – buprenorphine ( 丁丙诺啡), partial agonist • synthetic – pethidine (哌替啶) – methadone (美沙酮) – fentanyl (芬太尼) – remifentanil (瑞芬太尼) – oxygodone (羟考酮)