
⑧ 上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 强 Chapter 6 Adrenoceptor drugs agonists and antagonists) 2产7AII7A00C7I/m-、. 。自。。 1Eg三
1896 1920 1987 2006 Chapter 6 Adrenoceptor drugs ( agonists and antagonists )
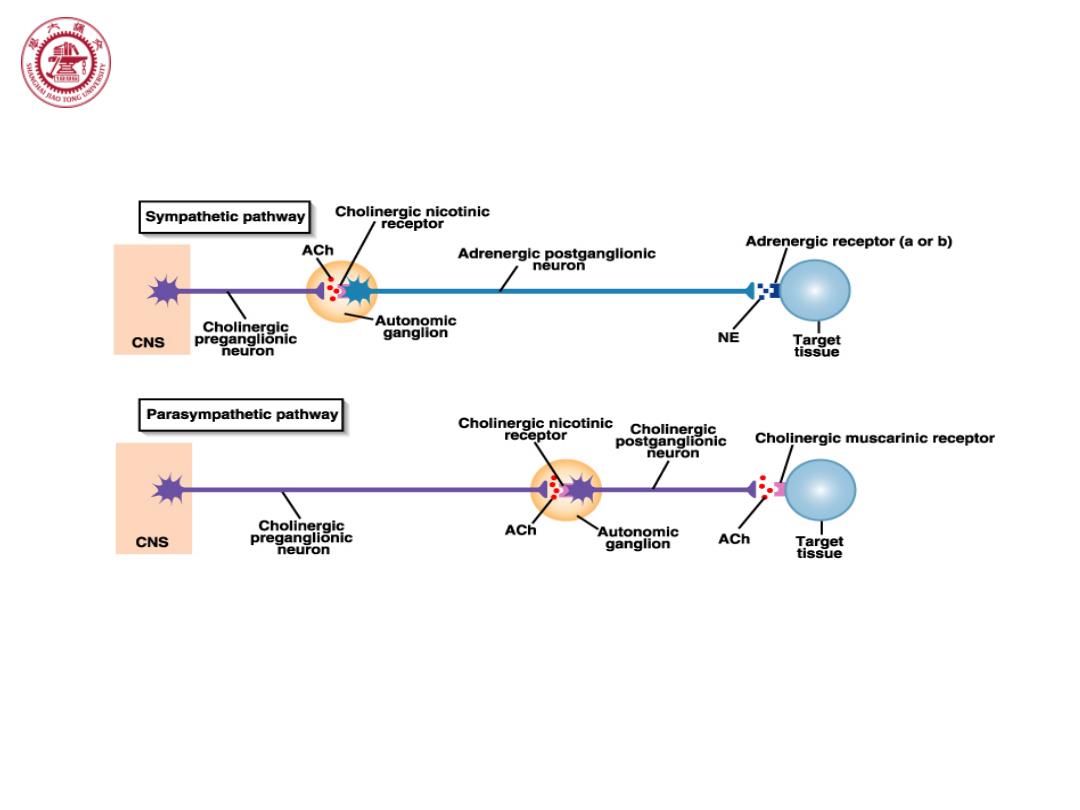
⑧ Sympathetic pathway Cholinergic nicotinic receptor ACh Adrenergic receptor(a or b) Adrenergic postganglionic neuron Cholinergic Autonomic CNS preganglionic ganglion NE Target neuron tissue Parasympathetic pathway Cholinergic nicotinic receptor Cholinergic postganglionic Cholinergic muscarinic receptor neuron Cholinergic ACh CNS preganglionic Autonomic ACh Target neuron ganglion tissue
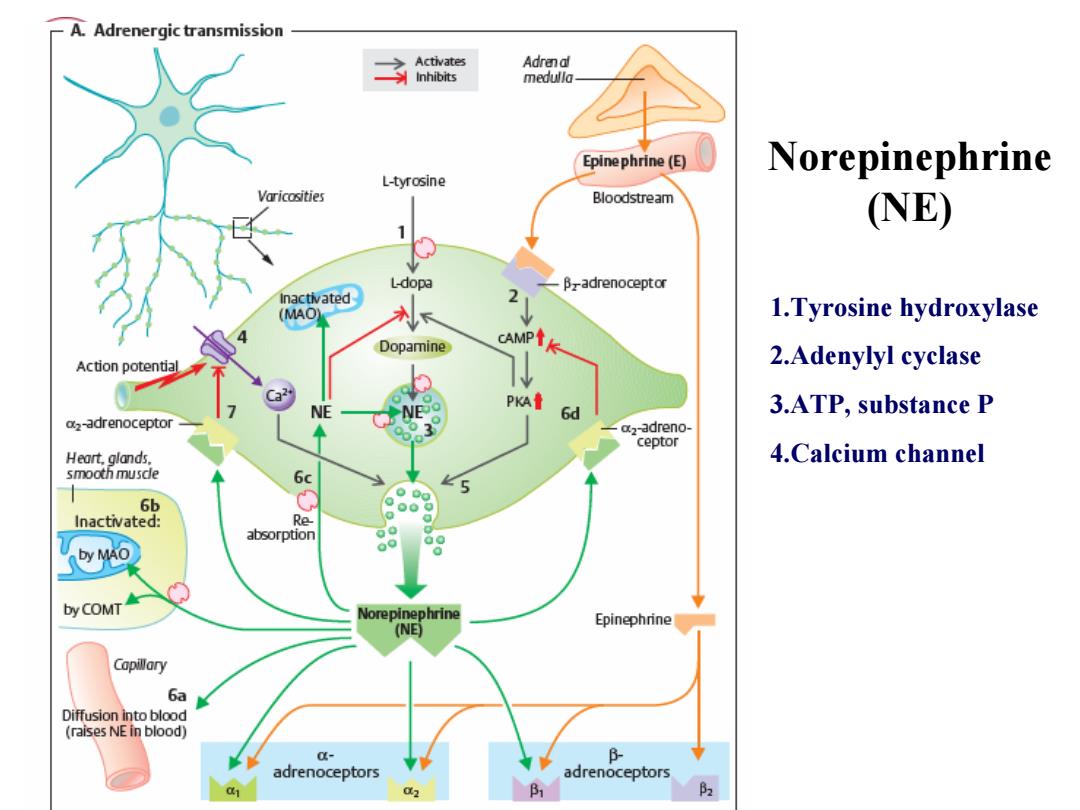
-A.Adrenergic transmission 3 Activates Adrenal Inhibits medulla Epinephrine(E) 0 Norepinephrine L-tyrosine Varicosities Bloodstream NE) L-dop阳 B-adrenoceptor Inactivated 2 (MAO) 1.Tyrosine hydroxylase Dopamine CAMP Action potential 2.Adenylyl cyclase PKA NE 6d 3.ATP,substance P az-adrenoceptor a2-adreno- ceptor Heart,glands. 4.Calcium channel smooth musde 6c 6b Inactivated: Re absorption by MAo by COMT Norepinephrine Epinephrine (NE) Capillary 6a Diffusion into blood (raises NE in blood) 0- adrenoceptors adrenoceptors P
Norepinephrine (NE) 1.Tyrosine hydroxylase 2.Adenylyl cyclase 3.ATP, substance P 4.Calcium channel
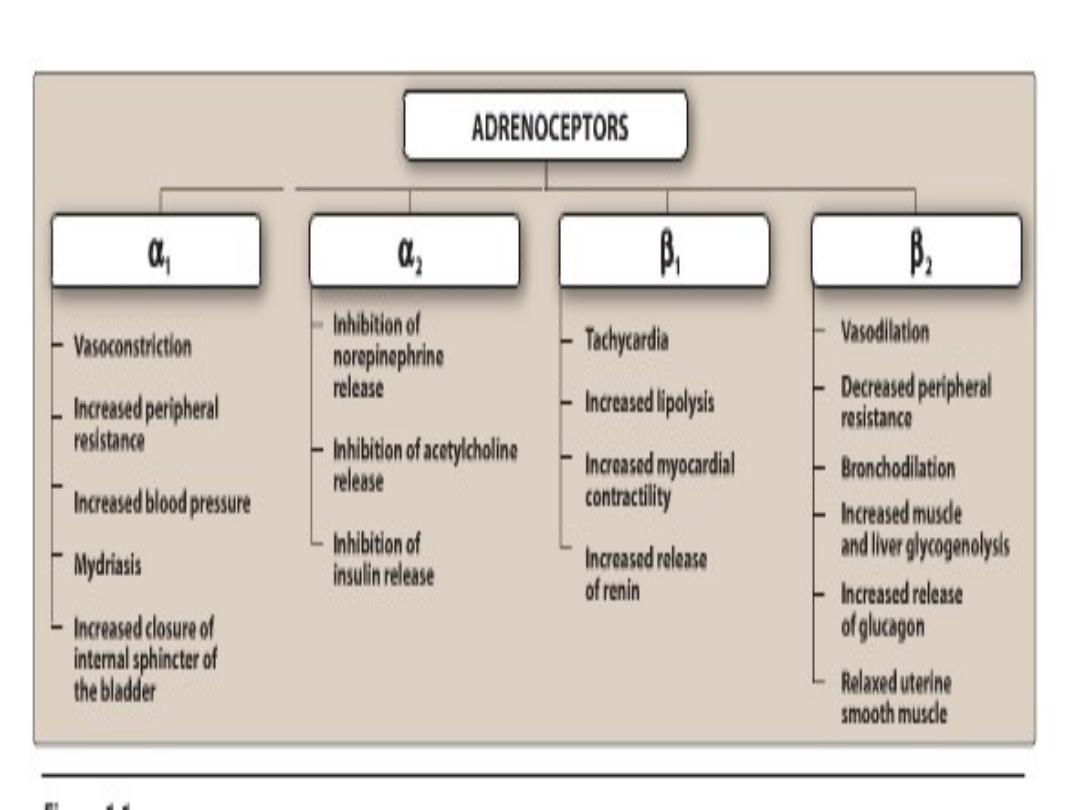
ADRENOCEPTORS C, B B: Inhibitionof Vasoconstriction norepinephrine -Tachycardia Vasodilation release nrsed periphera polysis Decreased peripheral resistance eS由(e nhibitionofactychoin release n myocardia Bronchodilation nreasedblood pressure onr时y Increased musde inhibition of ydi怕as站 casdeleas andwggyogenoysh insulin release of renin Increased release ofgluagn intemasphincter of the bladder Reaxedutri smooth musce
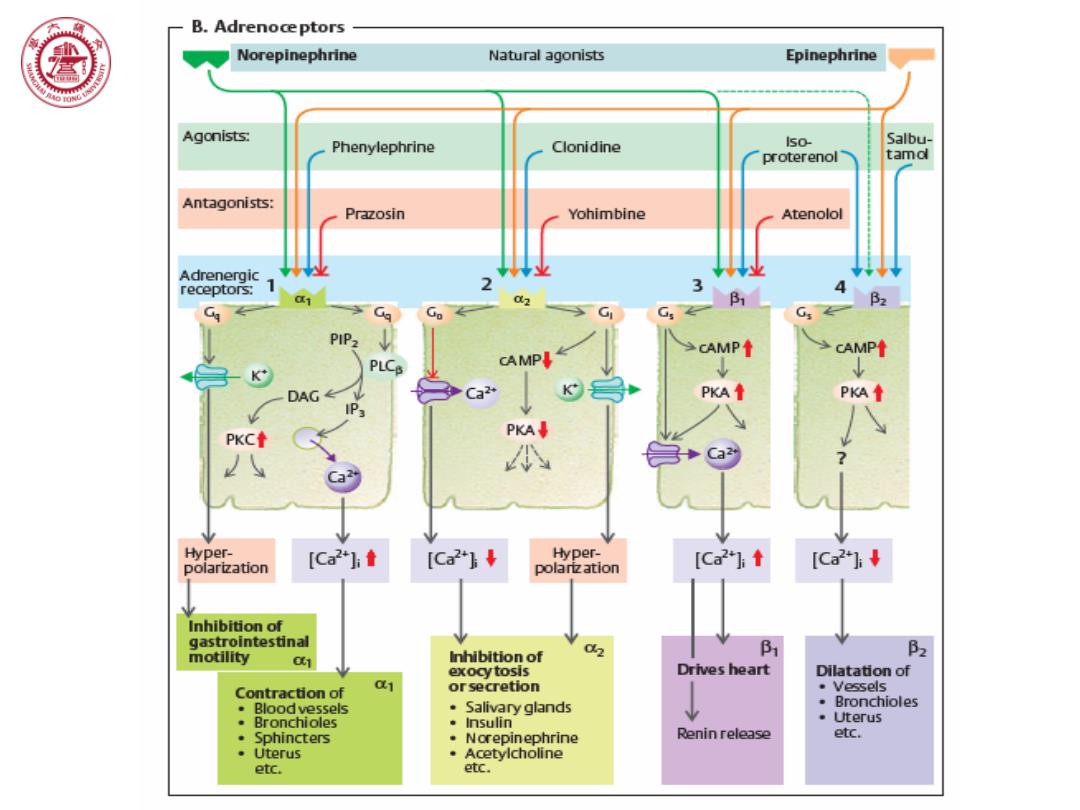
B.Adrenoceptors ⑧ Norepinephrine Natural agonists Epinephrine Agonists: Phenylephrine Clonidine Iso- Salbu- proterenol tamd Antagonists: Prazosin Yohimbine Atenolol Adrenergic receptors: 2 3 Go G, 4 B2 G CAMP CAMP↑ PLCp DAG PKA↑ PK↑ PKC PKA 公 当+a Hyper- Dolartzation [Ca2*] [Ca2*3↓ Hyper- polartzation [Ca2*]h↑ Inhibition of gastrointestinal motility Inhibition of d2 B2 01 exocytosis Drives heart Dilatation of Contraction of d orsecretion ·Vessels ·Blood vessels Salivary glands Bronchioles Bronchioles 。Insulin Uterus Sphincters ·Norepinephrine Renin release etc. Uterus ·Acetylcholine etc. etc
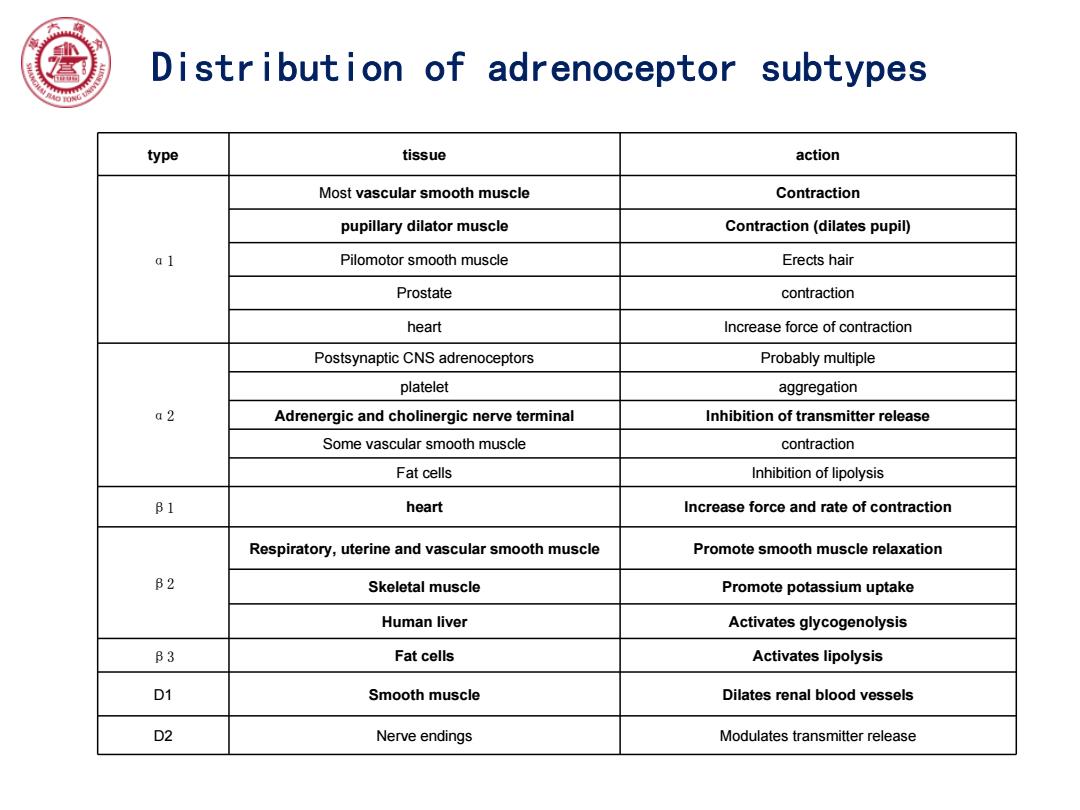
Distribution of adrenoceptor subtypes type tissue action Most vascular smooth muscle Contraction pupillary dilator muscle Contraction(dilates pupil) al Pilomotor smooth muscle Erects hair Prostate contraction heart Increase force of contraction Postsynaptic CNS adrenoceptors Probably multiple platelet aggregation a2 Adrenergic and cholinergic nerve terminal Inhibition of transmitter release Some vascular smooth muscle contraction Fat cells Inhibition of lipolysis B1 heart Increase force and rate of contraction Respiratory,uterine and vascular smooth muscle Promote smooth muscle relaxation B2 Skeletal muscle Promote potassium uptake Human liver Activates glycogenolysis B3 Fat cells Activates lipolysis D1 Smooth muscle Dilates renal blood vessels D2 Nerve endings Modulates transmitter release
type tissue action α1 Most vascular smooth muscle Contraction pupillary dilator muscle Contraction (dilates pupil) Pilomotor smooth muscle Erects hair Prostate contraction heart Increase force of contraction α2 Postsynaptic CNS adrenoceptors Probably multiple platelet aggregation Adrenergic and cholinergic nerve terminal Inhibition of transmitter release Some vascular smooth muscle contraction Fat cells Inhibition of lipolysis β1 heart Increase force and rate of contraction β2 Respiratory, uterine and vascular smooth muscle Promote smooth muscle relaxation Skeletal muscle Promote potassium uptake Human liver Activates glycogenolysis β3 Fat cells Activates lipolysis D1 Smooth muscle Dilates renal blood vessels D2 Nerve endings Modulates transmitter release Distribution of adrenoceptor subtypes
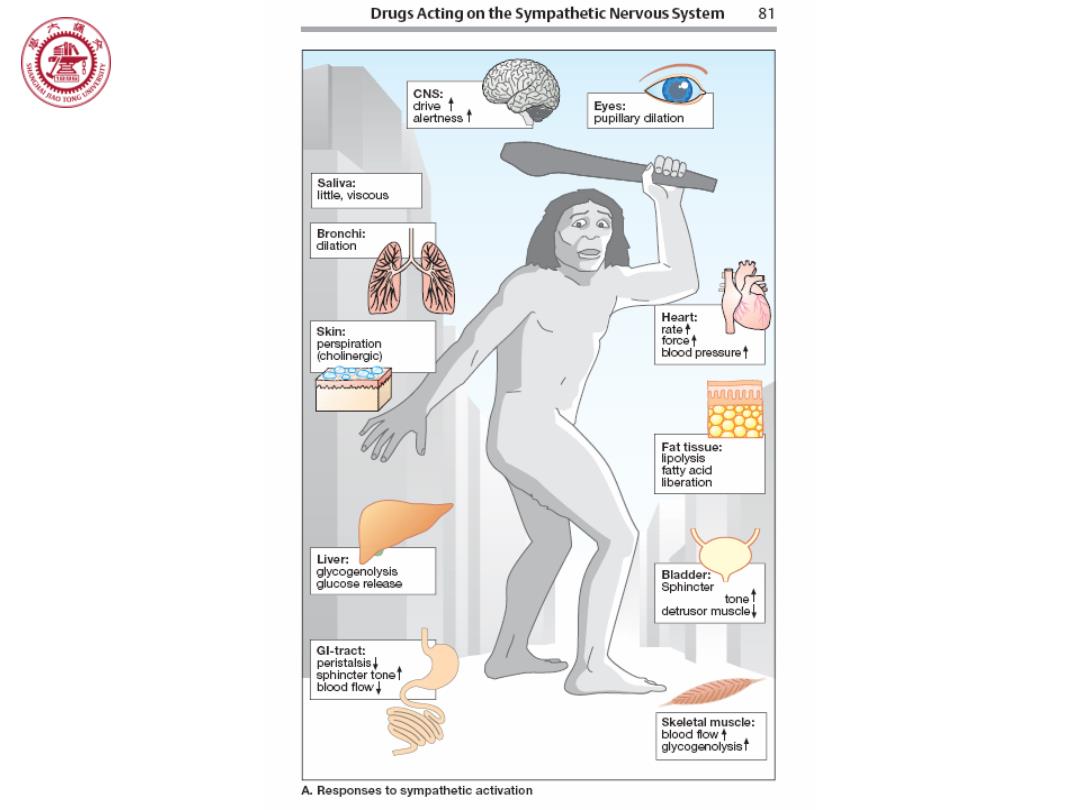
Drugs Acting on the Sympathetic Nervous System 81 ⑧ CNS: drive Eyes: alertness↑ pupillary dilation Saliva: little,visoous Bronchi: dilation Heart: Skin: rate perspiration foce↑ (cholinergic) blood pre8sure↑ ● Fat tissue: lipolysis fatty acid liberation Liver: glycogenolysis Bladder: glucose release Sphincter tonef detrusor muscle Gl-tract: peristalsis sphincter tonef blood flow Skeletal muscle: blood fow↑ glycogenotysist A.Responses to sympathetic activation

③ Sympathomimetic drugs Adrenergic agonists Adrenoceptor-acti vat ing drugs
Sympathomimetic drugs Adrenergic agonists Adrenoceptor-activating drugs
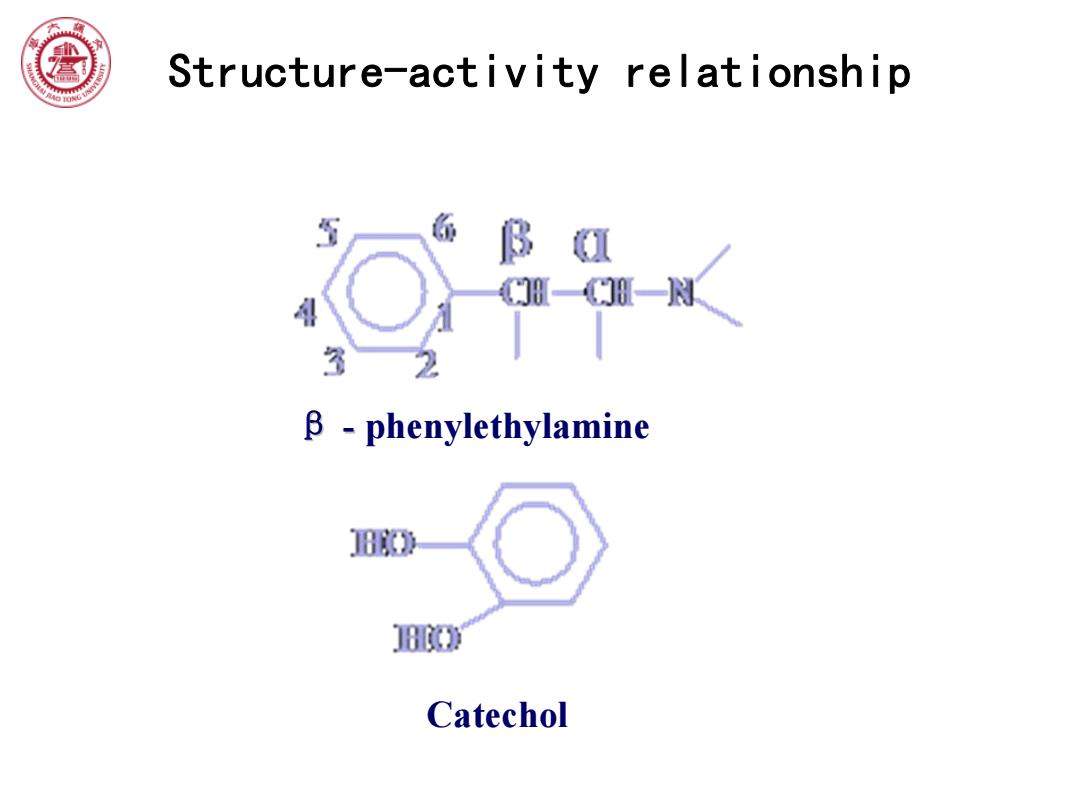
⑧ Structure-activity relationship 临 B I H-一N 2 B phenylethylamine 》 J80C Catechol
Structure-activity relationship β - phenylethylamine - Catechol
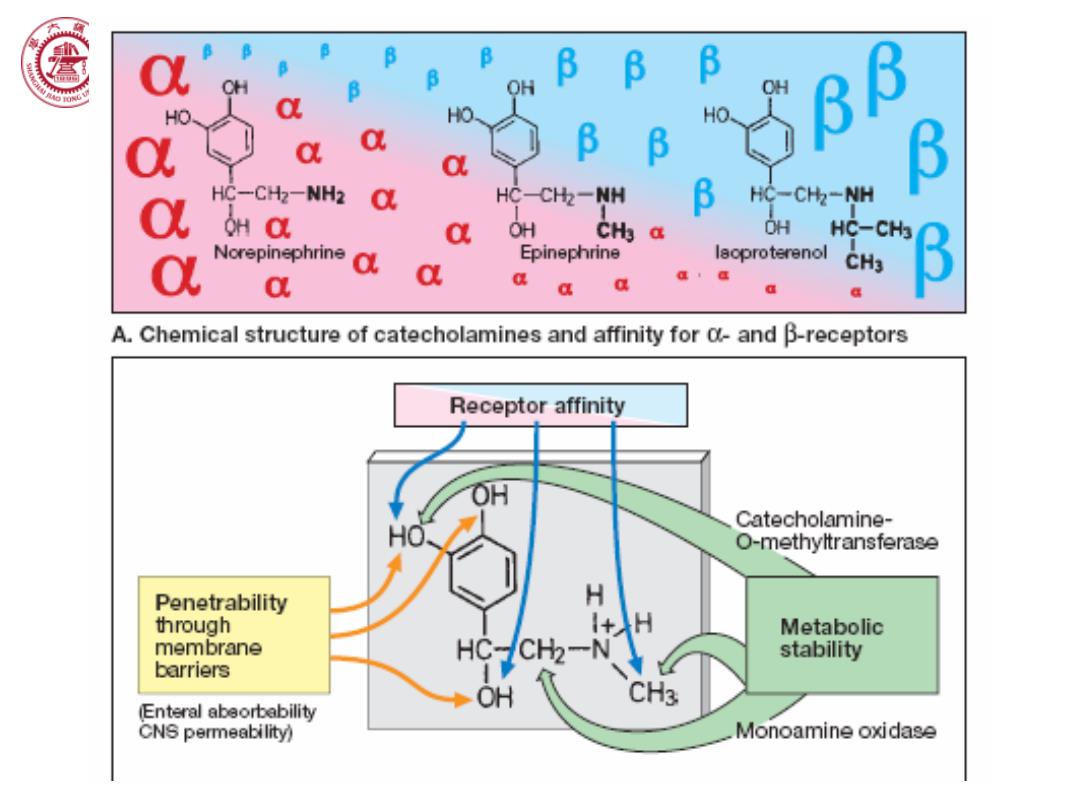
B OH B 6 B HO HO HO. a B B a HC-CH2-NH2 C HC-CH2-NH B HC-CH2-NH OH OL a OH CH3 OH HC-CH内 Norepinephrine Epinephrine laoproterenol CH3 a a 意 a a A.Chemical structure of catecholamines and affinity for 0-and B-receptors Receptor affinity H Catecholamine- O-methyltransferase Penetrability H through I+H Metabolic membrane stability barriers HCc地-N2 OH CH3 (Enteral abeorbability CNS permeability) Monoamine oxidase