
上游充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 ANTIANGINAL DRUGS 相 。 HAAA CHANCHALIAO TONG UNIVEDSEEN
ANTIANGINAL DRUGS
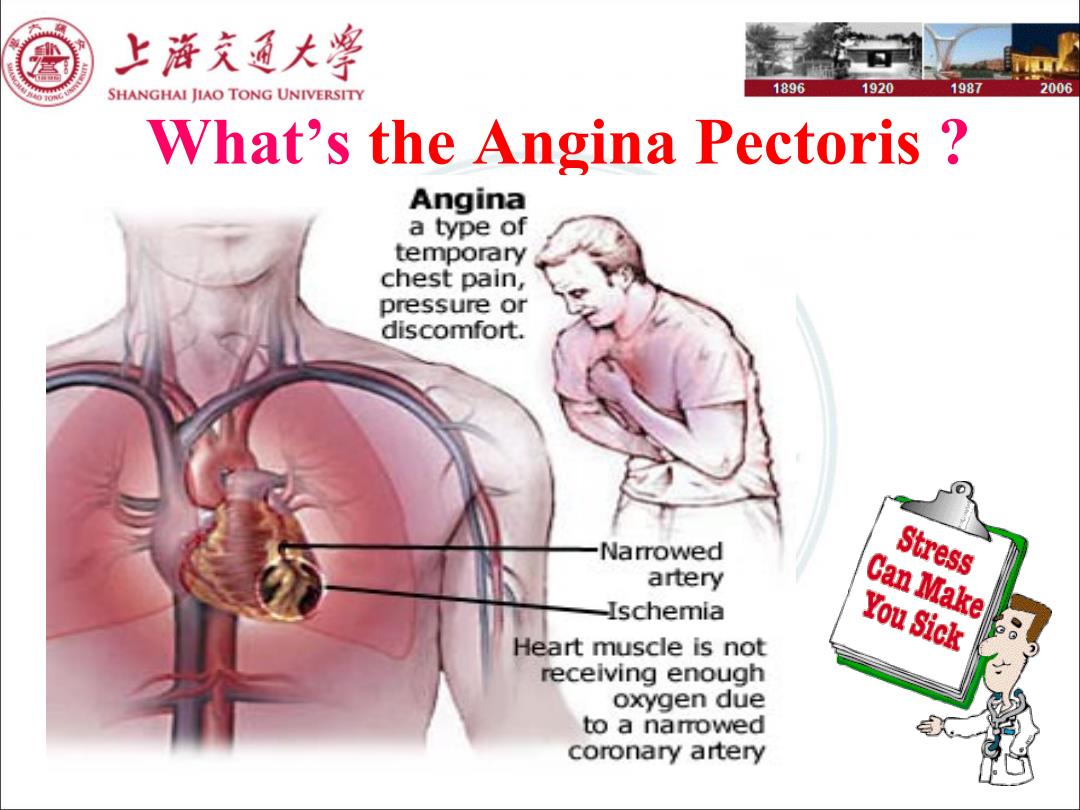
上游充通大淫 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 What's the Angina Pectoris Angina a type of temporary chest pain, pressure or discomfort. Narrowed Stress artery HIschemia Can Make Heart muscle is not You Sick 8 receiving enough oxygen due to a namowed coronary artery
What’s the Angina Pectoris ?
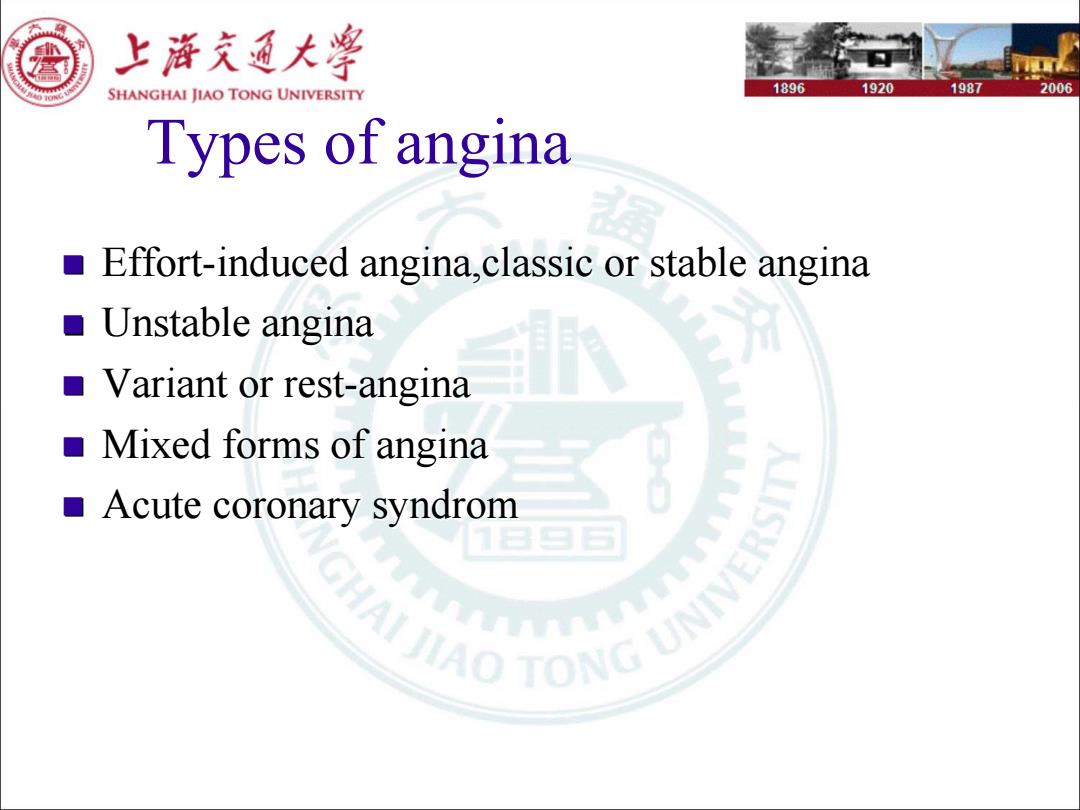
上游充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Types of angina Effort-induced angina,classic or stable angina o Unstable angina Variant or rest-angina a Mixed forms of angina Acute coronary syndrom IAO TONG UNIVERSITY v
Types of angina Effort -induced induced angina,classic angina,classic or stable angina or stable angina Unstable angina Unstable angina Variant or rest Variant or rest-angina Mixed forms of angina Mixed forms of angina Acute coronary Acute coronary syndrom syndrom
上游充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 We should know the physiological characterization of the heart Oxygen utilization Oxygen delivery
We should know the physiological characterization of the heart . Oxygen utilization Oxygen delivery
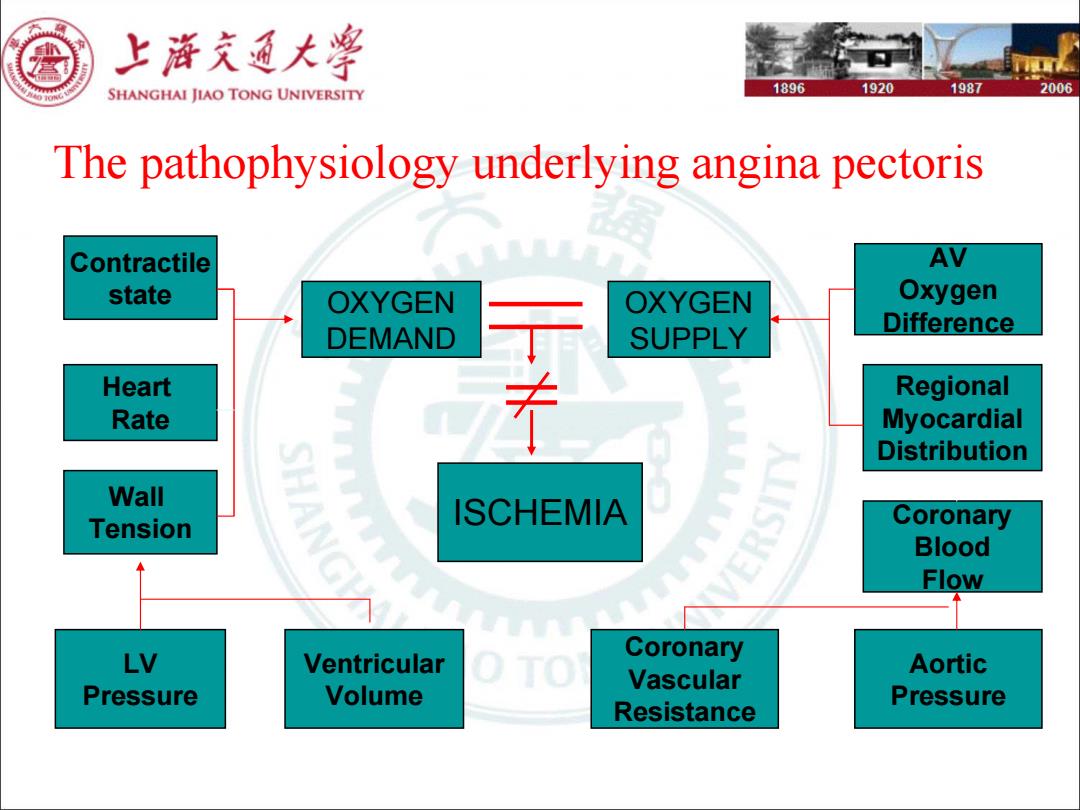
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 The pathophysiology underlying angina pectoris Contractile AV state OXYGEN OXYGEN Oxygen DEMAND SUPPLY Difference Heart Regional Rate Myocardial Distribution Wall ISCHEMIA Tension Coronary Blood Flow LV Ventricular Coronary Aortic Vascular Pressure Volume Pressure Resistance
The pathophysiology underlying angina pectoris OXYGEN DEMAND OXYGEN SUPPLY Contractile state Heart Rate Wall Tension ISCHEMIA AV Oxygen Difference Regional Myocardial Distribution Coronary Blood Flow LV Pressure Ventricular Volume Coronary Vascular Resistance Aortic Pressure
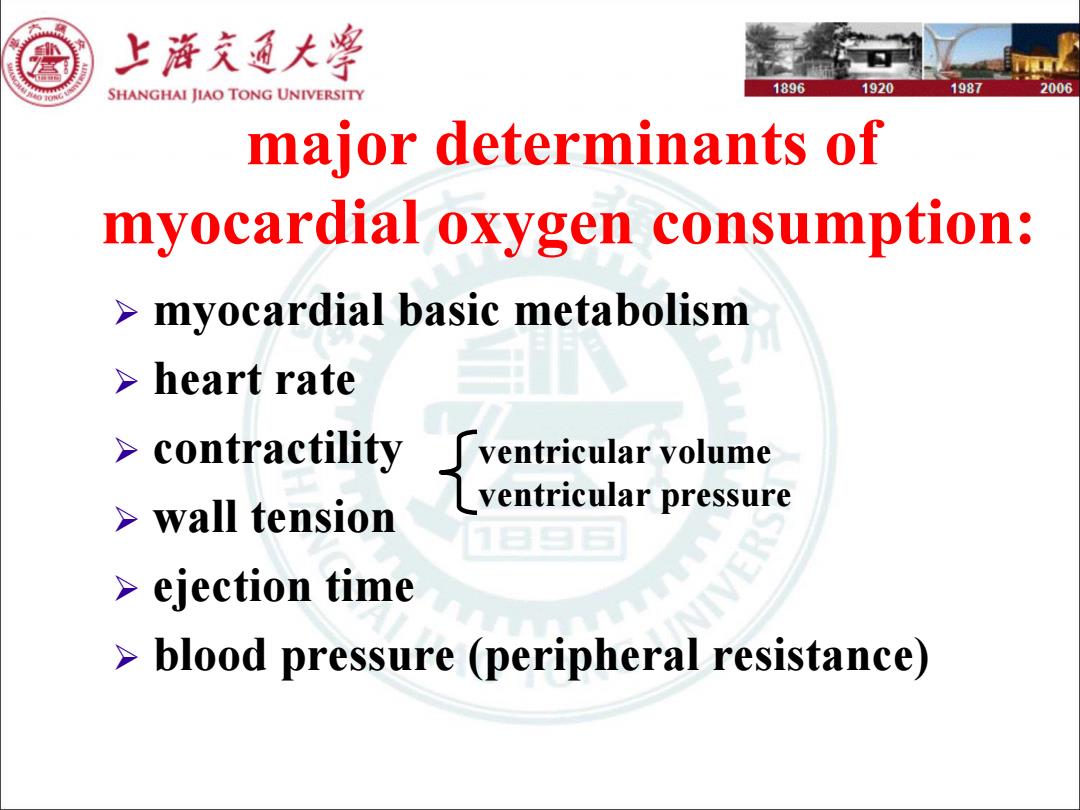
上降充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 major determinants of myocardial oxygen consumption: >myocardial basic metabolism heart rate contractility ventricular volume ventricular pressure >wall tension ejection time blood pressure (peripheral resistance)
major determinants of myocardial oxygen consumption: myocardial basic metabolism heart rate contractility wall tension ejection time blood pressure (peripheral resistance) ventricular volume ventricular pressure

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 The mechanism of antianginal drugs O2 increase supply and/or lower demand Myocardial O2 supply:Coronary blood flow, regional flow distribution Myocarial O2-demand:amount of energy required to support the work of the heart ■ Cardiac work influenced by:heart rate, heart contractility,myocardial wall tension
The mechanism of antianginal drugs O2 increase supply and/or lower demand Myocardial O2 supply: Coronary blood flow, regional flow distribution Myocarial O2 –demand: amount of energy required to support the work of the heart Cardiac work influenced by: heart rate, heart contractility, myocardial wall tension

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Section 2 Organic nitrates 1,Drugs: Nitroglycerin(硝酸甘油), isosorbide dinitrate(硝酸异山梨酯) isosorbide mononitrate(单硝酸异山梨酯)
Section 2 Organic nitrates 1.Drugs: 1.Drugs: Nitroglycerin ( Nitroglycerin (硝酸甘油) , isosorbide isosorbide dinitrate dinitrate (硝酸异山梨酯 ) isosorbide isosorbide mononitrate mononitrate (单硝酸异山梨酯 单硝酸异山梨酯 )
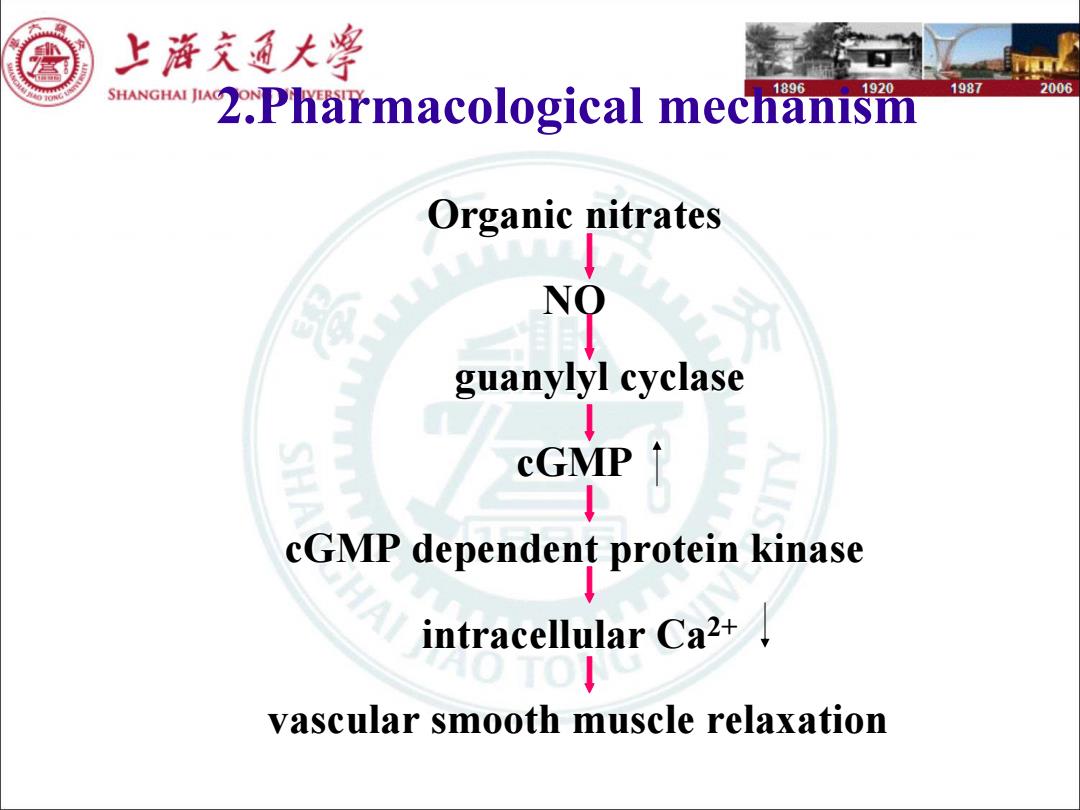
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIA 1896 920 1987 2006 2.Pharmacological mechanism Organic nitrates NO guanylyl cyclase cGMP CGMP dependent protein kinase intracellular Ca2+ vascular smooth muscle relaxation
2.Pharmacological mechanism Organic nitrates Organic nitrates NO guanylyl guanylyl cyclase cyclase cGMP cGMPdependent protein dependent protein kinase intracellular Ca intracellular Ca2+ 2+ vascular smooth muscle relaxation vascular smooth muscle relaxation

上游充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 3.Pharmacological action (1)decrease myocardiac oxygen consumption dilate venous decrease blood returning to heart-decrease ventricular end-diastolic volume and pressure (large dose)dilate arterial decrease peripheral resistance decrease afterload (2)increase blood supply to ischemia area
3. Pharmacological action (1) decrease (1) decrease myocardiac myocardiac oxygen consumption consumption dilate venous decrease blood returning dilate venous decrease blood returning to heart decrease ventricular end to heart decrease ventricular end -diastolic diastolic volume and pressure volume and pressure (large dose) dilate arterial decrease (large dose) dilate arterial decrease peripheral resistance decrease peripheral resistance decrease afterload afterload (2) increase blood supply to ischemia (2) increase blood supply to ischemia area