
Chapter 4: Pharmacology of Peripheral Nervous System Overview Prof.R.D.Ye 2012-09-24
Chapter 4: Pharmacology of Peripheral Nervous System - Overview Prof. R.D. Ye 2012-09-24
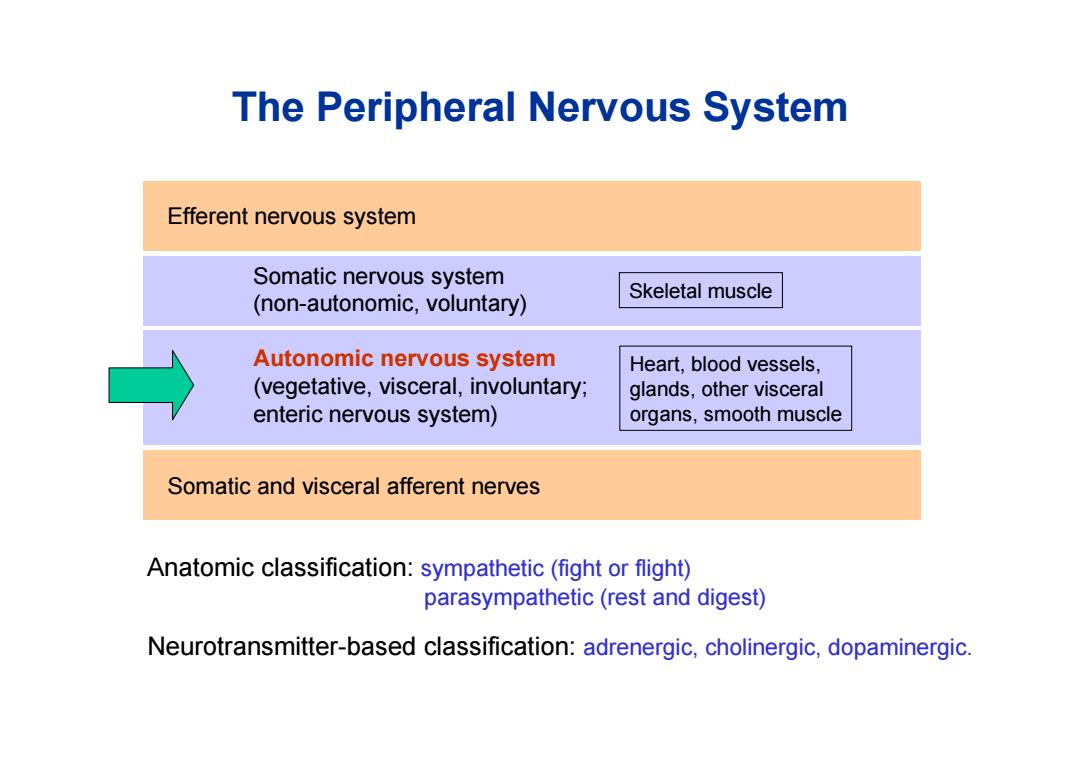
The Peripheral Nervous System Efferent nervous system Somatic nervous system Skeletal muscle (non-autonomic,voluntary) Autonomic nervous system Heart,blood vessels, (vegetative,visceral,involuntary; glands,other visceral enteric nervous system) organs,smooth muscle Somatic and visceral afferent nerves Anatomic classification:sympathetic (fight or flight) parasympathetic(rest and digest) Neurotransmitter-based classification:adrenergic,cholinergic,dopaminergic
Efferent nervous system Somatic nervous system (non-autonomic, voluntary) Skeletal muscle Autonomic nervous system (vegetative, visceral, involuntary; enteric nervous system) Heart, blood vessels, glands, other visceral organs, smooth muscle The Peripheral Nervous System Somatic and visceral afferent nerves Anatomic classification: sympathetic (fight or flight) parasympathetic (rest and digest) Neurotransmitter-based classification: adrenergic, cholinergic, dopaminergic

Otto Loewi (Nobel Laureate,1936) He discovered that stimulation of the vagus of a frog heart causes release of a substance that,when transferred to a second heart,could slow heart rate.He called this "Vagusstoff",demonstrating the chemical basis of neurotransmission. He also found that atropine can prevent the inhibitory action,but not the release of the "Vagusstoff. Incubation of the "Vagusstoff with frog heart homogenate inactivates it. Physostigmine enhances the effect of vagus stimulation on the heart,and prevents the destruction of "Vagusstoff
• He discovered that stimulation of the vagus of a frog heart causes release of a substance that, when transferred to a second heart, could slow heart rate. He called this “Vagusstoff”, demonstrating the chemical basis of neurotransmission. Otto Loewi (Nobel Laureate, 1936) • He also found that atropine can prevent the inhibitory action, but not the release of the “Vagusstoff”. • Incubation of the “Vagusstoff” with frog heart homogenate inactivates it. • Physostigmine enhances the effect of vagus stimulation on the heart, and prevents the destruction of “Vagusstoff
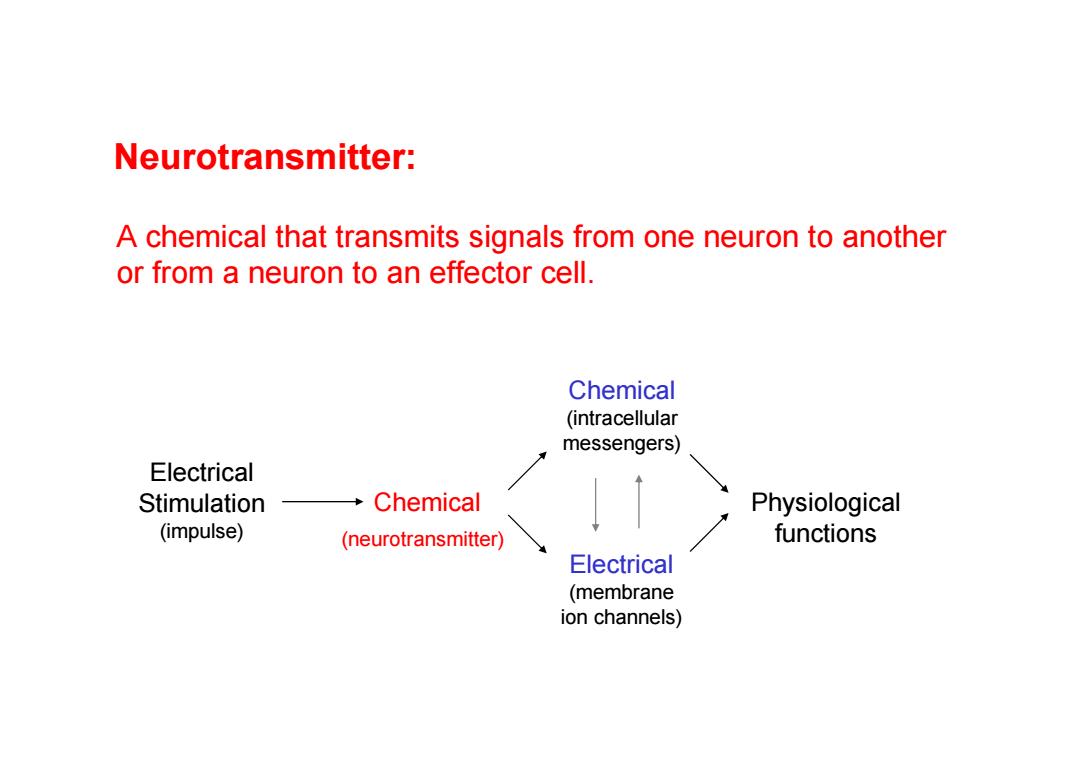
Neurotransmitter: A chemical that transmits signals from one neuron to another or from a neuron to an effector cell. Chemical (intracellular messengers) Electrical Stimulation Chemical Physiological (impulse) (neurotransmitter) functions Electrical (membrane ion channels)
Electrical Stimulation (impulse) Chemical (neurotransmitter) Neurotransmitter: A chemical that transmits signals from one neuron to another or from a neuron to an effector cell. Chemical (intracellular messengers) Electrical (membrane ion channels) Physiological functions
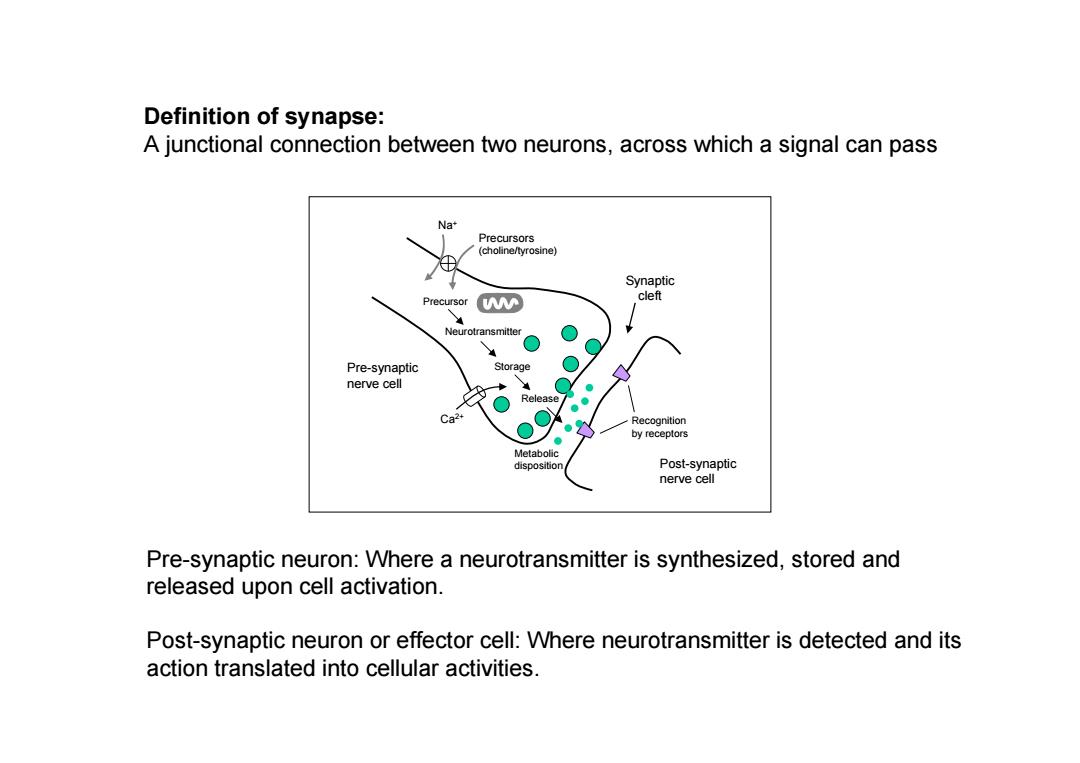
Definition of synapse: A junctional connection between two neurons,across which a signal can pass Na Precursors (choline/tyrosine) Synaptic Precursor cleft Neurotransmitter Pre-synaptic Stora nerve cell Ca Recognition by receptors Metabolic dispositior Post-synaptic nerve cell Pre-synaptic neuron:Where a neurotransmitter is synthesized,stored and released upon cell activation. Post-synaptic neuron or effector cell:Where neurotransmitter is detected and its action translated into cellular activities
Pre-synaptic nerve cell Post-synaptic nerve cell Synaptic cleft Ca2+ Na+ Precursors (choline/tyrosine) Definition of synapse: A junctional connection between two neurons, across which a signal can pass Precursor Neurotransmitter Storage Release Recognition by receptors Metabolic disposition Pre-synaptic neuron: Where a neurotransmitter is synthesized, stored and released upon cell activation. Post-synaptic neuron or effector cell: Where neurotransmitter is detected and its action translated into cellular activities
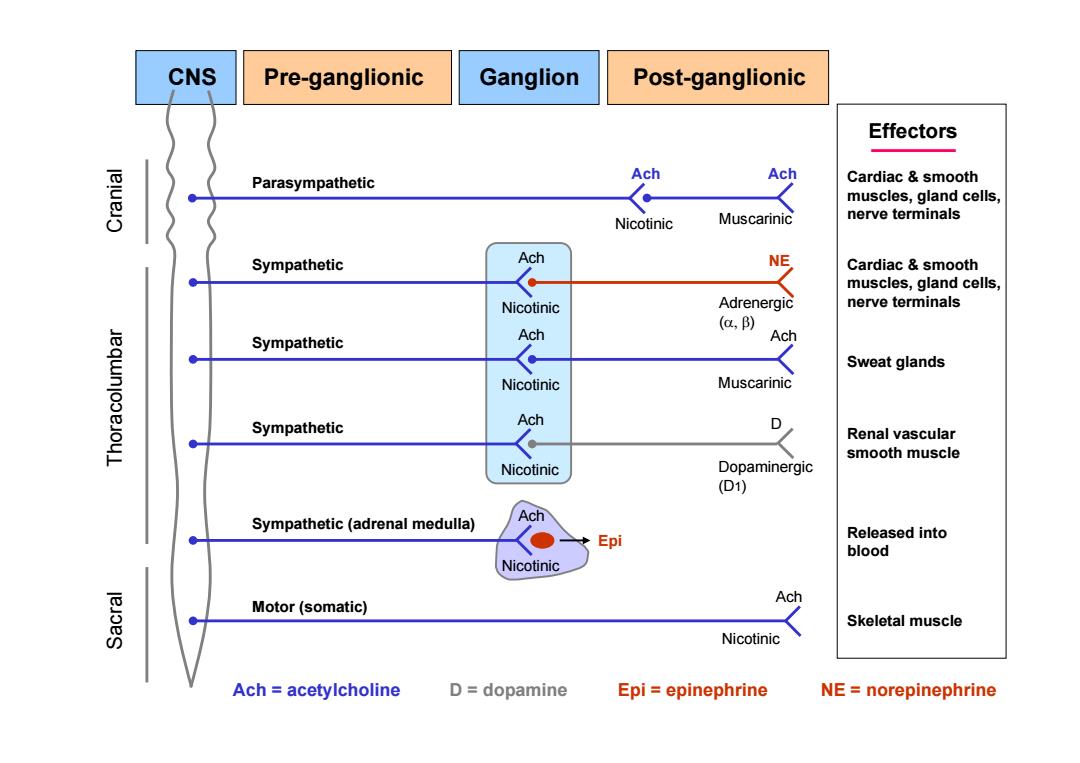
CNS Pre-ganglionic Ganglion Post-ganglionic Effectors Ach Ach lelueJo Parasympathetic Cardiac smooth muscles,gland cells, Nicotinic Muscarinic nerve terminals Sympathetic Ach NE Cardiac smooth muscles,gland cells, Nicotinic Adrenergic nerve terminals (a,) Sympathetic Ach Ach Sweat glands Nicotinic Muscarinic Sympathetic Ach D Renal vascular smooth muscle Nicotinic Dopaminergic (D1) Ach Sympathetic (adrenal medulla) Epi Released into blood Nicotinic Ach leJoes Motor (somatic) Skeletal muscle Nicotinic Ach acetylcholine D=dopamine Epi epinephrine NE norepinephrine
Thoracolumbar Cranial Sacral CNS Pre-ganglionic Ganglion Post-ganglionic Parasympathetic Ach Nicotinic Ach Nicotinic Ach Nicotinic Ach Nicotinic Ach Nicotinic Epi Sympathetic Sympathetic Sympathetic Sympathetic (adrenal medulla) Motor (somatic) Ach Ach Muscarinic Muscarinic NE Adrenergic () D Dopaminergic (D1) Ach Nicotinic Cardiac & smooth muscles, gland cells, nerve terminals Cardiac & smooth muscles, gland cells, nerve terminals Sweat glands Renal vascular smooth muscle Released into blood Skeletal muscle Ach = acetylcholine D = dopamine Epi = epinephrine NE = norepinephrine Effectors

Pharmacological division of cholinergic vs.adrenergic neurotransmission All preganglionic and parasympathetic postganglionic neurons use acetylcholine as neurotransmitter.Ach is the neurotransmitter at ganglia, nmj,and muscarinic tissue synapses. Most postganglionic sympathetic neurons use norepinephrine which is an adrenergic neurotransmitter. There are exceptions:Cholinergic transmission in sympathetic system all ganglia,adrenal medulla,sweat glads(muscarinic).Dopaminergic innervation in sympathetic system-renal blood vessels
• All preganglionic and parasympathetic postganglionic neurons use acetylcholine as neurotransmitter. Ach is the neurotransmitter at ganglia, nmj, and muscarinic tissue synapses. • Most postganglionic sympathetic neurons use norepinephrine which is an adrenergic neurotransmitter. Pharmacological division of cholinergic vs. adrenergic neurotransmission • There are exceptions: Cholinergic transmission in sympathetic system – all ganglia, adrenal medulla, sweat glads (muscarinic). Dopaminergic innervation in sympathetic system – renal blood vessels
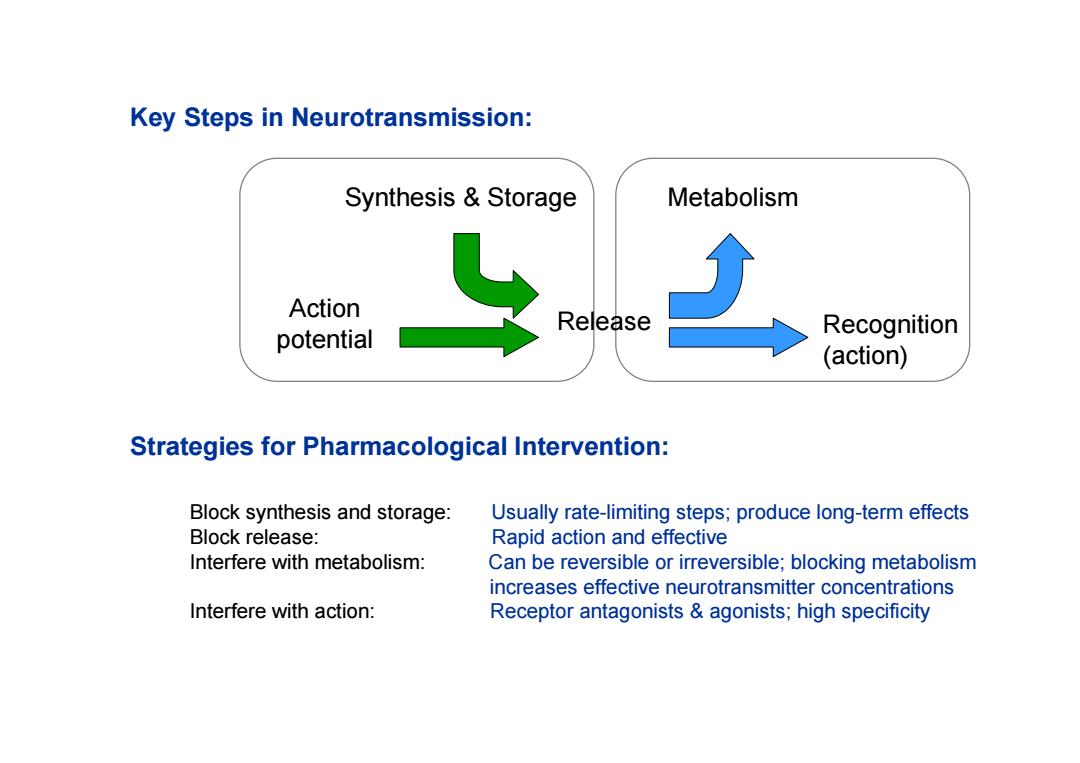
Key Steps in Neurotransmission: Synthesis Storage Metabolism Action Release potential Recognition (action) Strategies for Pharmacological Intervention: Block synthesis and storage: Usually rate-limiting steps;produce long-term effects Block release: Rapid action and effective Interfere with metabolism: Can be reversible or irreversible;blocking metabolism increases effective neurotransmitter concentrations Interfere with action: Receptor antagonists agonists;high specificity
Synthesis & Storage Action potential Metabolism Recognition (action) Key Steps in Neurotransmission: Strategies for Pharmacological Intervention: Block synthesis and storage: Usually rate-limiting steps; produce long-term effects Block release: Rapid action and effective Interfere with metabolism: Can be reversible or irreversible; blocking metabolism increases effective neurotransmitter concentrations Interfere with action: Receptor antagonists & agonists; high specificity Release
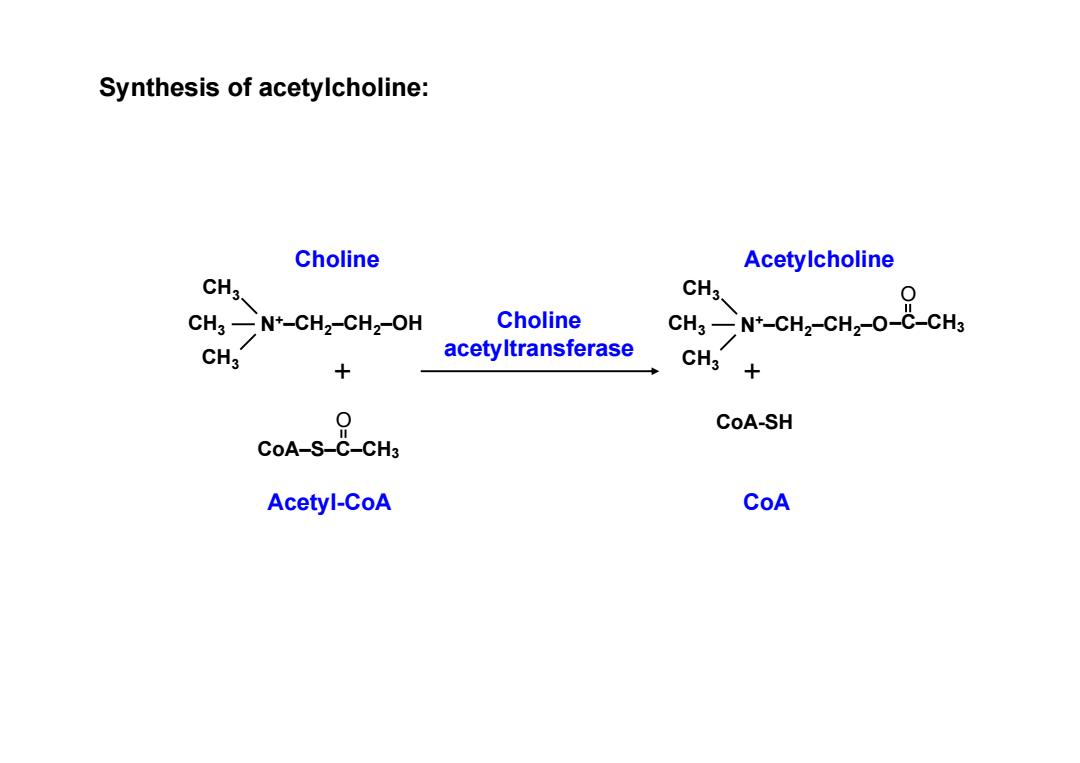
Synthesis of acetylcholine: Choline Acetylcholine CH3、 CH3、 CH3-N+-CH2-CH2-OH Choline CHs-N*-CHz-CHz-O-C-CHs CH3 acetyltransferase + CH3+ 9 CoA-SH CoA-S-C-CH3 Acetyl-CoA CoA
Synthesis of acetylcholine: CH3 CH3 CH3 N+–CH2–CH2–OH CoA–S–C–CH3 O Choline Acetyl-CoA + Choline acetyltransferase CH3 CH3 CH3 N+–CH2–CH2–O–C–CH3 O CoA-SH + CoA Acetylcholine

Synthesis,storage and release of acetylcholine: Na* Choline (10HM Choline Synaptic ChAT cleft Ac-CoA Antiporter Ach Ach Nerve Ach choline impulse Ach acetic acid Ach Pre-synaptic N Ca2+ cell Ach AchE Ca2 Recognition by receptors NM CAT choline acetyltransferase AchE Post-synaptic AchE acetylcholinesterase cell
Synthesis, storage and release of acetylcholine: Pre-synaptic cell Post-synaptic cell Ach Ca2+ Na+ Choline (10 M) Choline Recognition by receptors Ca2+ Ach Ach Ach Nerve impulse NN NM Ach Ac-CoA ChAT Ach AchE AchE choline + acetic acid CAT = choline acetyltransferase AchE = acetylcholinesterase Synaptic cleft Antiporter