
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 1/47 Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks Wentao Huang Xinbing Wang Department of Electronic Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University April 12,2011 4口“③·4E4色卡21=
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 1 / 47 Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks Wentao Huang Xinbing Wang Department of Electronic Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University April 12, 2011

Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 2147 Outline Introduction Backgrounds Motivation and Result System Models Basic Models Operation Rules The Hybrid Protocol Model Definition Feasibility Transmission Opportunities Cell Partitioning Round-Robin Mode Independent Relay Mode Optimal Performance Scaling 4口40·4E,4色下空引=
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 2 / 47 Outline Introduction Backgrounds Motivation and Result System Models Basic Models Operation Rules The Hybrid Protocol Model Definition Feasibility Transmission Opportunities Cell Partitioning Round-Robin Mode Independent Relay Mode Optimal Performance Scaling
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 3147 LIntroduction Outline Introduction Backgrounds Motivation and Result System Models Basic Models Operation Rules The Hybrid Protocol Model Definition Feasibility Transmission Opportunities Cell Partitioning Round-Robin Mode Independent Relay Mode Optimal Performance Scaling 4口4·4E,4色F主1=月QC
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 3 / 47 Introduction Outline Introduction Backgrounds Motivation and Result System Models Basic Models Operation Rules The Hybrid Protocol Model Definition Feasibility Transmission Opportunities Cell Partitioning Round-Robin Mode Independent Relay Mode Optimal Performance Scaling
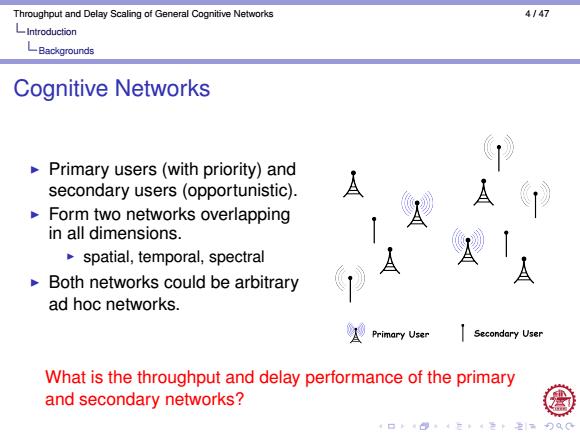
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 4147 LIntroduction LBackgrounds Cognitive Networks Primary users(with priority)and secondary users (opportunistic). A A Form two networks overlapping in all dimensions. spatial,temporal,spectral Both networks could be arbitrary A ad hoc networks. Primary User Secondary User What is the throughput and delay performance of the primary and secondary networks? 口94三卡4老卡2引马
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 4 / 47 Introduction Backgrounds Cognitive Networks I Primary users (with priority) and secondary users (opportunistic). I Form two networks overlapping in all dimensions. I spatial, temporal, spectral I Both networks could be arbitrary ad hoc networks. What is the throughput and delay performance of the primary and secondary networks?
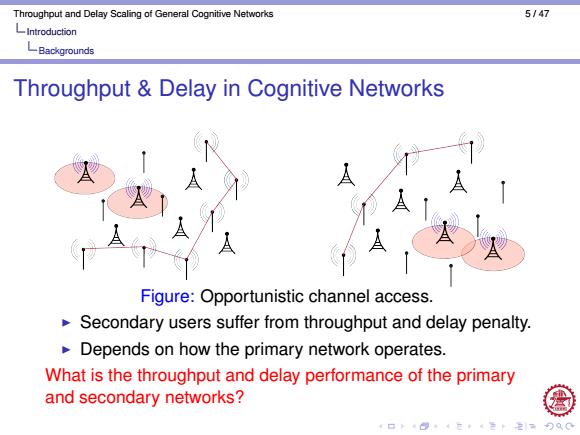
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 5147 LIntroduction LBackgrounds Throughput Delay in Cognitive Networks Figure:Opportunistic channel access. Secondary users suffer from throughput and delay penalty. Depends on how the primary network operates. What is the throughput and delay performance of the primary and secondary networks?
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 5 / 47 Introduction Backgrounds Throughput & Delay in Cognitive Networks Figure: Opportunistic channel access. I Secondary users suffer from throughput and delay penalty. I Depends on how the primary network operates. What is the throughput and delay performance of the primary and secondary networks?

Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 6/47 LIntroduction LBackgrounds Related Previous Works Sang-Woon Jeon et al.,submitted to TIT [14] Study two overlapping static ad hoc networks. Preservation regions to protect primary networks. Almost all secondary users could achieve the same throughput scaling as standalone networks. Changchuan Yin et al.,TON,2011 [15] Two overlapping static ad hoc networks. Both networks can achieve the same delay-throughput tradeoff as the optimal one for standalone networks. Cheng Wang et al.,MASS,2009 [18] Investigate multicast capacity in cognitive networks. Identify numerous sub-regimes,and in most cases multicast capacity is the same as or close to that in standalone networks. 4口4·4E,4色空1=
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 6 / 47 Introduction Backgrounds Related Previous Works I Sang-Woon Jeon et al., submitted to TIT [14] I Study two overlapping static ad hoc networks. I Preservation regions to protect primary networks. I Almost all secondary users could achieve the same throughput scaling as standalone networks. I Changchuan Yin et al., TON, 2011 [15] I Two overlapping static ad hoc networks. I Both networks can achieve the same delay-throughput tradeoff as the optimal one for standalone networks. I Cheng Wang et al., MASS, 2009 [18] I Investigate multicast capacity in cognitive networks. I Identify numerous sub-regimes, and in most cases multicast capacity is the same as or close to that in standalone networks

Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 7147 LIntroduction LMotivation and Result Motivation All previous works consider specific primary networks with predefined communication schemes,and then design secondary protocols accordingly. But primary networks could be arbitrary and diverse. All report similar or same results as standalone networks. May imply a stronger and more general conclusion exists. Figure:Various kinds of primary users in White Spaces networks. 4口4·4E,4色下空1
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 7 / 47 Introduction Motivation and Result Motivation I All previous works consider specific primary networks with predefined communication schemes, and then design secondary protocols accordingly. I But primary networks could be arbitrary and diverse. I All report similar or same results as standalone networks. I May imply a stronger and more general conclusion exists. Figure: Various kinds of primary users in White Spaces networks
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 8147 LIntroduction LMotivation and Result Motivation The Problem What is the performance of a general cognitive networks with arbitrary primary users? Mobility?TDMA?CSMA?,etc. Are there some general conditions that the cognitive networks can perform as well as standalone networks and how? 4口“0·4E4色t1=月QC
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 8 / 47 Introduction Motivation and Result Motivation The Problem What is the performance of a general cognitive networks with arbitrary primary users? I Mobility? TDMA? CSMA?, etc. Are there some general conditions that the cognitive networks can perform as well as standalone networks and how?

Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 9147 LIntroduction LMotivation and Result Results Yes,if: A1)Primary network operates at a SINR level slightly larger than reception threshold. such that there are opportunities for secondary users. A2)Primary network employs round-robin TDMA style scheduling schemes;or its traffic flows choose relays independently for routing. such that the opportunities are sufficient. A3)rma=o(Rin/R),where R,r are transmission ranges of primary and secondary networks. such that the primary scheduling is "homogeneous"and secondary users can conveniently detect opportunities. 4口40·4E,4色下空1=
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 9 / 47 Introduction Motivation and Result Results Yes, if: I A1) Primary network operates at a SINR level slightly larger than reception threshold. I such that there are opportunities for secondary users. I A2) Primary network employs round-robin TDMA style scheduling schemes; or its traffic flows choose relays independently for routing. I such that the opportunities are sufficient. I A3) r γ−2 max = o(R γ min/R 2 max), where R, r are transmission ranges of primary and secondary networks. I such that the primary scheduling is “homogeneous” and secondary users can conveniently detect opportunities
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 10/47 LSystem Models Outline Introduction Backgrounds Motivation and Result System Models Basic Models Operation Rules The Hybrid Protocol Model Definition Feasibility Transmission Opportunities Cell Partitioning Round-Robin Mode Independent Relay Mode Optimal Performance Scaling 4口140·4E4色F1=月QC
Throughput and Delay Scaling of General Cognitive Networks 10 / 47 System Models Outline Introduction Backgrounds Motivation and Result System Models Basic Models Operation Rules The Hybrid Protocol Model Definition Feasibility Transmission Opportunities Cell Partitioning Round-Robin Mode Independent Relay Mode Optimal Performance Scaling