
上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links Shizhen Zhao,Luoyi Fu,Xinbing Wang Department of Electronic Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University,China Qian Zhang Department of Computer Scien Engineering Hong Kong,China
Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links Shizhen Zhao, Luoyi Fu, Xinbing Wang Department of Electronic Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China Qian Zhang Department of Computer Scien Engineering Hong Kong, China

Outline 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ▣Background Large-scale Networks >Random Connection Model >First Passage Percolation Model Network Model Objective Q Main Results and Intuitions ▣Simulation Results ▣Concluding Remarks Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links 2
Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links 2 Outline ❑ Background ➢Large-scale Networks ➢Random Connection Model ➢First Passage Percolation Model ❑ Network Model & Objective ❑ Main Results and Intuitions ❑ Simulation Results ❑ Concluding Remarks
Large-scale Networks 上浒充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Network size is growing. Number of users is growing Need more base stations ▣Unreliable links. Communication between adjacent nodes is not always available Cause of the unreliability. Increased interference >Severe environment >Sleep-wake scheduling Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links 3
3 Large-scale Networks ❑ Network size is growing. ➢ Number of users is growing ➢ Need more base stations ❑ Unreliable links. ➢ Communication between adjacent nodes is not always available ❑ Cause of the unreliability. ➢ Increased interference ➢ Severe environment ➢ Sleep-wake scheduling Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links
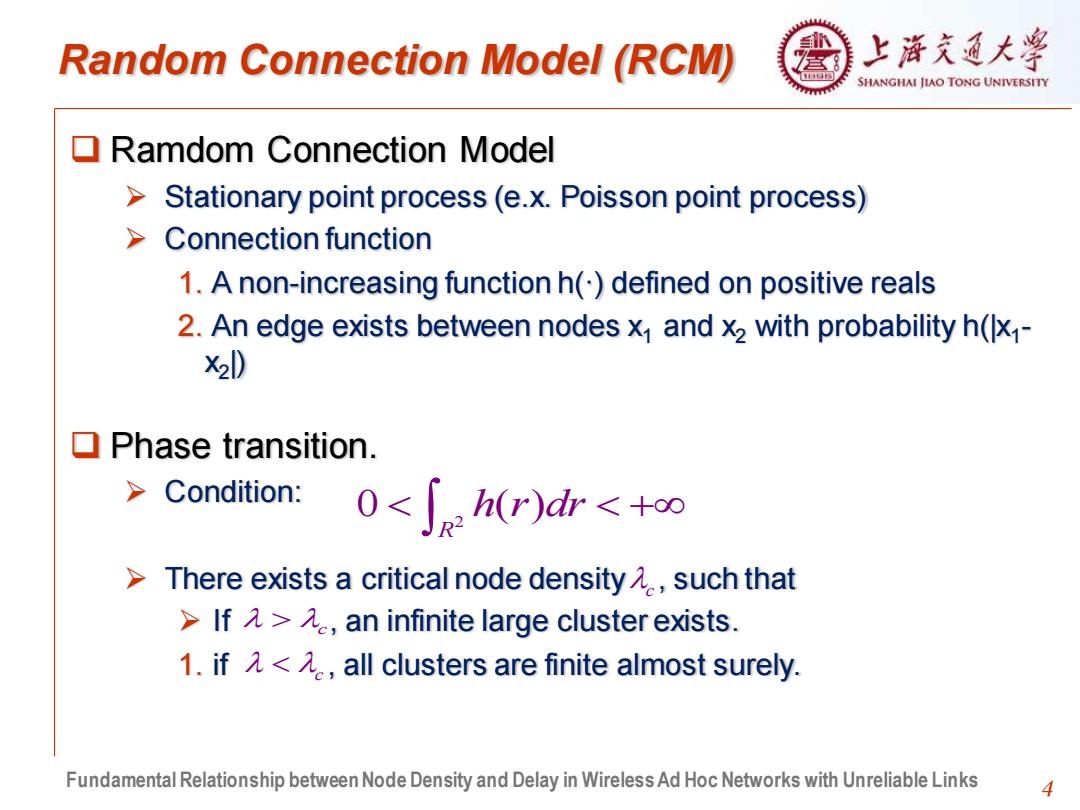
Random Connection Model (RCM) 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Ramdom Connection Model >Stationary point process(e.x.Poisson point process) Connection function 1.A non-increasing function h()defined on positive reals 2.An edge exists between nodes x1 and x2 with probability h(x1- X21) ▣Phase transition. Condition: There exists a critical node density such that >lf入>乙e,an infinite large cluster exists. 1.if元<元.,all clusters are finite almost surely. Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links 4
4 Random Connection Model (RCM) ❑ Ramdom Connection Model ➢ Stationary point process (e.x. Poisson point process) ➢ Connection function 1. A non-increasing function h(·) defined on positive reals 2. An edge exists between nodes x1 and x2 with probability h(|x1 - x2 |) ❑ Phase transition. ➢ Condition: ➢ There exists a critical node density , such that ➢ If , an infinite large cluster exists. 1. if , all clusters are finite almost surely. 2 0 ( ) R + h r dr c c c Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links
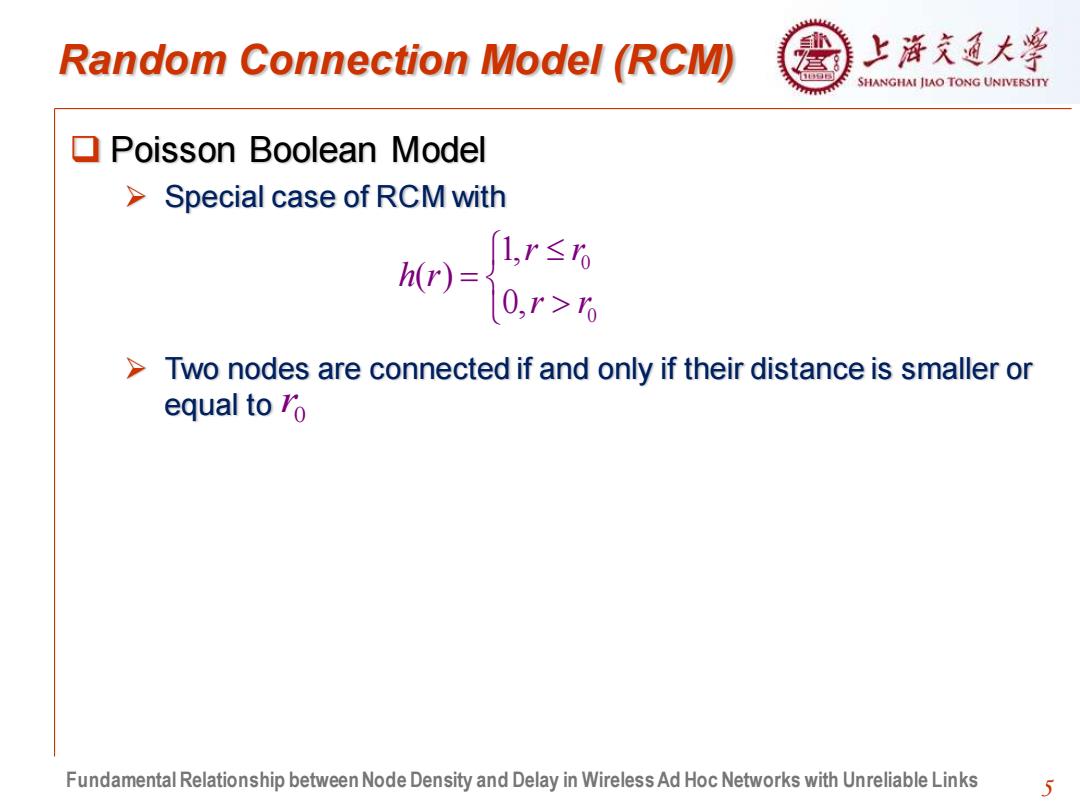
Random Connection Model (RCM) 上浒充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Poisson Boolean Model >Special case of RCM with hr)= 1,r≤0 0,r>6 >Two nodes are connected if and only if their distance is smaller or equal to 7o Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links 5
5 Random Connection Model (RCM) ❑ Poisson Boolean Model ➢ Special case of RCM with ➢ Two nodes are connected if and only if their distance is smaller or equal to 0 0 1, ( ) 0, r r h r r r = 0 r Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links
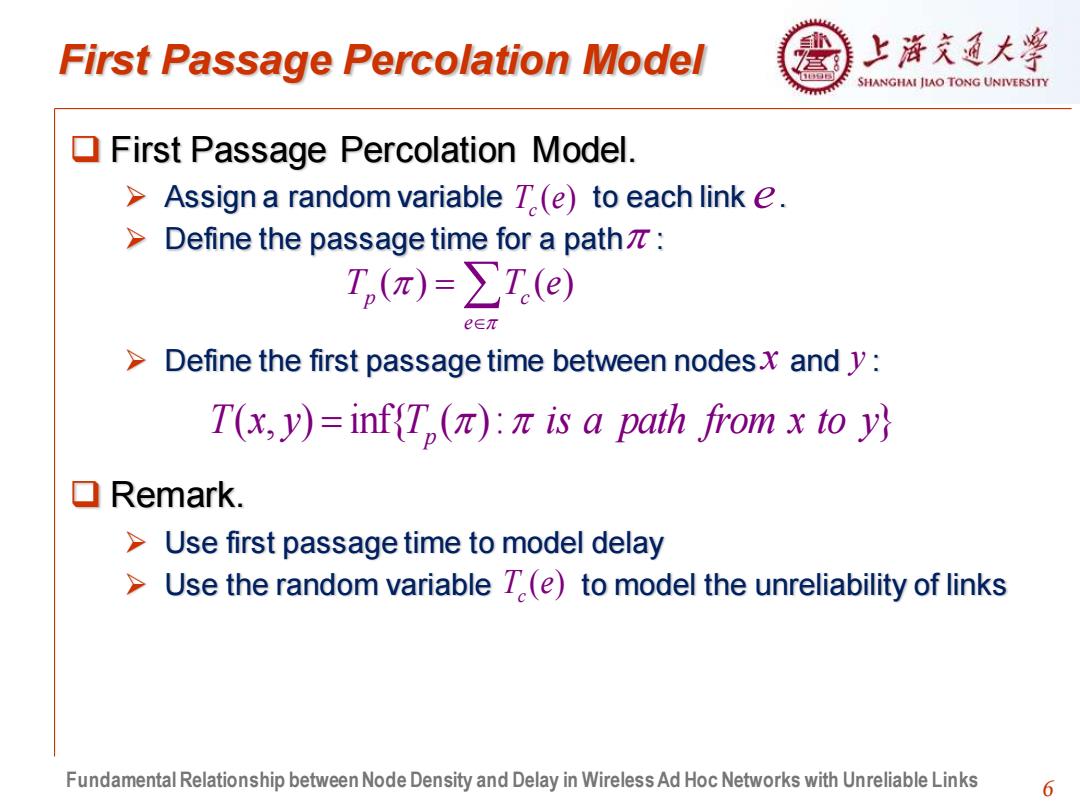
First Passage Percolation Model 上浒充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY First Passage Percolation Model. >Assign a random variable T(e)to each link e. > Define the passage time for a pathπ: T,(π)=∑T.(e) e∈π > Define the first passage time between nodesx and y: T(x,y)=infT,(π):πis a path from x to y ▣Remark. Use first passage time to model delay Use the random variable T(e)to model the unreliability of links Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links 6
6 First Passage Percolation Model ❑ First Passage Percolation Model. ➢ Assign a random variable to each link . ➢ Define the passage time for a path : ➢ Define the first passage time between nodes and : ❑ Remark. ➢ Use first passage time to model delay ➢ Use the random variable to model the unreliability of links ( ) T e c e ( ) ( ) p c e T T e = ( , ) inf{ ( ): } T x y T is a path from x to y = p x y ( ) T e c Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links

Outline 上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ▣Background QNetwork Model Objective Network Model >Objective QMain Results and Intuitions ▣Simulation Results ▣Concluding Remarks Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links 7
7 Outline ❑Background ❑Network Model & Objective ➢Network Model ➢ Objective ❑Main Results and Intuitions ❑Simulation Results ❑Concluding Remarks Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links
Network Model-Connectivity 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Delay is a basic concern in designing and implementing large scale wireless networks.However,the premise of communication is connectivity. In large scale wireless network with unreliable links,it is too costly to maintain full connectivity.Therefore,we consider a slightly weaker connectivity-connectivity in percolation sense. Random Connection Model(RCM) Instantaneous and Long-term Connectivity Instantaneous Critical Density()and Long-term Critical Density (九z) Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links 8
8 Network Model-Connectivity ❑ Delay is a basic concern in designing and implementing large scale wireless networks. However, the premise of communication is connectivity. ❑ In large scale wireless network with unreliable links, it is too costly to maintain full connectivity. Therefore, we consider a slightly weaker connectivity-connectivity in percolation sense. ➢ Random Connection Model (RCM) ➢ Instantaneous and Long-term Connectivity ➢ Instantaneous Critical Density ( ) and Long-term Critical Density ( ) I L Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links

Network Model-Connectivity 上洋充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY g(r) 8(r) O 几,灵4, Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links 9
9 I I L L Network Model-Connectivity g r( ) g r( ) O r0 r Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links
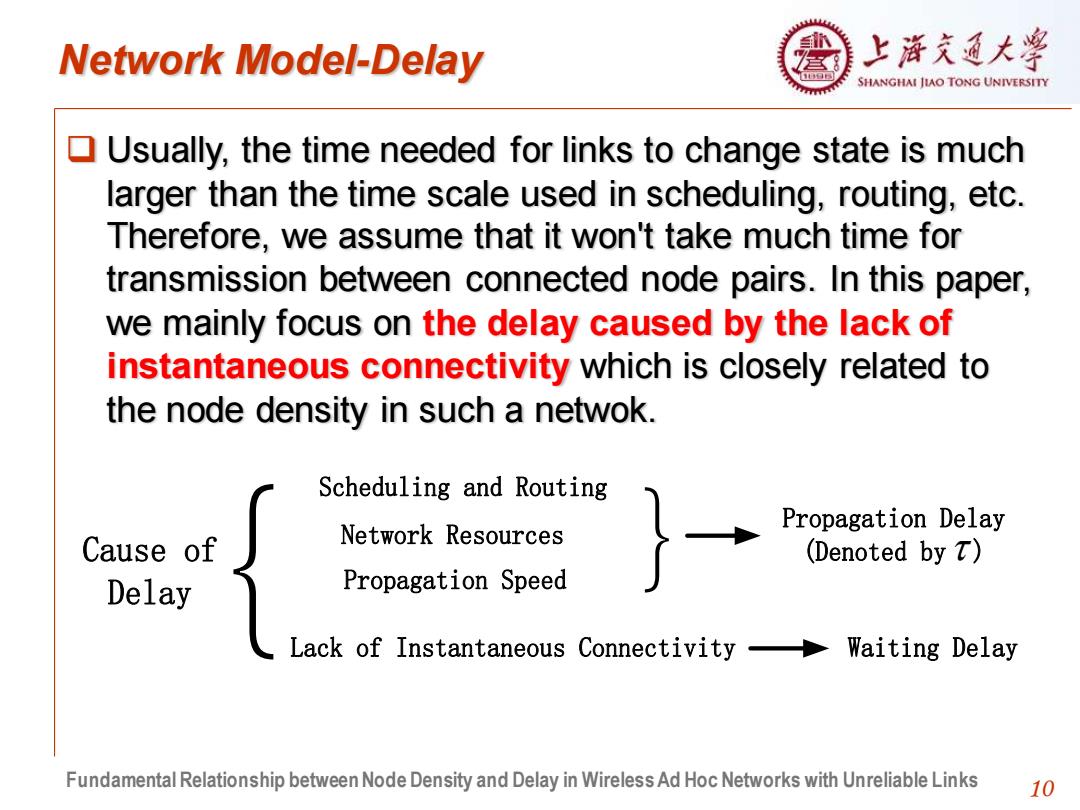
Network Model-Delay 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Usually,the time needed for links to change state is much larger than the time scale used in scheduling,routing,etc. Therefore,we assume that it won't take much time for transmission between connected node pairs.In this paper, we mainly focus on the delay caused by the lack of instantaneous connectivity which is closely related to the node density in such a netwok. Scheduling and Routing Propagation Delay Cause of Network Resources (Denoted by t) Delay Propagation Speed Lack of Instantaneous Connectivity- Waiting Delay Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links 10
10 Network Model-Delay ❑ Usually, the time needed for links to change state is much larger than the time scale used in scheduling, routing, etc. Therefore, we assume that it won't take much time for transmission between connected node pairs. In this paper, we mainly focus on the delay caused by the lack of instantaneous connectivity which is closely related to the node density in such a netwok. {Cause of Delay Waiting Delay Scheduling and Routing Network Resources Propagation Speed Lack of Instantaneous Connectivity } Propagation Delay (Denoted by ) Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links