
上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks Qingsi Wang,Xinbing Wang Department of Electronic Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University,China Xiaojun Lin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University,USA
Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks Qingsi Wang, Xinbing Wang Department of Electronic Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China Xiaojun Lin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, USA

Outline 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ▣Introduction >Background >Motivations >Objectives QK-hop Clustered Network Models Q Main Results and Intuitions Q The Impact of Mobility ▣Concluding Remarks Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 2
Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 2 Outline ❑ Introduction ➢Background ➢Motivations ➢ Objectives ❑ K-hop Clustered Network Models ❑ Main Results and Intuitions ❑ The Impact of Mobility ❑ Concluding Remarks

Background-V/lI 上浒充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Connectivity is a basic concern in designing and implementing wireless networks. Three main schemes of connecting strategies are proposed in the literature. Distance-based strategy Number-of-neighbor-based strategy Sector-based strategy Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 3
3 Background – I/II ❑ Connectivity is a basic concern in designing and implementing wireless networks. ❑ Three main schemes of connecting strategies are proposed in the literature. ➢ Distance-based strategy ➢ Number-of-neighbor-based strategy ➢ Sector-based strategy Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks
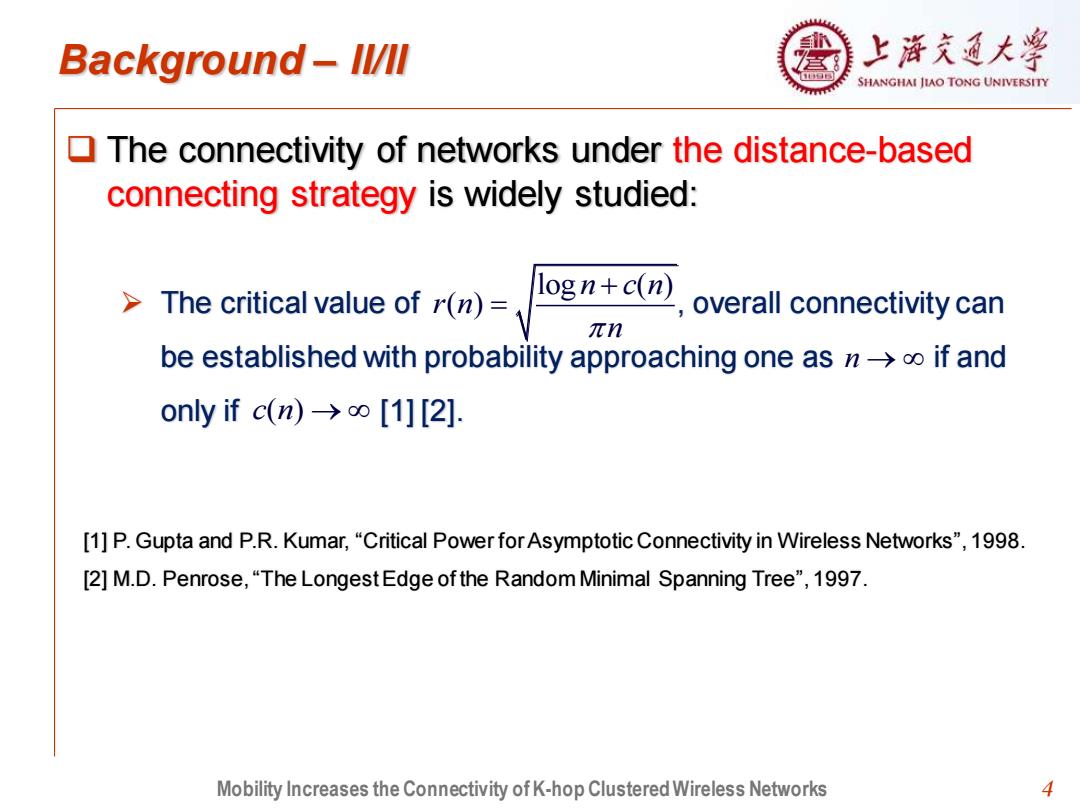
Background-ll/lI 上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY The connectivity of networks under the distance-based connecting strategy is widely studied: >The critical value of r(n)= logn+c(n) overall connectivity can πn be established with probability approaching one as n>o if and only if c(n)>o [1][2]. [1]P.Gupta and P.R.Kumar,"Critical Power for Asymptotic Connectivity in Wireless Networks",1998. [2]M.D.Penrose,"The Longest Edge of the Random Minimal Spanning Tree",1997. Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 4
4 Background – II/II ❑ The connectivity of networks under the distance-based connecting strategy is widely studied: ➢ The critical value of , overall connectivity can be established with probability approaching one as if and only if [1] [2]. Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks log ( ) ( ) n c n r n n + = n → c n( ) → [1] P. Gupta and P.R. Kumar, “Critical Power for Asymptotic Connectivity in Wireless Networks”, 1998. [2] M.D. Penrose, “The Longest Edge of the Random Minimal Spanning Tree”, 1997

Motivation 上浒充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY The network models studied in these prior works are non-clustered (or flat)and stationary networks. Clustering and mobility have been found to improve various aspects of network performance. Studies on the connectivity of mobile and clustered networks are quite limited. ---We don't even know the definition of the connectivity under such circumstances. Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 5
5 Motivation ❑The network models studied in these prior works are non-clustered (or flat) and stationary networks. ❑Clustering and mobility have been found to improve various aspects of network performance. ❑Studies on the connectivity of mobile and clustered networks are quite limited. --- We don’t even know the definition of the connectivity under such circumstances. Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks
Objective-VlI 上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ▣Open question: >What is the impact of mobility on connectivity of clustered networks subject to delay constraints? ▣Ve study The critical transmission range for connectivity >K-hop mobile clustered networks (delay guarantee) >Random walk mobility model with non-trivial velocity >iid.mobility model (fast mobility) Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 6
Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 6 Objective – I/II ❑Open question: ➢What is the impact of mobility on connectivity of clustered networks subject to delay constraints? ❑We study ➢The critical transmission range for connectivity ➢K-hop mobile clustered networks (delay guarantee) ➢Random walk mobility model with non-trivial velocity ➢i.i.d. mobility model (fast mobility)
Objective-ll/II 上浒充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY We compare with the critical transmission range for connectivity in stationary k-hop clustered networks. ▣Implications on >the power-delay trade-off the energy efficiency Our results show that: Mobility does improve connectivity in k-hop clustered networks,and it also significantly decreases the energy consumption and the power-delay trade-off. Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 7
Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 7 Objective – II/II ❑ We compare with the critical transmission range for connectivity in stationary k-hop clustered networks. ❑ Implications on ➢the power-delay trade-off ➢the energy efficiency ❑ Our results show that: Mobility does improve connectivity in k-hop clustered networks, and it also significantly decreases the energy consumption and the power-delay trade-off
Outline 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ▣Introduction K-hop Clustered Network Models >An overview of flat networks >K-hop clustered network models QMain Results and Intuitions QThe Impact of Mobility QConcluding Remarks Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 8
8 Outline ❑Introduction ❑K-hop Clustered Network Models ➢An overview of flat networks ➢K-hop clustered network models ❑Main Results and Intuitions ❑The Impact of Mobility ❑Concluding Remarks Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks
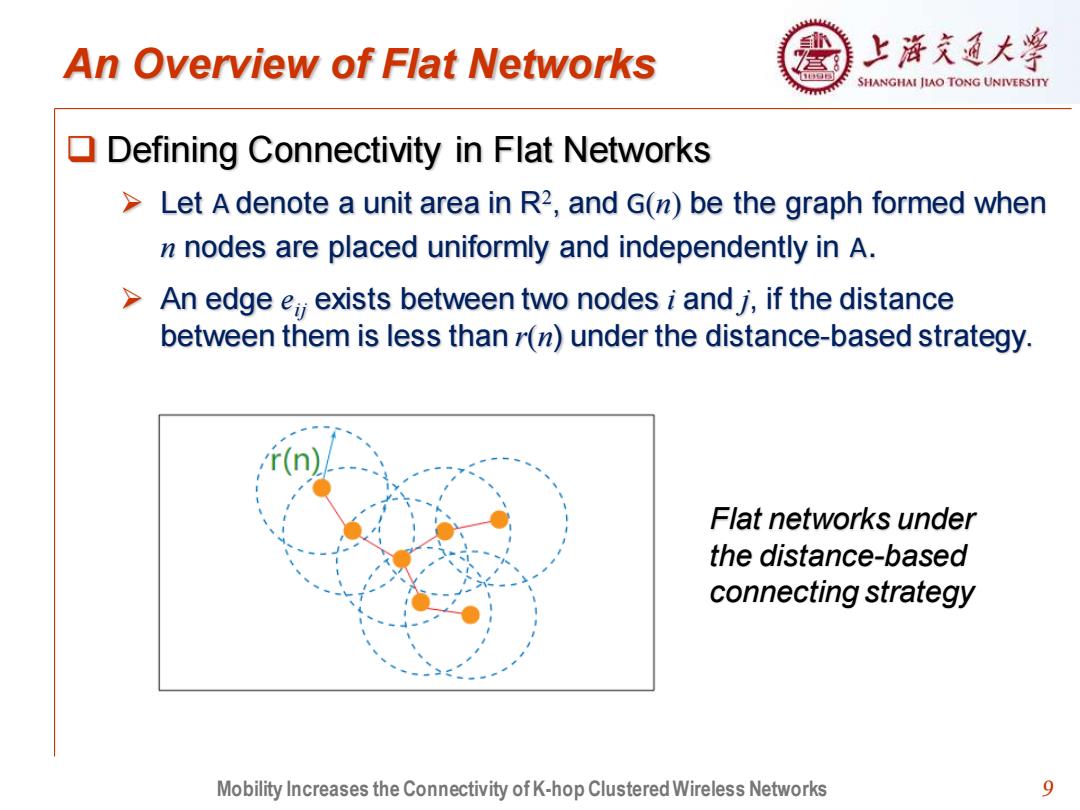
An Overview of Flat Networks 上浒充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Defining Connectivity in Flat Networks Let A denote a unit area in R2,and G(n)be the graph formed when n nodes are placed uniformly and independently in A. An edge e;exists between two nodes i and j,if the distance between them is less than r(n)under the distance-based strategy. Flat networks under the distance-based connecting strategy Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 9
9 An Overview of Flat Networks ❑ Defining Connectivity in Flat Networks ➢ Let A denote a unit area in R2 , and G(n) be the graph formed when n nodes are placed uniformly and independently in A. ➢ An edge eij exists between two nodes i and j, if the distance between them is less than r(n) under the distance-based strategy. Flat networks under the distance-based connecting strategy Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks
K-hop Clustered Network Models 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ▣Clustered networks >n normal nodes and nd cluster-head nodes >Static or mobile ▣Mobility Model Random Walk Mobility Model with Non-Trivial Velocity -Uniformly chosen direction -Constantvelocity (continuous path) >I.I.D.Mobility Model -Independently and uniformly reshuffled -Staticwithin a single time slot Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 10
10 K-hop Clustered Network Models ❑Clustered networks ➢n normal nodes and n d cluster-head nodes ➢Static or mobile ❑Mobility Model ➢Random Walk Mobility Model with Non-Trivial Velocity – Uniformly chosen direction – Constant velocity (continuous path) ➢I.I.D. Mobility Model – Independently and uniformly reshuffled – Static within a single time slot Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks