
中国缚学程术大学 University of Science and Technology of China 伽马射线天文 杨睿智
伽马射线天⽂ 杨睿智

Outline 中国斜学我术大学 University of Science and Technology of China 1.spaceborne gamma-ray detectors 2.ground based gamma-ray detectors 3.Scientific output and prospect
Outline 1. spaceborne gamma-ray detectors 2. ground based gamma-ray detectors 3.Scientific output and prospect
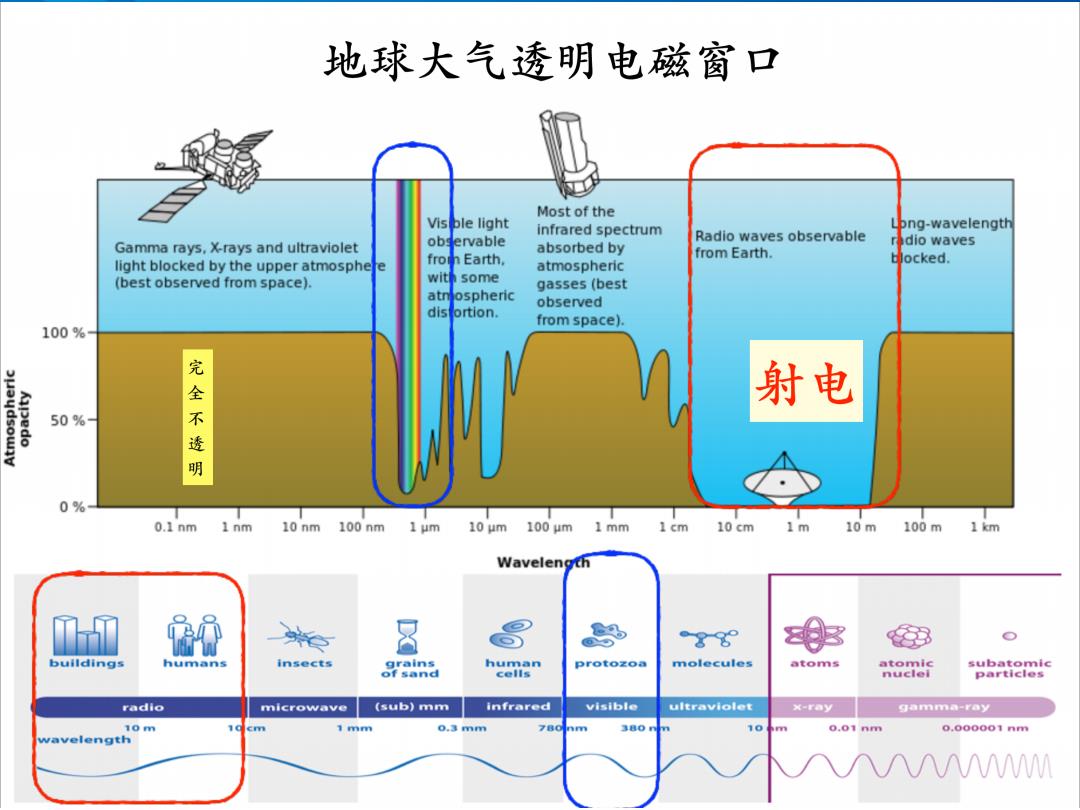
地球大气透明电磁窗口 Most of the Vis ble light infrared spectrum png-wavelength Radio waves observable Gamma rays,X-rays and ultraviolet obs ervable absorbed by dio waves from Earth. light blocked by the upper atmosphe fro Earth, ocked. e atmospheric (best observed from space). wit some gasses(best atn ospheric observed distortion. from space). 100% 完全不 射电 50% 透明 0% 0.1nm 1nm 10 nm 100 nm 1 um 10 um 100 um 1mm 1 cm 10cm ,1m10m100m1km Wavelength cb 86 bulldings humans insects grains human protozoa molecules atoms atomic subatomic ⊙fs线nd cells nuclel particles radio microwave (sub)mm infrared visible ultraviolet ×-my gamma-ray 10 1 mm 0.3mm 780 380 10 0.01nm 0.000001nm wavelength AAAAM
Gamma-ray Astronomy

Gamma-ray Astronomy 中国斜学我术大学 University of Science and Technology of China Atmosphere is opaque for gamma-rays Satellite or air shower Fermi LAT H.E.S.S LHAASO (0.1~1000GeV) (0.1~10TeV) (1Te)
Gamma-ray Astronomy • Atmosphere is opaque for gamma-rays • Satellite or air shower Fermi LAT (0.1 ~ 1000 GeV) LHAASO (>1 TeV) H.E.S.S (0.1 ~ 10 TeV)

Spaceborne detectors 中国斜学我术大学 University of Science and Technology of China pair conversion telescopes Large FOV (~3 sr) 0.1~1000GeV small effective area (~1 m^2) Fermi LAT moderate PSF(0.1-1 degree) continuous monitoring Dampe
Spaceborne detectors • pair conversion telescopes • Large FOV (~ 3 sr) • 0.1~ 1000 GeV • small effective area (~ 1 m^2) • moderate PSF (0.1 - 1 degree) • continuous monitoring Fermi LAT Dampe
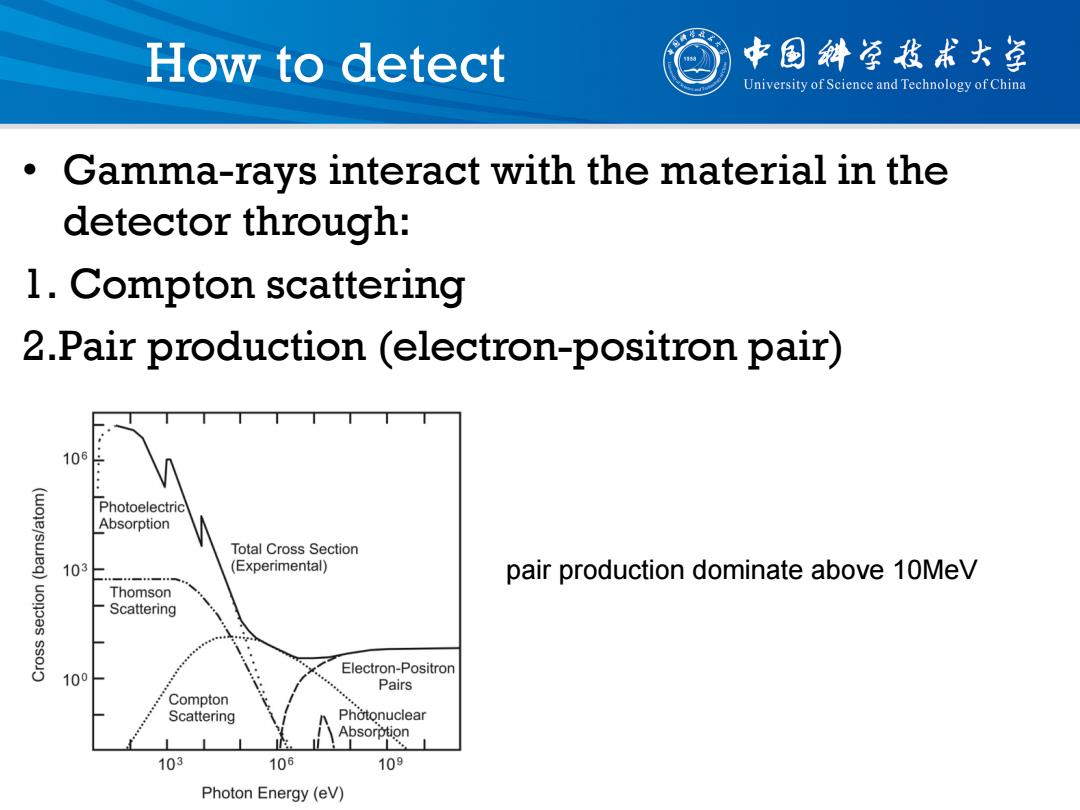
How to detect 中国斜草我术大学 University of Science and Technology of China Gamma-rays interact with the material in the detector through: 1.Compton scattering 2.Pair production (electron-positron pair) 106 Photoelectric Absorption Total Cross Section 103 (Experimental) pair production dominate above 10MeV Thomson Scattering Electron-Positron 100 i Pairs Compton Scattering Photonuclear Absorption 103 106 109 Photon Energy(eV)
How to detect • Gamma-rays interact with the material in the detector through: 1. Compton scattering 2.Pair production (electron-positron pair) pair production dominate above 10MeV
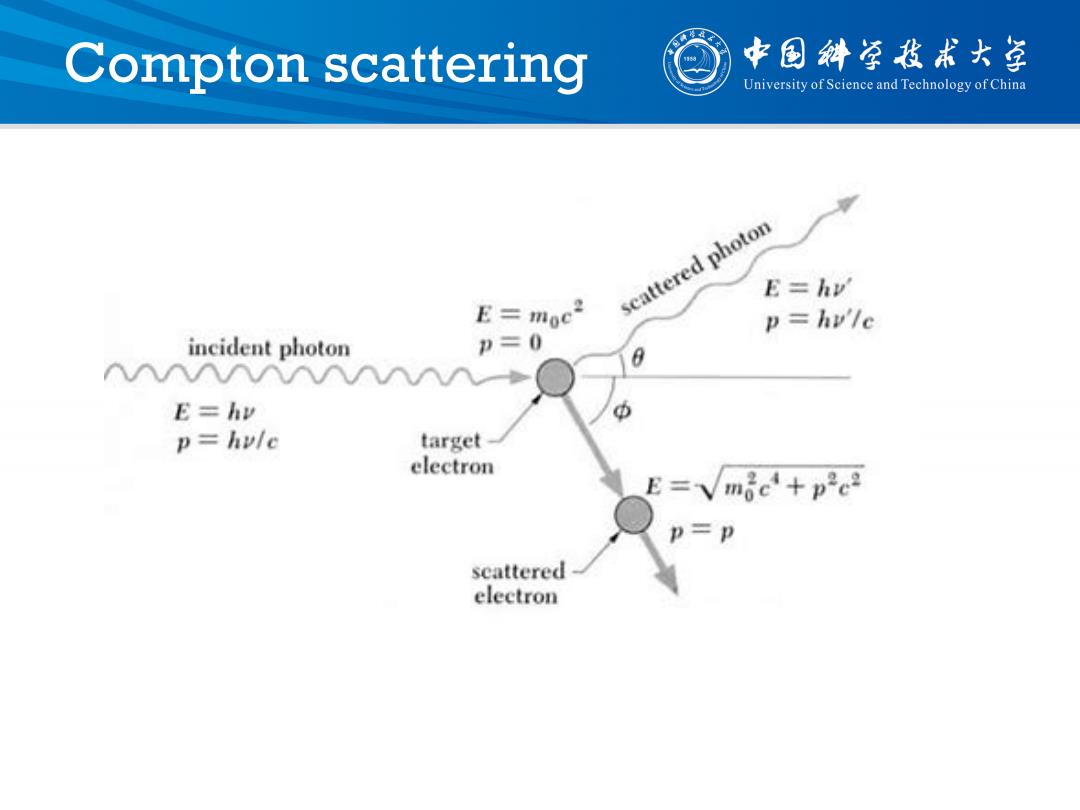
Compton scattering 中国斜学我术大学 University of Science and Technology of China scattered photon E=hy' E=moe2 p=hv'le ineident photon =0 AAAAAAAAAAAA E=hy p=hule target- electron P=P scattered electron
Compton scattering
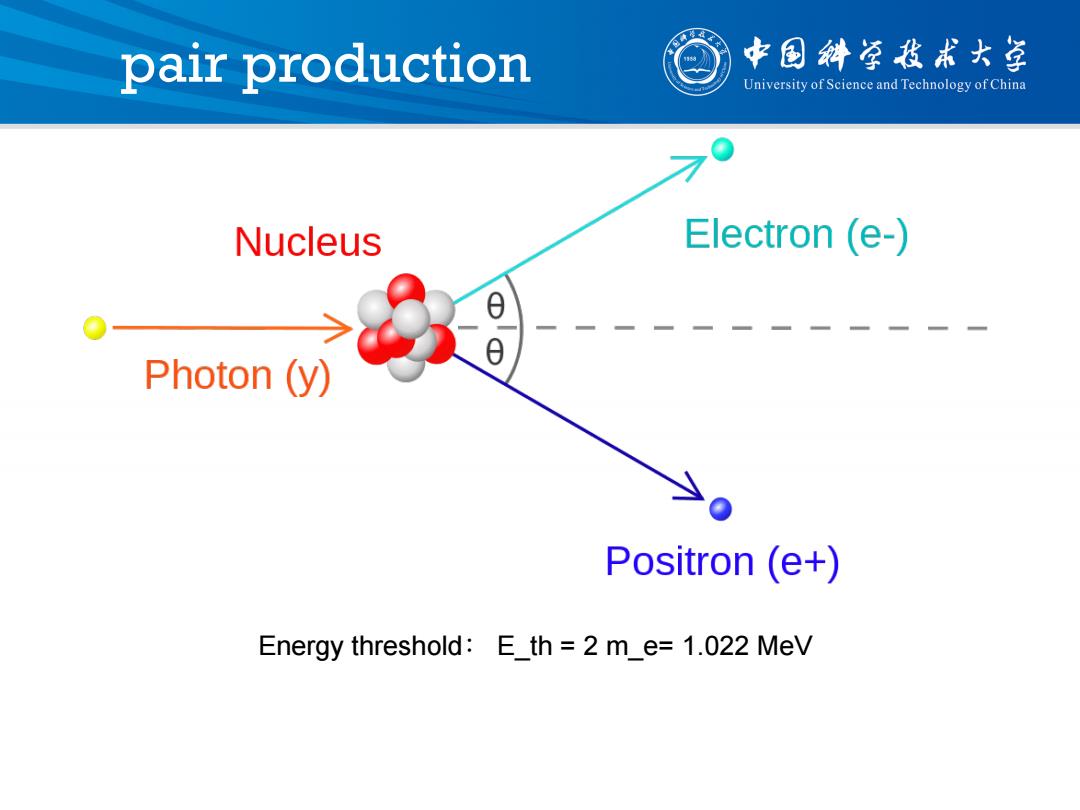
pair production 中国斜学我术大学 University of Science and Technology of China Nucleus Electron (e-) Photon (y) Positron (e+) Energy threshold:E_th 2 m_e=1.022 MeV
pair production Energy threshold: E_th = 2 m_e= 1.022 MeV
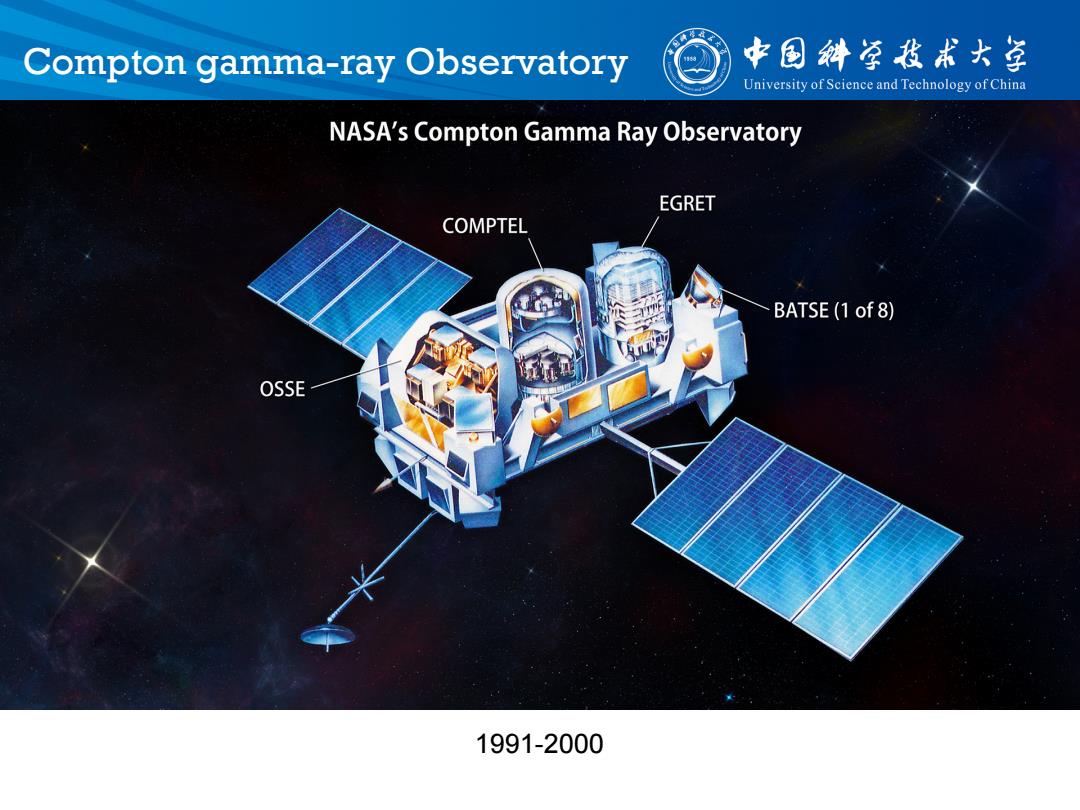
Compton gamma-ray Observatory 中国斜草我术大草 University of Science and Technology of China NASA's Compton Gamma Ray Observatory EGRET COMPTEL BATSE(1 of 8) OSSE 1991-2000
Compton gamma-ray Observatory 1991-2000
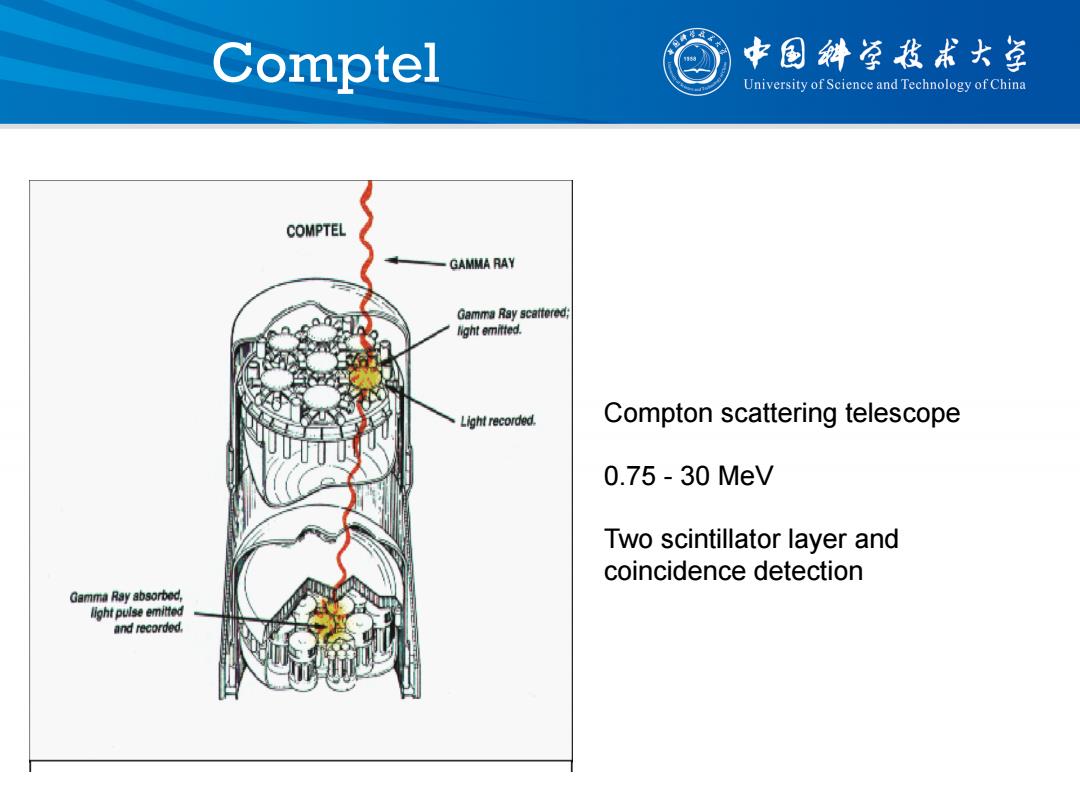
Comptel 中国斜学我术大学 University of Science and Technology of China COMPTEL GAMMA RAY Gamma Ray scattered; light emitted. Light recorded. Compton scattering telescope 0.75-30MeV Two scintillator layer and coincidence detection Gamma Ray absorbed, light pulse emitted and recorded
Comptel Compton scattering telescope 0.75 - 30 MeV Two scintillator layer and coincidence detection