
光谱应用
光谱应用
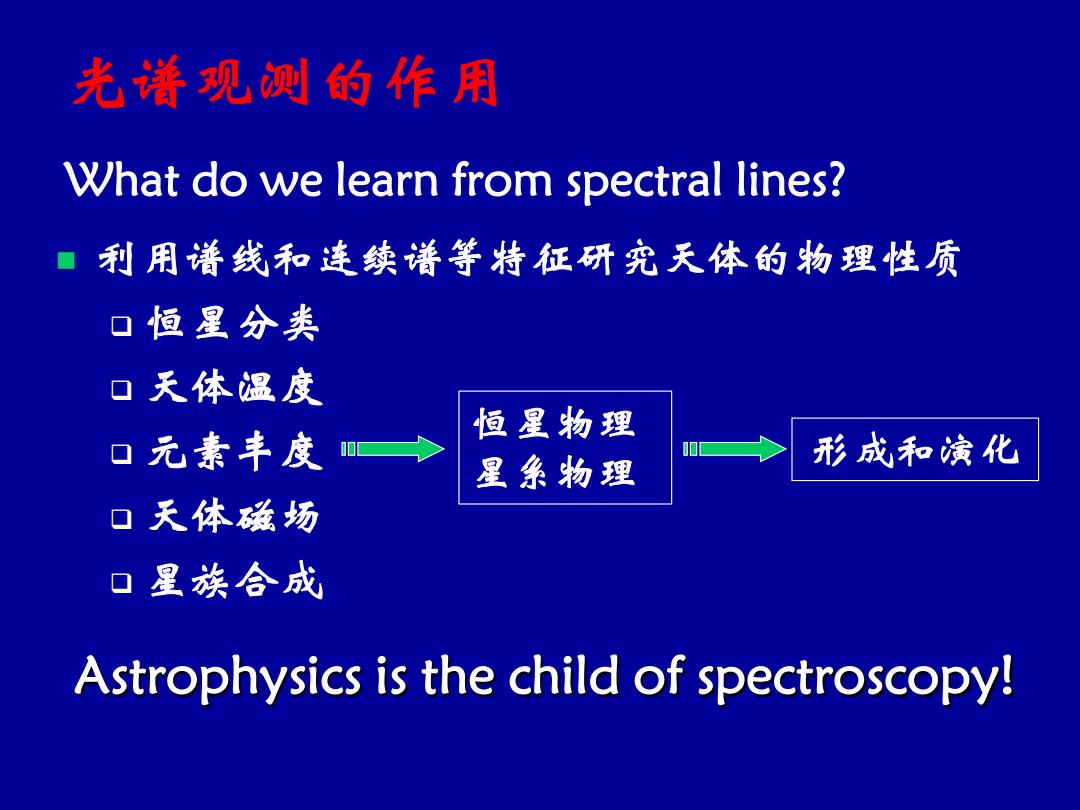
光着观测的作用 What do we learn from spectral lines? 利用谱线和连续谱等特征研究天体的物理性质 口恒星分类 口天体温度 恒星物理 口元素丰度 星系物理 形成和演化 口天体磁场 口星族合成 Astrophysics is the child of spectroscopy!
光谱观测的作用 n 利用谱线和连续谱等特征研究天体的物理性质 q 恒星分类 q 天体温度 q 元素丰度 q 天体磁场 q 星族合成 恒星物理 星系物理 形成和演化 Astrophysics is the child of spectroscopy! What do we learn from spectral lines?

光谱应用 1.恒星光谱分类 2.星系星族分析 3.星象自转速度 4.星际消光 5.话动星系分类 6.恒星形成率 7.测量气体电子密度 8.测量气体电子温度 9测量星系全属丰度
光谱应用 1. 恒星光谱分类 2. 星系星族分析 3. 星系自转速度 4. 星际消光 5. 活动星系分类 6. 恒星形成率 7. 测量气体电子密度 8. 测量气体电子温度 9. 测量星系金属丰度
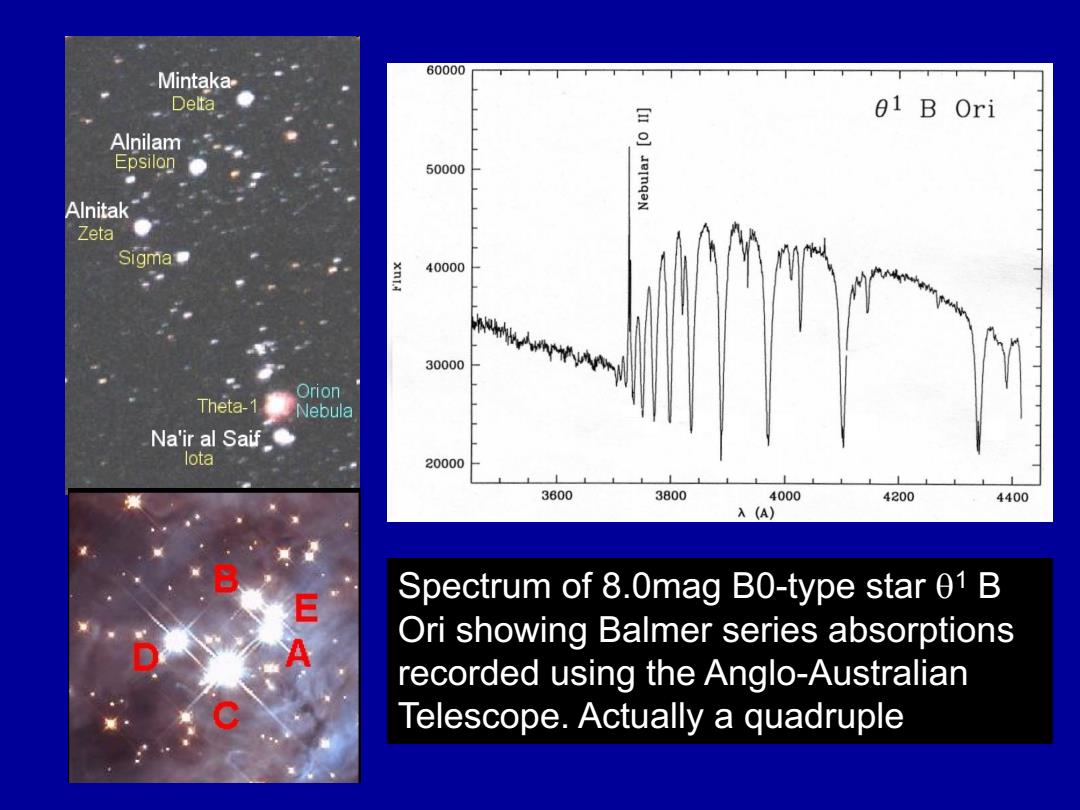
60000 Mintaka- Delta 01 B Ori Alnilam Epsilon 50000 JeInqaN Alnitak Zeta Sigma 40000 30000 Orion Theta-1 Nebula Na''ir al Saif● lota 20000 3600 3800 4000 4200 4400 入(A) E Spectrum of 8.0mag B0-type star 01 B A Ori showing Balmer series absorptions recorded using the Anglo-Australian Telescope.Actually a quadruple
Spectrum of 8.0mag B0-type star q1 B Ori showing Balmer series absorptions recorded using the Anglo-Australian Telescope. Actually a quadruple
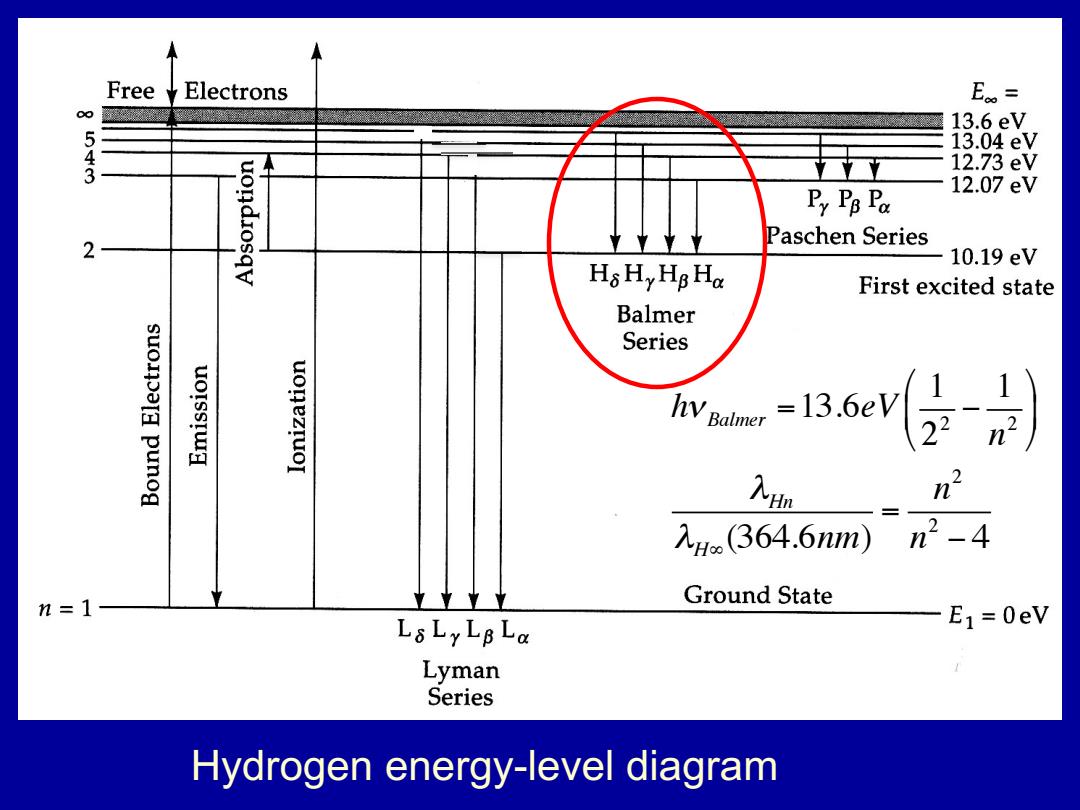
Free Electrons E。= 13.6eV 543 13.04eV 12.73eV 12.07eV Py PB Fa Paschen Series 2 10.19eV HsHyHg Ha First excited state Balmer Series uonezruol n 入H(364.6nm) n2-4 n=1 Ground State L8LyLBLa E1=0eV Lyman Series Hydrogen energy-level diagram
Hydrogen energy-level diagram hν Balmer =13.6eV 1 22 − 1 n 2 ⎛ ⎝ ⎜ ⎞ ⎠ ⎟ λHn λH∞ (364.6nm) = n 2 n 2 − 4

Balmer series f() Blackbody absorption lines Balmer series Balmer continuum limit 365nm Schematic spectrum of a star,showing hydrogen Balmer lines and continuum.Absorption in Balmer continuum causes large deviation of stellar continuum from a blackbody spectrum and the U-B color index difference
Schematic spectrum of a star, showing hydrogen Balmer lines and continuum. Absorption in Balmer continuum causes large deviation of stellar continuum from a blackbody spectrum and the U-B color index difference
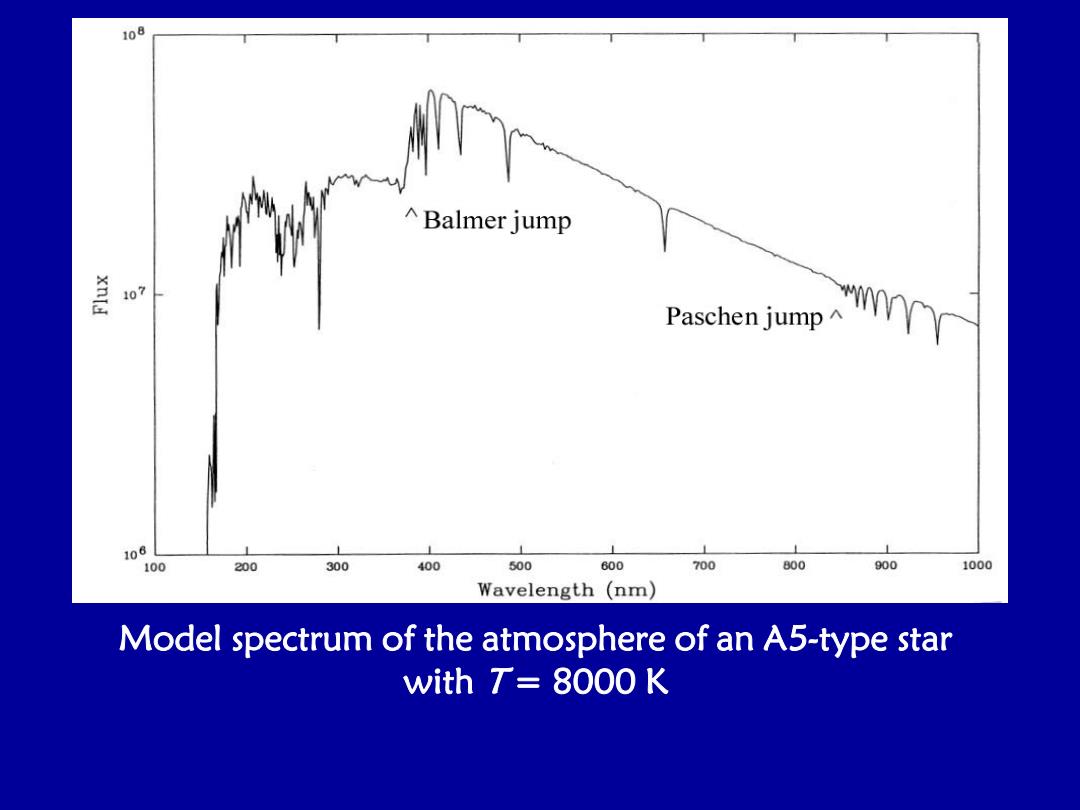
108 ^Balmer jump 盖 107 Pascthen jump 106 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Wavelength (nm) Model spectrum of the atmosphere of an A5-type star with T=8000 K
Model spectrum of the atmosphere of an A5-type star with T = 8000 K
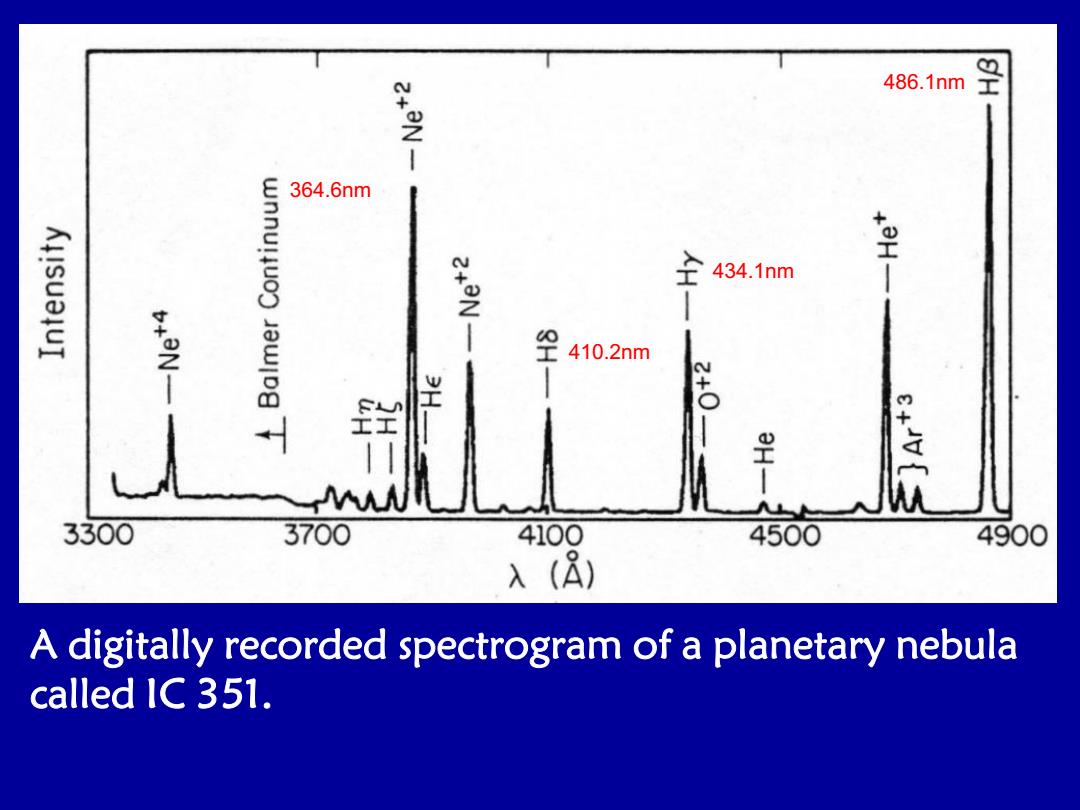
486.1nm 364.6nm 2+ON 434.1nm +2- 空 410.2nm 群 罡 3300 3700 4100 4500 4900 λ(A) A digitally recorded spectrogram of a planetary nebula called IC 351
A digitally recorded spectrogram of a planetary nebula called IC 351. 486.1nm 434.1nm 410.2nm 364.6nm

恒星的光谱分类 ■恒星光谱:连续谱上叠加 700 nmHydrogen- 400nm 吸收线,少数恒星兼有发射 30,000K 线,或只有发射线 Helium 20,000K B 光谱分类:恒星连续谱的 Carbon- Helium 能量分布,谱线的数目和强 10,000K Calcium 度,特征谱线种类 7000K Sodium-Magnesium Oxygen Iron 光谱差异:不是因为化学 6000K 成分的不同;而是在不同温 Oxygen 4000K 度和压力下由恒星大气物质 的激发和电离状态的变化形 3000K 成的。 Titanium axide -Methyladine (CH)
恒星的光谱分类 n 恒星光谱:连续谱上叠加 吸收线﹐少数恒星兼有发射 线﹐或只有发射线 n 光谱分类:恒星连续谱的 能量分布﹐谱线的数目和强 度﹐特征谱线种类 n 光谱差异:不是因为化学 成分的不同;而是在不同温 度和压力下由恒星大气物质 的激发和电离状态的变化形 成的
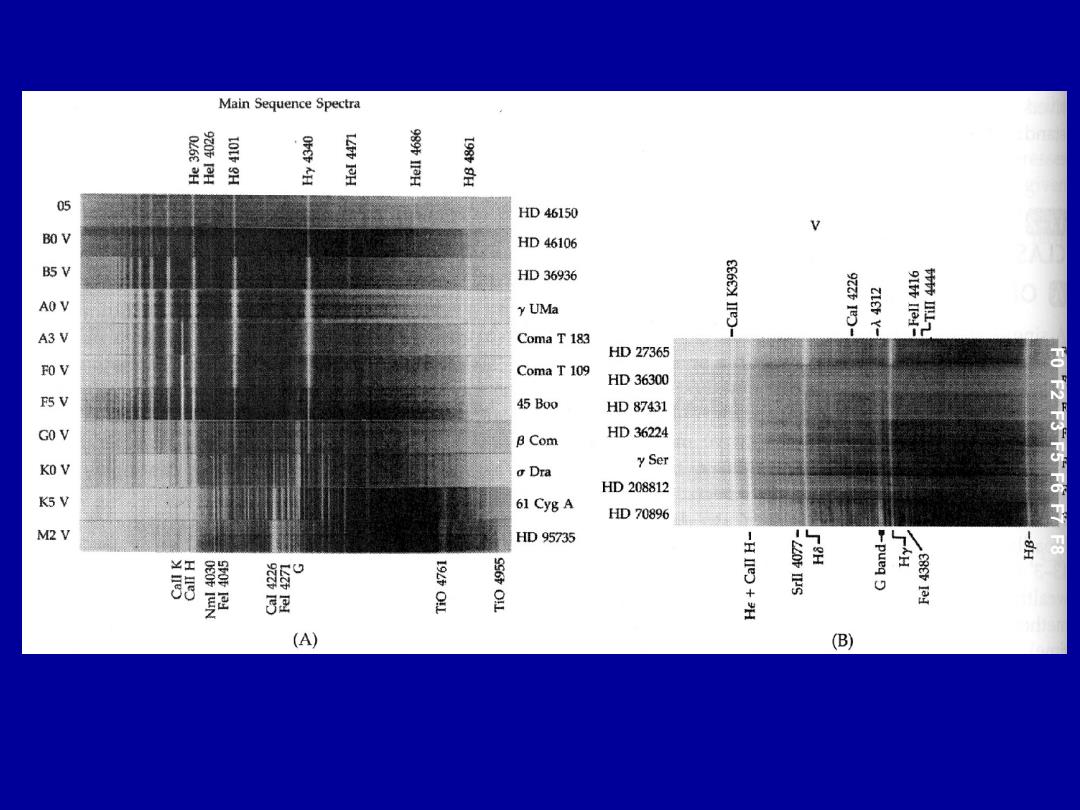
Main Sequence Spectra L049L 19940H 05 HD46150 BO V HD46106 B5 V HD36936 y UMa 196V1 A3 V Coma T 183 HD27365 FO V Coma T 109 HD36300 F5 V 45Bo0 HD87431 GO V B Com HD36224 KO V y Ser oDra HD208812 F0 F2 F3F5 F6 F7 K5 V 61 Cyg A HD70896 M2V HD95735 ¥工 W56603 -H Il +H H pueq 189610 32 (A) (B)
F0 F2 F3 F5 F6 F7 F8