
Machine Components Introduction to Engineering
1 Introduction to Engineering Machine Components

Bearings 2 Introduction to Engineering
2 Introduction to Engineering Bearings Bearings Bearings
"Bearing"-Definitions A device that >Supports >Guides >Reduces the friction of motion between fixed and moving machine parts Introduction to Engineering
3 Introduction to Engineering “Bearing” –Definitions A device that Supports Guides Reduces the friction of motion between fixed and moving machine parts

Bearing Types Journal bearings >Rolling-element bearings Introduction to Engineering
4 Introduction to Engineering Bearing Types Journal bearings Rolling-element bearings

Lubrication & Journal Bearings 0 5 Introduction to Engineering
5 Introduction to Engineering Lubrication & Journal Bearings Lubrication & Lubrication & Journal Bearings Journal Bearings

Lubricant Purposes Prevent metal-to-metal contact Remove or help dissipate heat Protect metal surfaces from corrosion Protect parts from contamination Any interposed substance that reduces friction and wear is a lubricant Lubricants are usually liquid but can be a solid,such as graphite,or a gas,such as pressurized air 6 Introduction to Engineering
6 Introduction to Engineering Lubricant Purposes Prevent metal-to-metal contact Remove or help dissipate heat Protect metal surfaces from corrosion Protect parts from contamination Any interposed substance that reduces friction and wear is a lubricant Lubricants are usually liquid but can be a solid, such as graphite, or a gas, such as pressurized air

Liquid Lubricants ·Generally oils Characterized by their viscosity Introduction to Engineering
7 Introduction to Engineering Liquid Lubricants • Generally oils • Characterized by their viscosity

Modern oil lubricants usually contain one or more additives designed to > Cause the oil to flow at lower temperatures Have less variation of viscosity with temperature Resist foaming when agitated by high-speed machinery Resist oxidation at high temperatures Prevent corrosion of metal surfaces > Reduce friction and wear when full lubricating films cannot be maintained 8 Introduction to Engineering
8 Introduction to Engineering Modern oil lubricants usually contain one or more additives designed to Cause the oil to flow at lower temperatures Have less variation of viscosity with temperature Resist foaming when agitated by high-speed machinery Resist oxidation at high temperatures Prevent corrosion of metal surfaces Reduce friction and wear when full lubricating films cannot be maintained

Greases Thickened liguid lubricants Can stay in position Prevent harmful contaminants from entering between the bearing surfaces Cannot circulate 9 Introduction to Engineering
9 Introduction to Engineering Greases Thickened liquid lubricants Can stay in position Prevent harmful contaminants from entering between the bearing surfaces Cannot circulate
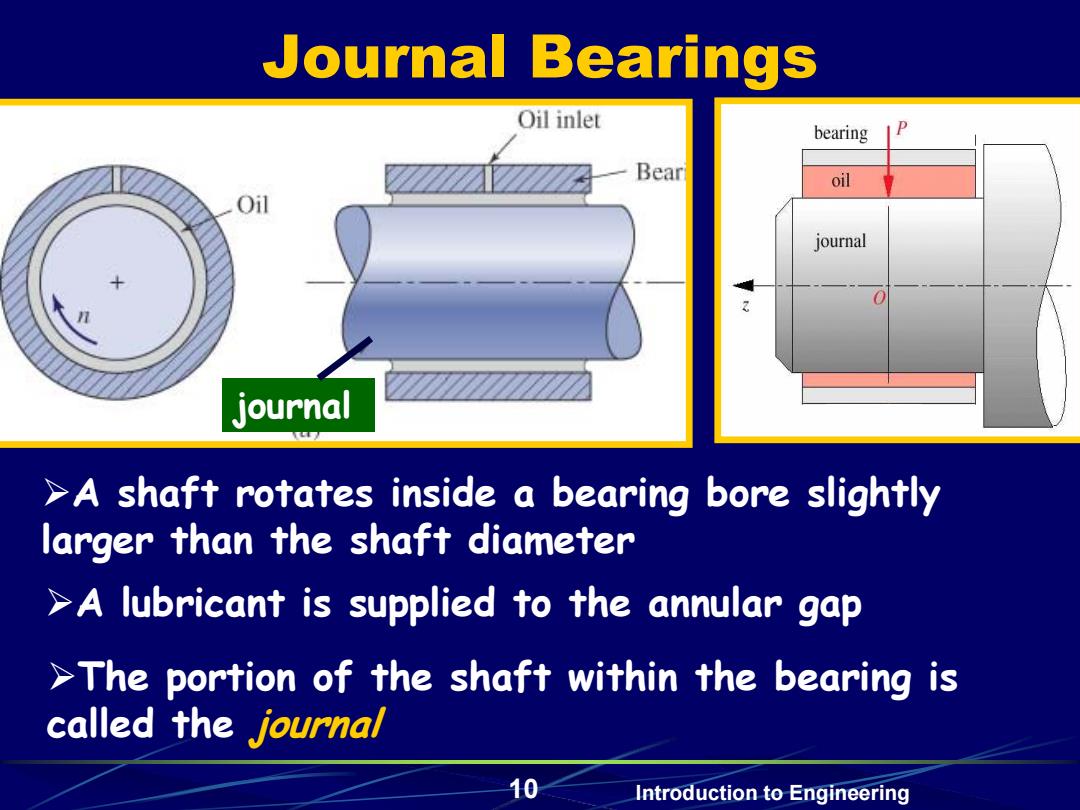
Journal Bearings Oil inlet bearing D Beart oil Oil journal journal >A shaft rotates inside a bearing bore slightly larger than the shaft diameter >A lubricant is supplied to the annular gap >The portion of the shaft within the bearing is called the journal 10 Introduction to Engineering
10 Introduction to Engineering Journal Bearings A shaft rotates inside a bearing bore slightly larger than the shaft diameter journal A lubricant is supplied to the annular gap The portion of the shaft within the bearing is called the journal