
上游充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Chapter 5 Product Specifications HAI 1月回后
Chapter 5 Product Specifications

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Product Design and Development Karl T.Ulrich and Steven D.Eppinger 5th edition,Irwin McGraw-Hill,2012. Chapter Table of Contents: 1.Introduction 2.Development Processes and Organizations 3.Product Planning 4.Identifying Customer Needs 5.Product Specifications 6.Concept Generation 7.Concept Selection 8.Concept Testing 9.Product Architecture 10.Industrial Design 11.Design for Environment 12.Design for Manufacturing 13.Prototyping 14.Robust Design 15.Patents and Intellectual Property FIFTH EDITION 16.Product Development Economics Product Design 17.Managing Projects and Development KARL T.ULRICH STEVEN D.EPPINGER
Product Design and Development Karl T. Ulrich and Steven D. Eppinger 5th edition, Irwin McGraw-Hill, 2012. Chapter Table of Contents: 1.Introduction 2.Development Processes and Organizations 3.Product Planning 4.Identifying Customer Needs 5.Product Specifications 6.Concept Generation 7.Concept Selection 8.Concept Testing 9.Product Architecture 10.Industrial Design 11.Design for Environment 12.Design for Manufacturing 13.Prototyping 14.Robust Design 15.Patents and Intellectual Property 16.Product Development Economics 17.Managing Projects

上游充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY What are Specifications? Product specifications represent an unambiguous agreement on what the team will attempt to achieve in order to satisfy the customer needs. It doesn't tell the team how to address the customer needs It is the precise description of what the product has to do. From Product Design and Development by Karl Ulrich and Steven Eppinger (McGraw-Hill/Irwin)
What are Specifications? Product specifications represent an unambiguous agreement on what the team will attempt to achieve in order to satisfy the customer needs. It doesn’t tell the team how to address the customer needs It is the precise description of what the product has to do

上游充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Product Specifications Example: Mountain Bike Suspension Fork 购 00
Product Specifications Example: Mountain Bike Suspension Fork

cǚtome降Needs for the Suspension Fork and SHANGHAI JIAU TONG UN Their relative importance # NEED Imp 1 The suspension reduces vibration to the hands 3 2 The suspension allows easy traversal of slow,difficult terrain. 2 3 The suspension enables high speed descents on bumpy trails. 5 4 The suspension|allows sensitivity adjustment. 3 5 The suspension preserves the steering characteristics of the bike. 4 6 The suspension remains rigid during hard cornering. 4 7 The suspension is lightweight. 4 8 The suspension provides stiff mounting points for the brakes. 2 9 The suspension fits a wide variety of bikes,wheels,and tires. 5 10 The suspension is easy to install. 11 The suspension works with fenders. 12 The suspension instills pride. 5 13 The suspension is affordable for an amateur enthusiast. 5 14 The suspension is not contaminated by water. 5 15 The suspension is not contaminated by grunge. 5 16 The suspension can be easily accessed for maintenance. 3 17 The suspension allows easy replacement of worn parts. 1 18 The suspension can be maintained with readily available tools. 3 19 The suspension lasts a long time. 5 20 The suspension is safe in a crash. 5
Customer Needs for the Suspension Fork and Their relative importance
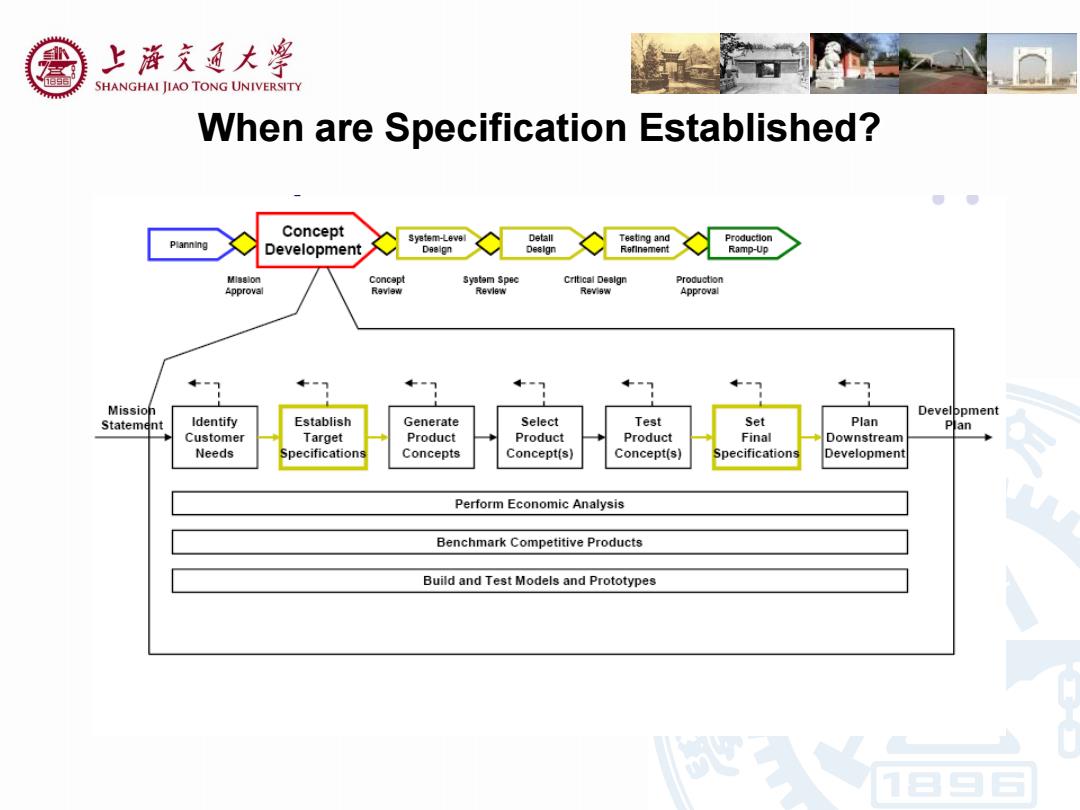
上游充通大 e SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY When are Specification Established? Concept Syetem-Level Detall Testing and Productlon Development Ramp-Up System Spec Critical Design Production Approval Revlew Revlew Review Approval Mission Develppment Statement Identify Establish Generate Select Test Set Plan Plan Customer Target Product Product Product Final Downstream Needs Specifications Concepts Concept(s) Concept(s) Specifications Development Perform Economic Analysis Benchmark Competitive Products Build and Test Models and Prototypes
When are Specification Established?
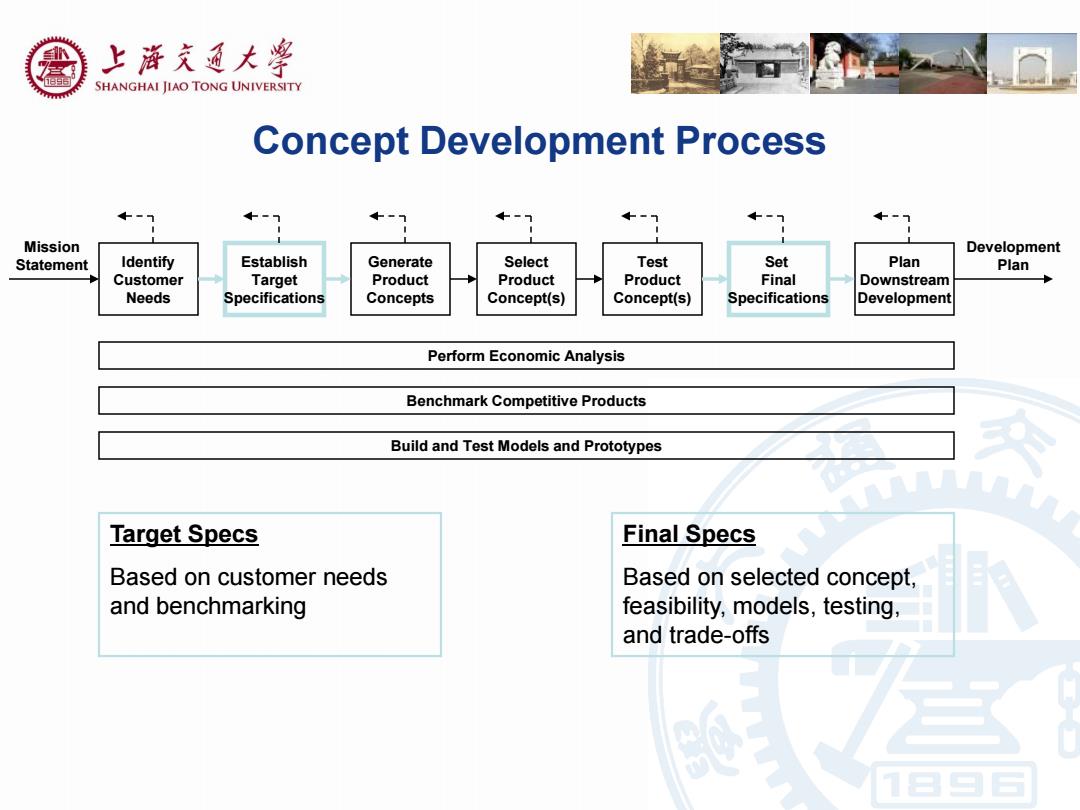
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Concept Development Process Mission Development Statement Identify Establish Generate Select Test Set Plan Plan Customer Target Product Product Product Final Downstream Needs Specifications Concepts Concept(s) Concept(s) Specifications Development Perform Economic Analysis Benchmark Competitive Products Build and Test Models and Prototypes Target Specs Final Specs Based on customer needs Based on selected concept, and benchmarking feasibility,models,testing, and trade-offs
Concept Development Process Perform Economic Analysis Benchmark Competitive Products Build and Test Models and Prototypes Identify Customer Needs Establish Target Specifications Generate Product Concepts Select Product Concept(s) Set Final Specifications Plan Downstream Development Mission Statement Test Product Concept(s) Development Plan Target Specs Based on customer needs and benchmarking Final Specs Based on selected concept, feasibility, models, testing, and trade-offs

上游充通大 e SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY The Product Specs Process Set Target Specifications Based on customer needs and benchmarks >Develop metrics for each need >Set ideal and acceptable values Refine Specifications Based on selected concept and feasibility testing >Technical modeling >Trade-offs are critical Reflect on the Results and the Process >Critical for ongoing improvement
The Product Specs Process Set Target Specifications Based on customer needs and benchmarks Develop metrics for each need Set ideal and acceptable values Refine Specifications Based on selected concept and feasibility testing Technical modeling Trade-offs are critical Reflect on the Results and the Process Critical for ongoing improvement

上游充通大 e SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Establish Target Specifications The process of establishing the target specifications contains four steps: 1.Prepare the list of metrics. 2.Collect competitive benchmarking information. 3.Set ideal and marginally acceptable target values. 4.Reflect on results and the process
Establish Target Specifications The process of establishing the target specifications contains four steps: 1. Prepare the list of metrics. 2. Collect competitive benchmarking information. 3. Set ideal and marginally acceptable target values. 4. Reflect on results and the process
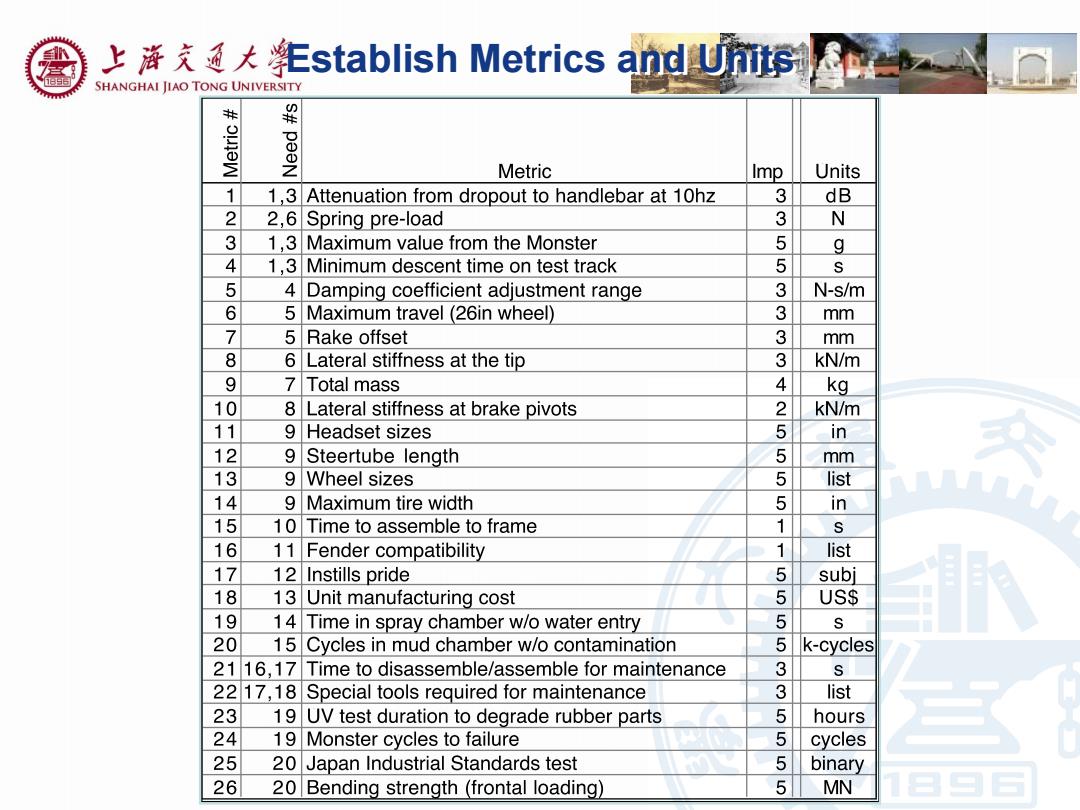
上译克通大Establish Metrics and Uhits e SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 粱 Metric Imp Units 1 1,3 Attenuation from dropout to handlebar at 10hz 3 dB 2 2,6 Spring pre-load 3 N 3 1,3 Maximum value from the Monster 5 g 4 1,3 Minimum descent time on test track 5 心 5 4Damping coefficient adjustment range 3 N-s/m 6 5Maximum travel(26in wheel) 3 mm 7 5 Rake offset 3 mm 8 6 Lateral stiffness at the tip 3 kN/m 9 7Total mass 4 kg 10 8 Lateral stiffness at brake pivots 2 kN/m 11 9 Headset sizes 5 in 12 9 Steertube length 5 mm 13 9 Wheel sizes 5 list 14 9Maximum tire width 5 in 15 10Time to assemble to frame 1 s 16 11 Fender compatibility 1 list 17 12 Instills pride 5 subj 18 13 Unit manufacturing cost 5 US$ 19 14Time in spray chamber w/o water entry 5 S 20 15 Cycles in mud chamber w/o contamination 5k-cycles 21 16,17 Time to disassemble/assemble for maintenance 3 s 22 17,18 Special tools required for maintenance 3 list 23 19 UV test duration to degrade rubber parts 5 hours 24 19 Monster cycles to failure 5 cycles 25 20Japan Industrial Standards test 5 binary 26 20 Bending strength(frontal loading) 5 MN
Establish Metrics and Units