
Chapter 20,part A Antimicrobial Drugs
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 20, part A Antimicrobial Drugs

Antimicrobial Drugs 。Chemotherapy The use of drugs to treat a disease 。Antimicrobial drugs Interfere with the growth of microbes within a host 。Antibiotic Substance produced by a microbe that,in small amounts, inhibits another microbe 。Selective toxicity A drug that kills harmful microbes without damaging the host
Antimicrobial Drugs • Chemotherapy The use of drugs to treat a disease • Antimicrobial drugs Interfere with the growth of microbes within a host • Antibiotic Substance produced by a microbe that, in small amounts, inhibits another microbe • Selective toxicity A drug that kills harmful microbes without damaging the host
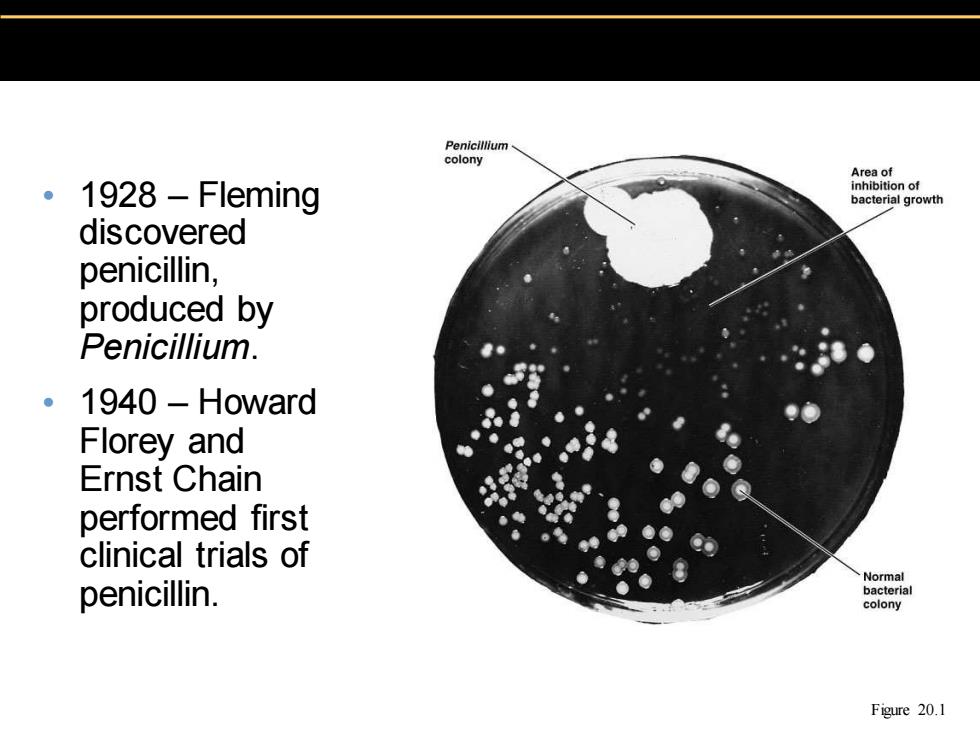
Penicillium colony Area of 。1928-Fleming inhibition of bacterial growth discovered penicillin, produced by Penicillium. 1940 Howard Florey and Ernst Chain performed first clinical trials of Normal penicillin. bacterial colony Figure 20.1
• 1928 – Fleming discovered penicillin, produced by Penicillium . • 1940 – Howard Florey and Ernst Chain performed first clinical trials of penicillin. Figure 20.1
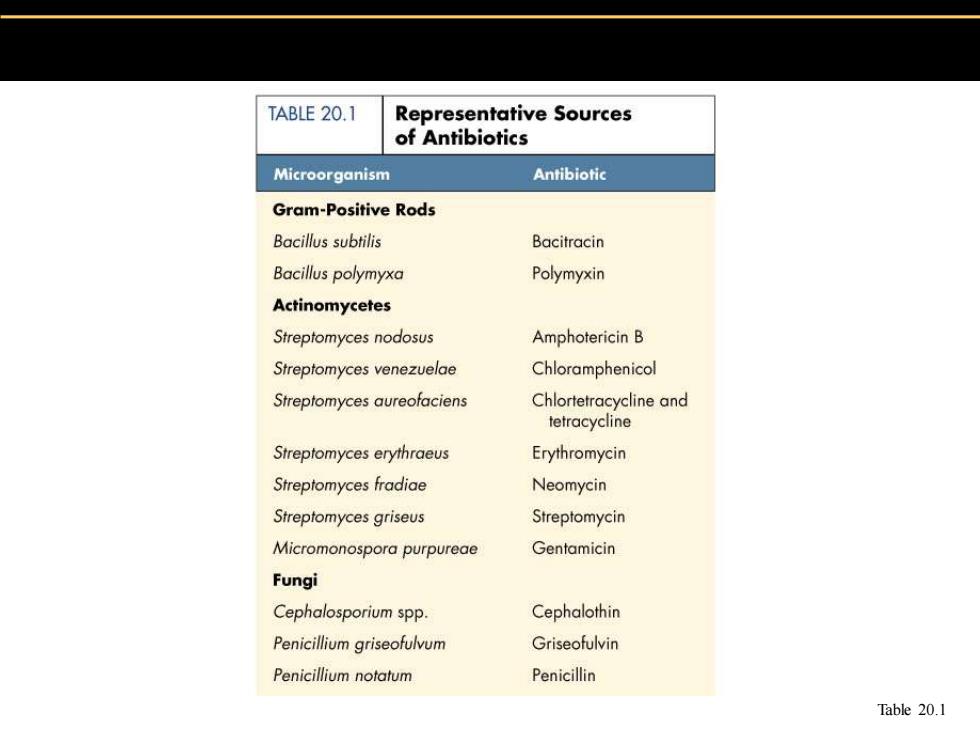
TABLE 20.1 Representative Sources of Antibiotics Microorganism Antibiotic Gram-Positive Rods Bacillus subtilis Bacitracin Bacillus polymyxa Polymyxin Actinomycetes Streptomyces nodosus Amphotericin B Streptomyces venezuelae Chloramphenicol Streptomyces aureofaciens Chlortetracycline and tetracycline Streptomyces erythraeus Erythromycin Streptomyces fradiae Neomycin Streptomyces griseus Streptomycin Micromonospora purpureae Gentamicin Fungi Cephalosporium spp. Cephalothin Penicillium griseofulvum Griseofulvin Penicillium notatum Penicillin Table 20.1
Table 20.1
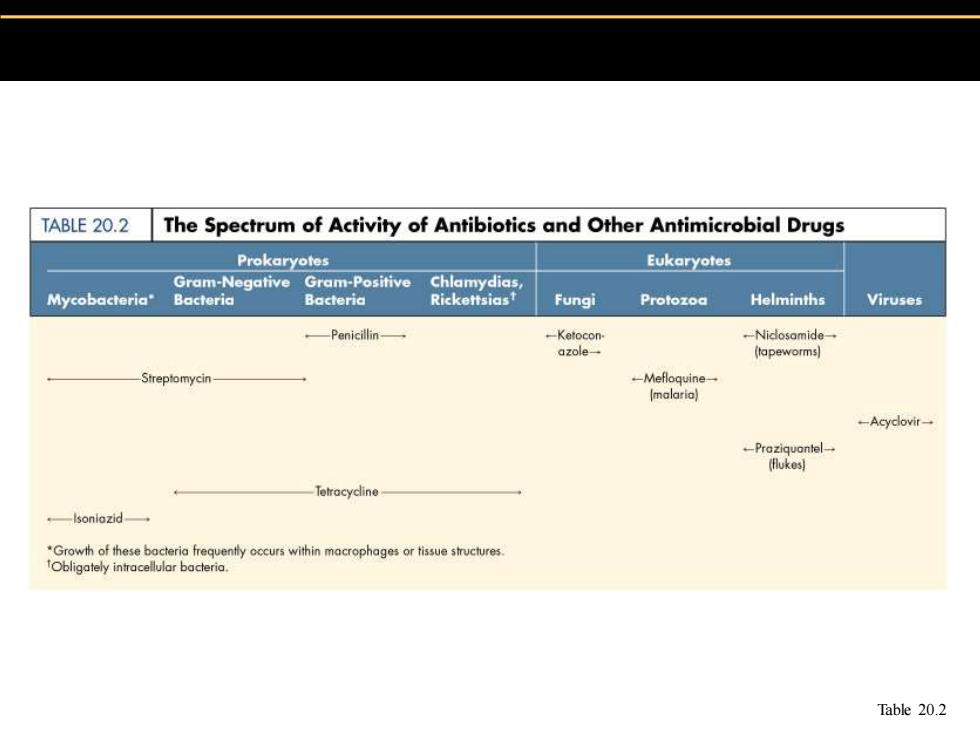
TABLE 20.2 The Spectrum of Activity of Antibiotics and Other Antimicrobial Drugs Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Gram-Negative Gram-Positive Chlamydias Mycobacteria" Bacteria Bacteria Rickettsias Fungi Protozoa Helminths Viruses —Penicil诽in一 -Ketocon -Niclosamide azole (tapeworms] Streptomycin- -Mefloquine一 (malaria) -Acyclovir- -Praziquontel-一 (flukes] Tetracycline -lsoniozid *Growth of these bacteria frequently occurs within macrophages or tissue structures. Obligately inraceuabacterio. Table 20.2
Table 20.2

The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs 。Broad-spectrum 。Superinfection 。Bactericidal Bacteriostatic
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs • Broad-spectrum • Superinfection • Bactericidal • Bacteriostatic
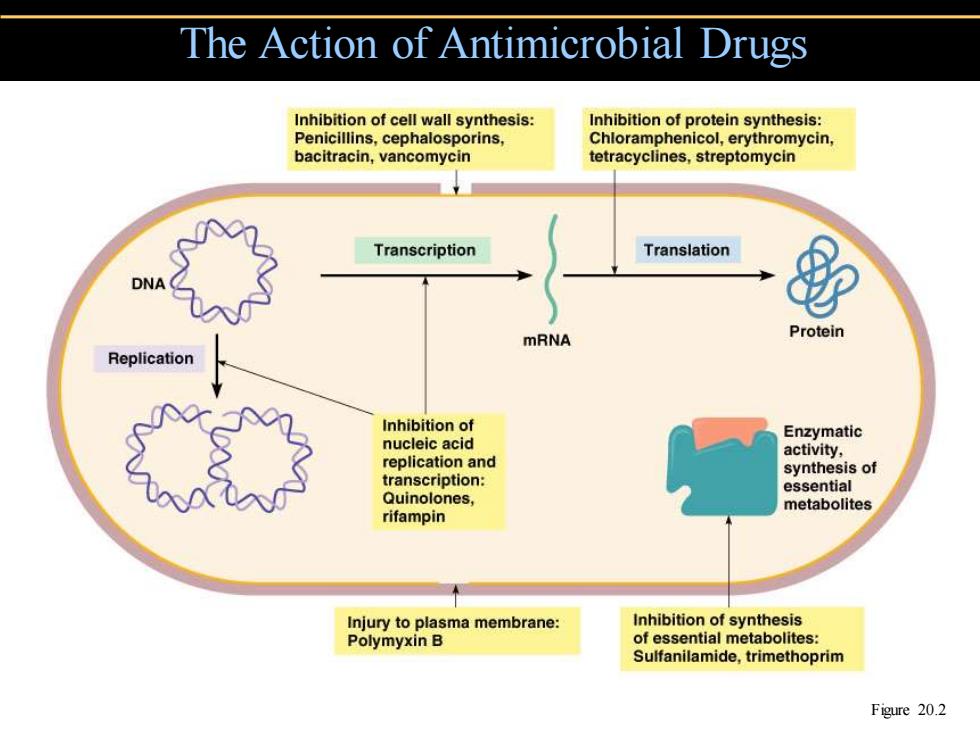
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Inhibition of cell wall synthesis: Inhibition of protein synthesis: Penicillins,cephalosporins, Chloramphenicol,erythromycin, bacitracin,vancomycin tetracyclines,streptomycin Transcription Translation mRNA Protein Replication Inhibition of Enzymatic nucleic acid activity, replication and synthesis of transcription: essential Quinolones, metabolites rifampin Injury to plasma membrane: Inhibition of synthesis Polymyxin B of essential metabolites: Sulfanilamide,trimethoprim Figure 20.2
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Figure 20.2
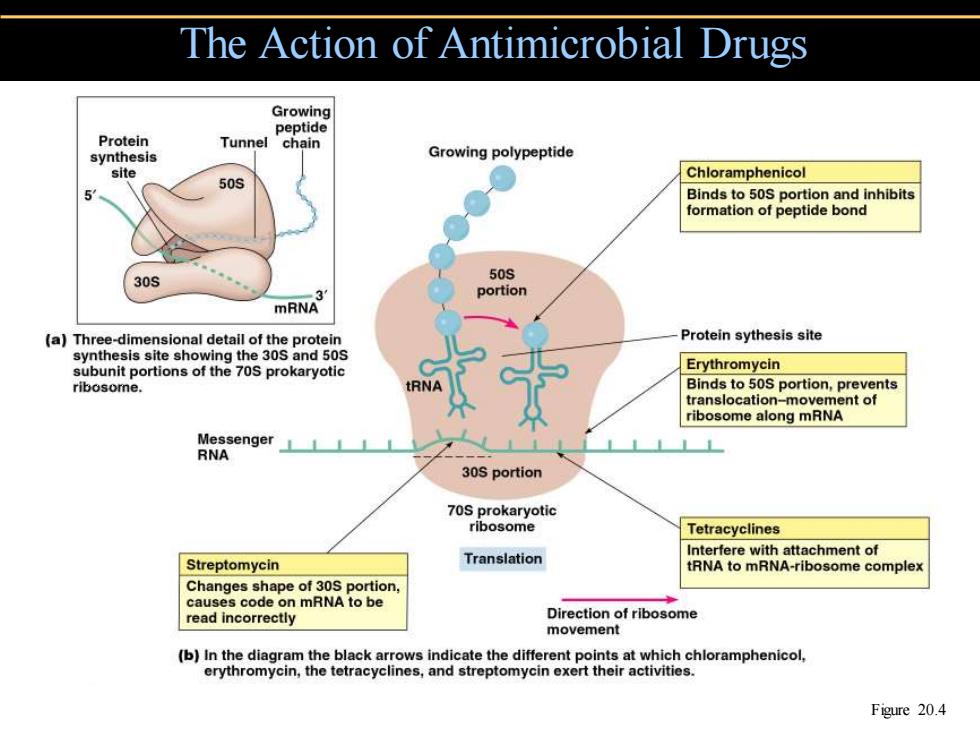
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Growing peptide Protein Tunnel chain synthesis Growing polypeptide site Chloramphenicol 50S Binds to 50S portion and inhibits formation of peptide bond 30S 50S portion mRNA (a)Three-dimensional detail of the protein Protein sythesis site synthesis site showing the 30S and 50S subunit portions of the 70S prokaryotic Erythromycin ribosome. RNA Binds to 50S portion,prevents translocation-movement of ribosome along mRNA Messenger RNA 30S portion 70S prokaryotic ribosome Tetracyclines Interfere with attachment of Streptomycin Translation tRNA to mRNA-ribosome complex Changes shape of 30S portion. causes code on mRNA to be read incorrectly Direction of ribosome movement (b)In the diagram the black arrows indicate the different points at which chloramphenicol, erythromycin,the tetracyclines,and streptomycin exert their activities. Figure 20.4
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Figure 20.4
Antibacterial Antibiotics Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis 。Penicillin ·Natural penicillins Semisynthetic penicillins
• Penicillin • Natural penicillins • Semisynthetic penicillins Antibacterial Antibiotics Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis

Penicillins Common nucleus S、/CH Penicillin G(Requires injection) CH2-C-NH-CH-CH C CH2 O=C—N—CH-COOH 0 S、/CH Penicillin V(Can be taken orally) OCH2-C-NH-CH-CH O-CN CH COOM B-lactam ring (a)Natural(antibiotic)penicillins Common nucleus 0 S、CH Oxacillin C-NH-CH-CH (Resistant to penicillinase) CH3 0=C十N—GHC地ooH B-lactam ring S、CH Ampicillin(Extended spectrum) CH-C-NH-CH-CH CH3 NH2 O=C—N—CH-COOH (b)Semisynthetic penicillins Figure 20.6
Penicillins Figure 20.6