
Chapter 9,part A Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 9, part A Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA
Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA 。 Biotechnology: The use of microorganisms,cells,or cell components to make a product Foods,antibiotics,vitamins,enzymes Recombinant DNA Technology: Insertion or modification of genes to produce desired proteins
Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA • Biotechnology: • The use of microorganisms, cells, or cell components to make a product • Foods, antibiotics, vitamins, enzymes • Recombinant DNA Technology: • Insertion or modification of genes to produce desired proteins
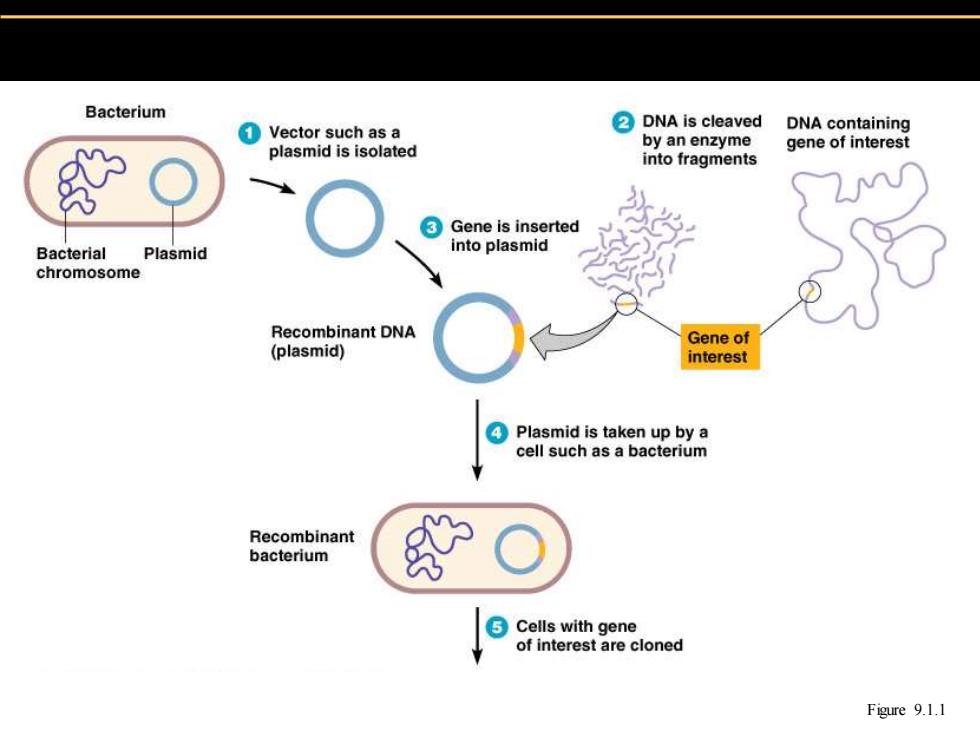
Bacterium ①Vector such as a DNA is cleaved DNA containing by an enzyme plasmid is isolated gene of interest into fragments 3 Gene is inserted Bacterial Plasmid into plasmid chromosome Recombinant DNA Gene of (plasmid) interest Plasmid is taken up by a cell such as a bacterium Recombinant bacterium ⑤Cells with gene of interest are cloned Figure 9.1.1
Figure 9.1.1
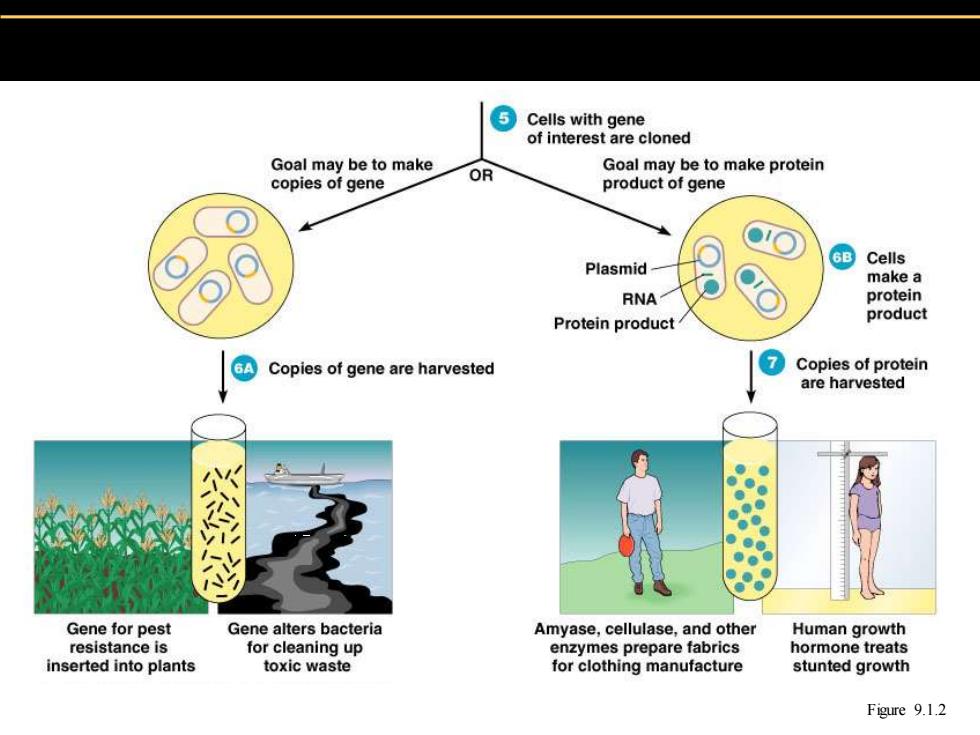
Cells with gene of interest are cloned Goal may be to make OR Goal may be to make protein copies of gene product of gene 6B Cells Plasmid make a RNA protein Protein product product Copies of gene are harvested Copies of protein are harvested ● Gene for pest Gene alters bacteria Amyase,cellulase,and other Human growth resistance is for cleaning up enzymes prepare fabrics hormone treats inserted into plants toxic waste for clothing manufacture stunted growth Figure 9.1.2
Figure 9.1.2
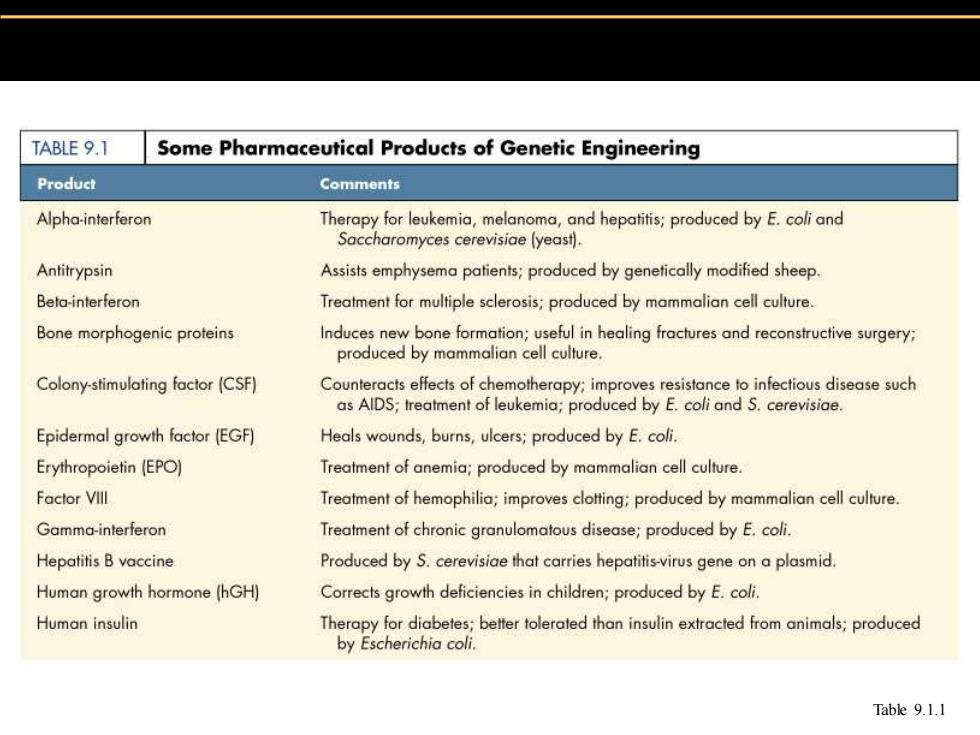
TABLE 9.1 Some Pharmaceutical Products of Genetic Engineering Product Comments Alpha-interferon Therapy for leukemia,melanoma,and hepatitis;produced by E.coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast). Antitrypsin Assists emphysema patients;produced by genetically modified sheep. Beta-interferon Treatment for multiple sclerosis;produced by mammalian cell culture. Bone morphogenic proteins Induces new bone formation;useful in healing fractures and reconstructive surgery; produced by mammalian cell culture. Colony-stimulating factor (CSF) Counteracts effects of chemotherapy:improves resistance to infectious disease such as AlDS;treatment of leukemia;produced by E.coli and S.cerevisiae. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) Heals wounds,burns,ulcers;produced by E.coli. Erythropoietin (EPO) Treatment of anemia;produced by mammalian cell culture. Factor VIlI Treatment of hemophilia;improves clotting:produced by mammalian cell culture. Gamma-interferon Treatment of chronic granulomatous disease;produced by E.coli. Hepatitis B vaccine Produced by S.cerevisiae that carries hepatitis-virus gene on a plasmid. Human growth hormone (hGH) Corrects growth deficiencies in children;produced by E.coli. Human insulin Therapy for diabetes;better tolerated than insulin extracted from animals;produced by Escherichia coli. Table 9.1.1
Table 9.1.1
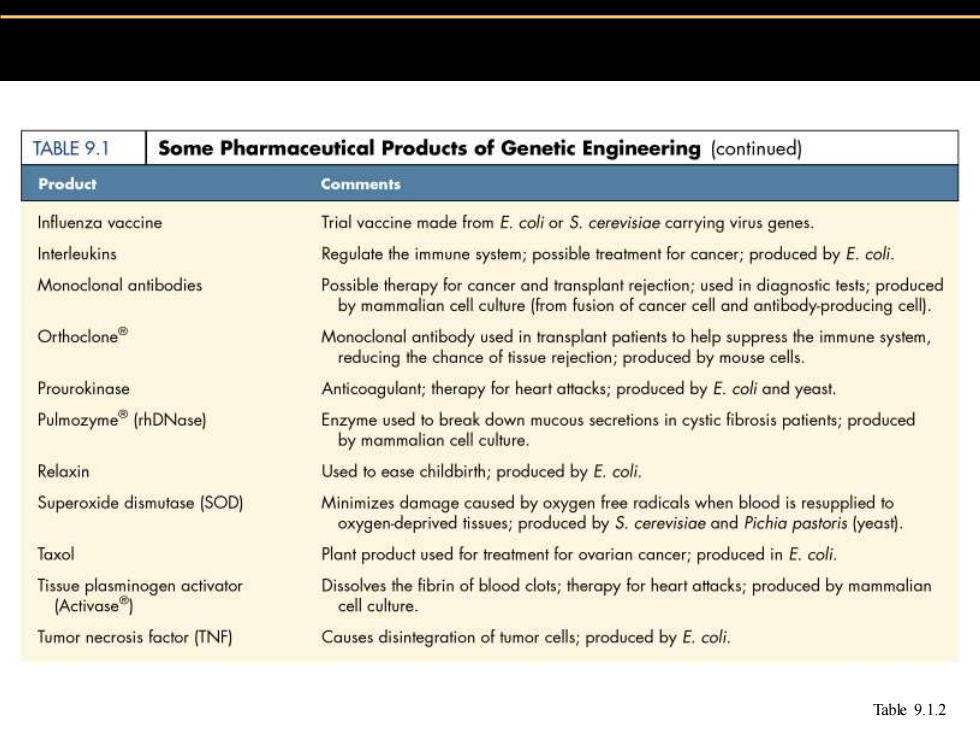
TABLE 9.1 Some Pharmaceutical Products of Genetic Engineering(continued) Product Comments Influenza vaccine Trial vaccine made from E.coli or S.cerevisiae carrying virus genes. Interleukins Regulate the immune system;possible treatment for cancer;produced by E.coli. Monoclonal antibodies Possible therapy for cancer and transplant rejection;used in diagnostic tests;produced by mammalian cell culture(from fusion of cancer cell and antibody-producing cell). Orthoclone Monoclonal antibody used in transplant patients to help suppress the immune system, reducing the chance of tissue rejection;produced by mouse cells. Prourokinase Anticoagulant;therapy for heart attacks;produced by E.coli and yeast. Pulmozyme(rhDNase) Enzyme used to break down mucous secretions in cystic fibrosis patients;produced by mammalian cell culture. Relaxin Used to ease childbirth;produced by E.coli. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) Minimizes damage caused by oxygen free radicals when blood is resupplied to oxygen-deprived tissues;produced by S.cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris (yeast). Taxol Plant product used for treatment for ovarian cancer;produced in E.coli. Tissue plasminogen activator Dissolves the fibrin of blood clots;therapy for heart atacks;produced by mammalian (Activase) cell culture. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) Causes disintegration of tumor cells;produced by E.coli. Table 9.1.2
Table 9.1.2
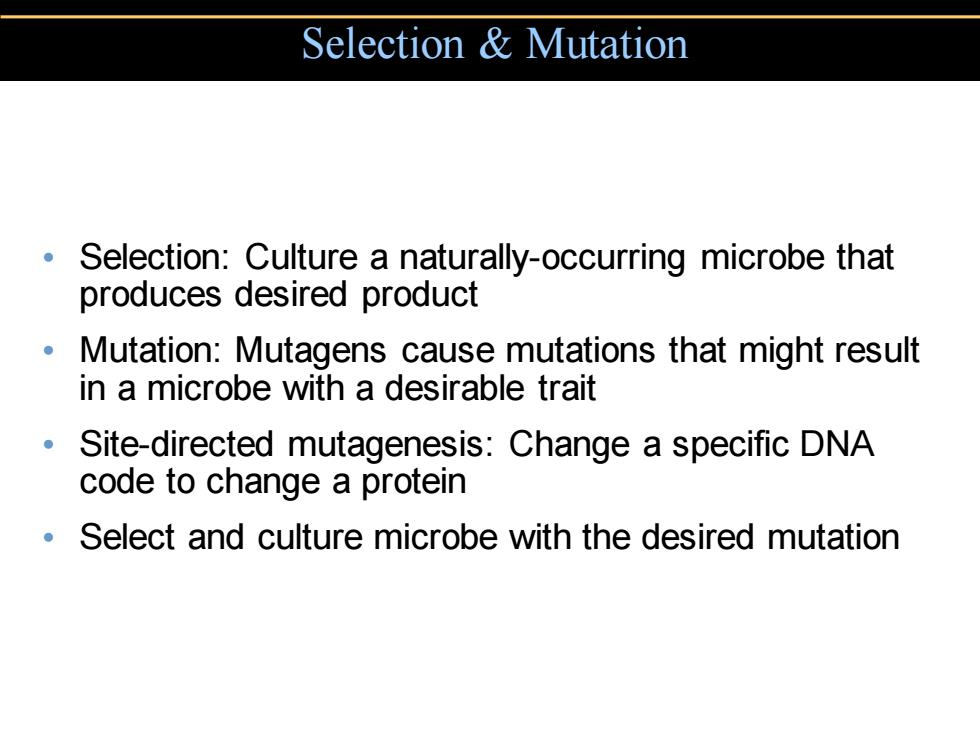
Selection Mutation Selection:Culture a naturally-occurring microbe that produces desired product Mutation:Mutagens cause mutations that might result in a microbe with a desirable trait ● Site-directed mutagenesis:Change a specific DNA code to change a protein Select and culture microbe with the desired mutation
• Selection: Culture a naturally-occurring microbe that produces desired product • Mutation: Mutagens cause mutations that might result in a microbe with a desirable trait • Site-directed mutagenesis: Change a specific DNA code to change a protein • Select and culture microbe with the desired mutation Selection & Mutation

Restriction Enzymes Cut specific sequences of DNA Destroy bacteriophage DNA in bacterial cells Cannot digest(host)DNA with methylated cytosines
• Cut specific sequences of DNA • Destroy bacteriophage DNA in bacterial cells • Cannot digest (host) DNA with methylated cytosines Restriction Enzymes
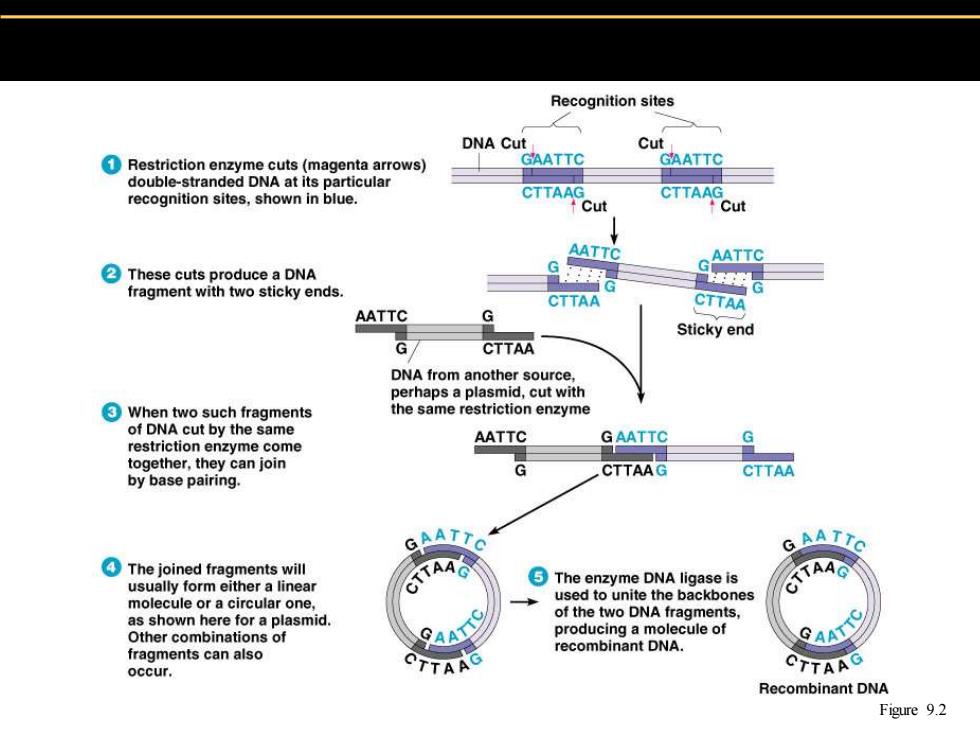
Recognition sites DNA Cut Cut Restriction enzyme cuts(magenta arrows) GAATTC GAATTC double-stranded DNA at its particular recognition sites,shown in blue. CTTAAG CTTAAG Cut cut AATTC AATTC These cuts produce a DNA G fragment with two sticky ends. G CTTAA CTTAA AATTC Sticky end CTTAA DNA from another source. perhaps a plasmid,cut with When two such fragments the same restriction enzyme of DNA cut by the same restriction enzyme come AATTC GAATTC ⊙ together,they can join CTTAAG CTTAA by base pairing. GAATIG The joined fragments will usually form either a linear TA。 The enzyme DNA ligase is molecule or a circular one, used to unite the backbones as shown here for a plasmid. of the two DNA fragments. Other combinations of GAAT producing a molecule of recombinant DNA. fragments can also occur. CTTAAG Recombinant DNA Figure 9.2
Figure 9.2

Vectors Carry new DNA to desired cell Shuttle vectors can exist in several different species Plasmids and viruses can be used as vectors
• Carry new DNA to desired cell • Shuttle vectors can exist in several different species • Plasmids and viruses can be used as vectors Vectors