
Chapter 12,part C The Eukaryotes:Fungi,Algae,Protozoa,and Helminths
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 12, part C The Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, and Helminths
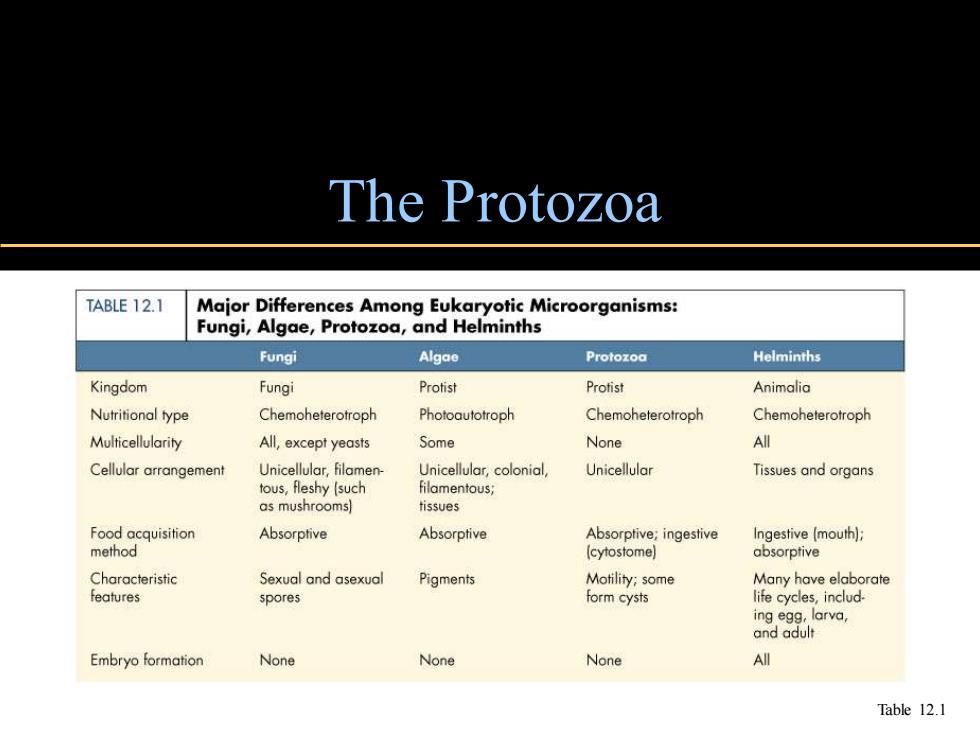
The Protozoa TABLE 12.1 Major Differences Among Eukaryotic Microorganisms: Fungi,Algae,Protozoa,and Helminths Fungi Algae Protozoa Helminths Kingdom Fungi Protist Protist Animalia Nutritional type Chemoheterotroph Photoautotroph Chemoheterotroph Chemoheterotroph Multicellularity All,except yeasts Some None All Cellular arrangement Unicellular,filamen- Unicellular,colonial, Unicellular Tissues and organs tous,fleshy (such filamentous; as mushrooms) tissues Food acquisition Absorptive Absorptive Absorptive;ingestive Ingestive (mouth); method (cytostome) absorptive Characteristic Sexual and asexual Pigments Motility;some Many have elaborate features spores form cysts life cycles,includ. ing egg,larva, and adult Embryo formation None None None All Table 12.1
The Protozoa Table 12.1
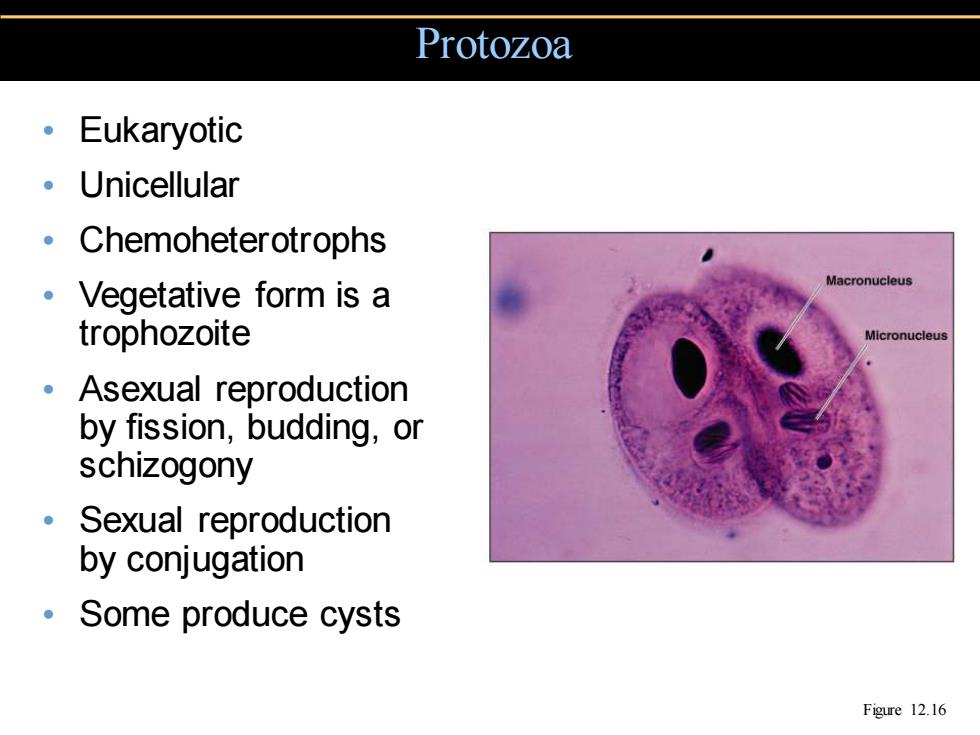
Protozoa 。Eukaryotic 。Unicellular 。Chemoheterotrophs 。Vegetative form is a Macronucleus trophozoite Micronucleus Asexual reproduction by fission,budding,or schizogony 。Sexual reproduction by conjugation 。Some produce cysts Figure 12.16
• Eukaryotic • Unicellular • Chemoheterotrophs • Vegetative form is a trophozoite • Asexual reproduction by fission, budding, or schizogony • Sexual reproduction by conjugation • Some produce cysts Protozoa Figure 12.16
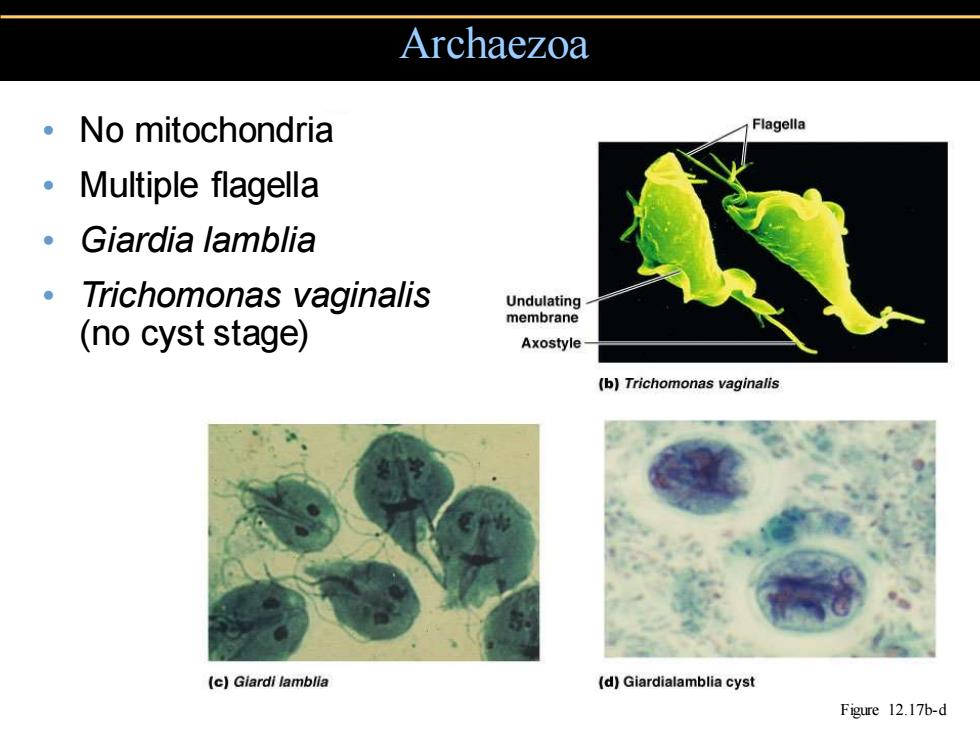
Archaezoa 。No mitochondria Flagella 。Multiple flagella 。Giardia lamblia Trichomonas vaginalis Undulating membrane (no cyst stage) Axostyle (b)Trichomonas vaginalis (c)Giardi lamblla (d)Giardialamblia cyst Figure 12.17b-d
• No mitochondria • Multiple flagella • Giardia lamblia • Trichomonas vaginalis (no cyst stage) Archaezoa Figure 12.17b-d

Microspora ·No mitochondria 。Nonmotile Intracellular parasites 。Nosema
• No mitochondria • Nonmotile • Intracellular parasites • Nosema Microspora

Rhizopoda (amoebas) Food vacuole 。love by Pseudopods pseudopods 。Entamoeba Nucleus 。Acanthamoeba (a)Amoeba proteus No jpeg for Figure 21.21 Figure 12.18a
• Move by pseudopods • Entamoeba • Acanthamoeba Rhizopoda (amoebas) No jpeg for Figure 21.21 Figure 12.18a

Apicomplexa 。Nonmotile Intracellular parasites 。 Complex life cycles 。Plasmodium 。Babesia Cryptosporidium Cyclospora
• Nonmotile • Intracellular parasites • Complex life cycles • Plasmodium • Babesia • Cryptosporidium • Cyclospora Apicomplexa

Plasmodium Sporozoites Infected mosquito bites Sporozoites in salivary human;sporozoites undergo gland migrate through schizogony in bloodstream to liver cell; liver of human merozoites are produced 9Resulting sporozoites migrate to salivary glands of mosquito 3Merozoites Sexual released into reproduction bloodsteam from liver may infect 8 In mosquito's Asexual new red blood Zygote cells digestive tract, reproduction gametocytes Female unite to form Intermediate host gametocyte zygote ④Merozoite develops Male into ring stage in red gametocyte blood cell Ring 5Ring stage stage grows and Definitive host divides, )Another mosquito bites 6Merozoites are released producing infected humnan and merozoites when red blood cell ingests gametocytes ruptures;some merozoites infect new red blood cells, and some develop into male and female gametocytes Merozoites Figure 12.19
Plasmodium Figure 12.19 Infected mosquito bites human; sporozoites migrate through bloodstream to liver of human Sporozoites undergo schizogony in liver cell; merozoites are produced Merozoites released into bloodsteam from liver may infect new red blood cells Merozoites are released when red blood cell ruptures; some merozoites infect new red blood cells, and some develop into male and female gametocytes 1 2 3 4 6 Asexual reproduction Intermediate host Merozoite develops into ring stage in red blood cell Ring stage Merozoites Another mosquito bites infected humnan and ingests gametocytes 7 5 Ring stage grows and divides, producing merozoites Definitive host In mosquito’s digestive tract, gametocytes unite to form zygote 8 Male gametocyte Female gametocyte Zygote Sexual reproduction Resulting sporozoites migrate to salivary glands of mosquito 9 Sporozoites in salivary gland
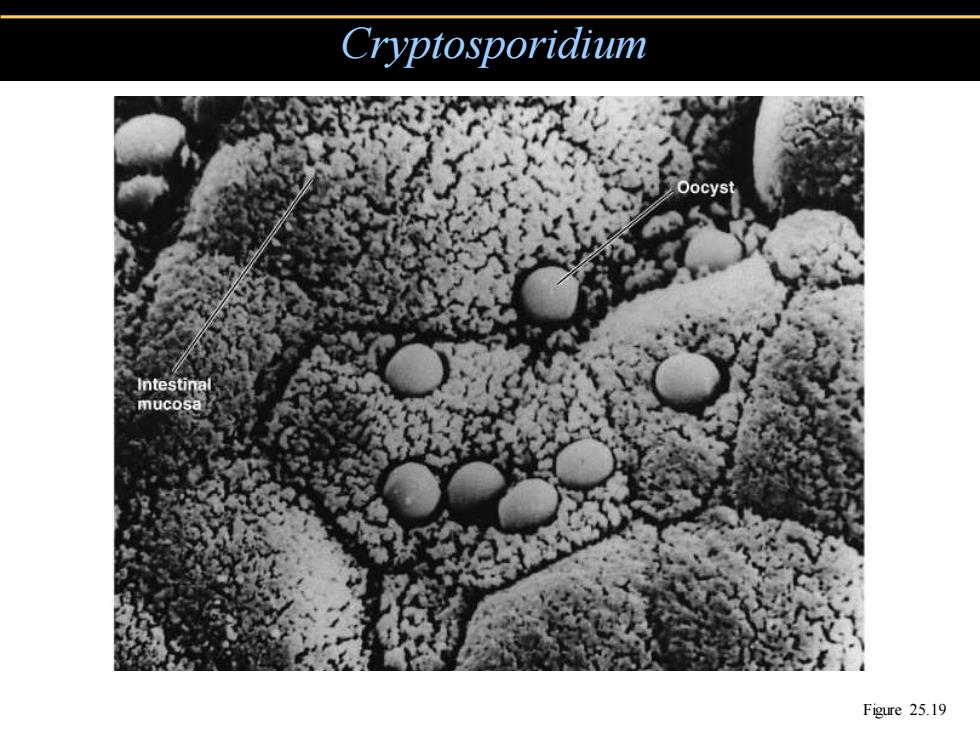
Cryptosporidium Intestina mucosa Figure 25.19
Cryptosporidium Figure 25.19
