
Chapter 25,part B Microbial Diseases of the Digestive System
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 25, part B Microbial Diseases of the Digestive System

Escherichia coli Gastroenteritis Occurs as traveler's diarrhea and epidemic diarrhea in nurseries 50%of feedlot cattle may have enterohemorrhagic strains in their intestines Enterohemorrhagic strains such as E.coli O157:H7 produce Shiga toxin ·o=cell wall antigen 。H=flagellar antigen
• Occurs as traveler's diarrhea and epidemic diarrhea in nurseries • 50% of feedlot cattle may have enterohemorrhagic strains in their intestines • Enterohemorrhagic strains such as E. coli O157:H7 produce Shiga toxin • O = cell wall antigen • H = flagellar antigen Escherichia coli Gastroenteritis

Campylobacter Gastroenteritis Campylobacter jejuni Usually transmitted in cow's milk
• Campylobacter jejuni • Usually transmitted in cow's milk Campylobacter Gastroenteritis
Helicobacter Peptic ulcer disease Flagella Treated with antibiotics ·H.pylori causes stomach cancer Figure 11.11
Helicobacter Peptic ulcer disease • Treated with antibiotics • H. pylori causes stomach cancer Figure 11.11
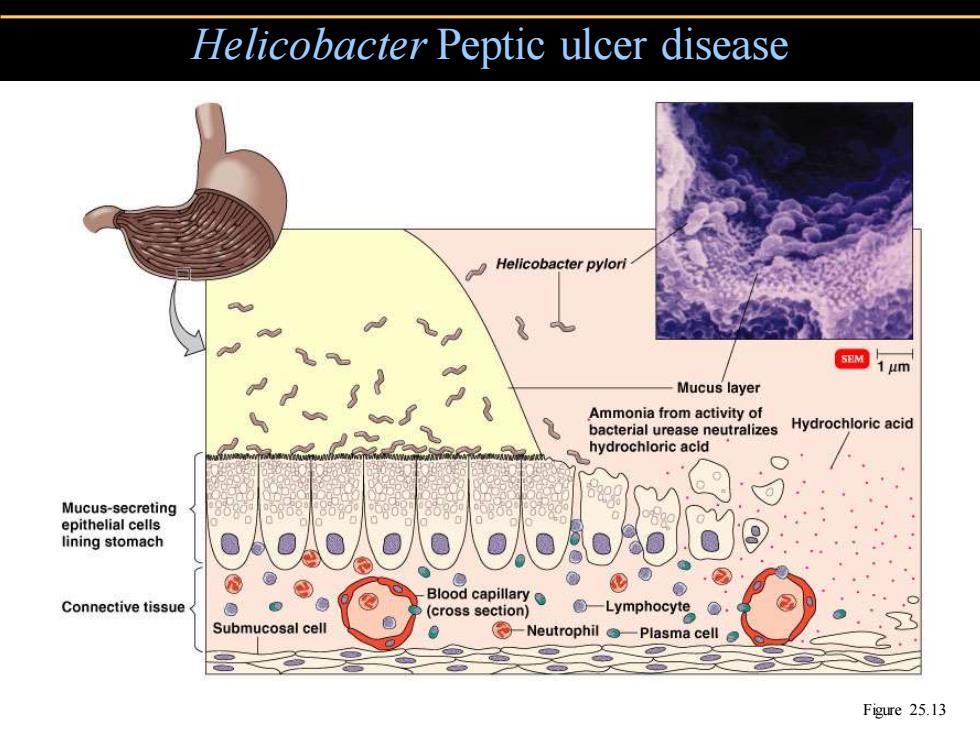
Helicobacter Peptic ulcer disease Helicobacter pylori 1um Mucus layer Ammonia from activity of bacterial urease neutralizes Hydrochloric acid hydrochloric acld Mucus-secreting epithelial cells lining stomach Blood capillary● Connective tissue (cross section) Lymphocyte Submucosal cell -Neutrophil -Plasma cell Figure 25.13
Helicobacter Peptic ulcer disease Figure 25.13

Yersinia Gastroenteritis Y.enterocolitica and Y.pseudotuberculosis ·Can reproduce at4°C Usually transmitted in meat and milk
• Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis • Can reproduce at 4°C • Usually transmitted in meat and milk Yersinia Gastroenteritis

Clostridium perfringens Gastroenteritis Grow in intestinal tract producing exotoxin
• Grow in intestinal tract producing exotoxin Clostridium perfringens Gastroenteritis

Bacillus cereus Gastroenteritis Ingestion of bacterial exotoxin produces mild symptoms
• Ingestion of bacterial exotoxin produces mild symptoms Bacillus cereus Gastroenteritis
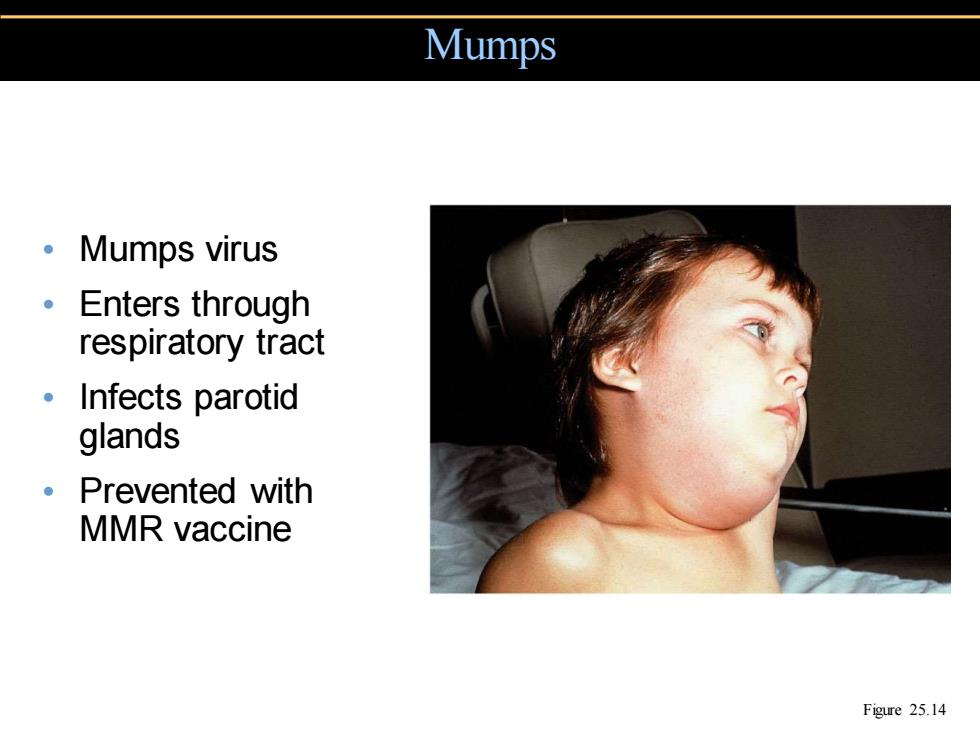
Mumps 。Mumps virus 。Enters through respiratory tract 。Infects parotid glands ·Prevented with MMR vaccine Figure 25.14
Mumps Figure 25.14 • Mumps virus • Enters through respiratory tract • Infects parotid glands • Prevented with MMR vaccine

Hepatitis Inflammation of the liver Hepatitis may result from drug or chemical toxicity,EB virus,CMV,or the Hepatitis viruses
• Inflammation of the liver • Hepatitis may result from drug or chemical toxicity, EB virus, CMV, or the Hepatitis viruses Hepatitis