
Chapter 8,part A Microbial Genetics
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 8, part A Microbial Genetics
Terminology Genetics Study of what genes are,how they carry information,how information is expressed,and how genes are replicated 。Gene Segment of DNA that encodes a functional product,usually a protein
Terminology • Genetics Study of what genes are, how they carry information, how information is expressed, and how genes are replicated • Gene Segment of DNA that encodes a functional product, usually a protein

Terminology Genome All of the genetic material in a cell Genomics Molecular study of genomes Genotype Genes of an organism 。Phenotype Expression of the genes
Terminology • Genome All of the genetic material in a cell • Genomics Molecular study of genomes • Genotype Genes of an organism • Phenotype Expression of the genes
E.coli Figure 8.1a
E. coli Figure 8.1a
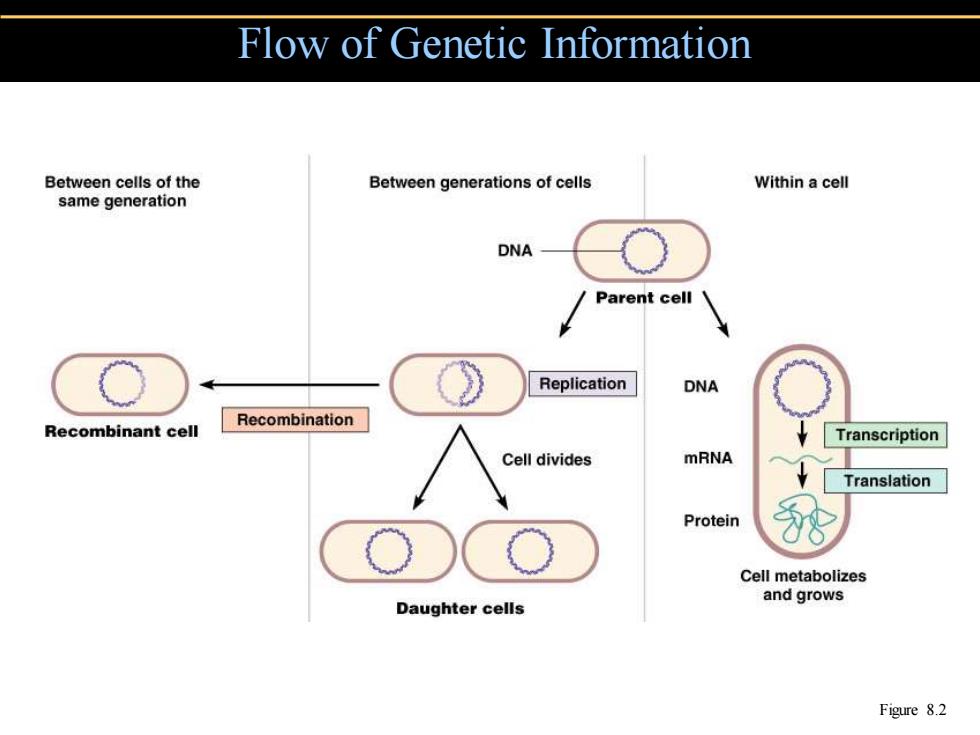
Flow of Genetic Information Between cells of the Between generations of cells Within a cell same generation DNA Parent cell Replication DNA Recombination Recombinant cell Transcription Cell divides mRNA Translation Protein Cell metabolizes and grows Daughter cells Figure 8.2
Flow of Genetic Information Figure 8.2
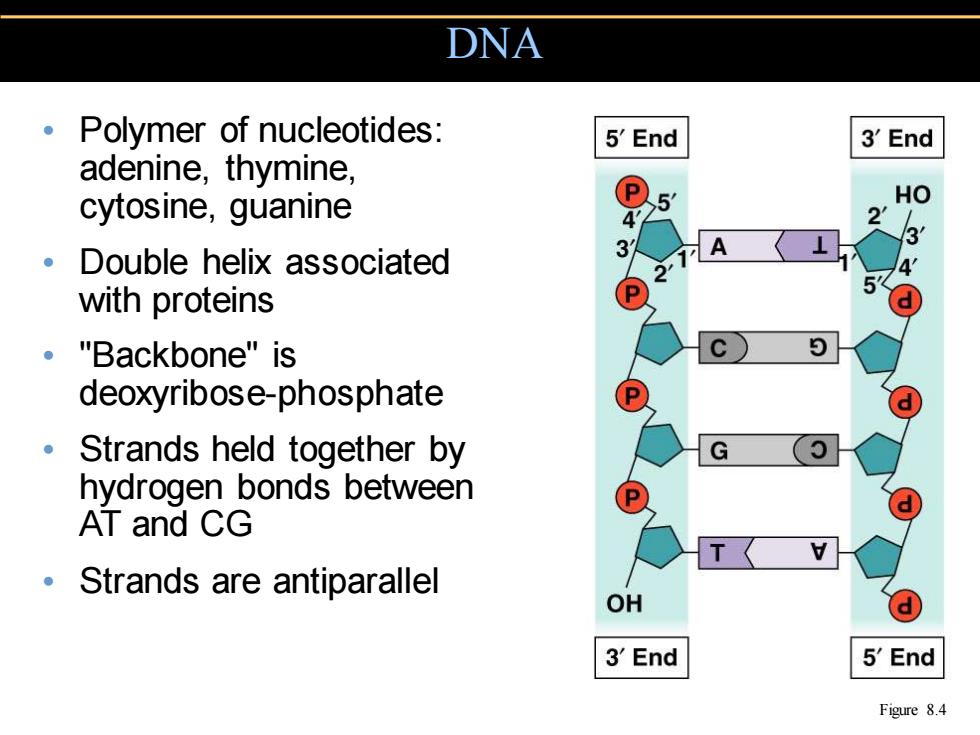
DNA Polymer of nucleotides: 5'End 3End adenine,thymine, cytosine,guanine ⊙5 HO Double helix associated 31 1A 2 with proteins ® "Backbone"is deoxyribose-phosphate ● Strands held together by G hydrogen bonds between AT and CG Strands are antiparallel OH 3'End 5'End Figure 8.4
• Polymer of nucleotides: adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine • Double helix associated with proteins • "Backbone" is deoxyribose-phosphate • Strands held together by hydrogen bonds between AT and CG • Strands are antiparallel DNA Figure 8.4
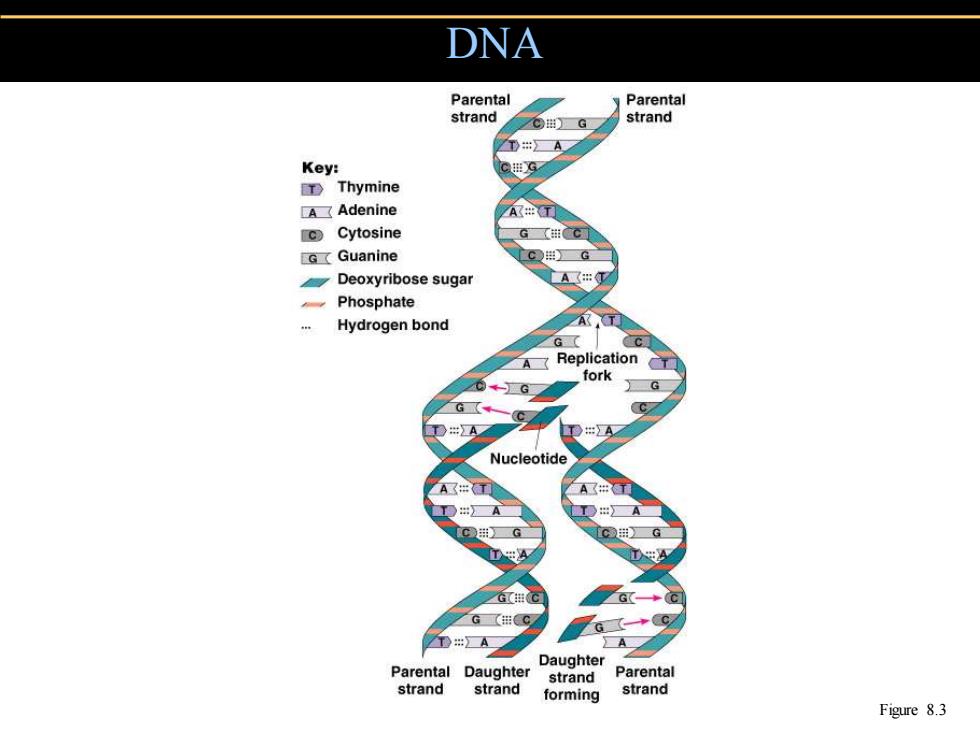
DNA Parenta Parental strand CG strand A Key: TThymine A☐Adenine A c Cytosine G Guanine C#》G Deoxyribose sugar A出 Phosphate Hydrogen bond A G【 Replication fork G G Nucleotide A C》G D#A■ Daughter Parental Daughter strand Parental strand strand forming strand Figure 8.3
DNA Figure 8.3
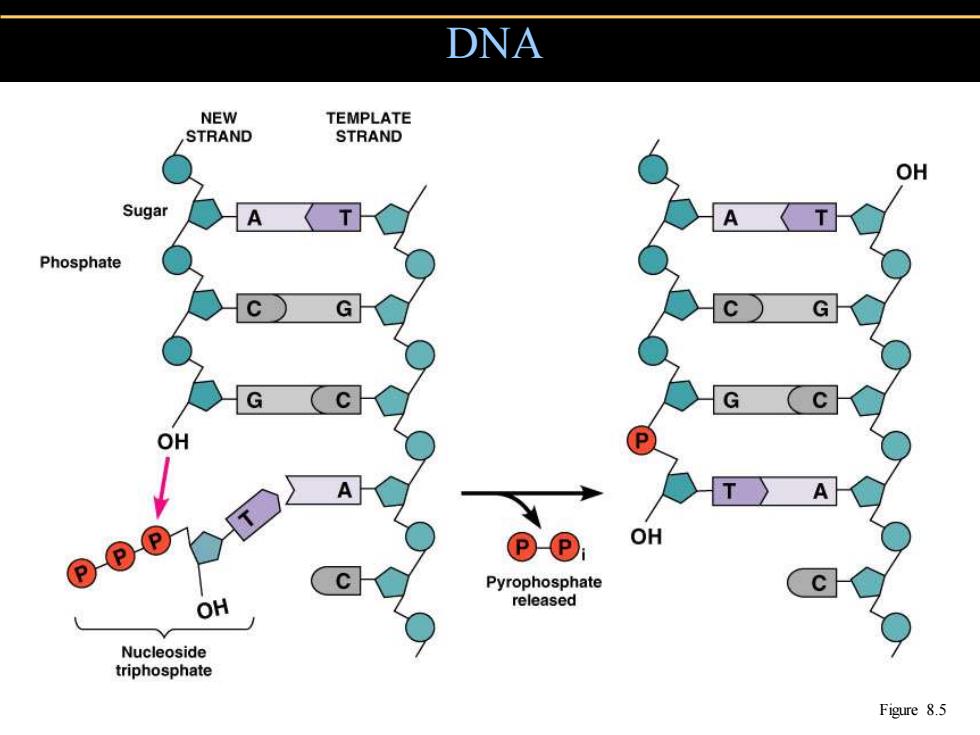
DNA NEW TEMPLATE STRAND STRAND OH Sugar Phosphate T〉 OH Pyrophosphate OH released Nucleoside triphosphate Figure 8.5
DNA Figure 8.5
DNA DNA is copied by DNA polymerase 。In the5'→3'direction Initiated by an RNA primer Leading strand synthesized continuously Lagging strand synthesized discontinuously 。Okazaki fragments RNA primers are removed and Okazaki fragments joined by a DNA polymerase and DNA ligase
• DNA is copied by DNA polymerase • In the 5 → 3 direction • Initiated by an RNA primer • Leading strand synthesized continuously • Lagging strand synthesized discontinuously • Okazaki fragments • RNA primers are removed and Okazaki fragments joined by a DNA polymerase and DNA ligase DNA

DNA maanmW Replication Proteins stabilize the ③The leading strand is unwound parental DNA. synthesized continuously by DNA polymerase. 3 DNA polymerase ①Enzymes unwind the 5 parental double helix. Replication fork RNA primer 5 RNA polymerase DNA polymerase uHhL0uu5000M0W Okazaki fragment DNA ligase Parental 3 DNA strand polymerase 51 ④The lagging strand is ⑤DNA polymerase DNA ligase joins synthesized discontinuously. digests RNA primer the discontinuous RNA polymerase synthesizes a and replaces it with DNA. fragments of the short RNA primer,which is then lagging strand. extended by DNA polymerase. Figure 8.6
DNA Figure 8.6