
Chapter 17,part B Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 17, part B Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response

The Results of Ag-Ab Binding Agglutination PROTECTIVE MECHANISM OF BINDING ANTIBODIES Activation of TO ANTIGENS complement Cell lysis units to be ealt with Complement Bacteria Lysis Opsonization Inflammation Disruption of cell by complement/ reactive protein attracts phagocytic and other defensive immune system cells Blood vessel Phagocyte Infecting cell Macrophage Neutralization Antibody-dependent Blocks adhesion of cell-mediated cytotoxicity bacteria and viruses Blocks active Antibodies attached to target cell to mucosa site of toxin cause destruction by non-specific Virus immune system cells Toxin Figure 17.9
The Results of Ag-Ab Binding Figure 17.9
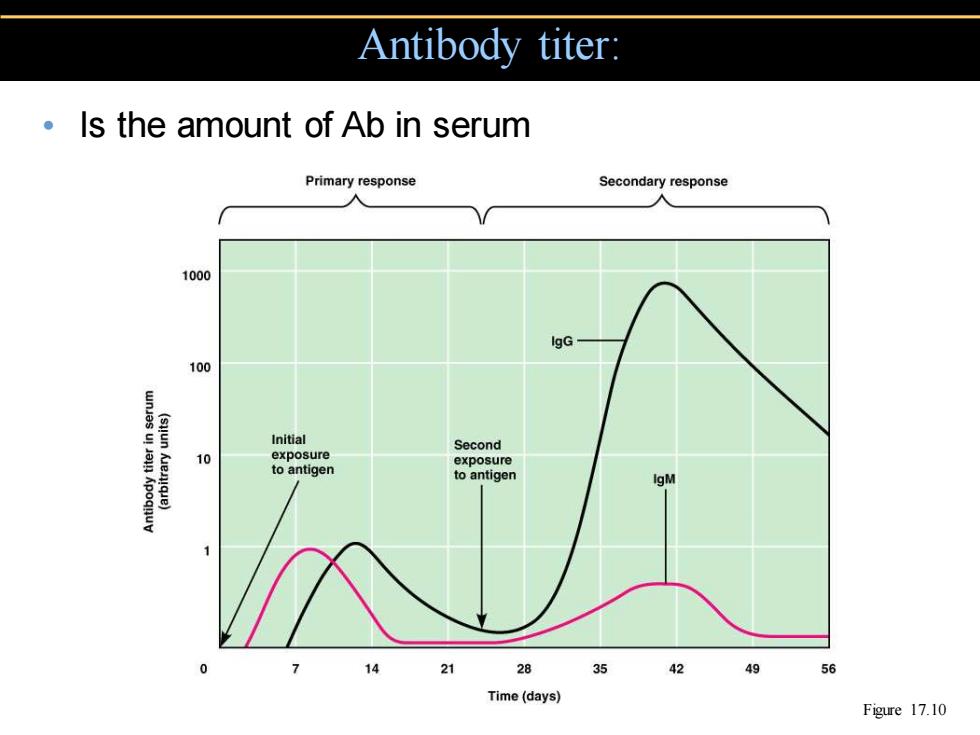
Antibody titer: Is the amount of Ab in serum Primary response Secondary response 1000 IgG 100 Initial Second 10 exposure exposure to antigen to antigen 14 28 35 42 49 56 Time(days) Figure 17.10
Antibody titer: • Is the amount of Ab in serum Figure 17.10
Monoclonal Antibodies Hybridomas are produced by fusing a cancer cell with an Ab-secreting plasma cells The hybridoma cell culture is immortal and produces monoclonal Abs (Mabs) Immunotoxins:Mabs conjugated with a toxin to target cancer cells Chimeric Mabs:Genetically modified mice that produce Ab with a human constant region Humanized Mabs:Mabs that are mostly human,except for mouse antigen-binding
Monoclonal Antibodies • Hybridomas are produced by fusing a cancer cell with an Ab-secreting plasma cells • The hybridoma cell culture is immortal and produces monoclonal Abs (Mabs) • Immunotoxins: Mabs conjugated with a toxin to target cancer cells • Chimeric Mabs: Genetically modified mice that produce Ab with a human constant region • Humanized Mabs: Mabs that are mostly human, except for mouse antigen-binding
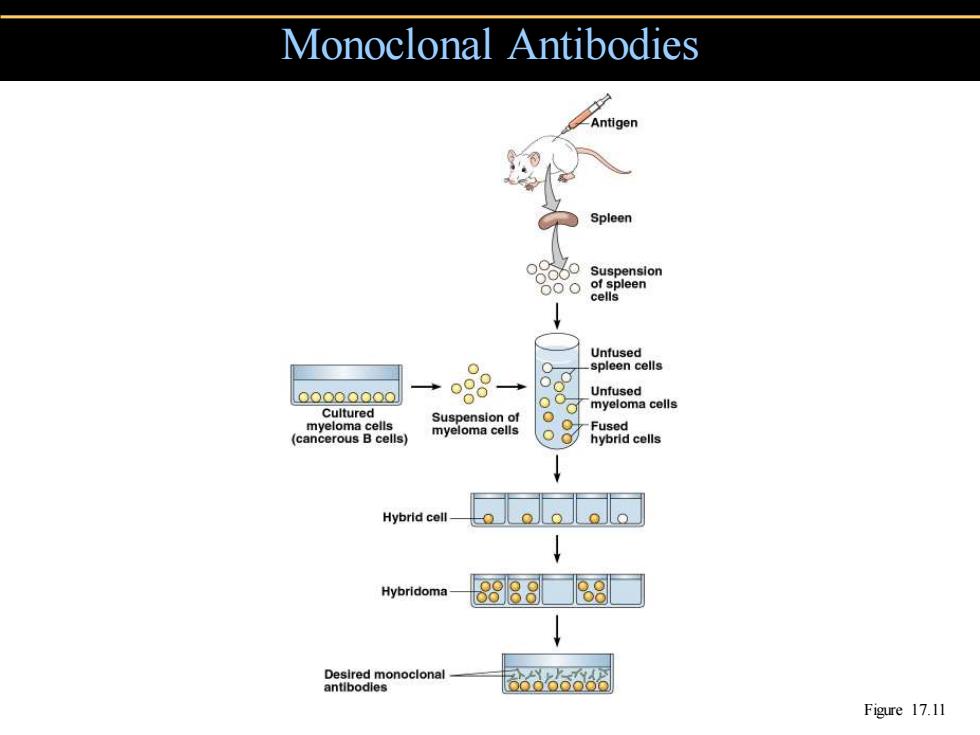
Monoclonal Antibodies Antigen Spleen Suspension of spleen cells Unfused ● spleen cells 0O000000 Unfused Cultured myeloma cells (cmo) Suspension of myeloma cells Fused hybrid cells Hybrid cell Hybridoma 89888 sb8dmonociona Figure 17.11
Monoclonal Antibodies Figure 17.11
Immune system cells communicate via cytokines 。Interleukin-1 Stimulates TH cells 。Interleukin-2 Activates TH,B,Tc,and NK cells 。Interleukin-12 Differentiation of CD4 cells 。y-Interferon Increase activity of macrophages Chemokines Cause leukocytes to move to an infection
• Interleukin-1 Stimulates TH cells • Interleukin-2 Activates TH, B, TC, and NK cells • Interleukin-12 Differentiation of CD4 cells • -Interferon Increase activity of macrophages • Chemokines Cause leukocytes to move to an infection Immune system cells communicate via cytokines
Cell-Mediated Immunity Specialized lymphocytes,mostly T cells,respond to intracellular Ags After differentiating in the thymus,T cells migrate to lymphoid tissue T cells differentiate into effector T cells when stimulated by an Ag Some effector T cells become memory cells
• Specialized lymphocytes, mostly T cells, respond to intracellular Ags • After differentiating in the thymus, T cells migrate to lymphoid tissue • T cells differentiate into effector T cells when stimulated by an Ag • Some effector T cells become memory cells Cell-Mediated Immunity

Pathogens entering the gastrointestinal or respiratory tracts pass through: 。M(microfold)cells in Peyer's patches which contains Dendritic cells which are antigen-presenting cells and 。T cells
• M (microfold) cells in • Peyer's patches which contains • Dendritic cells which are antigen-presenting cells and • T cells Pathogens entering the gastrointestinal or respiratory tracts pass through:
Dendritic cells present antigens Figure 17.12
Dendritic cells present antigens Figure 17.12
T Cells Helper T Cells (CD4,TH) 。TH1 Activate cells related to cell-mediated immunity TH2 Activate B cells to produce eosinophils,IgM, and IgE Cytotoxic T Cells (CD8,Tc) Destroy target cells with perforin
• Helper T Cells (CD4, TH) • TH1 Activate cells related to cell-mediated immunity • TH2 Activate B cells to produce eosinophils, IgM, and IgE • Cytotoxic T Cells (CD8, TC) • Destroy target cells with perforin T Cells