Chapter 2 Cell Biology
Chapter 2 Cell Biology

Chapter Outline 2.1 Overview of the structure of microbial cells 2.2 Procaryotic cell wall 2.3 Cytoplasmic membrane 2.4 Cellular genetic information 2.5 Cytoplasmic matrix -Ribosome and Inclusions 2.6 Components external to the cell wall 2.7 Bacterial endospores 2.8 Comparison of the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
2.1 Overview of the structure of microbial cells 2.2 Procaryotic cell wall 2.3 Cytoplasmic membrane 2.4 Cellular genetic information 2.5 Cytoplasmic matrix – Ribosome and Inclusions 2.6 Components external to the cell wall 2.7 Bacterial endospores 2.8 Comparison of the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell Chapter Outline

Concepts Prokaryotes are small and simple in structure when compared with eukaryotes,yet they often have characteristic shape and size. Prokaryotic genetic material is located in an area called the nucleoid and is not enclosed by a membrane. The prokaryotic cell wall almost always has peptidoglycan and is chemically and morphologically complex
Concepts • Prokaryotes are small and simple in structure when compared with eukaryotes , yet they often have characteristic shape and size. • Prokaryotic genetic material is located in an area called the nucleoid and is not enclosed by a membrane. • The prokaryotic cell wall almost always has peptidoglycan and is chemically and morphologically complex
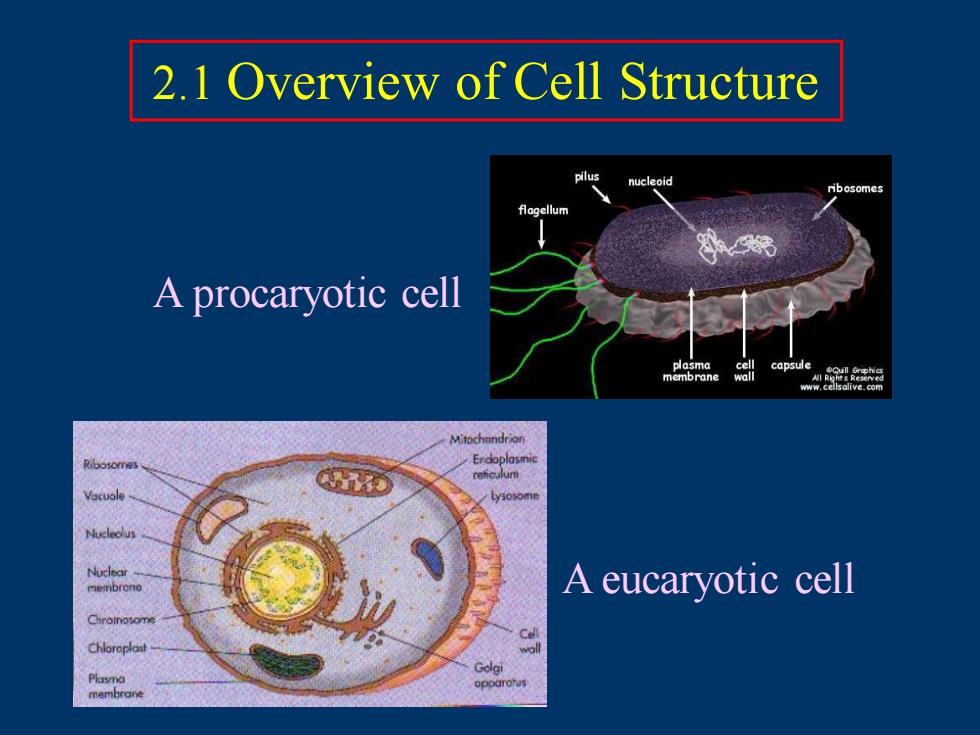
2.1 Overview of Cell Structure nucleoid A procaryotic cell A eucaryotic cell
A procaryotic cell A eucaryotic cell 2.1 Overview of Cell Structure

The Prokaryotic Cell 1.Their genetic material (DNA)is not enclosed within a membrane and they lack other membrane -bounded organelles 2.Their DNA is not associated with histidine 3.Their cell wall almost always contain the complex polysaccharide peptidoglycan 4.They are very small!!
3. Their cell wall almost always contain the complex polysaccharide peptidoglycan The Prokaryotic Cell 1. Their genetic material (DNA) is not enclosed within a membrane and they lack other membrane – bounded organelles 2. Their DNA is not associated with histidine 4. They are very small!!
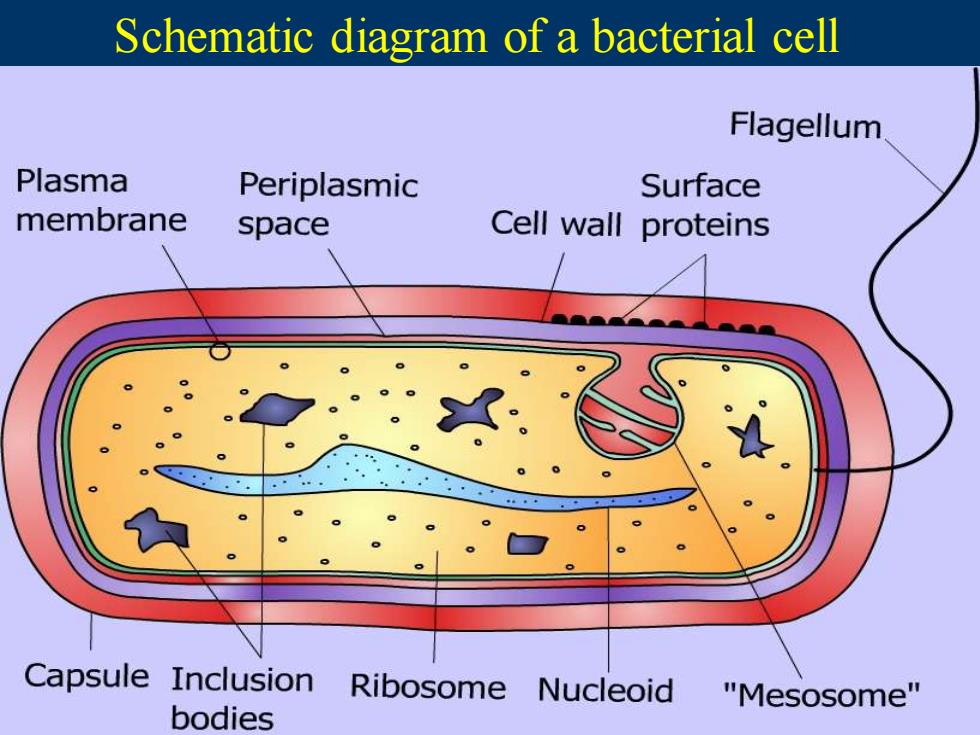
Schematic diagram of a bacterial cell Flagellum Plasma Periplasmic Surface membrane space Cell wall proteins Capsule Inclusion Ribosome Nucleoid "Mesosome" bodies
Schematic diagram of a bacterial cell
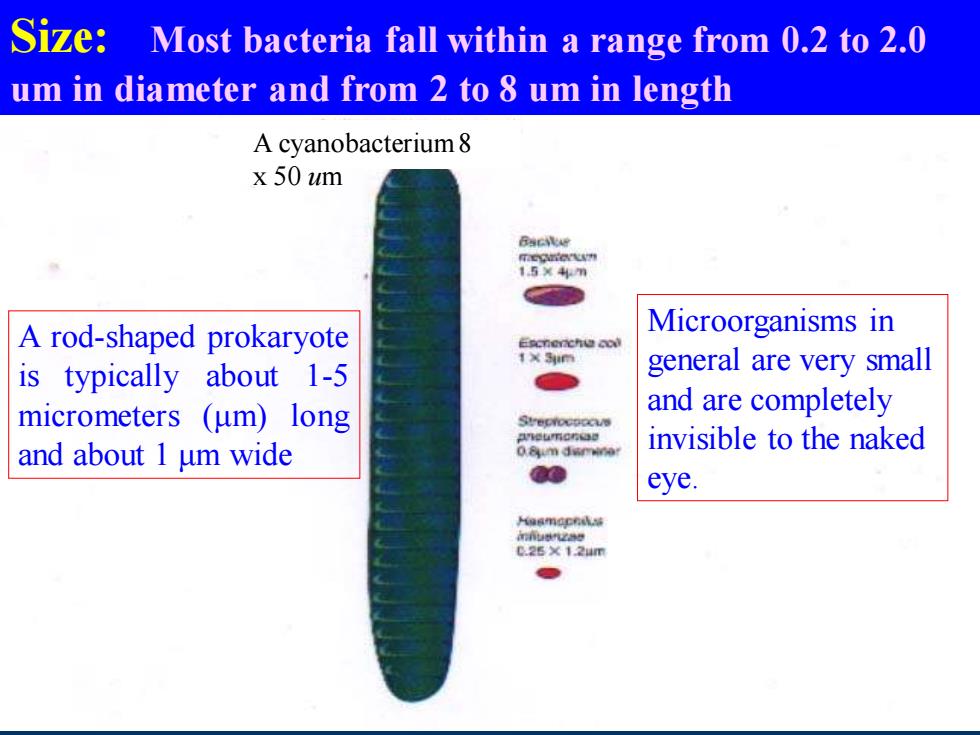
Size:Most bacteria fall within a range from 0.2 to 2.0 um in diameter and from 2 to 8 um in length A cyanobacterium8 x 50 um BscNe 1544m A rod-shaped prokaryote Microorganisms in Escnerchu cod 1×利m is typically about 1-5 general are very small micrometers (um)long and are completely eu有C量 and about 1 um wide 0.8um dumin invisible to the naked eye. 每餐m工有城 0.26×124m
Size: Most bacteria fall within a range from 0.2 to 2.0 um in diameter and from 2 to 8 um in length A rod-shaped prokaryote is typically about 1-5 micrometers (μm) long and about 1 μm wide Microorganisms in general are very small and are completely invisible to the naked eye. A cyanobacterium 8 x 50 um
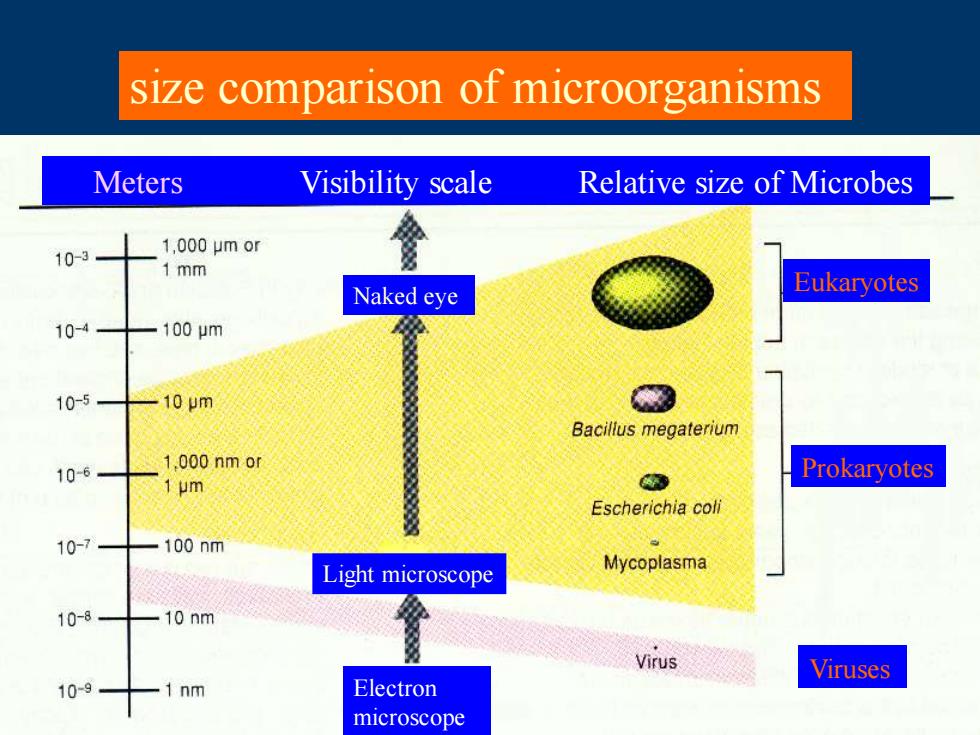
size comparison of microorganisms Meters Visibility scale Relative size of Microbes 10-3 1,000μmor 1 mm Naked eye Eukaryotes 10-4 100m 10-5 10m Bacillus megaterium 10-6 1.000 nm or Prokaryotes 1 um Escherichia coli 10-7 100nm Light microscope Mycoplasma 10-8 10 nm Virus Viruses 10-9 1nm Electron microscope
size comparison of microorganisms Meters Visibility scale Relative size of Microbes Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Viruses Naked eye Light microscope Electron microscope
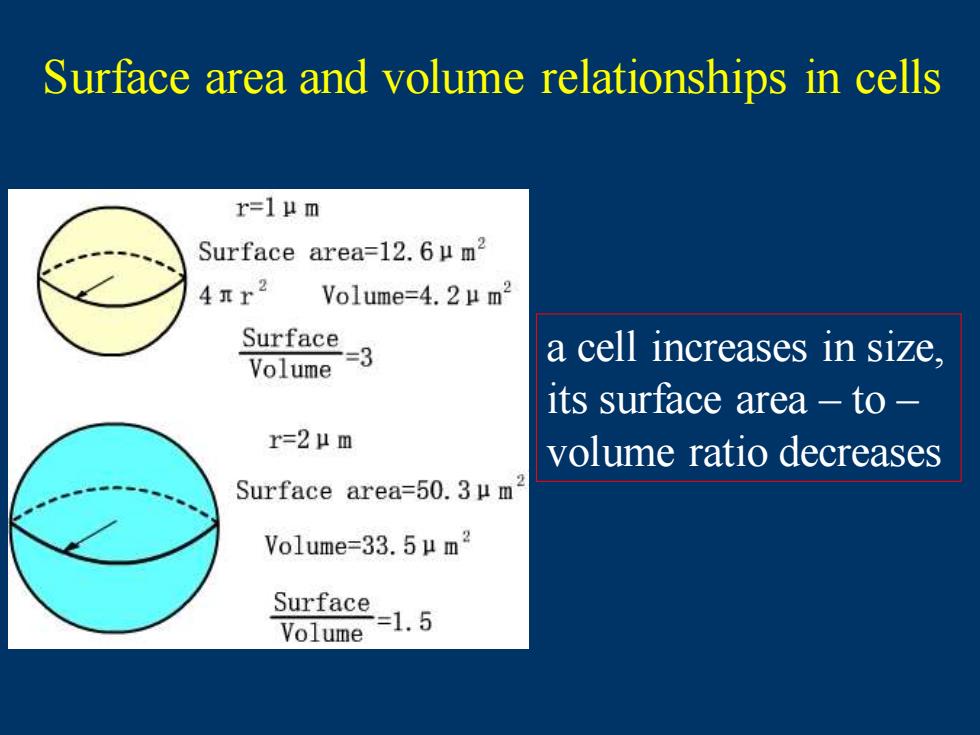
Surface area and volume relationships in cells r=1μm Surface area=l2.6μm2 4nr2 Volume=4.2μm2 Surface Volume 另 a cell increases in size, its surface area to r=2μm volume ratio decreases Surface area=50.3μm Volume=-33.5μm2 Surface=1.5 Volume
a cell increases in size, its surface area – to – volume ratio decreases Surface area and volume relationships in cells
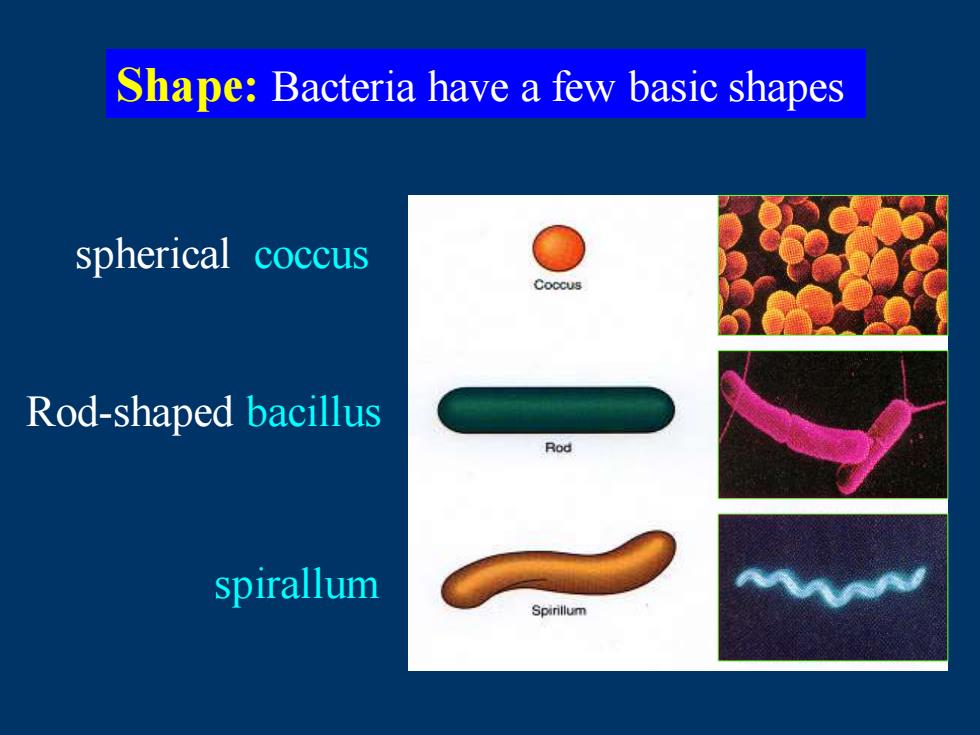
Shape:Bacteria have a few basic shapes spherical coccus Coccus Rod-shaped bacillus Ro spirallum
spirallum Shape: Bacteria have a few basic shapes spherical coccus Rod-shaped bacillus