
Chapter 8 Microbial genetics
Chapter 8 Microbial genetics

Chapter outline 8.1 Mutations and Mutants 8.2 Genetic Recombination 8.3 Genetic Transformation 8.4 Transduction 8.5 Conjugation 8.6 Plasmids 8.7 Transposons and Insertion Sequences 8.8 Comparative Prokaryotic Genomics
8.1 Mutations and Mutants 8.2 Genetic Recombination 8.3 Genetic Transformation 8.4 Transduction 8.5 Conjugation 8.6 Plasmids 8.7 Transposons and Insertion Sequences 8.8 Comparative Prokaryotic Genomics Chapter outline
Concepts 。 DNA replication is a very complex process involving a variety of proteins and a number of steps.It is designed to operate rapidly while minimizing errors and correcting those that arise when the DNA sequence is copied. The actual transfer of genetic material between bacteria usually takes place in one of three ways:direct transfer between two bacteria temporarily in physical contact (conjugation),transfer of a naked DNA fragment (transformation),or transport of bacterial DNA by bacteriophages (transduction)
Concepts • DNA replication is a very complex process involving a variety of proteins and a number of steps. It is designed to operate rapidly while minimizing errors and correcting those that arise when the DNA sequence is copied. • The actual transfer of genetic material between bacteria usually takes place in one of three ways: direct transfer between two bacteria temporarily in physical contact (conjugation), transfer of a naked DNA fragment (transformation), or transport of bacterial DNA by bacteriophages (transduction)
Importance of study on microbial genetics simple systems 。 studying genetic phenomena useful tools decipher the genetics mechanisms *molecular cloning isolate and duplicate specific genes from other organisms genes are manipulated and placed in a microorganism where they can be induced to increase in numbers
❖ simple systems • studying genetic phenomena ❖ useful tools • decipher the genetics mechanisms ❖ molecular cloning • isolate and duplicate specific genes from other organisms • genes are manipulated and placed in a microorganism where they can be induced to increase in numbers Importance of study on microbial genetics

Value in industry Antibiotics Increase yields and improve manufacturing processes Diseases Understanding the genetics of disease-causing microorganisms Genetic transfer in prokaryotes How genes can be transferred from one organism to another,even from one species to another
❖ Value in industry • Antibiotics • Increase yields and improve manufacturing processes ❖ Diseases • Understanding the genetics of disease-causing microorganisms ❖ Genetic transfer in prokaryotes • How genes can be transferred from one organism to another, even from one species to another
8.1 Mutation and recombination Mutation is an inherited change in the base sequence of the nucleic acid comprising the genome of an organism.Mutation usually brings about only a very small amount of genetic change in a cell. Mutant an organism whose genome carries a mutation.Depending on the mutation,a mutant may or may not show an altered phenotype from its parent
8.1 Mutation and recombination Mutation is an inherited change in the base sequence of the nucleic acid comprising the genome of an organism. Mutation usually brings about only a very small amount of genetic change in a cell. Mutant an organism whose genome carries a mutation. Depending on the mutation, a mutant may or may not show an altered phenotype from its parent
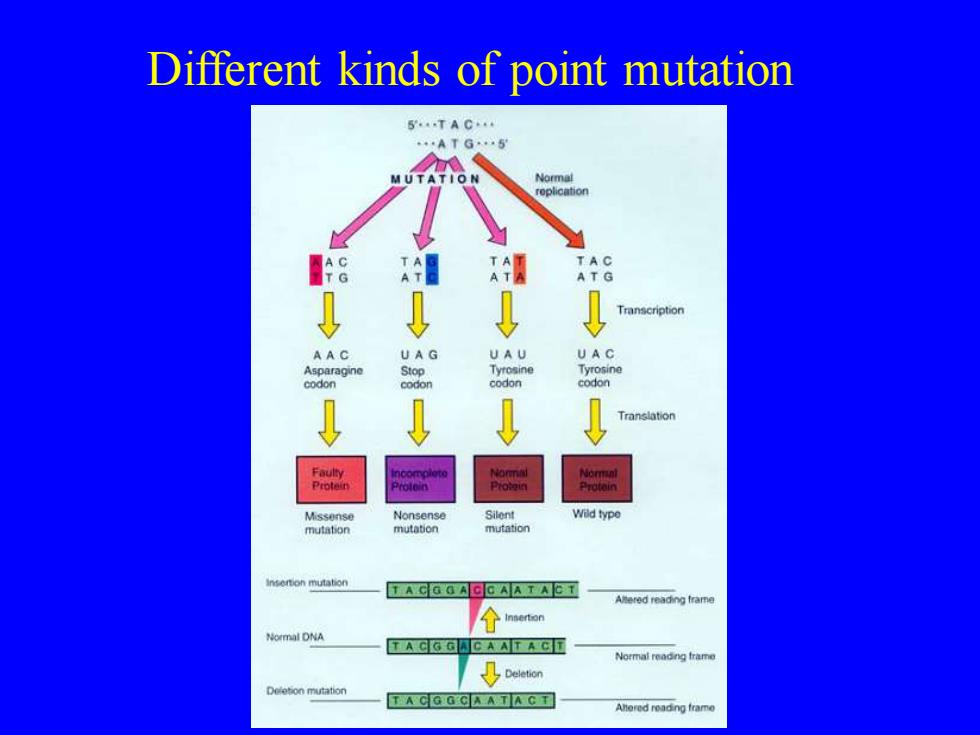
Different kinds of point mutation G.5 Normal oplicatio 8 TAC ATG Transcription UAG UAU codon Translation Faulty Nonsense Wild type mutation insenion mutation Alered reading frame Normal DNA Normal readng trame Deletion mutation TA CGG C A AT A C T
Different kinds of point mutation

Mutation *Selectable *Nonselectable Spontaneous *Induced
Mutation ❖ Selectable ❖ Nonselectable ❖ Spontaneous ❖ Induced

Nutritional mutants replica plating method The photograph on the left shows the master plate The colonies not appearing on the replica plate are marked with an X The replica plate lacked one nutrient (leucine) present in the master plate Therefore,the colonies marked with an X are leucine auxotrophs
Nutritional mutants replica plating method • The photograph on the left shows the master plate • The colonies not appearing on the replica plate are marked with an X • The replica plate lacked one nutrient (leucine) present in the master plate • Therefore, the colonies marked with an X are leucine auxotrophs
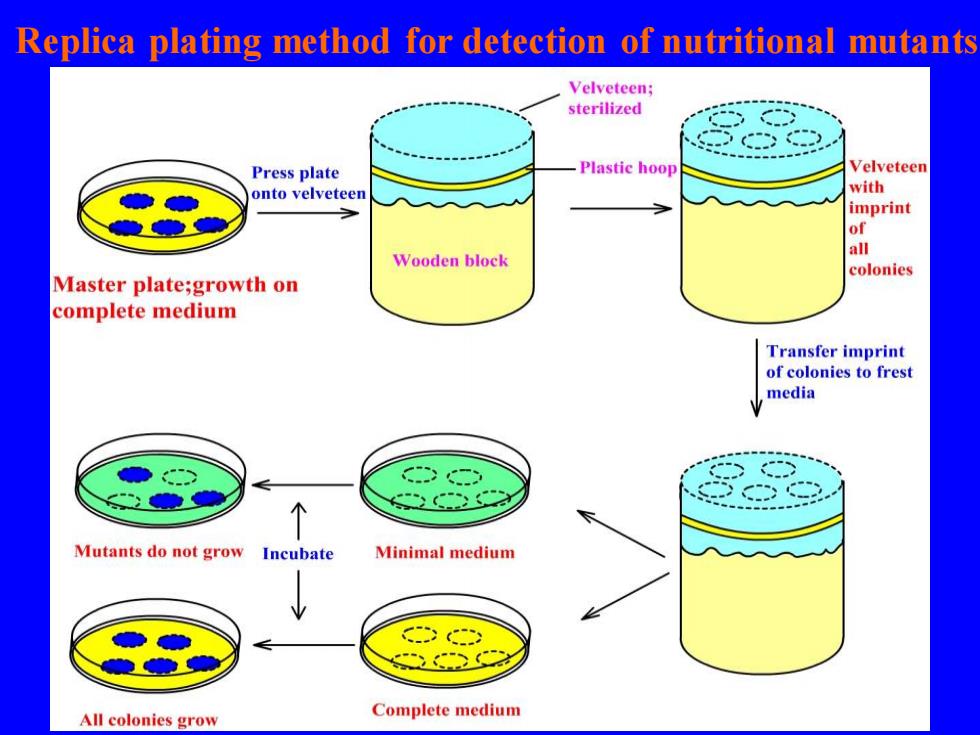
Replica plating method for detection of nutritional mutants Velveteen: sterilized Press plate Plastic hoop Velveteen onto velveteen with imprint of all Wooden block colonies Master plate;growth on complete medium Transfer imprint of colonies to frest media 个 Mutants do not grow Incubate Minimal medium All colonies grow Complete medium
Replica plating method for detection of nutritional mutants