
Chapter 5,part C Microbial Metabolism
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 5, part C Microbial Metabolism
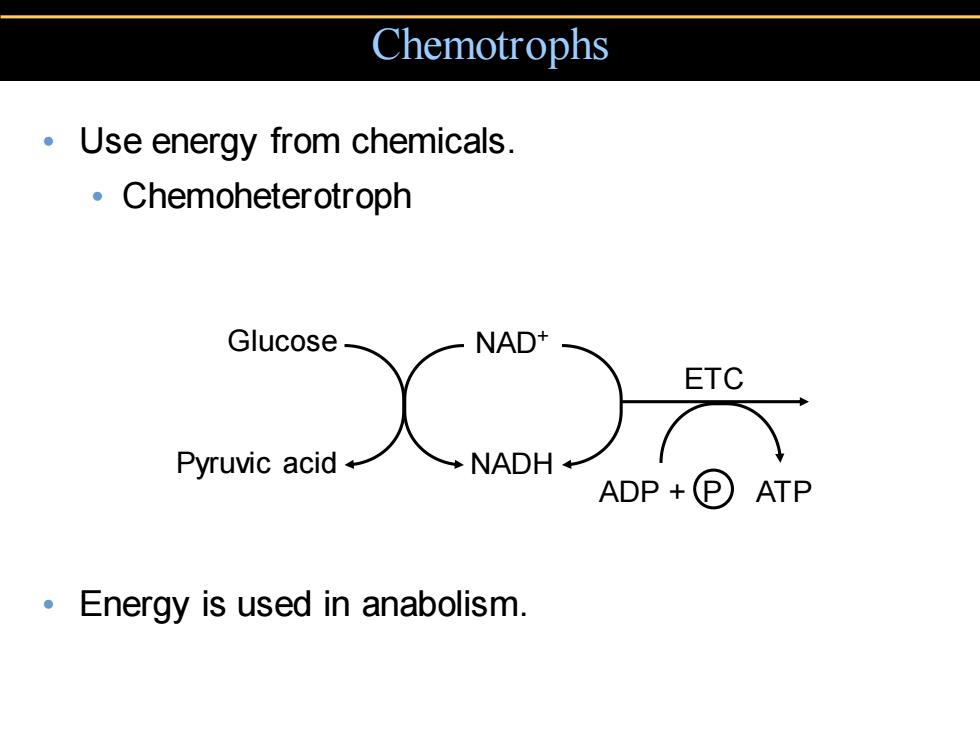
Chemotrophs Use energy from chemicals. 。Chemoheterotroph X Glucose ·NAD ETC Pyruvic acid ADP+P)ATP Energy is used in anabolism
Chemotrophs • Use energy from chemicals. • Chemoheterotroph • Energy is used in anabolism. Glucose Pyruvic acid NAD+ NADH ETC ADP + P ATP
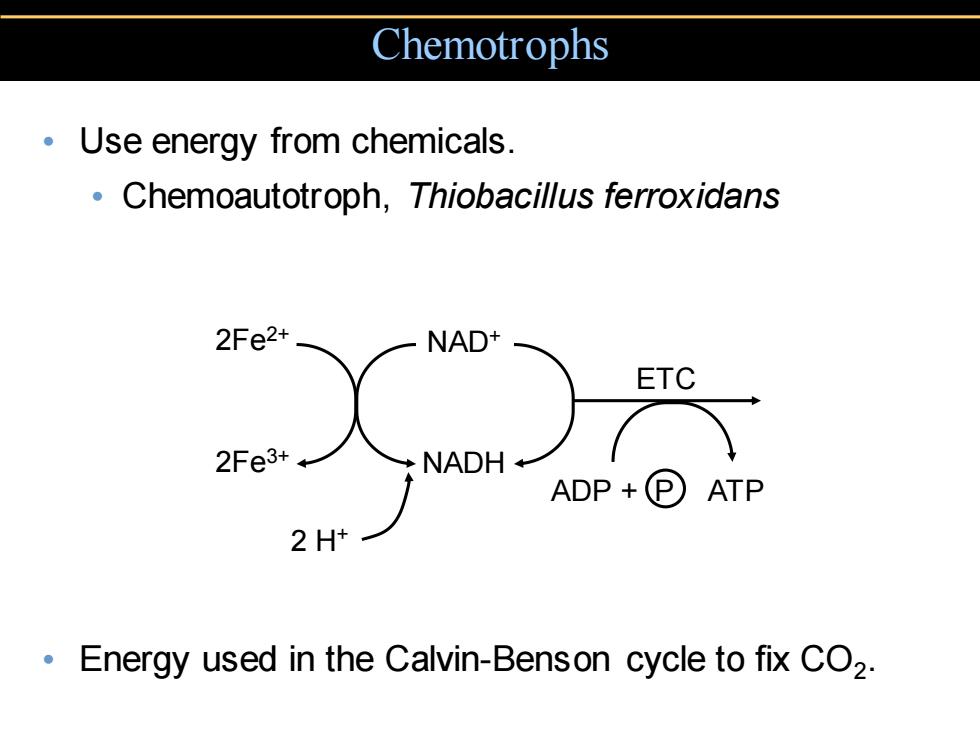
Chemotrophs Use energy from chemicals. Chemoautotroph,Thiobacillus ferroxidans 2Fe2+ NAD ETC 2Fe3++ 2 Energy used in the Calvin-Benson cycle to fix CO2
Chemotrophs • Use energy from chemicals. • Chemoautotroph, Thiobacillus ferroxidans • Energy used in the Calvin-Benson cycle to fix CO2 . 2Fe2+ 2Fe3+ NAD+ NADH ETC ADP + P ATP 2 H+
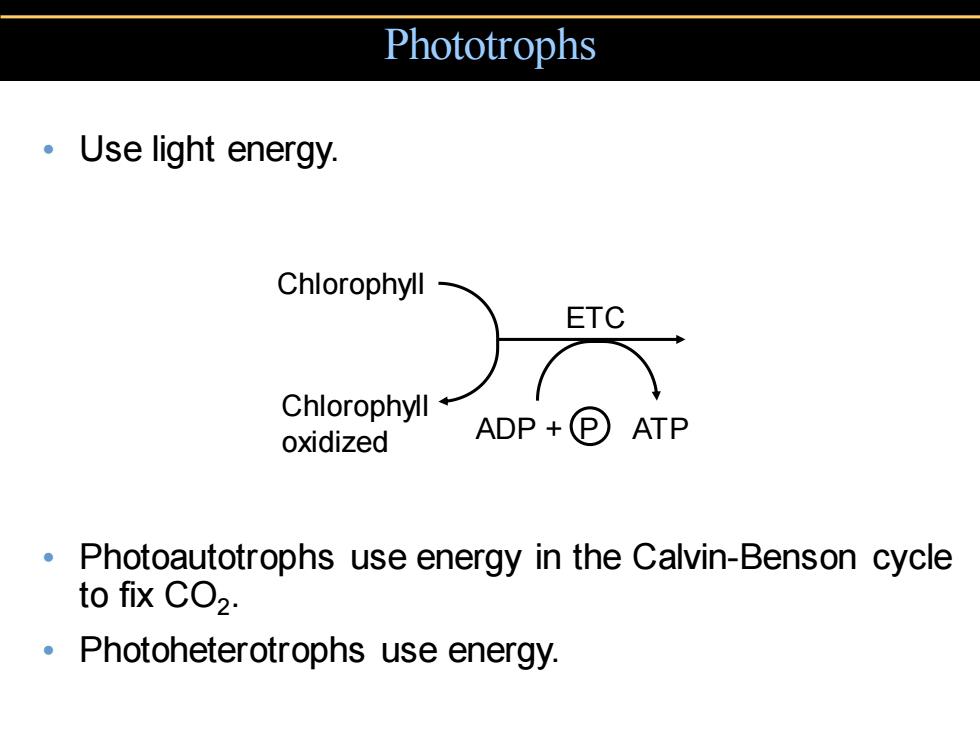
Phototrophs ·Use light energy. Chlorophyll oxidized Photoautotrophs use energy in the Calvin-Benson cycle to fix CO2. Photoheterotrophs use energy
Phototrophs • Use light energy. • Photoautotrophs use energy in the Calvin-Benson cycle to fix CO2 . • Photoheterotrophs use energy. Chlorophyll Chlorophyll oxidized ETC ADP + P ATP
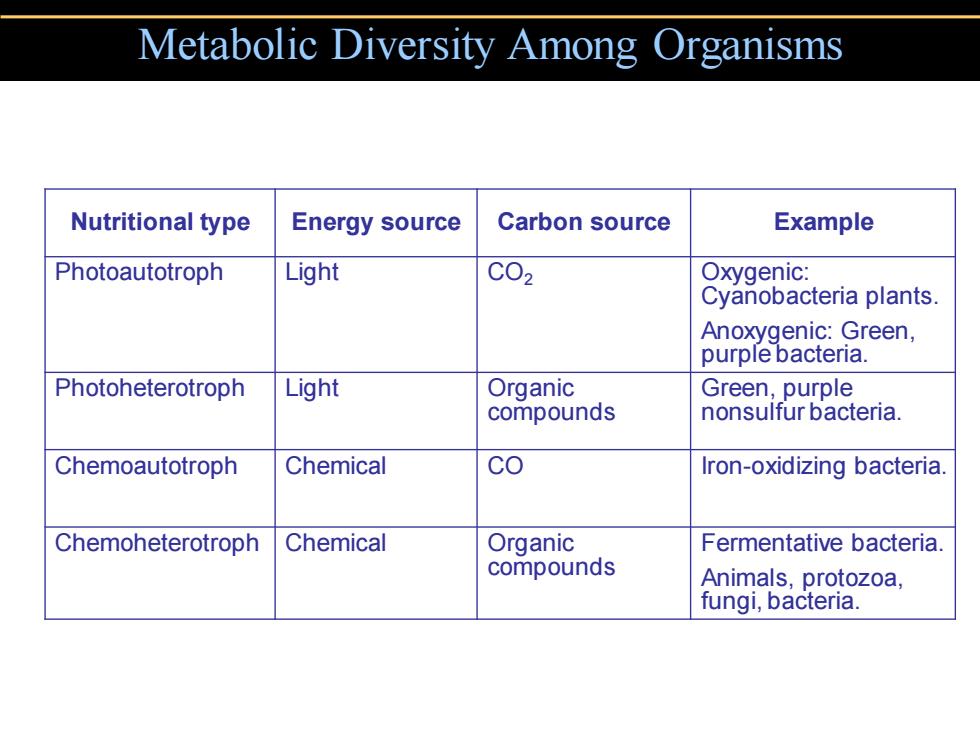
Metabolic Diversity Among Organisms Nutritional type Energy source Carbon source Example Photoautotroph Light C02 Oxygenic: Cyanobacteria plants. Anoxygenic:Green, purple bacteria. Photoheterotroph Light Organic Green,purple compounds nonsulfur bacteria. Chemoautotroph Chemical co Iron-oxidizing bacteria. Chemoheterotroph Chemical Organic Fermentative bacteria. compounds Animals,protozoa, fungi,bacteria
Metabolic Diversity Among Organisms Nutritional type Energy source Carbon source Example Photoautotroph Light CO2 Oxygenic: Cyanobacteria plants. Anoxygenic: Green, purple bacteria. Photoheterotroph Light Organic compounds Green, purple nonsulfur bacteria. Chemoautotroph Chemical CO Iron-oxidizing bacteria. Chemoheterotroph Chemical Organic compounds Fermentative bacteria. Animals, protozoa, fungi, bacteria

Metabolic Pathways of Energy Use Polysaccharide Biosynthesis Glycolysis Glucose ADPG Glycogen (in bacteria) Glucose 6-phosphate UDPG Glycogen (in animals) Fructose 6-phosphate UDPNAc Peptidoglycan (in bacteria) Pyruvic acid Figure 5.28
• Polysaccharide Biosynthesis Metabolic Pathways of Energy Use Figure 5.28
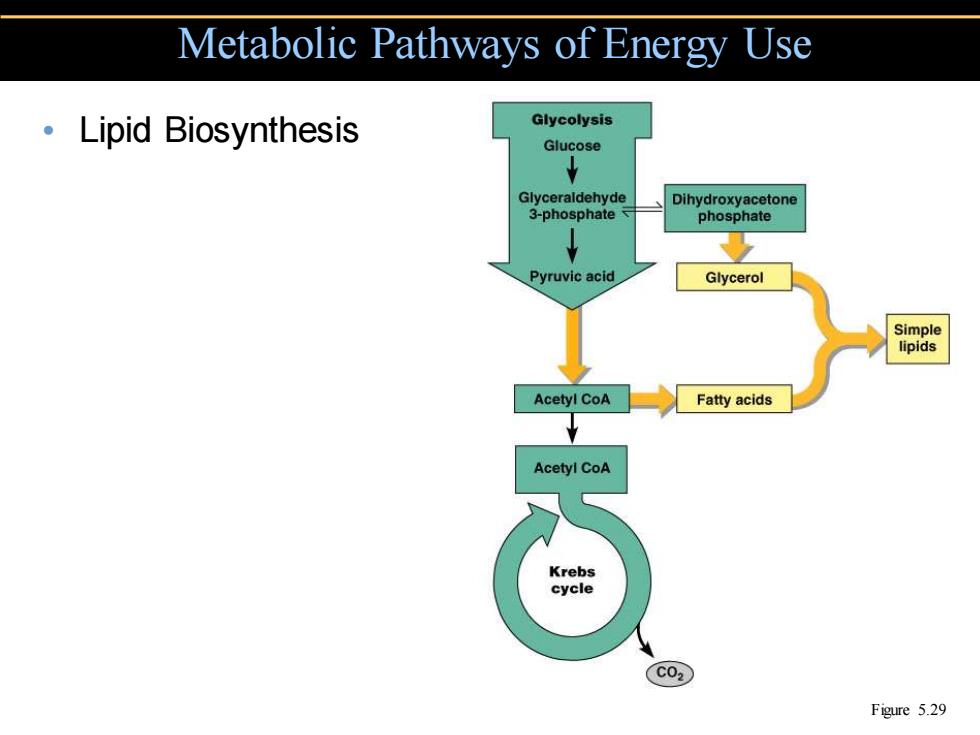
Metabolic Pathways of Energy Use ·Lipid Biosynthesis Glycolysis Glucose Glyceraldehyde Dihydroxyacetone 3-phosphate phosphate Pyruvic acid Glycerol Simple lipids Acetyl CoA Fatty acids Acetyl CoA Krebs cycle C02 Figure 5.29
• Lipid Biosynthesis Metabolic Pathways of Energy Use Figure 5.29

Metabolic Pathways of Energy Use Amino Acid and Protein Biosynthesis Pentose phosphate pathway Acetyl CoA Amination or transamination Krebs Amino cycle acids Entner-Doudoroff pathway (EDP) (a)Amino acid biosynthesis Figure 5.30a
• Amino Acid and Protein Biosynthesis Metabolic Pathways of Energy Use Figure 5.30a
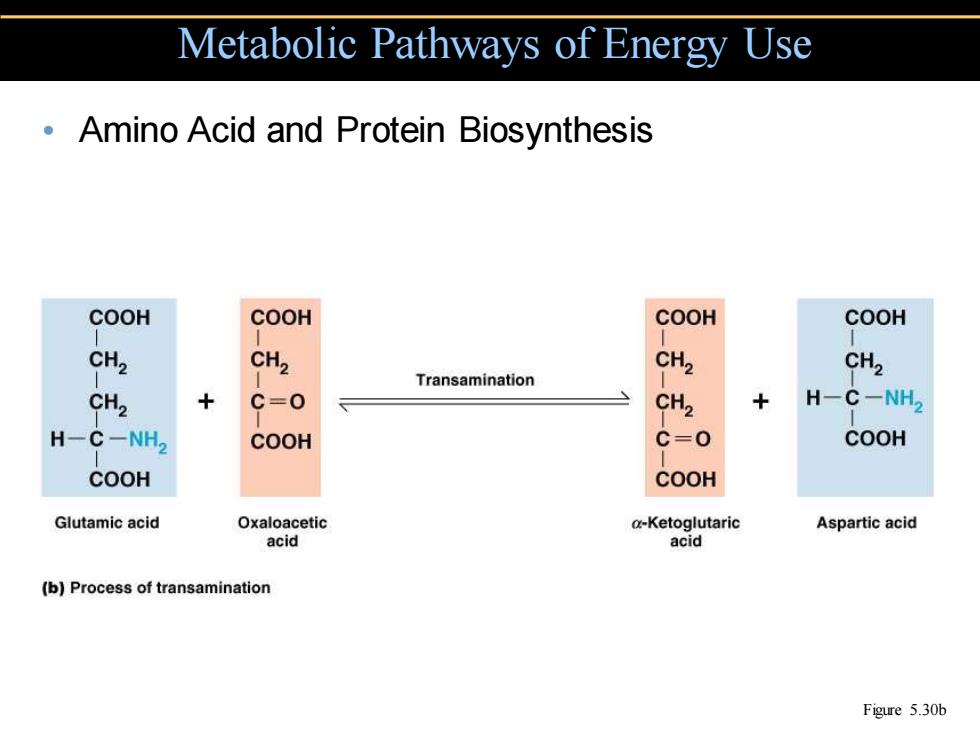
Metabolic Pathways of Energy Use Amino Acid and Protein Biosynthesis COOH COOH COOH COOH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 Transamination CH2 + C=0 CH2 + H-C-NH2 H-C-NH2 COOH C=0 COOH COOH COOH Glutamic acid Oxaloacetic a-Ketoglutaric Aspartic acid acid acid (b)Process of transamination Figure 5.30b
• Amino Acid and Protein Biosynthesis Metabolic Pathways of Energy Use Figure 5.30b

Metabolic Pathways of Energy Use Purine and Glycolysis Pyrimidine Glucose Biosynthesis Glucose Pentose phosphate pathway or 6-phosphate Entner-Doudoroff pathway (EDP) Phosphoglyceric acid Glycine Pentose (five-carbon sugar) Pyruvic acid Purine Pyrimidine Acetyl CoA nucleotides nucleotides Acetyl CoA Glutamine Aspartic acid Krebs cycle Figure 5.31
• Purine and Pyrimidine Biosynthesis Metabolic Pathways of Energy Use Figure 5.31