
Chapter 22,part A Microbial Diseases of the Nervous System
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 22, part A Microbial Diseases of the Nervous System
Microbes enter the nervous system via: Skull or backbone fractures ·Medical procedures Along peripheral nerves 。Blood or lymph
Microbes enter the nervous system via: • Skull or backbone fractures • Medical procedures • Along peripheral nerves • Blood or lymph
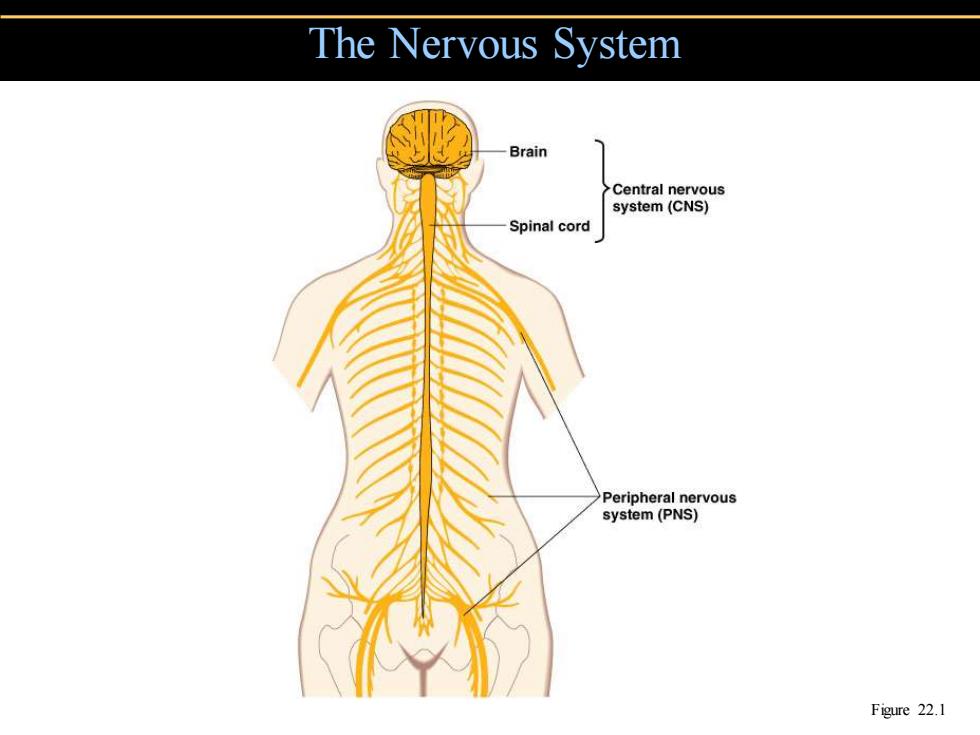
The Nervous System Brain Central nervous system(CNS) Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system(PNS) Figure 22.1
The Nervous System Figure 22.1
Microbial Diseases of the Nervous System Bacteria can grow in the cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space of the CNS The blood brain barrier (capillaries)prevents passage of some materials (such as antimicrobial drugs)into the CNS 。Meningitis Inflammation of meninges 。Encephalitis Inflammation of the brain
Microbial Diseases of the Nervous System • Bacteria can grow in the cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space of the CNS • The blood brain barrier (capillaries) prevents passage of some materials (such as antimicrobial drugs) into the CNS • Meningitis • Inflammation of meninges • Encephalitis • Inflammation of the brain
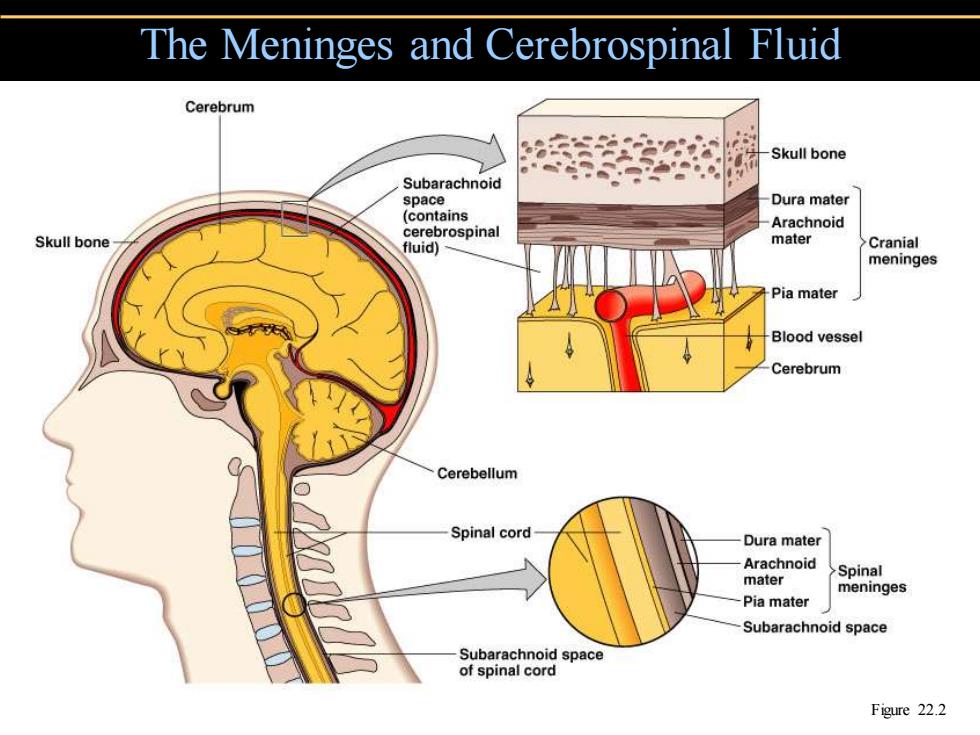
The Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid Cerebrum Skull bone Subarachnoid space Dura mater (contains Arachnoid Skull bone cerebrospinal mater fluid) >Cranial meninges -Pia mater Blood vessel Cerebrum Cerebellum Spinal cord Dura mater Arachnoid mater Spinal meninges Pia mater Subarachnoid space Subarachnoid space of spinal cord Figure 22.2
The Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid Figure 22.2
Bacterial Meningitis Fever,headache,stiff neck Followed by nausea and vomiting May progress to convulsions and coma Diagnosis by Gram stain of CSF Treated with cephalosporins
• Fever, headache, stiff neck • Followed by nausea and vomiting • May progress to convulsions and coma • Diagnosis by Gram stain of CSF • Treated with cephalosporins Bacterial Meningitis
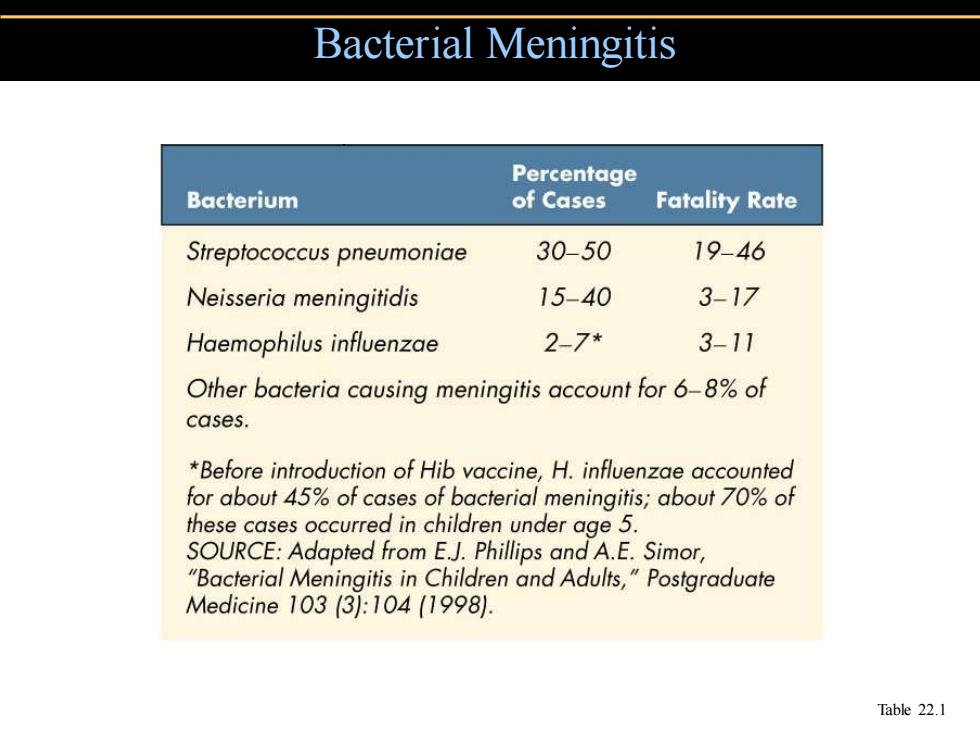
Bacterial Meningitis Percentage Bacterium of Cases Fatality Rate Streptococcus pneumoniae 30-50 19-46 Neisseria meningitidis 15-40 3-17 Haemophilus influenzae 2-7* 3-11 Other bacteria causing meningitis account for 6-8%of cases. *Before introduction of Hib vaccine,H.influenzae accounted for about 45%of cases of bacterial meningitis;about 70%of these cases occurred in children under age 5. SOURCE:Adapted from E.J.Phillips and A.E.Simor, "Bacterial Meningitis in Children and Adults,"Postgraduate Medicine103(3:104(1998l. Table 22.1
Bacterial Meningitis Table 22.1

Haemophilus influenzae Meningitis Occurs mostly in children (6 months to 4 years) Gram-negative aerobic bacteria,normal throat microbiota Capsule antigen type b Prevented by Hib vaccine
• Occurs mostly in children (6 months to 4 years) • Gram-negative aerobic bacteria, normal throat microbiota • Capsule antigen type b • Prevented by Hib vaccine Haemophilus influenzae Meningitis
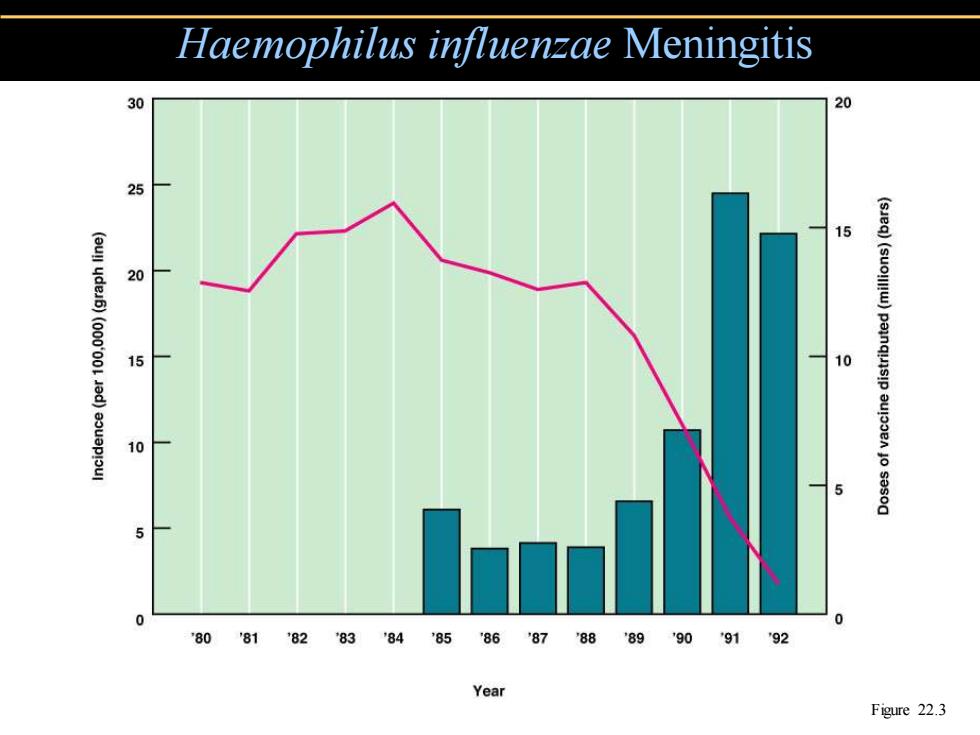
Haemophilus influenzae Meningitis 30 20 15 20 15 10 10 80 '8182838485868788899091 92 Year Figure 22.3
Haemophilus influenzae Meningitis Figure 22.3

Neisseria Meningitis,Meningococcal Meningitis 。N.meningitidis Gram-negative aerobic cocci,capsule 10%of people are healthy nasopharyngeal carriers Begins as throat infection,rash Serotype B is most common in the U.S Vaccine against some serotypes is available
• N. meningitidis • Gram-negative aerobic cocci, capsule • 10% of people are healthy nasopharyngeal carriers • Begins as throat infection, rash • Serotype B is most common in the U.S. • Vaccine against some serotypes is available Neisseria Meningitis, Meningococcal Meningitis