
Chapter 6,part B Microbial Growth
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 6, part B Microbial Growth

Preserving Bacteria Cultures 。Deep-freezing:-50°to-95°C 。Lyophilization(freeze-drying):Frozen(-54°to-72°C) and dehydrated in a vacuum
• Deep-freezing: -50°to -95°C • Lyophilization (freeze-drying): Frozen (-54° to -72°C) and dehydrated in a vacuum Preserving Bacteria Cultures
Reproduction in Prokaryotes 。Binary fission 。Budding 。 Conidiospores (actinomycetes) Fragmentation of filaments
• Binary fission • Budding • Conidiospores (actinomycetes) • Fragmentation of filaments Reproduction in Prokaryotes
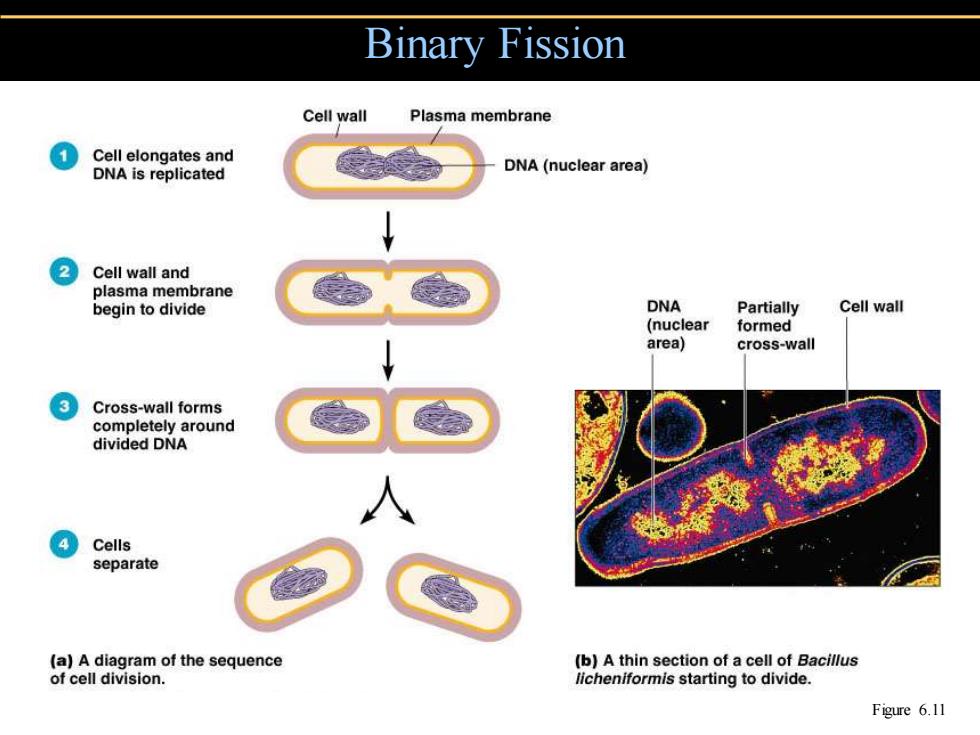
Binary Fission Cell wall Plasma membrane Cell elongates and DNA is replicated DNA(nuclear area) 2 Cell wall and plasma membrane begin to divide DNA Partially Cell wall (nuclear formed area) cross-wall 3 Cross-wall forms completely around divided DNA Cells separate (a)A diagram of the sequence (b)A thin section of a cell of Bacillus of cell division. licheniformis starting to divide. Figure 6.11
Binary Fission Figure 6.11
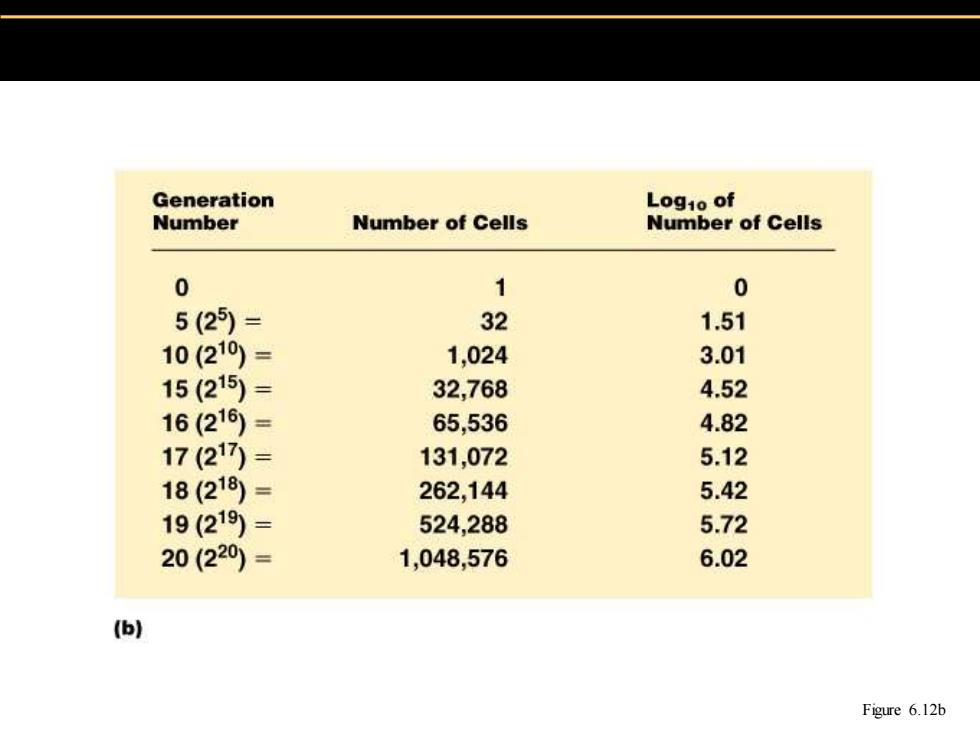
Generation Logio of Number Number of Cells Number of Cells 0 1 0 5(25)= 32 1.51 10(210)= 1,024 3.01 15(215)= 32,768 4.52 16(216)= 65,536 4.82 17(21)= 131,072 5.12 18(218)= 262,144 5.42 19(219)= 524,288 5.72 20(220)= 1,048,576 6.02 (b) Figure 6.12b
Figure 6.12b

If 100 cells growing for 5 hours produced 1,720,320 cells: Log number of cells(end)-Log number of cells(beginning) Number of generations 0.301 60min×hours Generation time -21 minutes/generation Number of generations
If 100 cells growing for 5 hours produced 1,720,320 cells:

(1,048,576) 6.0 1.000.000 (0g10=6.02) 5.0 (L0g10=4.52) 4.0 (524,288) (Log10=3.01) 3.0 500,000 (Log10=1.51) 2.0 (262,144) 1.0 (131,072) (65,536) 100,000 (32) (1024) (32,768) 0 10,000 5 10 15 20 Generations Figure 6.13
Figure 6.13
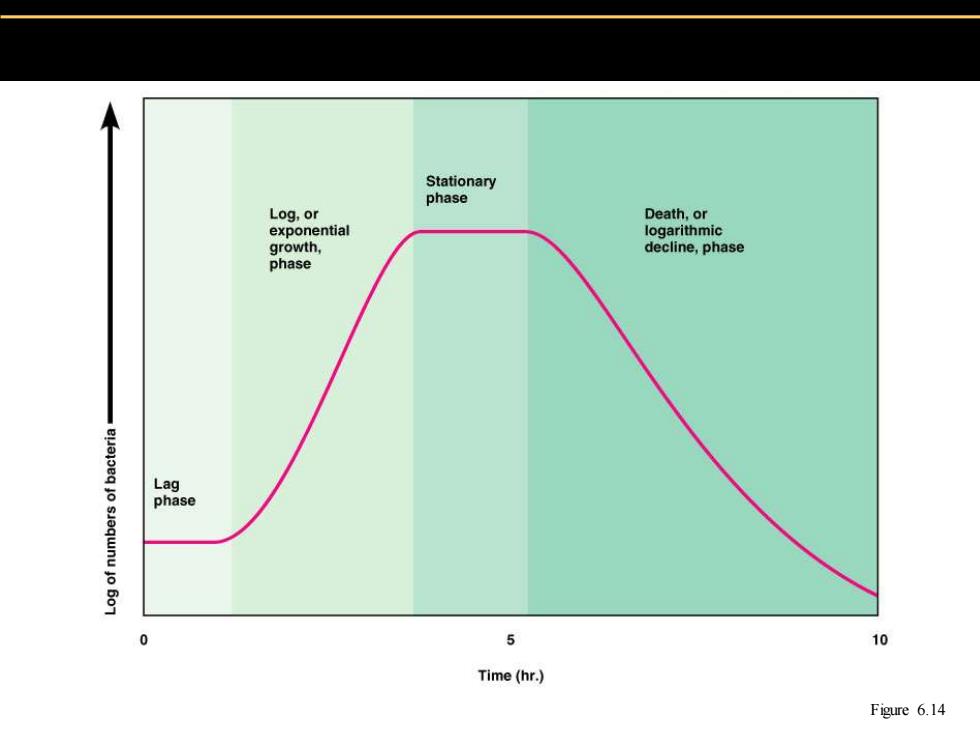
Stationary phase Log,or Death,or exponential logarithmic growth, decline,phase phase Lag phase 0 5 10 Time (hr.) Figure 6.14
Figure 6.14
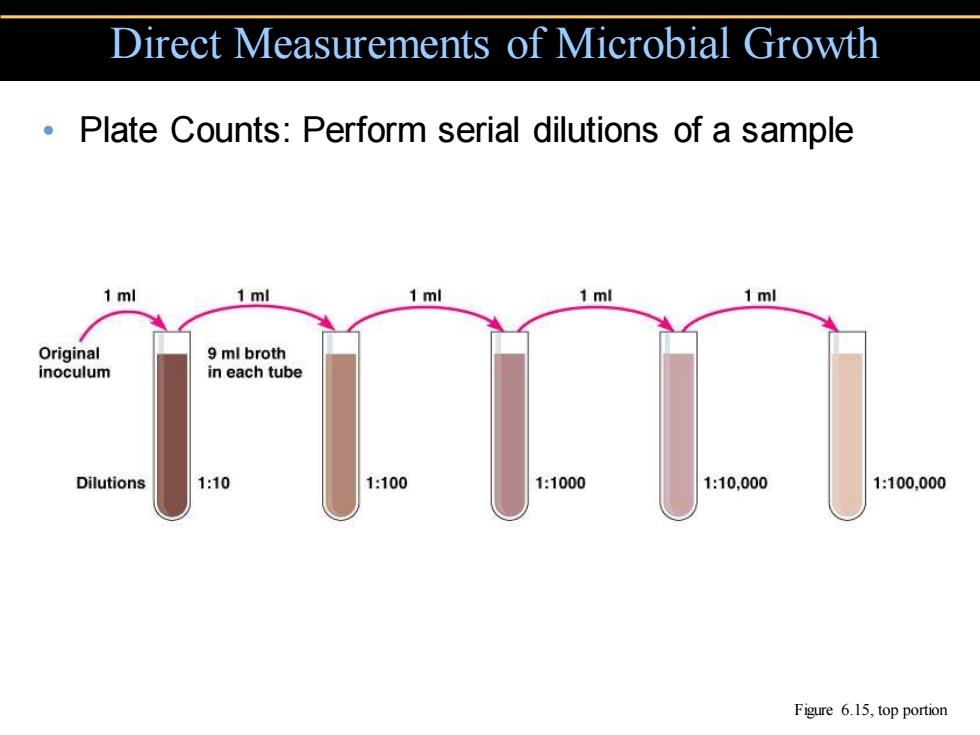
Direct Measurements of Microbial Growth Plate Counts:Perform serial dilutions of a sample 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml Original 9 ml broth inoculum in each tube Dilutions 1:10 1:100 1:1000 1:10,000 1:100,000 Figure 6.15,top portion
• Plate Counts: Perform serial dilutions of a sample Direct Measurements of Microbial Growth Figure 6.15, top portion

Plate Count (a)The pour plate method (b)The spread plate method Inoculate Petri 1.0or0.1ml 0.1ml plates from serial dilutions ①Inoculate ①Inoculate plate empty plate containing solid medium Bacterial dilution ②Add melted nutrient agar Spread inoculum over surface evenly Swirl to mix ④Colonies Colonies grow grow in and only on surface on solidified of medium medium Figure 6.16
• Inoculate Petri plates from serial dilutions Plate Count Figure 6.16