
Chapter 12,part D The Eukaryotes:Fungi,Algae,Protozoa,and Helminths
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 12, part D The Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, and Helminths
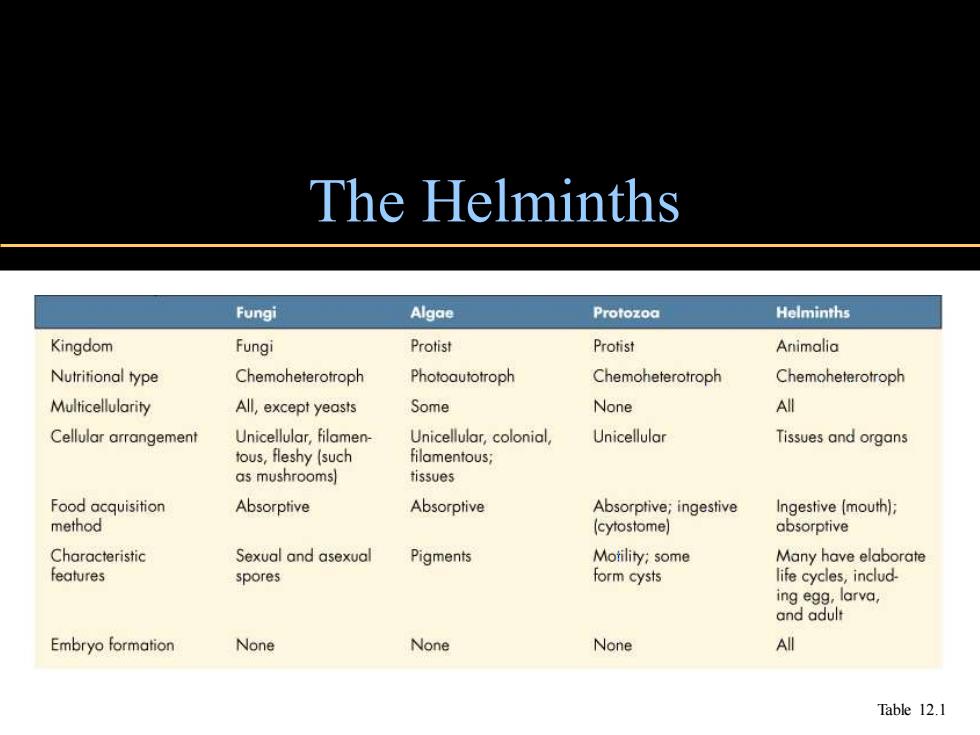
The Helminths Fungi Algae Protozoa Helminths Kingdom Fungi Protist Protist Animalia Nutritional type Chemoheterotroph Photoautotroph Chemoheterotroph Chemoheterotroph Multicellularity All,except yeasts Some None All Cellular arrangement Unicellular,filamen- Unicellular,colonial, Unicellular Tissues and organs tous,fleshy (such filamentous; as mushrooms) tissues Food acquisition Absorptive Absorptive Absorptive;ingestive Ingestive (mouth); method (cytostome) absorptive Characteristic Sexual and asexual Pigments Motility;some Many have elaborate features spores form cysts life cycles,includ- ing egg,larva, and adult Embryo formation None None None A Table 12.1
The Helminths Table 12.1

Helminths (parasitic worms) 。Eukaryotic Multicellular animals 。Chemoheterotrophic 。Kingdom:Animalia Phylum:Platyhelminthes (flatworms) Class:Trematodes (flukes) Class:Cestodes (tapeworms) Phylum:Nematodes (roundworms)
• Helminths (parasitic worms) • Eukaryotic • Multicellular animals • Chemoheterotrophic • Kingdom: Animalia • Phylum: Platyhelminthes (flatworms) • Class: Trematodes (flukes) • Class: Cestodes (tapeworms) • Phylum: Nematodes (roundworms)
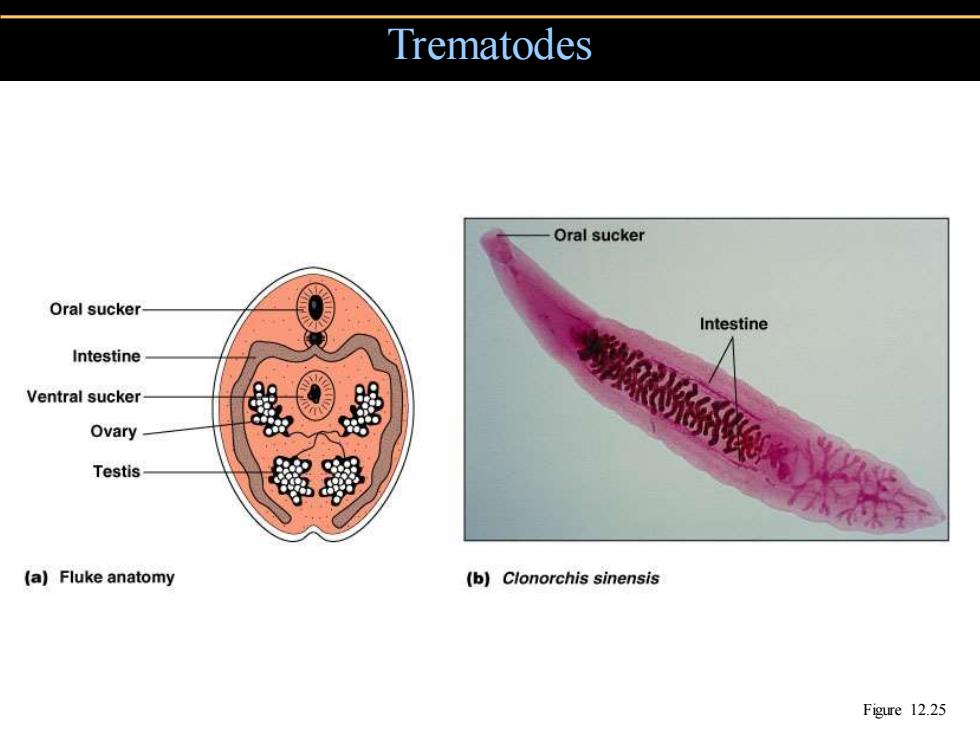
Trematodes Oral sucker Oral sucker Intestine Intestine Ventral sucker Ovary Testis (a)Fluke anatomy (b)Clonorchis sinensis Figure 12.25
Trematodes Figure 12.25
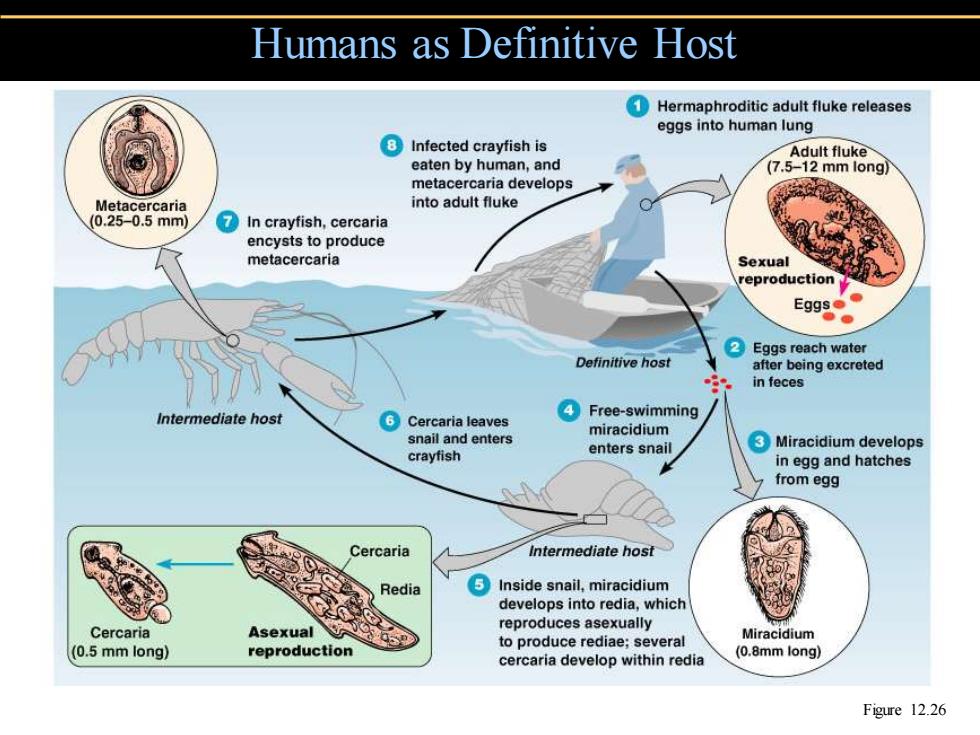
Humans as Definitive Host Hermaphroditic adult fluke releases eggs into human lung ⑧Infected crayfish is Adult fluke eaten by human,and (7.5-12 mm long metacercaria develops Metacercaria into adult fluke (0.25-0.5mm) In crayfish,cercaria encysts to produce metacercaria Sexual reproduction Eg9s● ②Eggs reach water Definitive host after being excreted in feces Intermediate host Cercaria leaves ④Free-swimming miracidium snail and enters enters snail Miracidium develops crayfish in egg and hatches from egg Cercaria Intermediate host Redia Inside snail,miracidium develops into redia,which reproduces asexually Cercaria Asexual Miracidium to produce rediae:several (0.5 mm long) reproduction (0.8mm long) cercaria develop within redia Figure 12.26
Humans as Definitive Host Figure 12.26
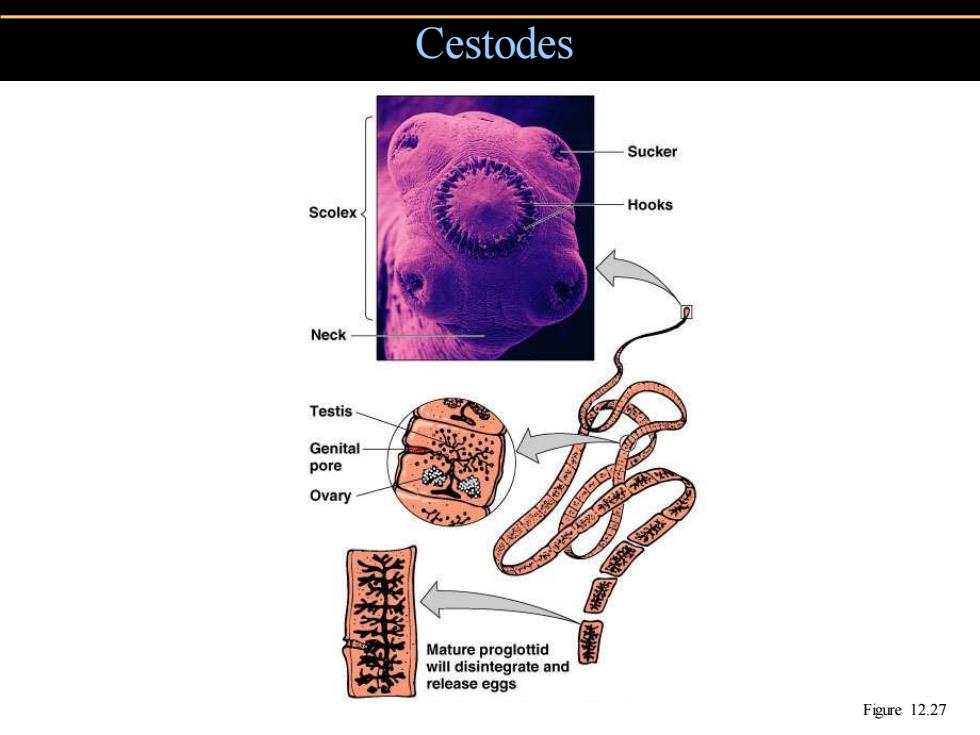
Cestodes Sucker Scolex Hooks Neck Testis Genital pore Ovary Mature proglottid will disintegrate and release eggs Figure 12.27
Cestodes Figure 12.27
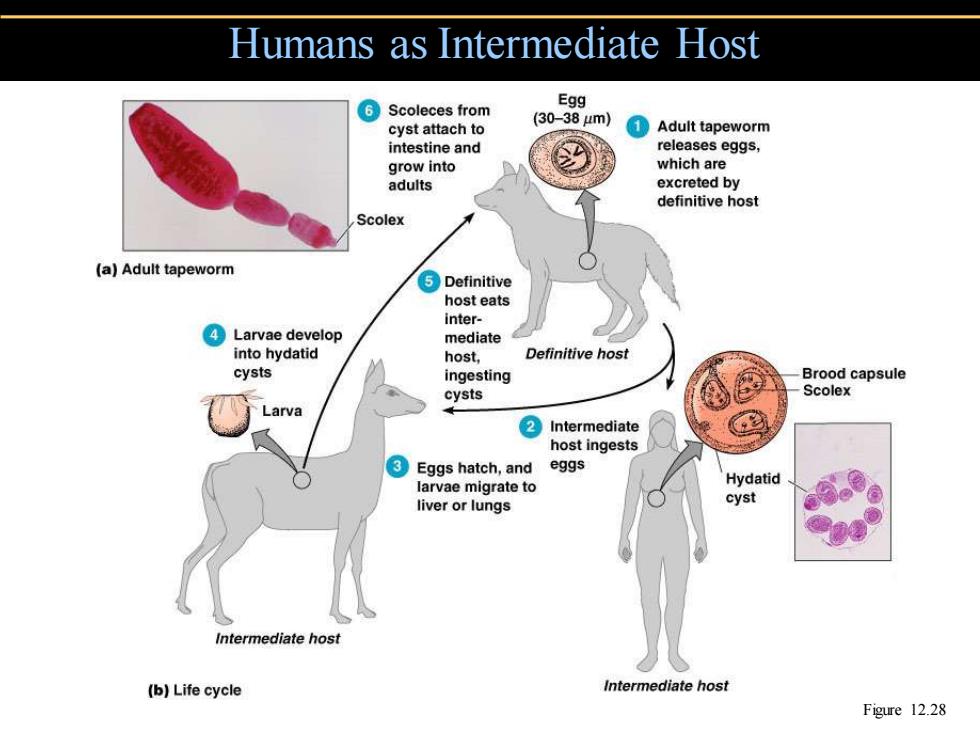
Humans as Intermediate Host ⑥Scoleces from Egg (30-38μm) cyst attach to ①Adult tapeworm intestine and releases eggs, grow into which are adults excreted by definitive host Scolex (a)Adult tapeworm ⑤Definitive host eats inter- ④Larvae develop mediate into hydatid host, Definitive host cysts ingesting Brood capsule cysts Scolex Larva ②Intermediate host ingests ③Eggs hatch,and eggs larvae migrate to Hydatid liver or lungs cyst Intermediate host (b)Life cycle Intermediate host Figure 12.28
Humans as Intermediate Host Figure 12.28
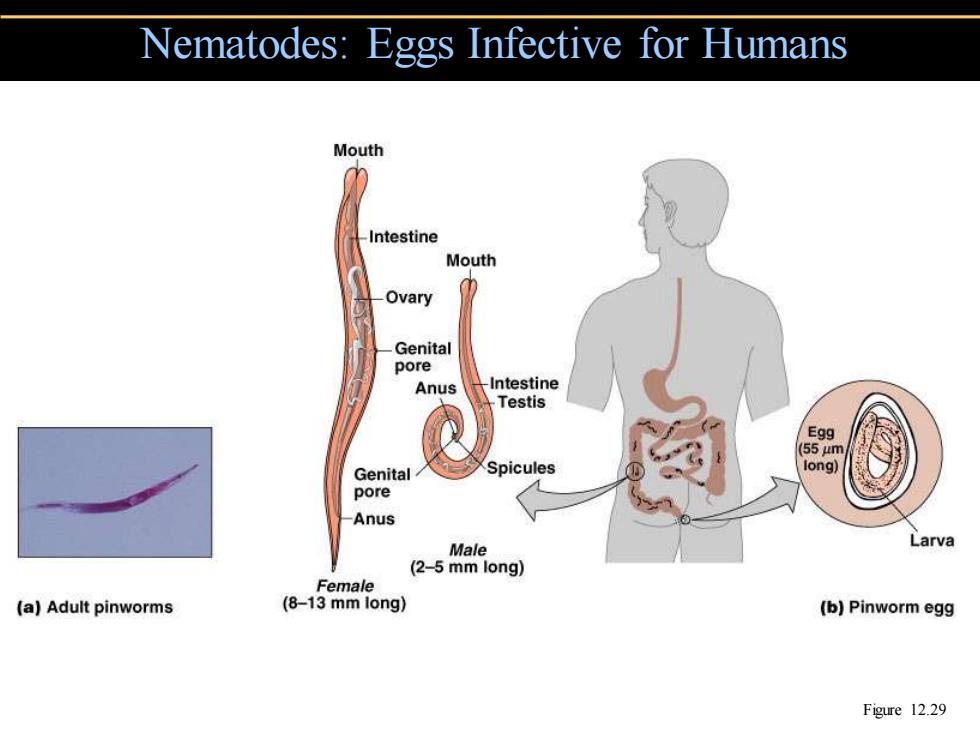
Nematodes:Eggs Infective for Humans Mouth Intestine Mouth Ovary Genital pore Anus -Intestine Testis Egg 155um Genital Spicules long) pore Anus Larva Male (2-5 mm long) Female (a)Adult pinworms (8-13 mm long) (b)Pinworm egg Figure 12.29
Nematodes: Eggs Infective for Humans Figure 12.29

Nematodes: Larvae Infective for Humans Adult Trichinella spiralis develop, invade intestinal wall of pig,and Capsule Garbage,including produce larvae that invade muscles. undercooked or Section showing T.spiralis raw pork larvae encysted in pig's muscle tissue(capsule is 0.25 to 0.5 mm in length). Section of T.spirolis. ⑤Meanwhile,.other animals are infected by eating infected meat that has been dumped. Undercooked pork Human eats undercooked pork containing cysts. ④In human intestine, cyst walls are removed, and T.spiralis adults develop.Adults produce larvae that encyst in muscles. (a)Life cycle of Trichinella spiralis,the causative agent of trichinosis (b)T.spiralis adult Figure 25.26
Nematodes: Larvae Infective for Humans Figure 25.26

Arthropods as Vectors Kingdom:Animalia ·Phylum:Arthropoda (exoskeleton,jointed legs) Class:Insecta (6 legs) 。Lice,fleas, (a)Female mosquito mosquitoes Class:Arachnida(8 legs) 。Mites and ticks 。May transmit diseases (vectors) Figure 12.31.32
• Kingdom: Animalia • Phylum: Arthropoda (exoskeleton, jointed legs) • Class: Insecta (6 legs) • Lice, fleas, mosquitoes • Class: Arachnida (8 legs) • Mites and ticks • May transmit diseases (vectors) Arthropods as Vectors Figure 12.31, 32