
Chapter 2,part B Chemical Principles
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 2, part B Chemical Principles

Important Biological Molecules Organic compounds always contain carbon and hydrogen. Inorganic compounds typically lack carbon
Important Biological Molecules • Organic compounds always contain carbon and hydrogen. • Inorganic compounds typically lack carbon
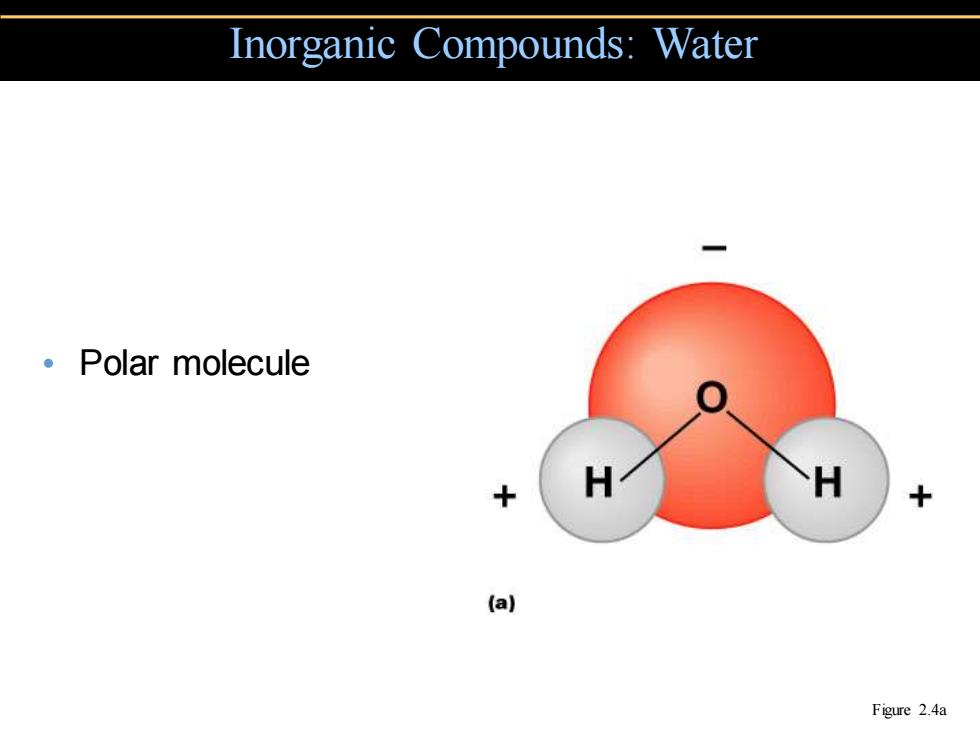
Inorganic Compounds:Water 。Polar molecule H (a) Figure 2.4a
• Polar molecule Inorganic Compounds: Water Figure 2.4a
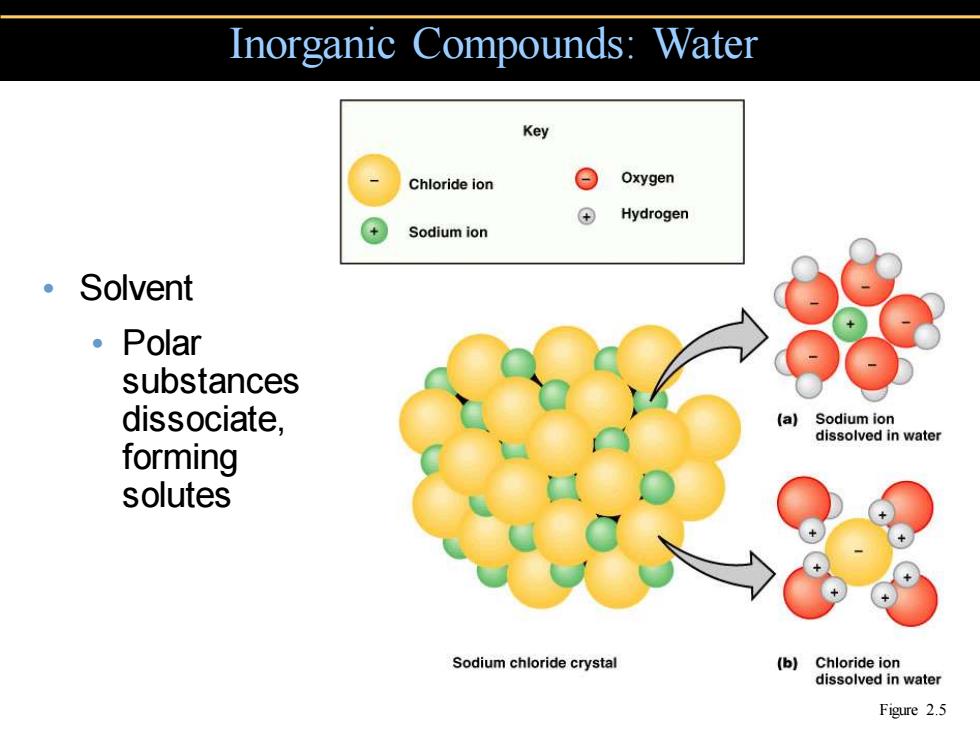
Inorganic Compounds:Water Key Chloride ion g Oxygen ⊕ Hydrogen Sodium ion 。Solvent 。Polar substances dissociate, (a)Sodium ion dissolved in water forming solutes Sodium chloride crystal (b)Chloride ion dissolved in water Figure 2.5
• Solvent • Polar substances dissociate, forming solutes Inorganic Compounds: Water Figure 2.5

Inorganic Compounds:Water H+and OH-participate in chemical reactions
• H+ and OH− participate in chemical reactions Inorganic Compounds: Water
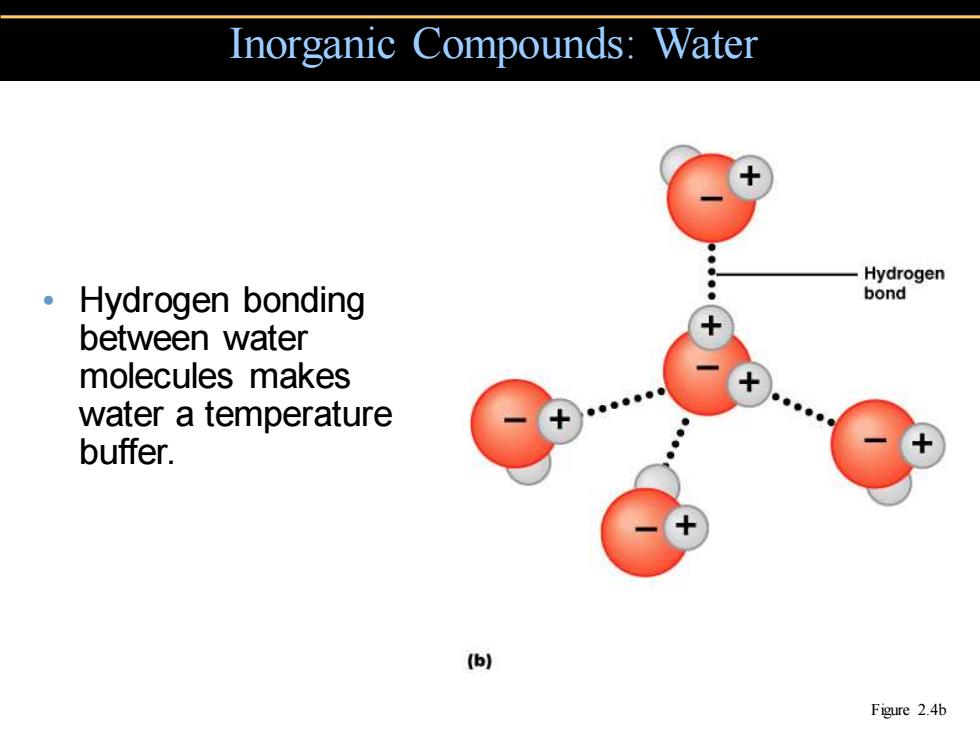
Inorganic Compounds:Water -Hydrogen ·Hydrogen bonding bond between water molecules makes water a temperature buffer. (b) Figure 2.4b
• Hydrogen bonding between water molecules makes water a temperature buffer. Inorganic Compounds: Water Figure 2.4b
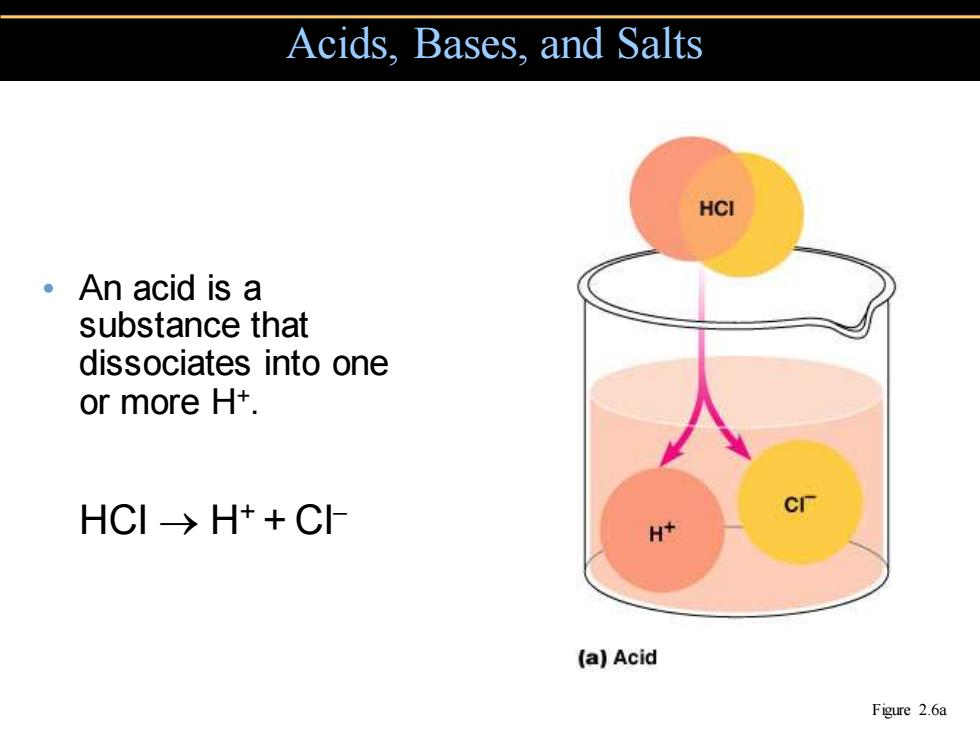
Acids,Bases,and Salts HCI 。An acid is a substance that dissociates into one or more H+. HCI→H++CH H+ (a】Acid Figure 2.6a
• An acid is a substance that dissociates into one or more H+. HCl → H+ + Cl− Acids, Bases, and Salts Figure 2.6a
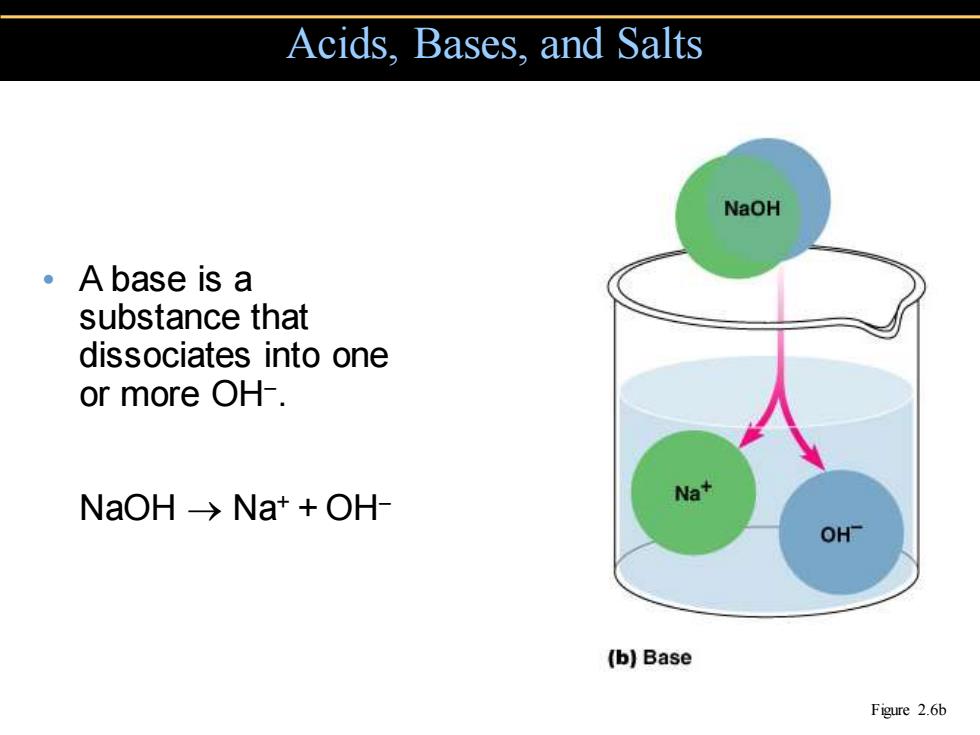
Acids.Bases,and Salts NaOH 。A base is a substance that dissociates into one or more OH-. NaOH->Na++OH- Na+ OH- (b)Base Figure 2.6b
• A base is a substance that dissociates into one or more OH− . NaOH → Na+ + OH− Acids, Bases, and Salts Figure 2.6b
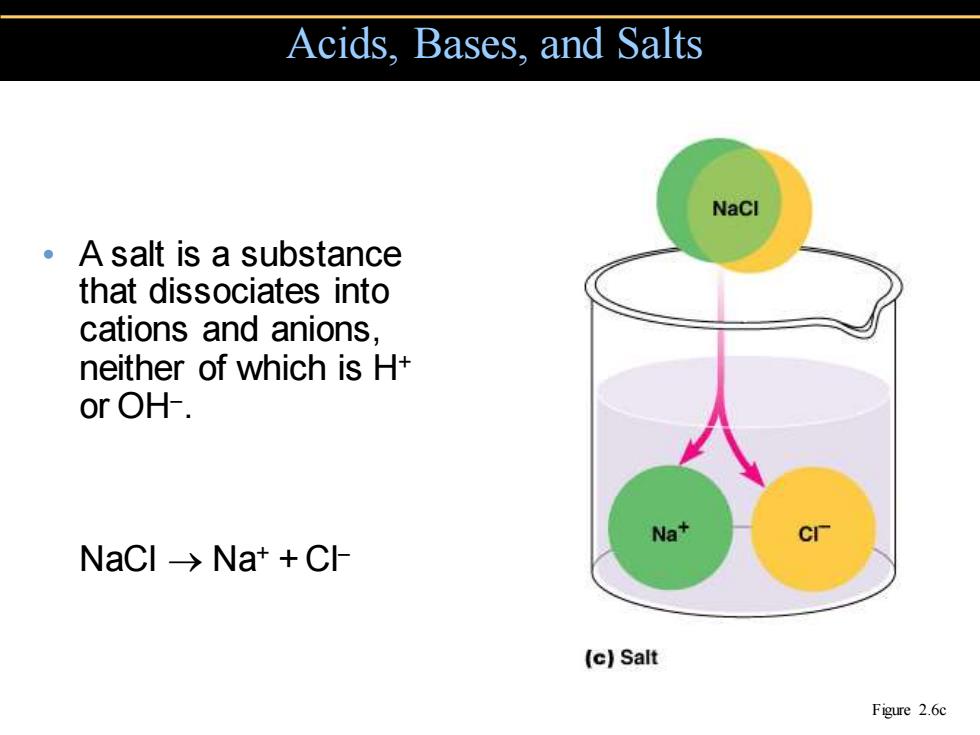
Acids,Bases,and Salts NaCI 。A salt is a substance that dissociates into cations and anions, neither of which is H+ or OH-. Na+ NaCl→Nat+CH (c)Salt Figure 2.6c
• A salt is a substance that dissociates into cations and anions, neither of which is H+ or OH− . NaCl → Na+ + Cl− Acids, Bases, and Salts Figure 2.6c
Acid-Base Balance The amount of H+in a solution is expressed as pH. 。pH=-log[Ht] Increasing [H+],increases acidity. Increasing [OH-]increases alkalinity. Most organisms grow best between pH 6.5 and 8.5
• The amount of H+ in a solution is expressed as pH. • pH = −log[H+] • Increasing [H+], increases acidity. • Increasing [OH− ] increases alkalinity. • Most organisms grow best between pH 6.5 and 8.5. Acid-Base Balance