
Chapter 2,part A Chemical Principles
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 2, part A Chemical Principles

Chemistry Chemistry is the study of interactions between atoms and molecules. The atom is the smallest unit of matter that enters into chemical reactions. Atoms interact to form molecules
Chemistry • Chemistry is the study of interactions between atoms and molecules. • The atom is the smallest unit of matter that enters into chemical reactions. • Atoms interact to form molecules

The Study of Atoms Atoms are composed of Electrons:negatively charged particles Protons:positively charged particles Neutrons:uncharged particles
Atoms are composed of • Electrons: negatively charged particles • Protons: positively charged particles • Neutrons: uncharged particles The Study of Atoms
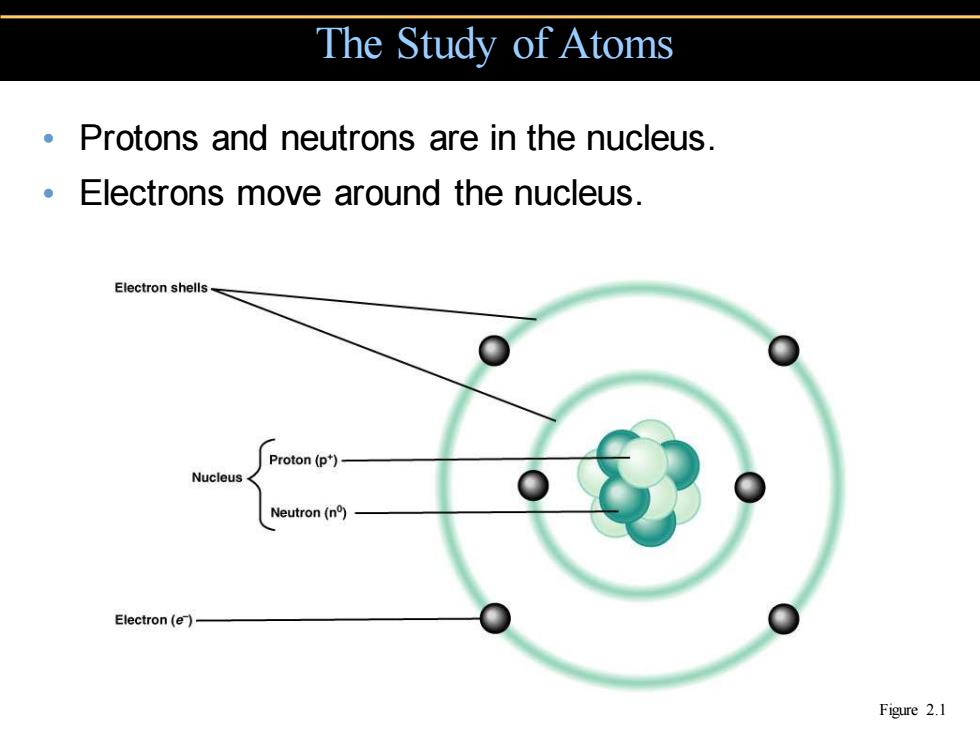
The Study of Atoms Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus. Electrons move around the nucleus. Electron shells Proton (p*) Nucleus Neutron(n) Electron(e)- Figure 2.1
• Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus. • Electrons move around the nucleus. The Study of Atoms Figure 2.1
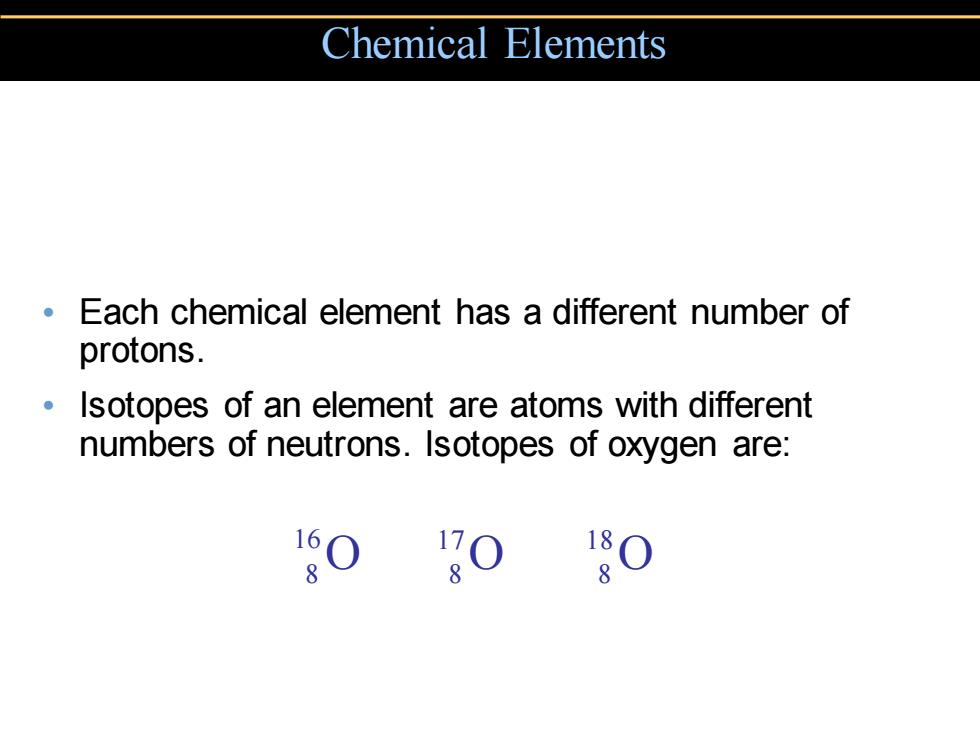
Chemical Elements Each chemical element has a different number of protons. Isotopes of an element are atoms with different numbers of neutrons.Isotopes of oxygen are: O 0
• Each chemical element has a different number of protons. • Isotopes of an element are atoms with different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes of oxygen are: Chemical Elements 16 8O 17 8O 18 8O
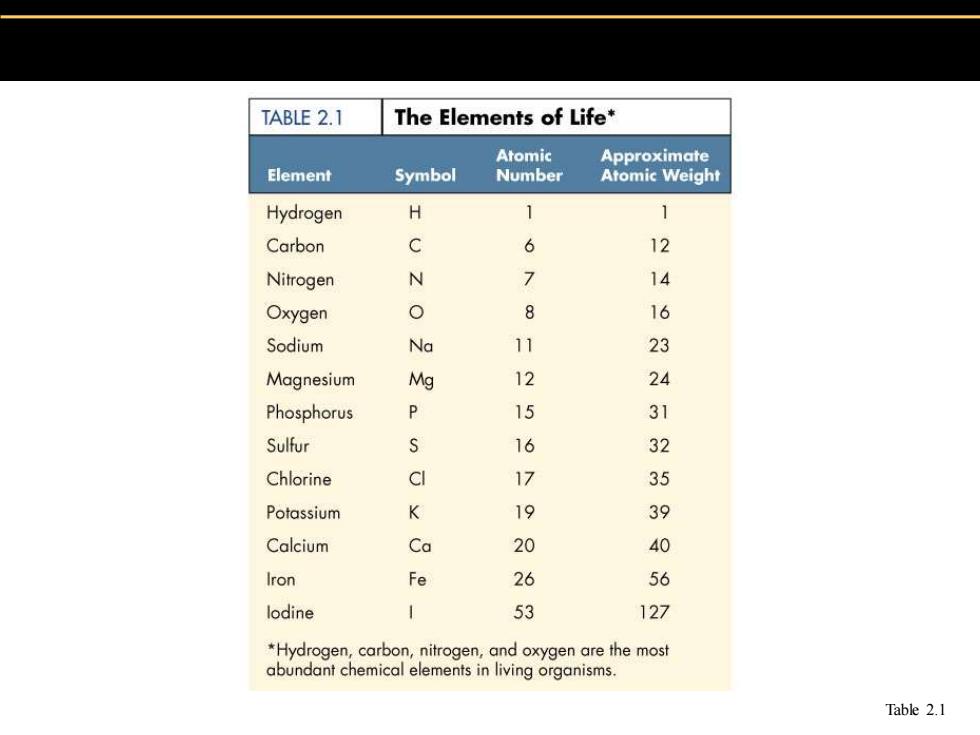
TABLE 2.1 The Elements of Life* Atomic Approximate Element Symbol Number Atomic Weight Hydrogen H 1 1 Carbon C 6 12 Nitrogen N > 14 Oxygen 0 0 16 Sodium Na 11 23 Magnesium Mg 12 24 Phosphorus P 15 31 Sulfur s 16 32 Chlorine CI 17 35 Potassium K 19 39 Calcium Ca 20 40 Iron Fe 26 56 lodine 53 127 *Hydrogen,carbon,nitrogen,and oxygen are the most abundant chemical elements in living organisms. Table 2.1
Table 2.1

Electronic Configurations Electrons are arranged in electron shells corresponding to different energy levels
• Electrons are arranged in electron shells corresponding to different energy levels. Electronic Configurations

Electronic Configurations TABLE 2.2 Electronic Configurations for the Atoms of Some Elements Found in Living Organisms Number First Second Third of Valence Number Maximum Electron Electron Electron (Outermost) of Unfilled Number of Element Shell Shell Shell Diagram Shell Electrons Spaces Bonds Formed Hydrogen 1 1 88 Carbon 4 00 Nitrogen 2 0 00 oo Oxygen 2 electron unfilled space Key:atomic nucleus Table 2.2.1
Electronic Configurations Table 2.2.1
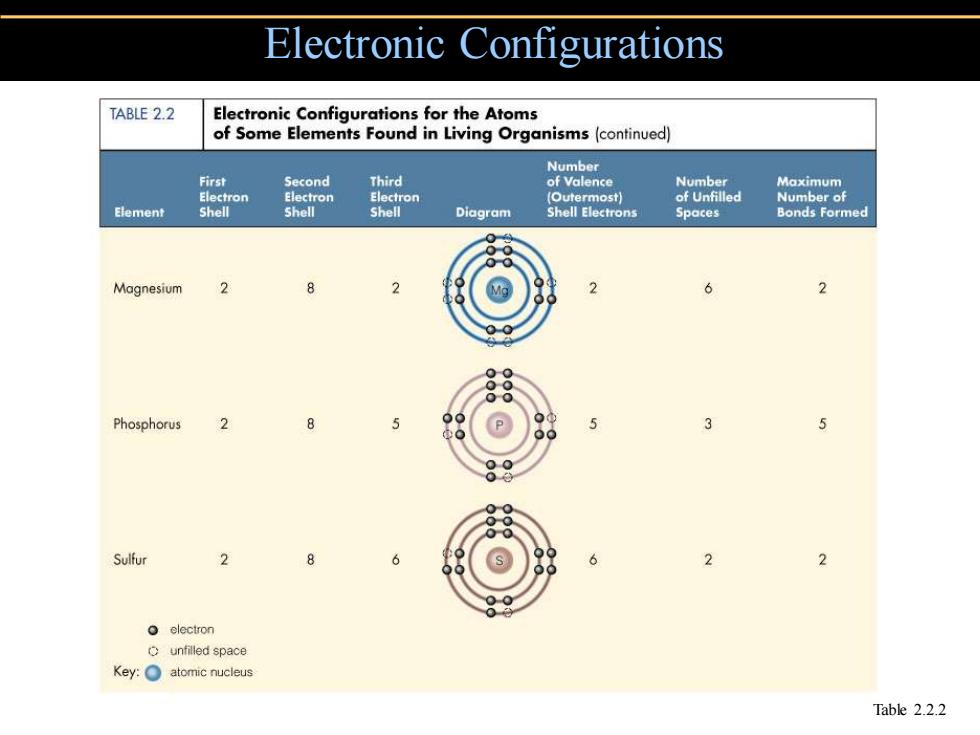
Electronic Configurations TABLE 2.2 Electronic Configurations for the Atoms of Some Elements Found in Living Organisms(continued) Number First Second Third of Valence Number Maximum Electron Electron Electron (Outermost) of Unfilled Number of Element Shell Shell Shell Diagram Shell Electrons Spaces Bonds Formed Magnesium 2 2 2 Phosphorus 2 Sulfur 2 6 2 electron Cunfilled space Key:atomic nucleus Table 2.2.2
Electronic Configurations Table 2.2.2

How Atoms Form Molecules:Chemical Bonds Atoms combine to complete the outermost shell. The number of missing or extra electrons in this shell is the valence
• Atoms combine to complete the outermost shell. • The number of missing or extra electrons in this shell is the valence. How Atoms Form Molecules: Chemical Bonds