
Chapter 23,part A Microbial Diseases of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 23, part A Microbial Diseases of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
The Cardiovascular System and Lymphatics System 。 Blood-Transports nutrients to and wastes from cells WBCs-Defend against infection Lymphatics-Transport interstitial fluid to blood Lymph nodes-Contain fixed macrophages
The Cardiovascular System and Lymphatics System • Blood—Transports nutrients to and wastes from cells • WBCs—Defend against infection • Lymphatics—Transport interstitial fluid to blood • Lymph nodes—Contain fixed macrophages
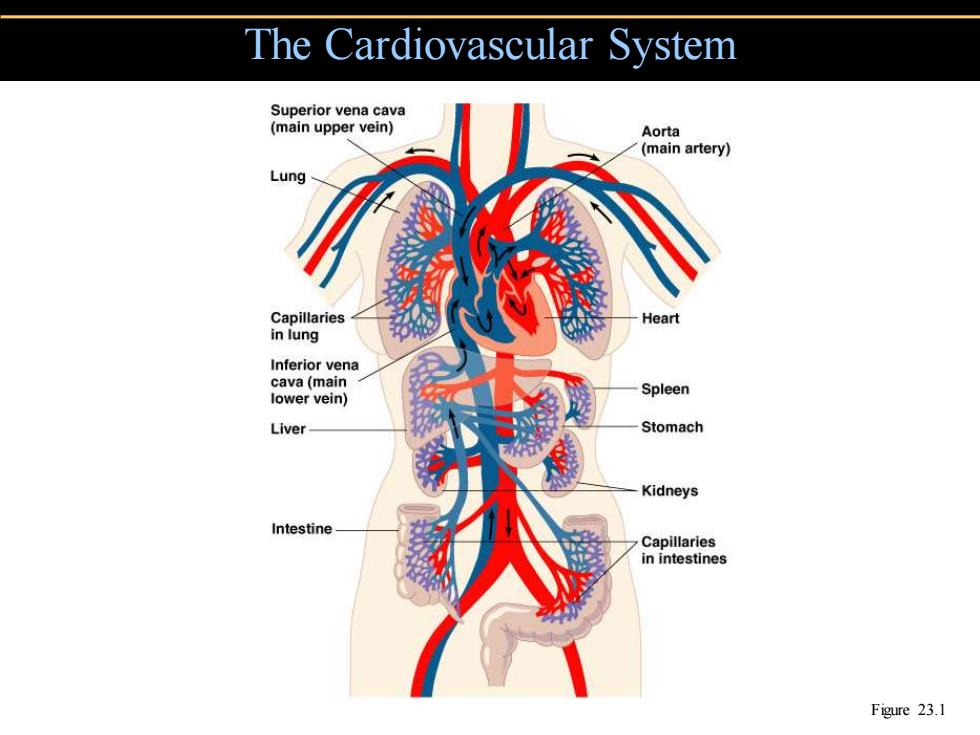
The Cardiovascular System Superior vena cava (main upper vein) Aorta (main artery) Lung Capillaries Heart in lung Inferior vena cava (main Spleen lower vein) Liver Stomach Kidneys Intestine Capillaries in intestines Figure 23.1
The Cardiovascular System Figure 23.1
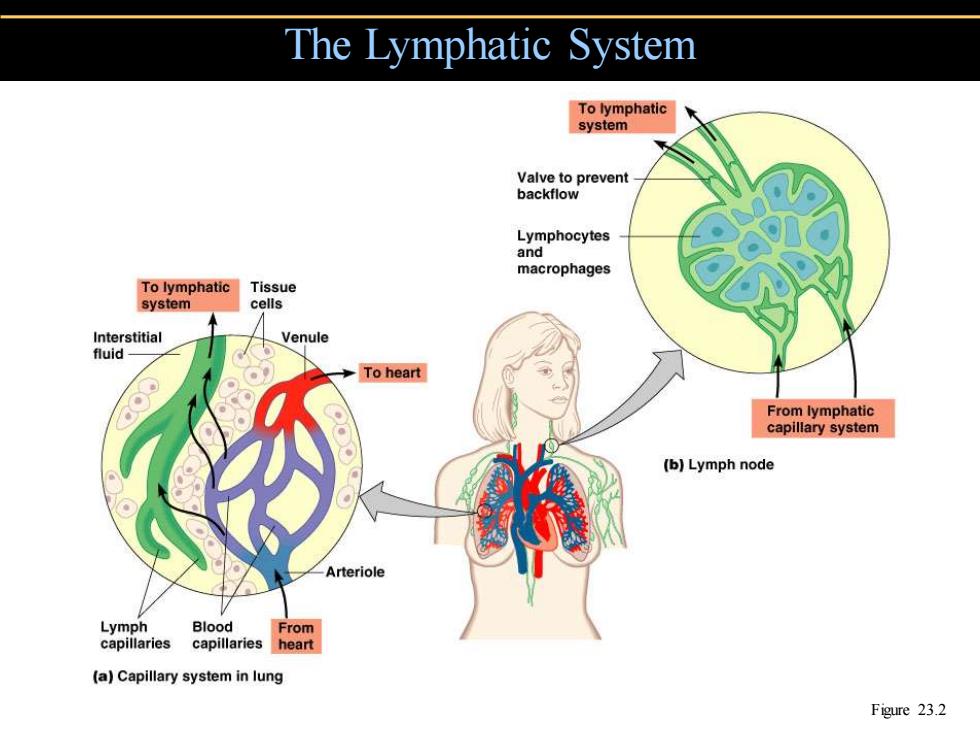
The Lymphatic System To lymphatic system Valve to prevent backflow Lymphocytes and macrophages To lymphatic Tissue system cells Interstitial Venule fluid- To heart From lymphatic capillary system (b)Lymph node Arteriole Lymph Blood From capillaries capillaries heart (a)Capillary system in lung Figure 23.2
The Lymphatic System Figure 23.2
Sepsis and Septic Shock 。Sepsis ·Bacteria growing in the blood 。Severe sepsis 。Decrease in blood pressure ·Septic shock ·Low blood pressure cannot be controlled Figure 23.3
• Sepsis • Bacteria growing in the blood • Severe sepsis • Decrease in blood pressure • Septic shock • Low blood pressure cannot be controlled Sepsis and Septic Shock Figure 23.3

Sepsis Gram-negative Sepsis Endotoxins caused blood pressure decrease Antibiotics can worsen condition by killing bacteria Gram-Positive Sepsis Nosocomial infections Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus pyogenes Group B streptococcus Enterococcus faecium and E.faecalis
• Gram-negative Sepsis • Endotoxins caused blood pressure decrease • Antibiotics can worsen condition by killing bacteria • Gram-Positive Sepsis • Nosocomial infections • Staphylococcus aureus • Streptococcus pyogenes • Group B streptococcus • Enterococcus faecium and E. faecalis Sepsis

Sepsis Puerperal Sepsis (Childbirth fever) Streptococcus pyogenes Transmitted to mother during childbirth by attending physicians midwives
• Puerperal Sepsis (Childbirth fever) • Streptococcus pyogenes • Transmitted to mother during childbirth by attending physicians & midwives Sepsis

Bacterial Infections of the Heart 。Endocarditis Inflammation of the endocardium Subacute bacterial endocarditis Alpha-hemolytic streptococci from mouth Acute bacterial endocarditis Staphylococcus aureus from mouth Pericarditis ·Streptococci
• Endocarditis • Inflammation of the endocardium • Subacute bacterial endocarditis • Alpha-hemolytic streptococci from mouth • Acute bacterial endocarditis • Staphylococcus aureus from mouth • Pericarditis • Streptococci Bacterial Infections of the Heart
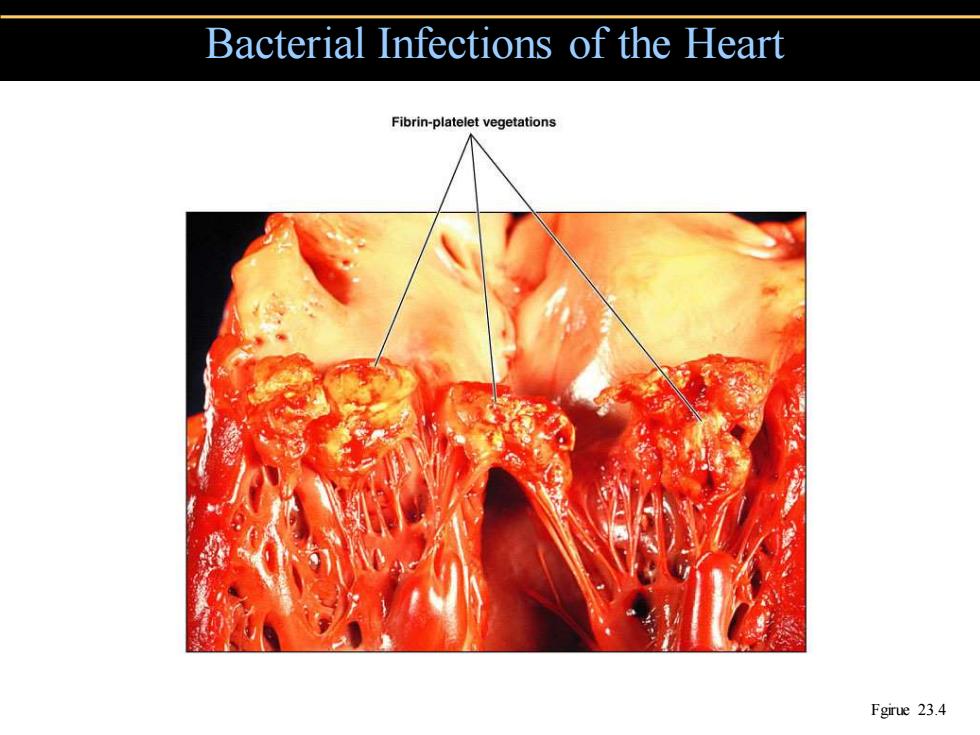
Bacterial Infections of the Heart Fibrin-platelet vegetations Fgirue 23.4
Bacterial Infections of the Heart Fgirue 23.4
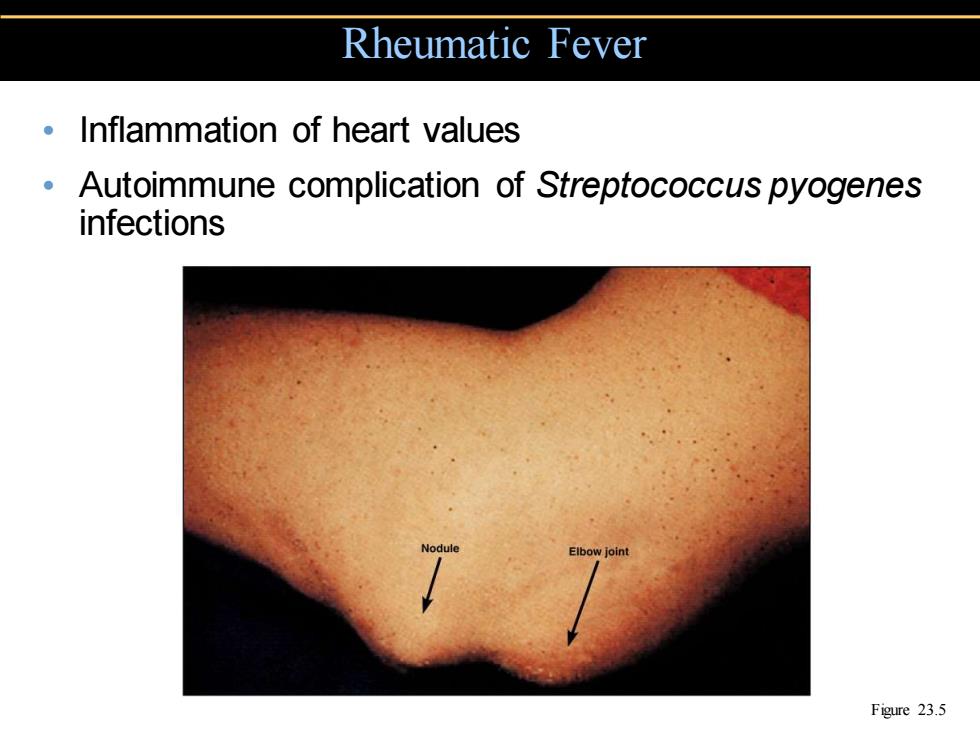
Rheumatic Fever Inflammation of heart values Autoimmune complication of Streptococcus pyogenes infections Figure 23.5
• Inflammation of heart values • Autoimmune complication of Streptococcus pyogenes infections Rheumatic Fever Figure 23.5