
Chapter 16 Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 16 Nonspecific Defenses of the Host

Nonspecific Defenses of the Host 。 Susceptibility Lack of resistance to a disease 。Resistance Ability to ward off disease Nonspecific resistance Defenses against any pathogen 。Specific resistance Immunity,resistance to a specific pathogen
Nonspecific Defenses of the Host • Susceptibility Lack of resistance to a disease • Resistance Ability to ward off disease • Nonspecific resistance Defenses against any pathogen • Specific resistance Immunity, resistance to a specific pathogen
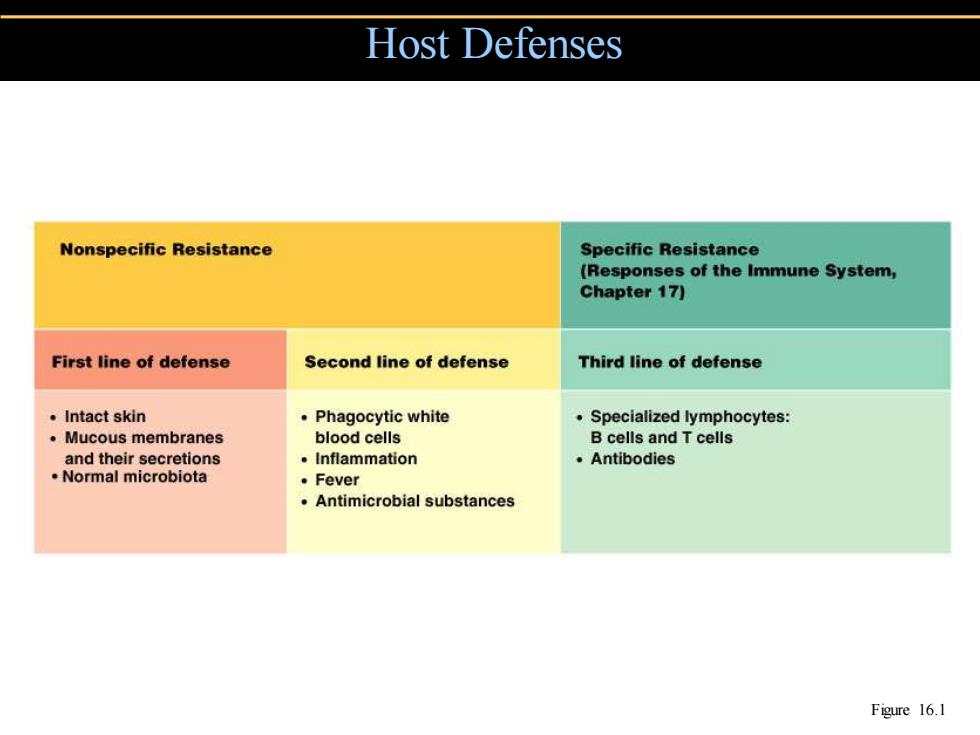
Host Defenses Nonspecific Resistance Specific Resistance (Responses of the Immune System, Chapter 17) First line of defense Second line of defense Third line of defense 。Intact skin ·Phagocytic white Specialized lymphocytes: 。Mucous membranes blood cells B cells and T cells and their secretions 。Inflammation ·Antibodies Normal microbiota ·Fever Antimicrobial substances Figure 16.1
Host Defenses Figure 16.1

Mechanical Factors 。Skin Epidermis consists of tightly packed cells with Keratin,a protective protein
• Skin • Epidermis consists of tightly packed cells with • Keratin, a protective protein Mechanical Factors

Mechanical Factors 。Mucous membranes Ciliary escalator:Microbes trapped in mucus are transported away from the lungs Lacrimal apparatus:Washes eye Saliva:Washes microbes off 。Urine:Flows out Vaginal secretions:Flow out
• Mucous membranes • Ciliary escalator: Microbes trapped in mucus are transported away from the lungs • Lacrimal apparatus: Washes eye • Saliva: Washes microbes off • Urine: Flows out • Vaginal secretions: Flow out Mechanical Factors

Chemical Factors Fungistatic fatty acid in sebum ·Low pH(3-5)of skin Lysozyme in perspiration,tears,saliva,and tissue fluids Low pH(1.2-3.0)of gastric juice Transferrins in blood find iron NO inhibits ATP production
• Fungistatic fatty acid in sebum • Low pH (3-5) of skin • Lysozyme in perspiration, tears, saliva, and tissue fluids • Low pH (1.2-3.0) of gastric juice • Transferrins in blood find iron • NO inhibits ATP production Chemical Factors
Normal Microbiota Microbial antagonism/competitive exclusion:Normal microbiota compete with pathogens
• Microbial antagonism/competitive exclusion: Normal microbiota compete with pathogens. Normal Microbiota
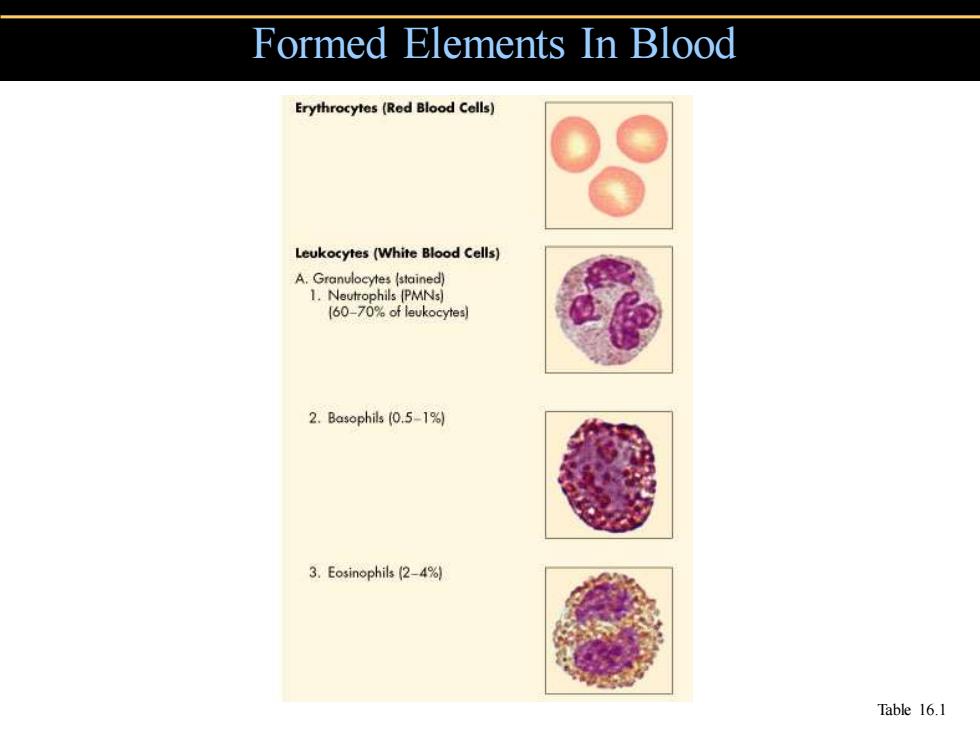
Formed Elements In Blood Erythrocytes(Red Blood Cells) Leukocytes(White Blood Cells) A.Granulocytes (stained) 1.Neutrophils (PMNs) 60-70%of leukocytes到 2.Basophils0.5-1购 3.Eosinophils(2-4%) Table 16.1
Formed Elements In Blood Table 16.1
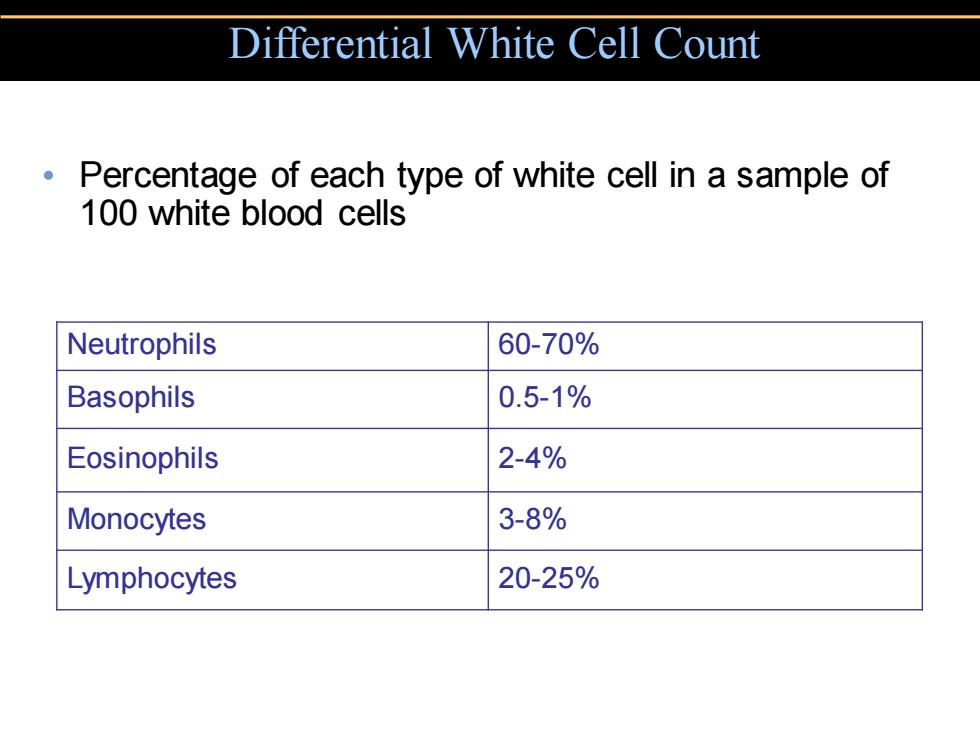
Differential White Cell Count Percentage of each type of white cell in a sample of 100 white blood cells Neutrophils 60-70% Basophils 0.5-1% Eosinophils 2-4% Monocytes 3-8% Lymphocytes 20-25%
• Percentage of each type of white cell in a sample of 100 white blood cells Differential White Cell Count Neutrophils 60-70% Basophils 0.5-1% Eosinophils 2-4% Monocytes 3-8% Lymphocytes 20-25%

White Blood Cells Neutrophils:Phagocytic Basophils:Produce histamine Eosinophils:Toxic to parasites,some phagocytosis Monocytes:Phagocytic as mature macrophages Fixed macrophages in lungs,liver,bronchi Wandering macrophages roam tissues Lymphocytes:Involved in specific immunity
• Neutrophils: Phagocytic • Basophils: Produce histamine • Eosinophils: Toxic to parasites, some phagocytosis • Monocytes: Phagocytic as mature macrophages • Fixed macrophages in lungs, liver, bronchi • Wandering macrophages roam tissues • Lymphocytes: Involved in specific immunity White Blood Cells