
Chapter 13,part A Viruses,Viroids,and Prions
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 13, part A Viruses, Viroids, and Prions

Viruses Viruses contain DNA or RNA 。And a protein coat Some are enclosed by an envelope 。 Some viruses have spikes Most viruses infect only specific types of cells in one host Host range is determined by specific host attachment sites and cellular factors
Viruses • Viruses contain DNA or RNA • And a protein coat • Some are enclosed by an envelope • Some viruses have spikes • Most viruses infect only specific types of cells in one host • Host range is determined by specific host attachment sites and cellular factors
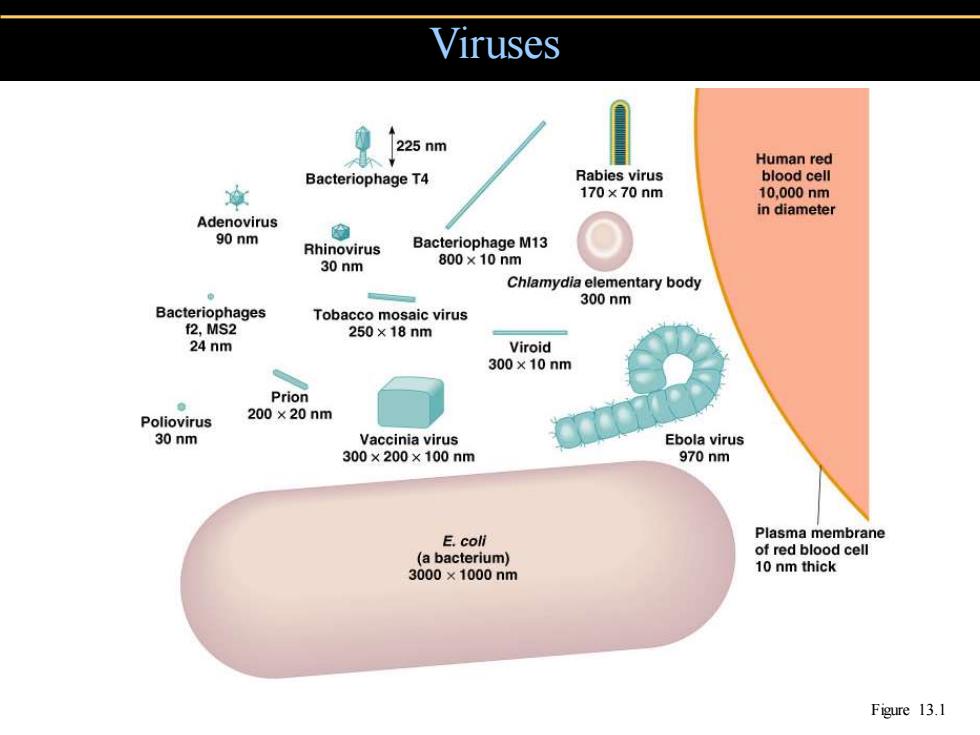
Viruses 225nm Human red Bacteriophage T4 Rabies virus blood cell 章 170×70nm 10,000nm in diameter Adenovirus 90 nm Rhinovirus Bacteriophage M13 30 nm 800×10nm Chlamydia elementary body 300nm Bacteriophages Tobacco mosaic virus 2,MS2 250×18nm 24 nm Viroid 300×10nm Prion Poliovirus 200×20nm 30 nm Vaccinia virus Ebola virus 300×200×100nm 970nm E.coli Plasma membrane (a bacterium) of red blood cell 3000×1000nm 10 nm thick Figure 13.1
Viruses Figure 13.1
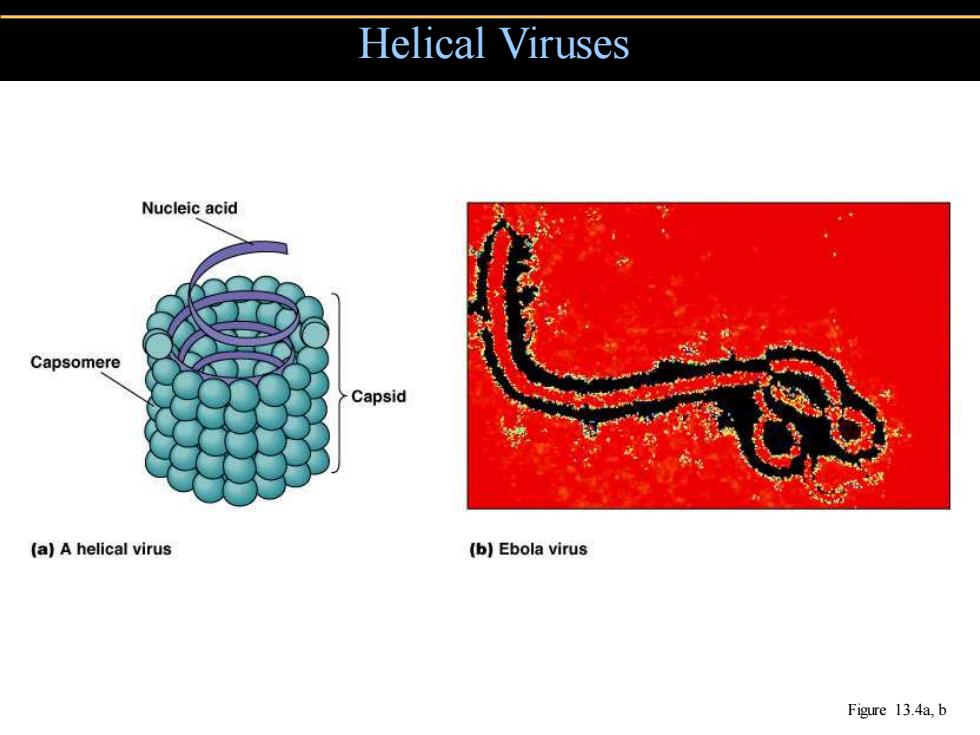
Helical Viruses Nucleic acid Capsomere Capsid (a)A helical virus (b)Ebola virus Figure 13.4a,b
Helical Viruses Figure 13.4a, b
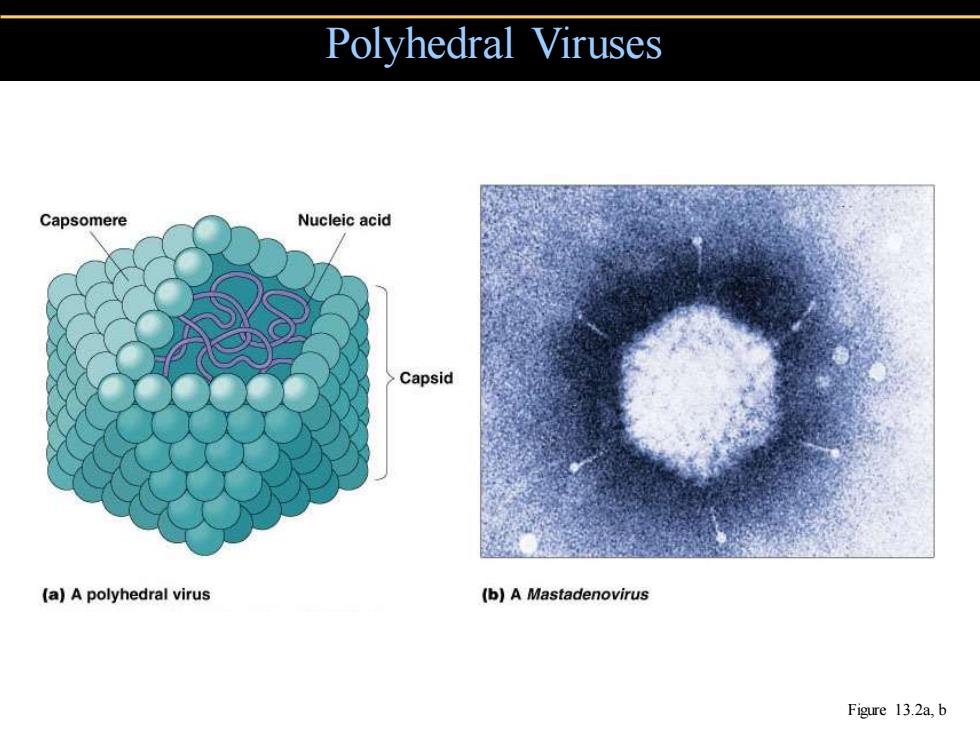
Polyhedral Viruses Capsomere Nucleic acid Capsid (a)A polyhedral virus (b)A Mastadenovirus Figure 13.2a,b
Polyhedral Viruses Figure 13.2a, b
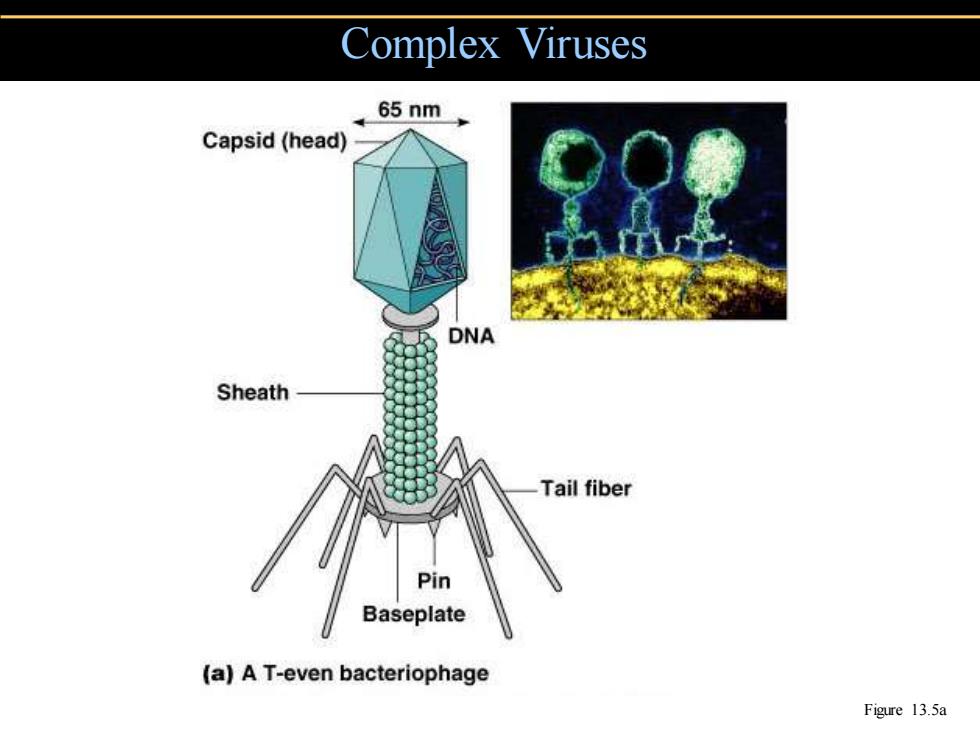
Complex Viruses 65nm, Capsid (head) DNA Sheath Tail fiber Pin Baseplate (a)A T-even bacteriophage Figure 13.5a
Complex Viruses Figure 13.5a

Viral Taxonomy Family names end in -viridae Genus names end in -virus Viral species:A group of viruses sharing the same genetic information and ecological niche (host). Common names are used for species Subspecies are designated by a number
Viral Taxonomy • Family names end in -viridae • Genus names end in -virus • Viral species: A group of viruses sharing the same genetic information and ecological niche (host). Common names are used for species • Subspecies are designated by a number
Viral Taxonomy 。Herpesviridae 。Retroviridae ·Herpesvirus 。Lentivirus 。Human herpes 。Human virus 1,HHV 2, Immunodeficiency Virus HHV 3 1,HIV 2
Viral Taxonomy • Herpesviridae • Herpesvirus • Human herpes virus 1, HHV 2, HHV 3 • Retroviridae • Lentivirus • Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1, HIV 2
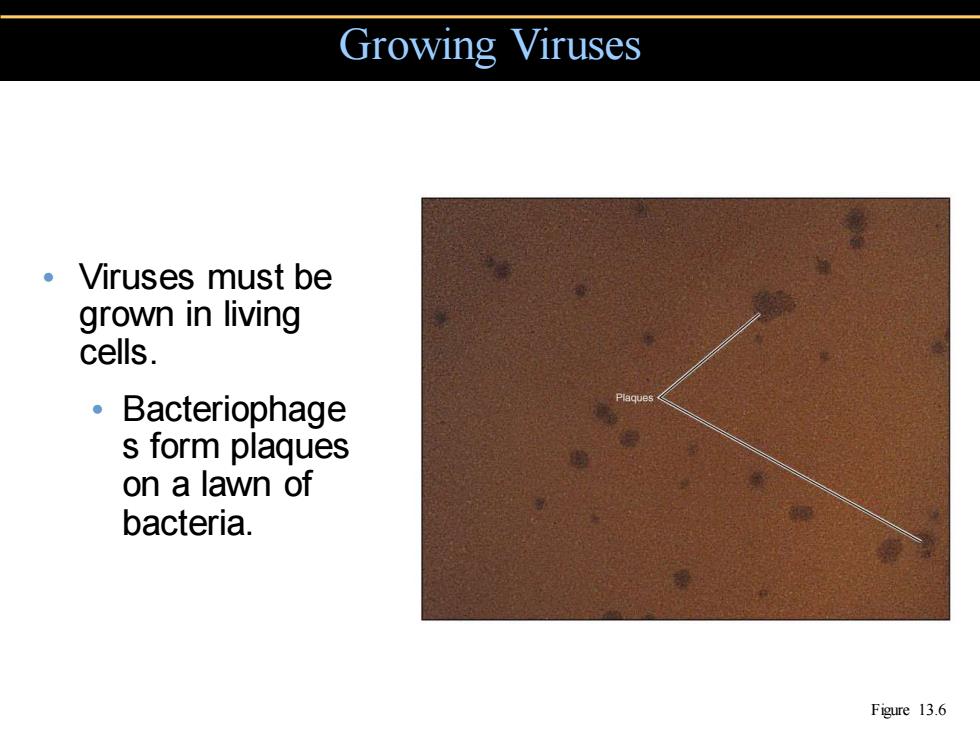
Growing Viruses ·Viruses must be grown in living cells. 。Bacteriophage s form plaques on a lawn of bacteria. Figure 13.6
Growing Viruses • Viruses must be grown in living cells. • Bacteriophage s form plaques on a lawn of bacteria. Figure 13.6

Growing Viruses Chorioallantoic membrane Air sac Shell Chorioallantoic Amniotic membrane cavity inoculation ·Animal viruses may be grown in Amniotic inoculation living animals or in embryonated eggs. Allantoic inoculation Shell Albumin Allantoic Yolk sac membrane cavity inoculation Figure 13.7
Growing Viruses • Animal viruses may be grown in living animals or in embryonated eggs. Figure 13.7