
Chapter 3 Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 3 Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope

Units of Measurement 。1μm=10-6m=103mm 。1nm=109m=10-6mm 。1000nm=1μm 。0.001μm=1nm
Units of Measurement • 1 µm = 10-6 m = 10-3 mm • 1 nm = 10-9 m = 10-6 mm • 1000 nm = 1 µm • 0.001 µm = 1 nm
Microscopy:The Instruments CENTIETERS Location of specimen Lens 。A simple microscope has only one lens. (b)Microscope replica Figure 1.2b
• A simple microscope has only one lens. Microscopy: The Instruments Figure 1.2b
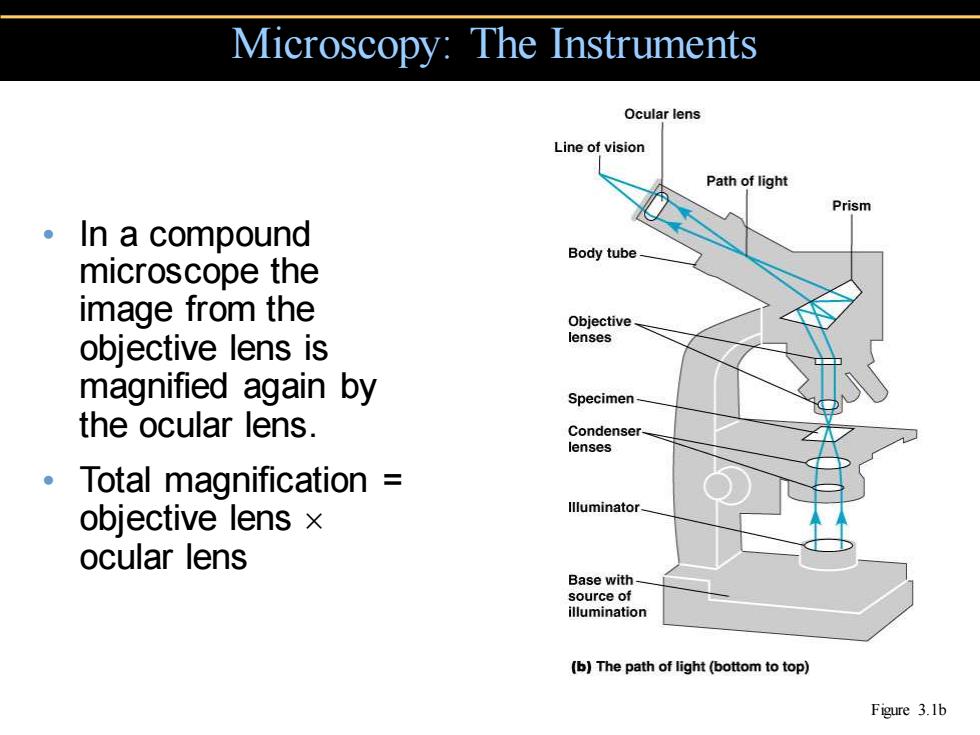
Microscopy:The Instruments Ocular lens Line of vision Path of light Prism 。In a compound Body tube microscope the image from the Objective objective lens is lenses magnified again by Specimen- the ocular lens. Condenser- lenses 。1 Total magnification objective lens x llluminator. ocular lens Base with source of illumination (b)The path of light(bottom to top) Figure 3.1b
• In a compound microscope the image from the objective lens is magnified again by the ocular lens. • Total magnification = objective lens ocular lens Microscopy: The Instruments Figure 3.1b
Microscopy:The Instruments Resolution is the ability of the lenses to distinguish two points. A microscope with a resolving power of 0.4 nm can distinguish between two points 0.4 nm. Shorter wavelengths of light provide greater resolution
• Resolution is the ability of the lenses to distinguish two points. • A microscope with a resolving power of 0.4 nm can distinguish between two points ≥ 0.4 nm. • Shorter wavelengths of light provide greater resolution. Microscopy: The Instruments
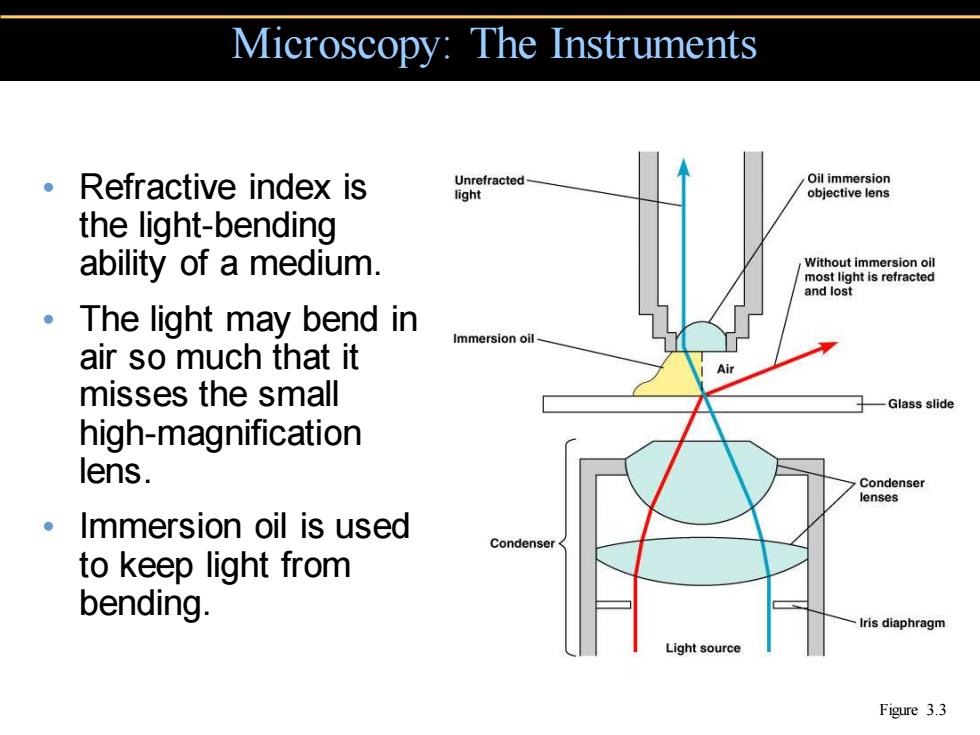
Microscopy:The Instruments 。Refractive index is Unrefracted Oil immersion light objective lens the light-bending ability of a medium. Without immersion oil ·The light may bend in Immersion oil air so much that it misses the small Glass slide high-magnification lens. Condenser lenses 。Immersion oil is used Condenser to keep light from bending. Iris diaphragm Light source Figure 3.3
• Refractive index is the light-bending ability of a medium. • The light may bend in air so much that it misses the small high-magnification lens. • Immersion oil is used to keep light from bending. Microscopy: The Instruments Figure 3.3
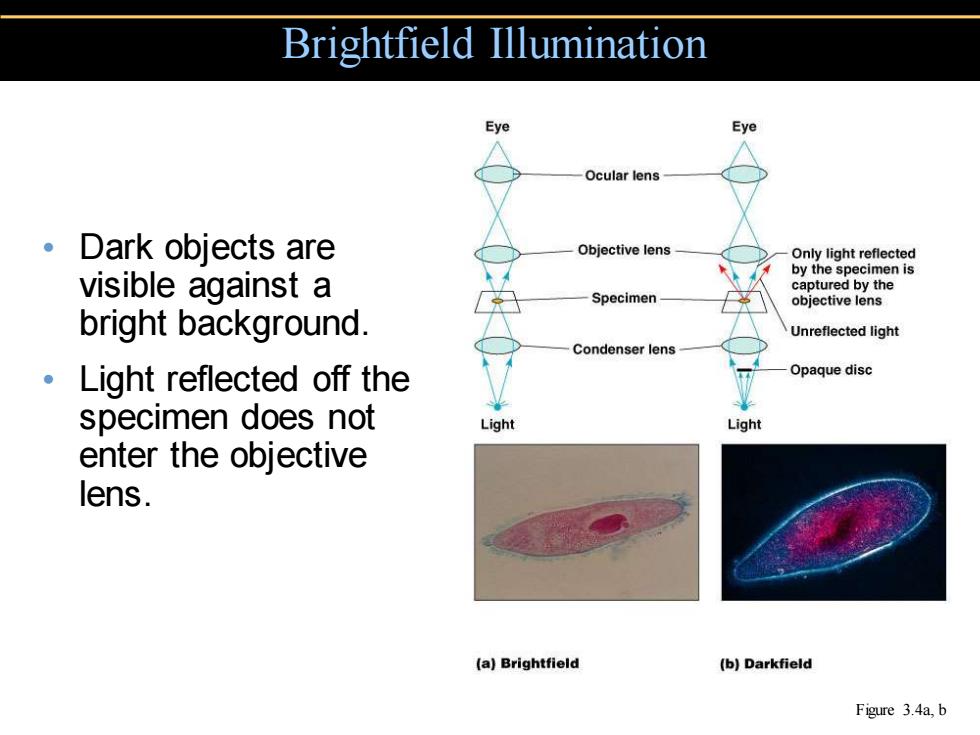
Brightfield Illumination Eye Eye Ocular lens 。Dark objects are Objective lens Only light reflected by the specimen is visible against a captured by the Specimen objective lens bright background. Unreflected light Condenser lens Light reflected off the Opaque disc specimen does not Light Light enter the objective lens. (a)Brightfield (b)Darkfield Figure 3.4a,b
• Dark objects are visible against a bright background. • Light reflected off the specimen does not enter the objective lens. Brightfield Illumination Figure 3.4a, b

Darkfield Illumination Eye Eye Ocular lens Objective lens Only light reflected by the specimen is 。Light objects are captured by the Specimen objective lens visible against a Unreflected light dark background. Condenser lens Opaque disc 。Light reflected off Light Light the specimen enters the objective lens. (a)Brightfield (b)Darkfield Figure 3.4a,b
• Light objects are visible against a dark background. • Light reflected off the specimen enters the objective lens. Darkfield Illumination Figure 3.4a, b

Phase-Contrast Microscopy Eye Ocular lens Diffraction plate Undiffracted light (unaltered by specimen) Objective lens Refracted or diffracted light(altered by specimen) Accentuates diffraction of Specimen Condenser lens the light that passes through a specimen. Annular diaphragm Light (c)Phase-contrast Figure 3.4c
• Accentuates diffraction of the light that passes through a specimen. Phase-Contrast Microscopy Figure 3.4c
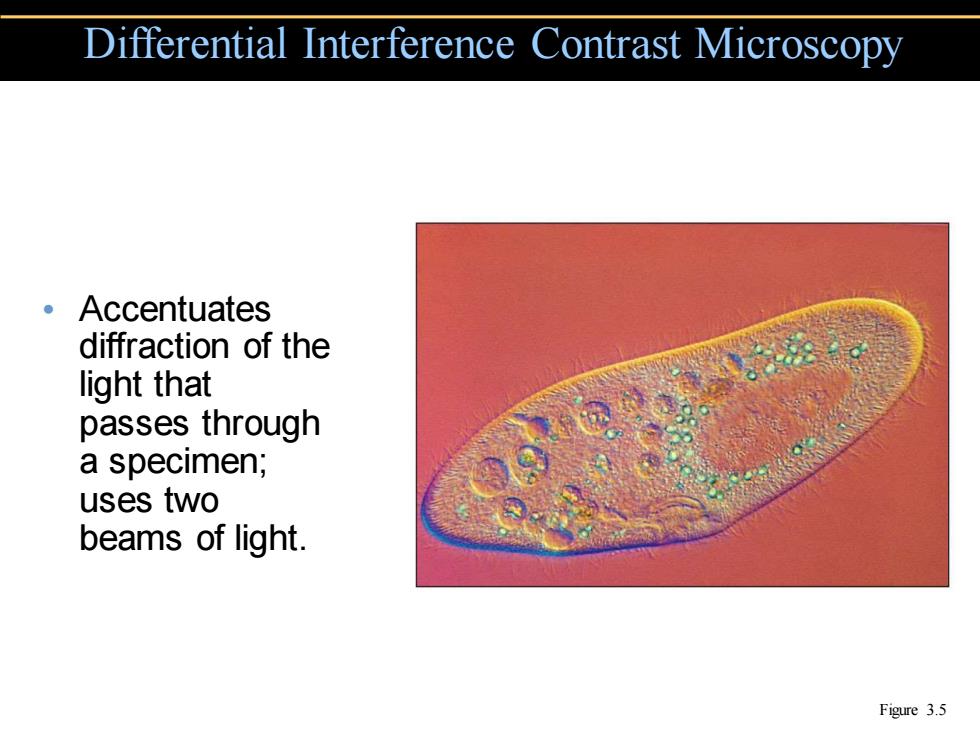
Differential Interference Contrast Microscopy 。Accentuates diffraction of the light that passes through a specimen; uses two beams of light. Figure 3.5
• Accentuates diffraction of the light that passes through a specimen; uses two beams of light. Differential Interference Contrast Microscopy Figure 3.5