
Chapter 17,part A Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 17, part A Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response
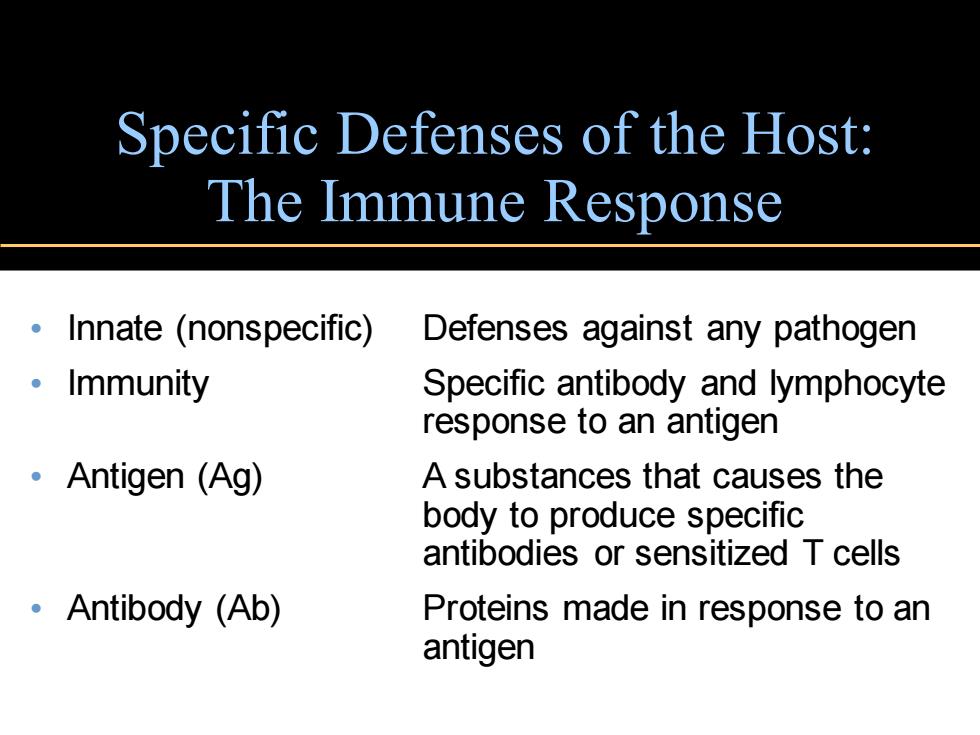
Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response Innate(nonspecific) Defenses against any pathogen 。Immunity Specific antibody and lymphocyte response to an antigen 。Antigen(Ag) A substances that causes the body to produce specific antibodies or sensitized T cells ·Antibody(Ab) Proteins made in response to an antigen
Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response • Innate (nonspecific) Defenses against any pathogen • Immunity Specific antibody and lymphocyte response to an antigen • Antigen (Ag) A substances that causes the body to produce specific antibodies or sensitized T cells • Antibody (Ab) Proteins made in response to an antigen
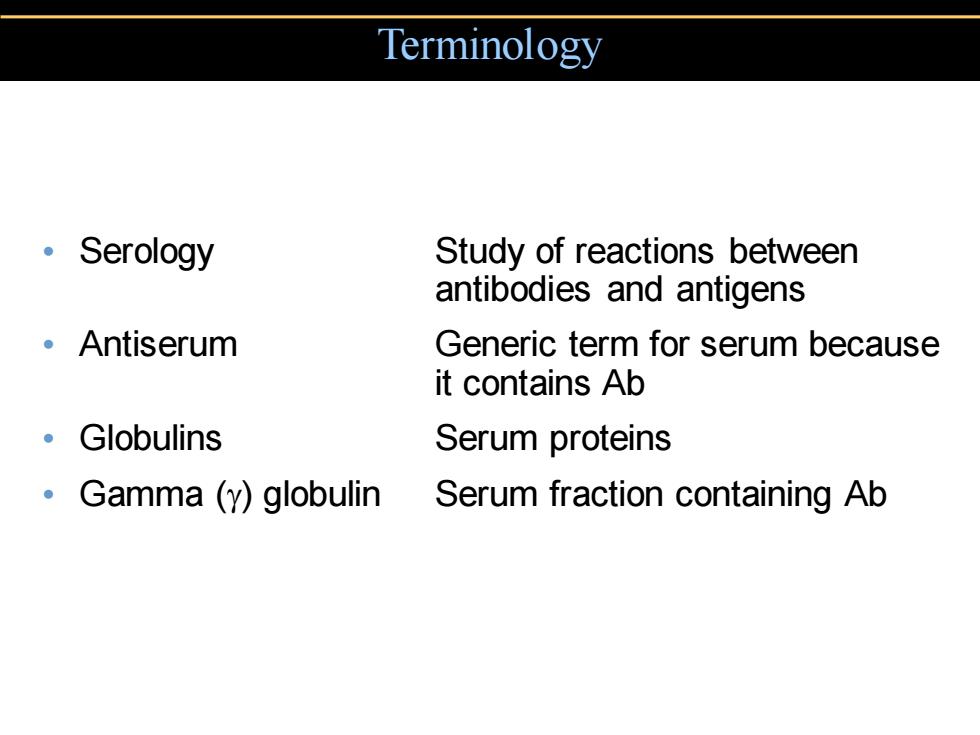
Terminology 。 Serology Study of reactions between antibodies and antigens 。Antiserum Generic term for serum because it contains Ab 。Globulins Serum proteins Gamma(y)globulin Serum fraction containing Ab
Terminology • Serology Study of reactions between antibodies and antigens • Antiserum Generic term for serum because it contains Ab • Globulins Serum proteins • Gamma () globulin Serum fraction containing Ab
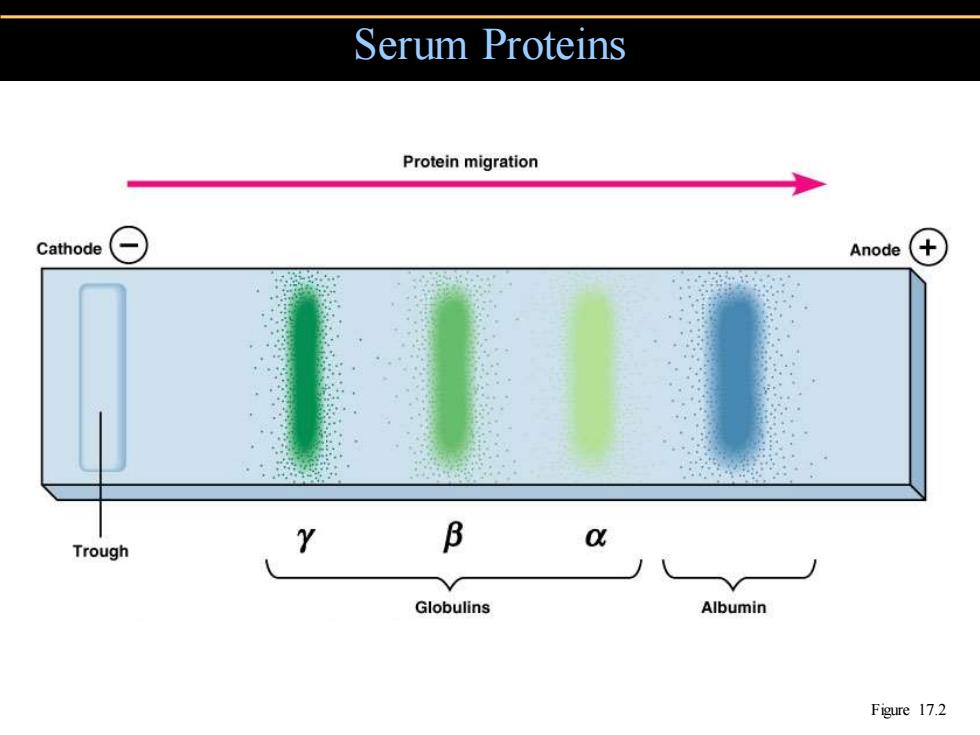
Serum Proteins Protein migration Cathode Anode Trough Y B Globulins Albumin Figure 17.2
Serum Proteins Figure 17.2
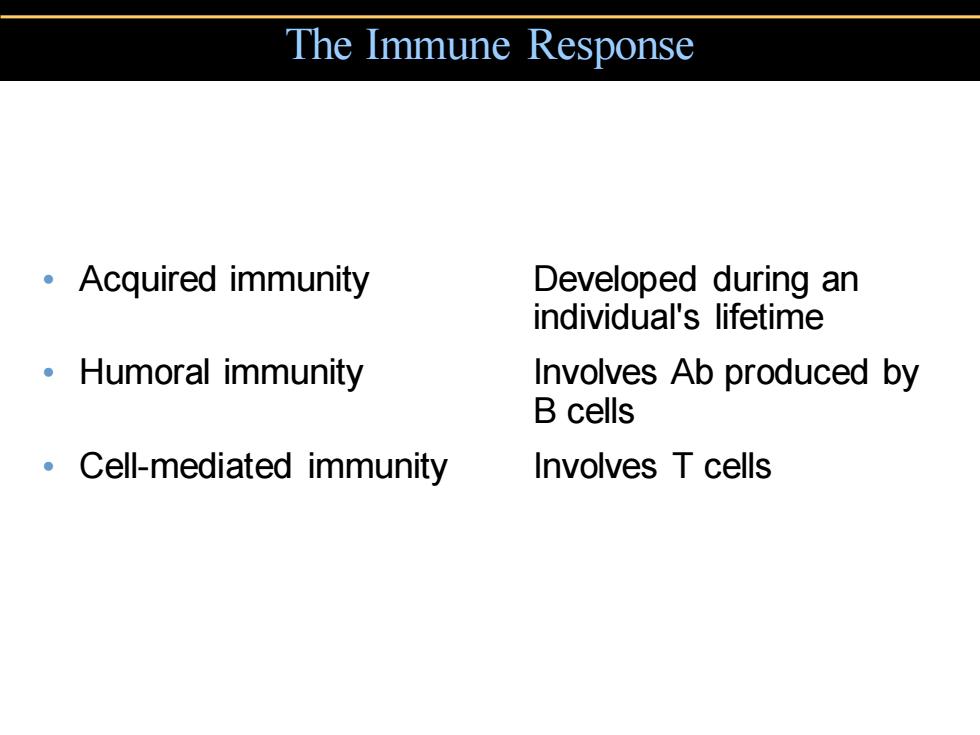
The Immune Response 。Acquired immunity Developed during an individual's lifetime 。Humoral immunity Involves Ab produced by B cells Cell-mediated immunity Involves T cells
The Immune Response • Acquired immunity Developed during an individual's lifetime • Humoral immunity Involves Ab produced by B cells • Cell-mediated immunity Involves T cells

Acquired Immunity Naturally acquired active immunity Resulting from infection Naturally acquired passive immunity Transplacental or via colostrum Artificially acquired active immunity Injection of Ag (vaccination) Artificially acquired passive immunity ·Injection of Ab
Acquired Immunity • Naturally acquired active immunity • Resulting from infection • Naturally acquired passive immunity • Transplacental or via colostrum • Artificially acquired active immunity • Injection of Ag (vaccination) • Artificially acquired passive immunity • Injection of Ab

Antigenic Determinants Antibodies recognize and react with antigenic determinants or epitopes. Antibody A Antigenic determinants on antigen Antigens: 68eo8 onents Binding sites O口O 口△ △0▣ Bacterial cell △△O 00△ Antibody B 口口U Figure 17.3
Antigenic Determinants • Antibodies recognize and react with antigenic determinants or epitopes. Figure 17.3

Haptens 凸 Hapten Carrier Complete molecules molecule antigen Figure 17.4
Haptens Figure 17.4
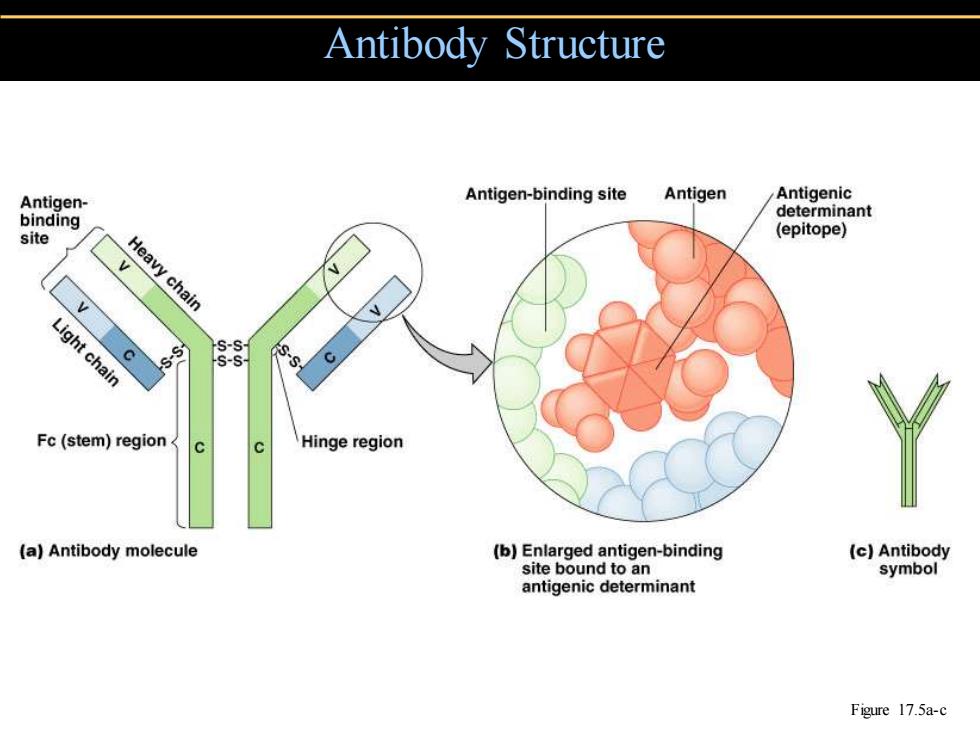
Antibody Structure Antigen- Antigen-binding site Antigen Antigenic determinant binding site (epitope) Heavy chain Light chain S-S- Fc(stem)region Hinge region (a)Antibody molecule (b)Enlarged antigen-binding (c)Antibody site bound to an symbol antigenic determinant Figure 17.5a-c
Antibody Structure Figure 17.5a-c

IgG antibodies 。Monomer 80%of serum antibodies 。Fix complement In blood,lymph,intestine 。Cross placenta Enhance phagocytosis; neutralize toxins viruses; protects fetus newborn 。Half-life=23days
• Monomer • 80% of serum antibodies • Fix complement • In blood, lymph, intestine • Cross placenta • Enhance phagocytosis; neutralize toxins & viruses; protects fetus & newborn • Half-life = 23 days IgG antibodies