上泽充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 11-2 Genetic Engineering Chapter 11in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS GHAI J UNIVE Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn
1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 11-2 Genetic Engineering Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn Chapter 11 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS

泽克通大学 上 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 II.Gene Cloning a。n。 am,.。A.1A00VCIr
1896 1920 1987 2006 II. Gene Cloning

11.5 Plasmids as Cloning Vectors Useful Properties of Plasmids as Cloning Vectors 1.Small size,easy to isolate and manipulate 2. Independent origin of replication,independently from direct chromosomal control?独立复制起点 3. Multiple copy number,making amplification of DNA possible:多拷贝数 4. Selectable markers,easy to detect and select the plasmid-containing clones:选择性标记 Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology 11.5 Plasmids as Cloning Vectors Useful Properties of Plasmids as Cloning Vectors 1. Small size, easy to isolate and manipulate 2. Independent origin of replication, independently from direct chromosomal control独立复制起点 3. Multiple copy number, making amplification of DNA possible多拷贝数 4. Selectable markers, easy to detect and select the plasmid-containing clones选择性标记

Plasmids pBR322 Clal 1.Relatively small,4361bp EcoRI Hind Ill Ampicillin BamHI resistance 2.20-30 copies per cell;can be Pst I amplified to 1000-3000 copies Sall per cell by inhibiting protein synthesis; direction of DNA 3.10kb foreign DNA can be replication from the origin inserted; Tetracycline 4.Single cleavage sites for resistance Origin of DNA various restriction enzymes; replication 5.Ampicillin resistance and tetracycline resistance. Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology Plasmids pBR322 direction of DNA replication from the origin 1.Relatively small, 4361bp 2.20-30 copies per cell; can be amplified to 1000-3000 copies per cell by inhibiting protein synthesis; 3. 10kb foreign DNA can be inserted; 4. Single cleavage sites for various restriction enzymes; 5. Ampicillin resistance and tetracycline resistance

Cloning with plasmid pBR322 BamHI site APR pBR322 TcR Insertion of foreign DNA BamHI sites causes inactivation of the BamHl digestion tetracycline resistance gene Foreign DNA BamHI (insertional inactivation) digestion Clal EcoRI Hind IIl DNA ligase Ampicillin BamHI Recyclized pBR322; Hybrid containing resistance no foreign DNA foreign DNA s PstI Sal I ApR TCR ApR Transformation of E.coli Transformants Transformants resistant to both resistant to ampicillin ampicillin and tetracycline but sensitive to tetracycline -Tetracycline resistance Figure 10-37 Brock Biology of Microorganisms 11/e Origin of DNA 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. replication
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology Cloning with plasmid pBR322 Insertion of foreign DNA causes inactivation of the tetracycline resistance gene (insertional inactivation)

11.6 Hosts for Cloning Vectors Ideal hosts should be Capable of rapid growth in inexpensive medium ·Nonpathogenic Capable of incorporating DNA Genetically stable in culture Equipped with appropriate enzymes to allow replication of the vector Escherichia coli,Bacillus subtilis,Saccharomyces cerevisiae Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology 11.6 Hosts for Cloning Vectors Ideal hosts should be • Capable of rapid growth in inexpensive medium • Nonpathogenic • Capable of incorporating DNA • Genetically stable in culture • Equipped with appropriate enzymes to allow replication of the vector Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae

Figure 11.13 Bacteria Eukaryote- Escherichia coli Bacillus subtilis Saccharomyces cerevisiae Well-developed Easily transformed Well-developed genetics Nonpathogenic genetics Many strains Naturally secretes Nonpathogenic available proteins Can process mRNA Best known Endospore formation and proteins bacterium simplifies culture Easy to grow Potentially Genetically unstable Plasmids unstable pathogenic Genetics less Will not replicate Periplasm traps developed than most bacterial proteins in E.coli plasmids Advantages Disadvantages 2012 Pearson Education,Inc
Figure 11.13 Well-developed genetics Many strains available Best known bacterium Easily transformed Nonpathogenic Naturally secretes proteins Endospore formation simplifies culture Well-developed genetics Nonpathogenic Can process mRNA and proteins Easy to grow Potentially pathogenic Periplasm traps proteins Genetically unstable Genetics less developed than in E. coli Plasmids unstable Will not replicate most bacterial plasmids Advantages Disadvantages Escherichia coli Bacillus subtilis Saccharomyces cerevisiae Bacteria Eukaryote © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc
Transfection:转染 Introduction of dNA into mammalian cells is called transfection Originally done through phagocytosis of DNA by host cell ·Can also be done using ·Microinjection ·Electroporation ·Gene gun Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology Transfection转染 Introduction of DNA into mammalian cells is called transfection • Originally done through phagocytosis of DNA by host cell • Can also be done using • Microinjection • Electroporation • Gene gun
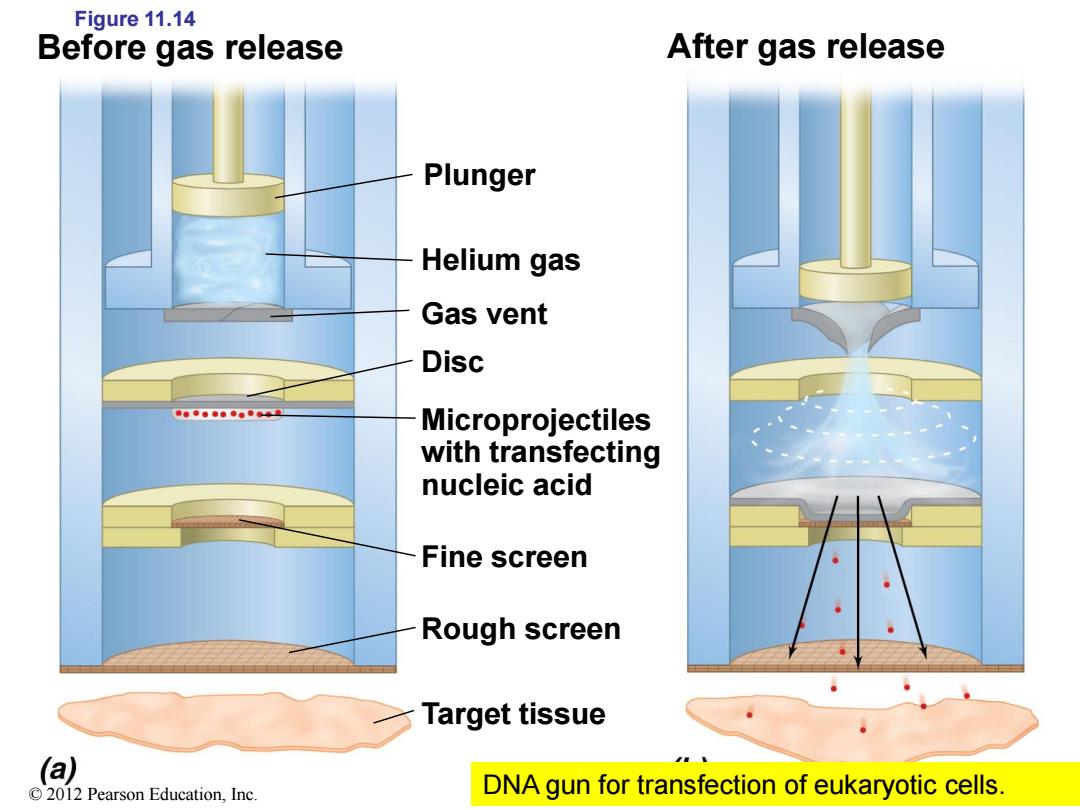
Figure 11.14 Before gas release After gas release Plunger Helium gas Gas vent Disc ●。9●●●●0●0。工 Microprojectiles with transfecting nucleic acid Fine screen Rough screen Target tissue (a) 2012 Pearson Education,Inc DNA gun for transfection of eukaryotic cells
Figure 11.14 Plunger Helium gas Gas vent Disc Microprojectiles with transfecting nucleic acid Fine screen Rough screen Target tissue Before gas release After gas release © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. DNA gun for transfection of eukaryotic cells
11.7 Shuttle Vectors and Expression Vectors Shuttle vecfors:vectors that are stably maintained in two or more unrelated host organisms (e.g.,E.coli and B. subtilis or E.coli and yeast)穿梭载体 Bacterial plasmid engineered to function in eukaryotes Add a eukaryotic origin of replication Add a centromere recognition sequence Chen Feng,Lecture of Microbiology
Chen Feng, Lecture of Microbiology 11.7 Shuttle Vectors and Expression Vectors Shuttle vectors: vectors that are stably maintained in two or more unrelated host organisms (e.g., E. coli and B. subtilis or E. coli and yeast) 穿梭载体 • Bacterial plasmid engineered to function in eukaryotes • Add a eukaryotic origin of replication • Add a centromere recognition sequence