
上泽充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 16-2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类 Chapter 16 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS GH Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn
1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 16-2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类 Chapter 16 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn

上泽充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 。© II.MICROBIAL EVOLUTION 月 CUAGUALIAO IONG UNIVEG
1896 1920 1987 2006 II. MICROBIAL EVOLUTION

12.5 The Evolutionary Process演化过程 Adaptive mutations are those that improve the fitness of an organism,increasing its survival capacity or reproductive success compared with that of competing organisms. Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 12.5 The Evolutionary Process演化过程 Adaptive mutations are those that improve the fitness of an organism, increasing its survival capacity or reproductive success compared with that of competing organisms
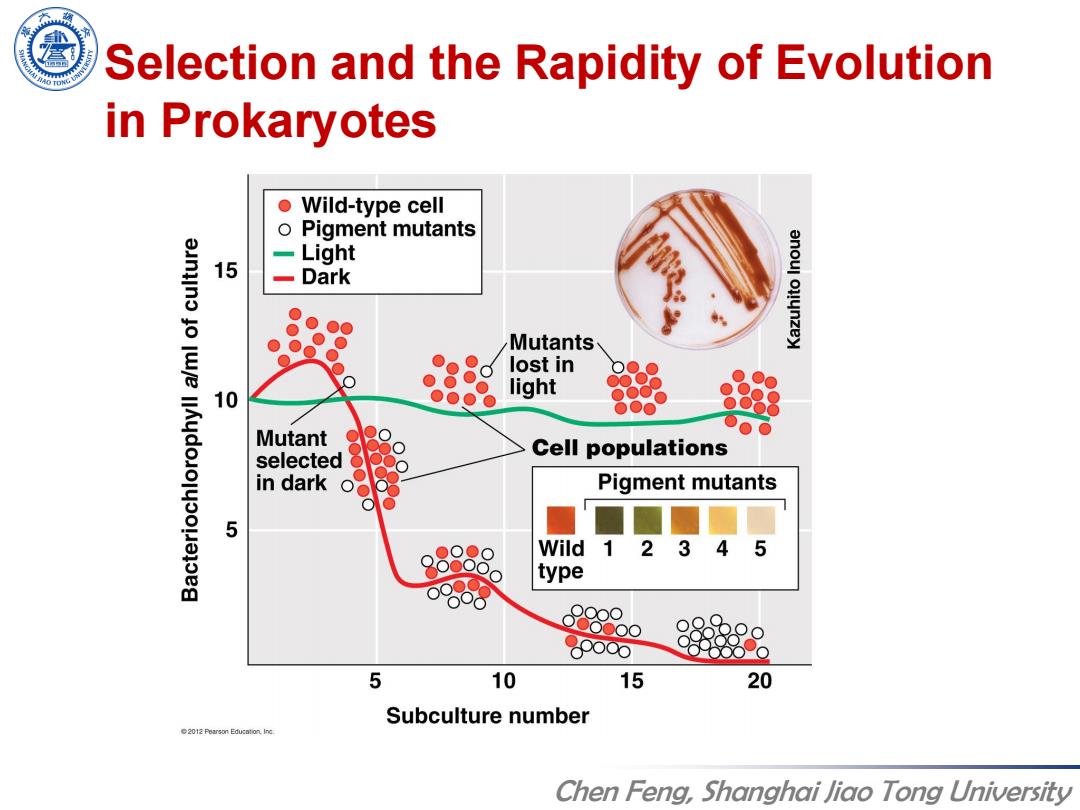
Selection and the Rapidity of Evolution in Prokaryotes Wild-type cell Pigment mutants Light 15 -Dark Mutants lost in 10 light 部8 Mutant Cell populations selected in dark Pigment mutants 5 Wild 1 2 3 45 type P880 pooo 5 10 15 20 Subculture number 2012 Pearson Education.inc Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Selection and the Rapidity of Evolution in Prokaryotes

11.6 Evolutionary Analysis:Theoretial Aspects Evolutionary chronometer-a molecule,such as rRNA, whose molecular sequence can be used as a comparative measure of evolutionary divergence. 分子序列可代表相对演化分岐的分子,如RNA,可作为演 化指针。 Criteria for being chronometers 1.Universal distribution across the group chosen for study广泛分布 2.Functionally homologous in each organisms.功能同源 3.Can be properly aligned to in order to identify sequence homology and variance.线性 4.Should change at a rate commensurate with the evolutionary distance measured.与进化距离相称的变化速率 Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 11.6 Evolutionary Analysis: Theoretial Aspects Evolutionary chronometer- a molecule, such as rRNA, whose molecular sequence can be used as a comparative measure of evolutionary divergence. 分子序列可代表相对演化分岐的分子,如rRNA,可作为演 化指针。 Criteria for being chronometers 1. Universal distribution across the group chosen for study广泛分布 2. Functionally homologous in each organisms功能同源 3. Can be properly aligned to in order to identify sequence homology and variance. 线性 4. Should change at a rate commensurate with the evolutionary distance measured.与进化距离相称的变化速率

Evolutionary chronometer Evolutionary distance between two organisms can be measured by differences in the nucleotide or amino acid sequence of homologous macromolecules isolated from them两物种的进化距离可通过比较来自它们的同 源大分子的核苷酸序列或氨基酸序列而测定 Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Evolutionary chronometer Evolutionary distance between two organisms can be measured by differences in the nucleotide or amino acid sequence of homologous macromolecules isolated from them 两物种的进化距离可通过比较来自它们的同 源大分子的核苷酸序列或氨基酸序列而测定
Ribosomal RNA as Molecular Chronometer 16S/18S rRNA gene(functionally constant, universally distributed,and moderately well conserved in sequence across broad phylogenetic distances) ATPase (membrane-bound enzyme complex that can synthesize and hydrolyze ATP) RecA(protein required for genetic recombination) Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Ribosomal RNA as Molecular Chronometer 16S/18S rRNA gene(functionally constant, universally distributed, and moderately well conserved in sequence across broad phylogenetic distances) ATPase (membrane-bound enzyme complex that can synthesize and hydrolyze ATP) RecA (protein required for genetic recombination)
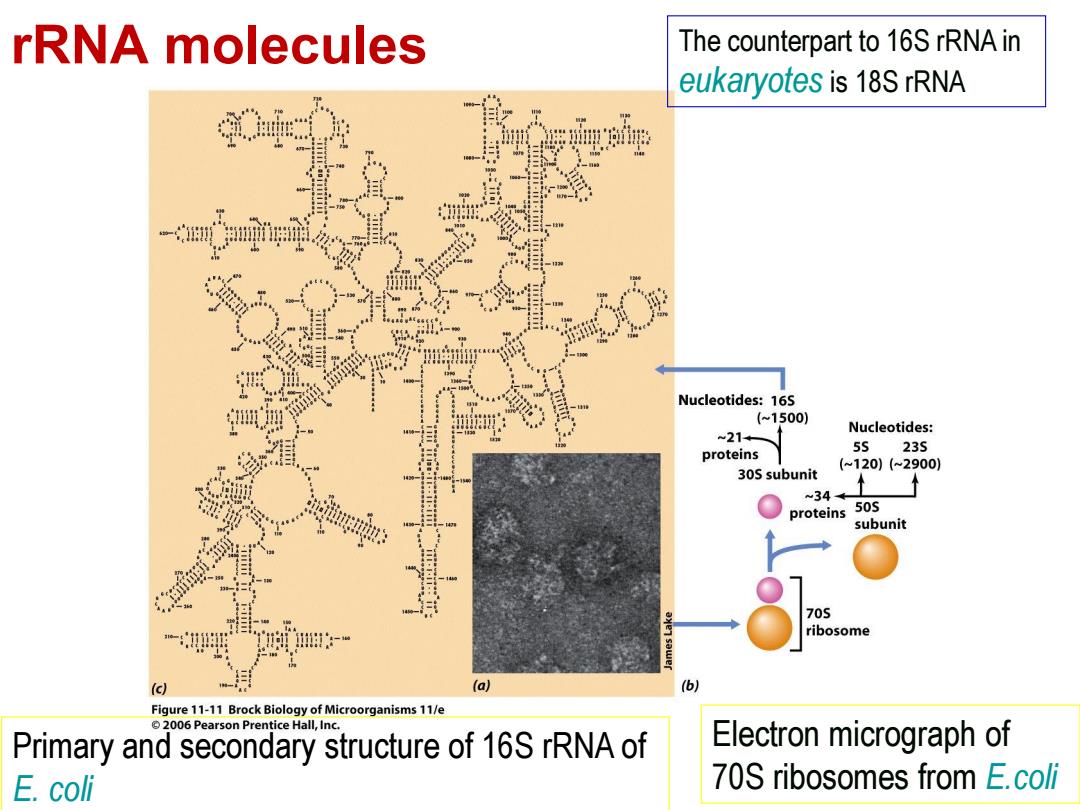
rRNA molecules The counterpart to 16S rRNA in eukaryotes is 18S rRNA Nucleotides:16S (~1500) Nucleotides: -21+ proteins 55 235 (~120)(~2900) 30S subunit ~34← proteins 50S subunit 705 ribosome (c) (a) (b) Figure 11-11 Brock Biology of Microorganisms 11/e 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc Primary and secondary structure of 16S rRNA of Electron micrograph of E.coli 70S ribosomes from E.coli
rRNA molecules Electron micrograph of 70S ribosomes from E.coli Primary and secondary structure of 16S rRNA of E. coli The counterpart to 16S rRNA in eukaryotes is 18S rRNA
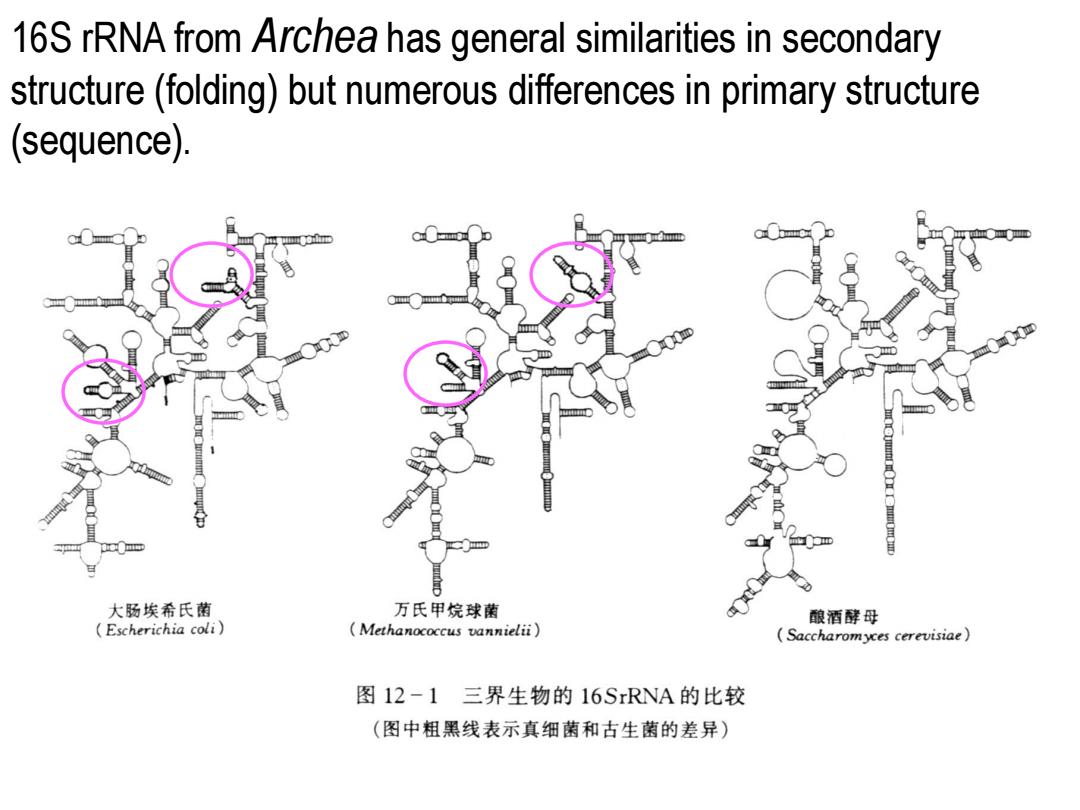
16S rRNA from Archea has general similarities in secondary structure(folding)but numerous differences in primary structure (sequence). 大肠埃希氏菌 万氏甲烷球菌 酿酒酵母 Escherichia coli) Methanococcus vannielii) Saccharomyces cerevisiae 图12-1三界生物的16 SrRNA的比较 (图中粗黑线表示真细菌和古生菌的差异)
16S rRNA from Archea has general similarities in secondary structure (folding) but numerous differences in primary structure (sequence)
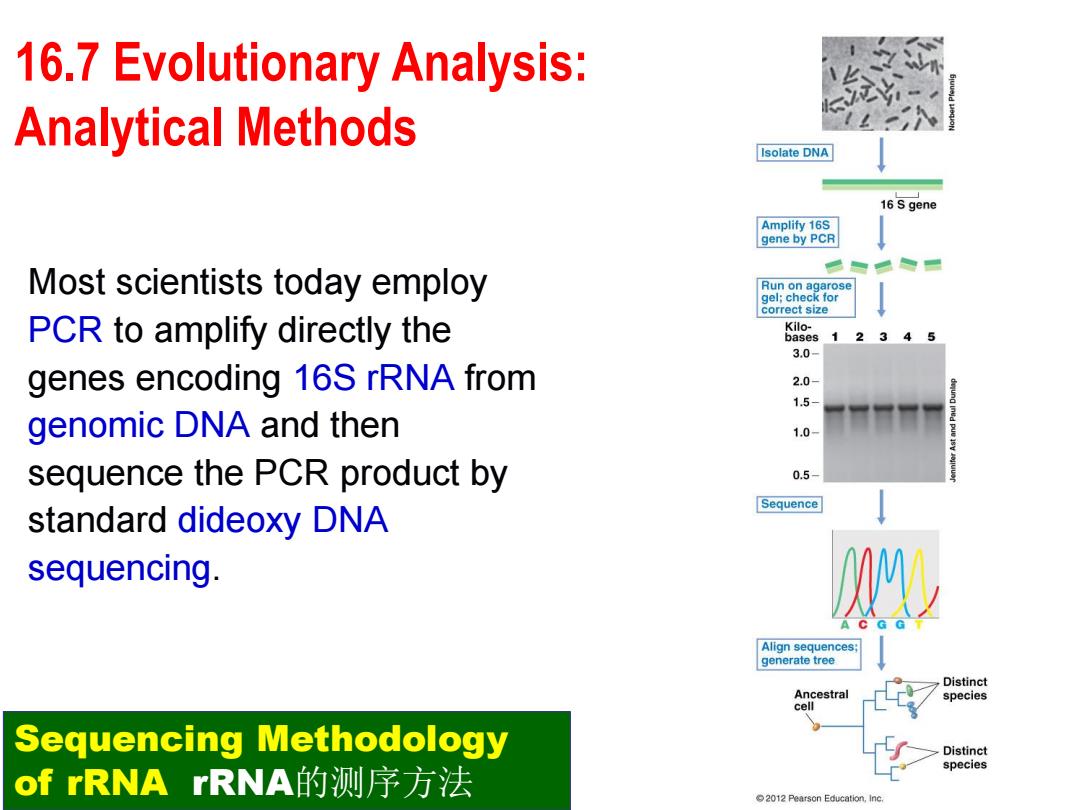
16.7 Evolutionary Analysis: Analytical Methods Isolate DNA 16S gene Amplify 16S gene by PCR Most scientists today employ Run on agarose gel:check for correct size PCR to amplify directly the Kilo- bases 1 2 3.0- genes encoding 16S rRNA from 2.0- 1.5- genomic DNA and then 1.0- sequence the PCR product by 0.5- Sequence standard dideoxy DNA sequencing Align sequences; generate tree Distinct Ancestral species cell Sequencing Methodology Distinct species of rRNArRNA的测序方法 2012 Pearson Education,Inc
Most scientists today employ PCR to amplify directly the genes encoding 16S rRNA from genomic DNA and then sequence the PCR product by standard dideoxy DNA sequencing. Sequencing Methodology of rRNA rRNA的测序方法 16.7 Evolutionary Analysis: Analytical Methods